MBIO 2700 / Topic 3: Solubility Equilibria
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
What is the Keq of H2O at 25ºC? What is the concentration of H2O? Heck, what is a Keq tell you?
1.8E-16 and 55.5M, respectively. Keq tells you how much products and reactants are in a solution when in equilibrium.
Once you arrange the Keq equation for the dissociation of water, what are the concentrations of H+ and OH-? When you multiply them together, what is the name of this constant? When can you only have this constant?
1E-14 is the Kw, the water dissociation equilibrium constant that is only true when you have pure water at 25ºC.
Different conditions will affect any biochemical process such as the Kw.
What is the common convention to express [H+]? What’s the equation for this?
pH = -log10[H+]
What is the common convention to express [OH-]? What’s the equation for this?
pOH = -log10[OH-]
If pH ↑, what does it mean for [H+] and [OH-]?
If pH ↓, what does it mean for [H+] and [OH-]?
[H+] ↓ [OH-] ↑
[H+] ↑ [OH-] ↓
> When is a solution considered neutral in terms of pH and pOH?
> What does this indicate about the concentrations of H⁺ and OH⁻ ions?
> Neutral when pH = 7 and pOH = 7.
> [H]+ = [OH-] ions → solution neither acidic nor basic.
Differentiate strong acids from weak acids and strong bases and weak bases.
> Strong acids dissociate completely. Weak acids dissociate incompletely.
> Strong bases dissociate completely. Weak bases dissociate incompletely.
↓ [strong acid] → more or less acidic?
↓ [strong base] → more or less acidic?
↓ [strong acid] → ↓ acidity
↓ [strong base] → ↑ acidity
In the realm of biochemistry, are most biological acids and bases strong or weak?
Weak.
what’s a weak acid/base in terms of protons?
how do biochemists use the term “weak acid”?
weak acid = proton donor
weak base = proton acceptor
“weak acid” = umbrella term for weak acids + weak bases
• Ka = ?
• What does it mean to have a high Ka?
• Ka = [A-][H+]/[HA] = how much product (the conjugate base) and reactant (the weak acid) you have.
• if you have a high Ka, you have a strong acid.
What is the common way of expressing Ka?
pKa = -log10[Ka]
Let’s talk Ka and pKa.
If Ka will go ↓, will pKa go ↑ or ↓? Does it mean that we have a weak acid or a strong acid?
If Ka will go ↑, will pKa go ↑ or ↓? Does it mean that we have a weak acid or a strong acid?
If pKa < 7.0, do we consider the species to be an acid or base? Why?
If pKa > 7.0, do we consider the species to be an acid or base? Why?
If Ka will go ↓ pKa ↑ ; we have a weak acid.
If Ka will go ↑, pKa ↓ ; we have a strong acid.
If pKa < 7.0, we consider the species to be an acid. Water’s pKa is 7 for our