Note 9 - Recycling
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
Two ways to reduce quantity of waste-producing goods?
1) Emissions tax
2) Pigovian tax
Emissions taxes and waste producing good
Emisions tax → shifts demand curve down. lower equilibrium quantity. We know that consumers do not consume the socially optimum quantity because they do not bear the full social cost of their waste-producing good.

Pigovian taxes and waste-producing good
Put a tax on the good → supply curve shifts up. Price up, Q down.
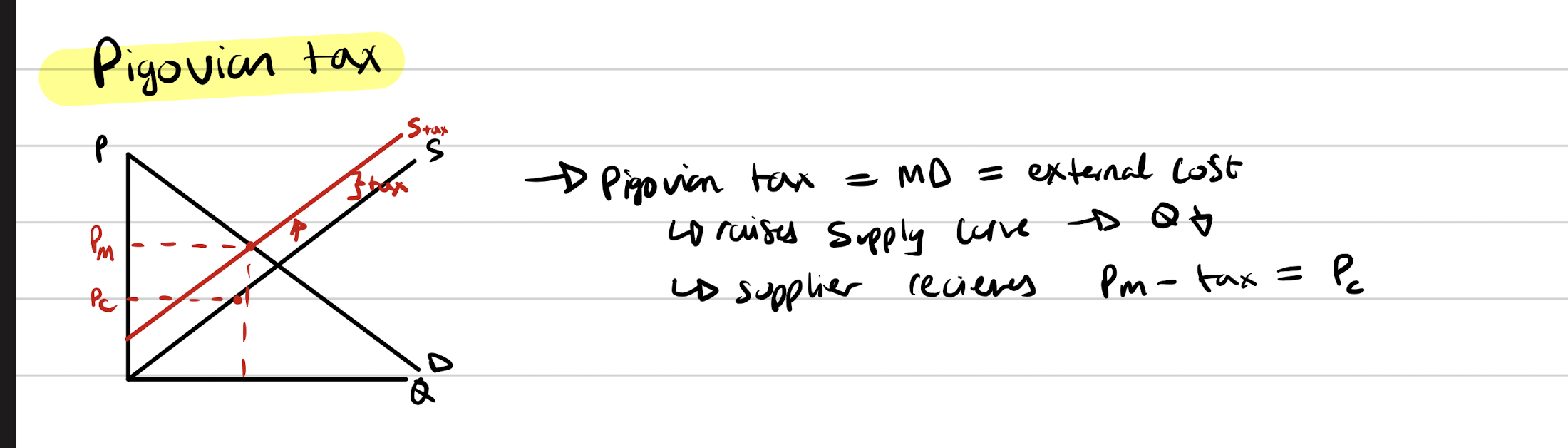
Ideal policy for reducing waste-producing good
Pigovian tax + Emissions tax
Both reduce quantity
Price consumer pays up
Price supplier gets down
Tax revenue in middle.
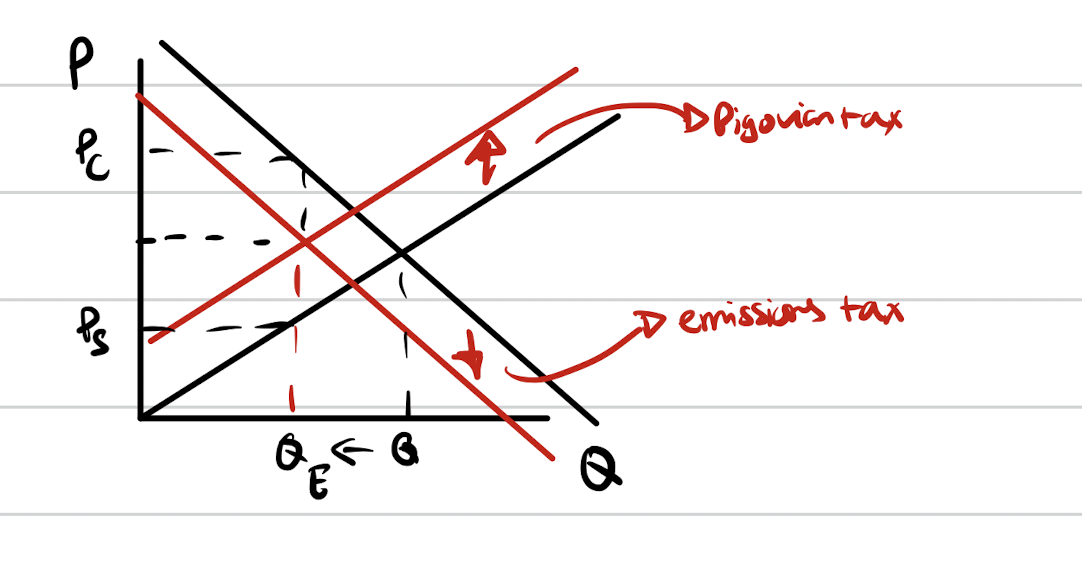
Total Materials =
Virgin materials + recycled materials
VM =
TM - RM
= TM( 1 - RM/TM)
RM/TM = reuse ratio = QV/QT
How to increase VM
By increasing RM or by decreasing TM
Can decrease TM by slowing down economic growth or by reducing material intensity
Material Intensity
the quantity of materials used per unit of production. (Amount of paper used to package burger)
How to get producers to increase VM
1) Pigovian tax on virgin paper
2) Emissions tax
3) Subside recycling
4) Mandate certain % of recycled material (Control instrument)
5) Non-tradeable permits
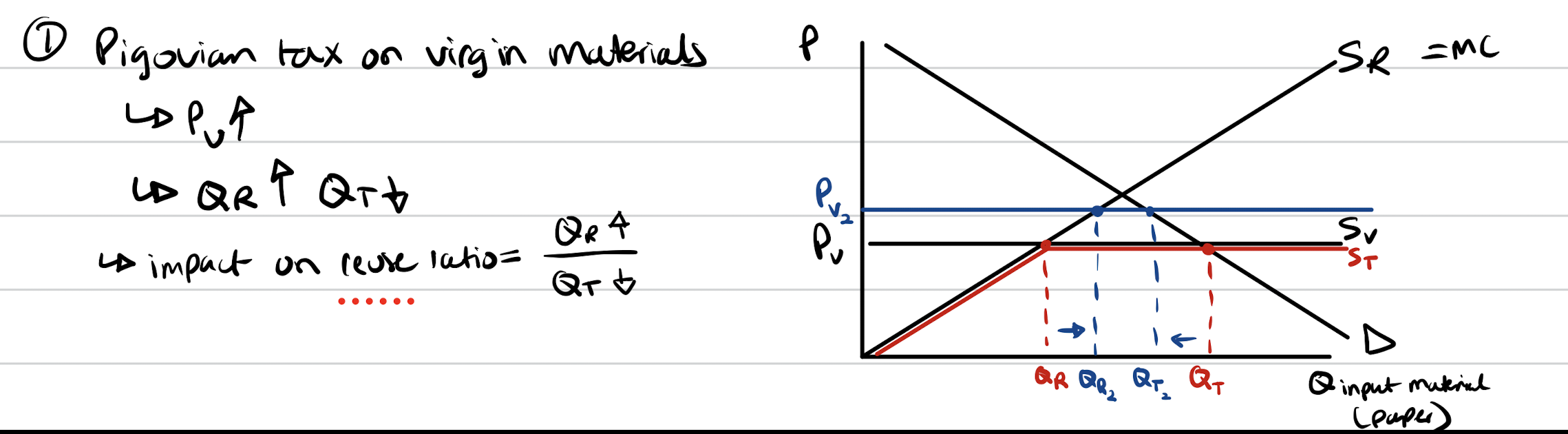
Pigovian tax on virgin paper
Increases price of virgin paper. Supply of virgin paper is perfectly elastic. Causes TM to decrease and RM to increase. Reuse ratio up
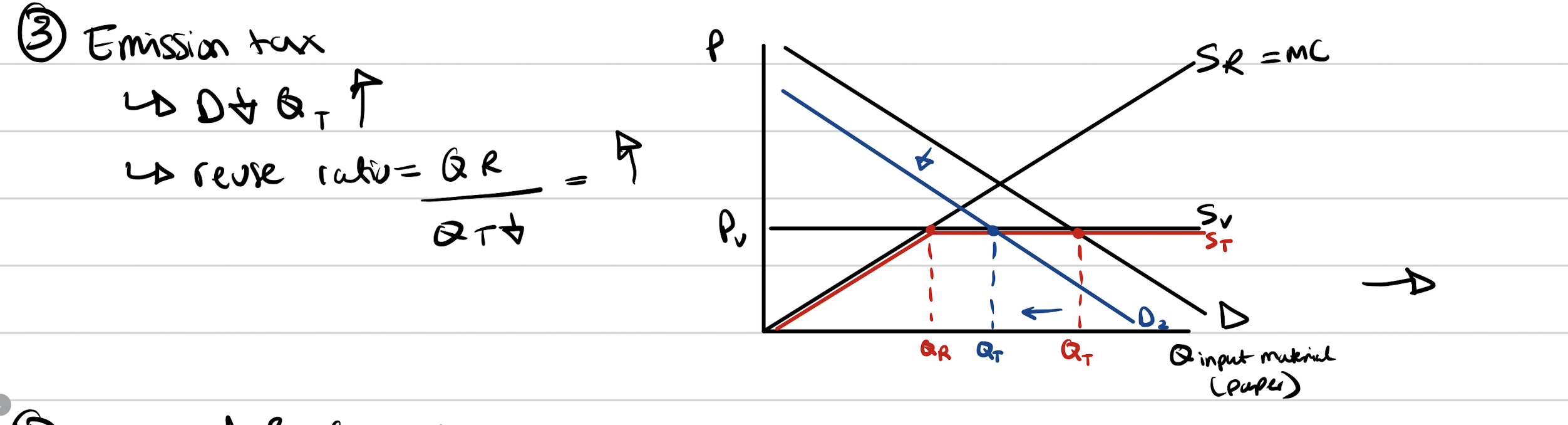
Emissions tax
Shifts demand curve down. TM down. RM unchanged. causes reuse ratio to increase.
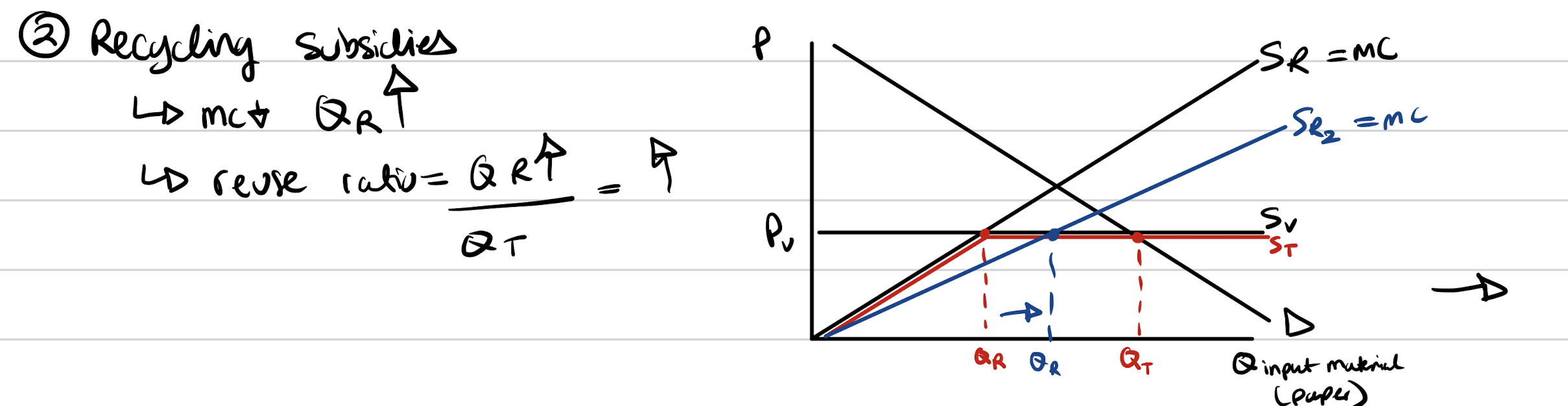
Recycling subsidy
Supply curve of recycling is upward sloping. MC of recycling is increasing. Subsidy moves Supply curve down. RM up, reuse ratio up.
Minimum content standards
Command and control instrument
Government requires certain % of material used to be recycled. inefficent as government does not know MCRecycling of production firms. Does not lead to least cost.
Tradeable permits
Allocate permits to people to use certain % recycled material.
Low cost firms recycle more than requirement and sell excess credits.
High cost firms recycle less than requirement and buy permits to make up difference.
3 recycling policies for consumers
1) Mandate recycling
2) Disposal tax
3) Disposal deposit/refund
Mandate recycling
Mandate recycling of recyclable resources. Removes option to garbage recyclable goods.
Disposal tax
tax consumers = external cost of good. Makes consumers make socially optimum decisions by facing the true social cost.
If recycle = no tax, subsidy = - cost of recycling + value of recovered materials
Deposit/refund
Charge deposit = External cost of not recycling. If recyle, get refund, if not, pay tax.
only on recycleable goods.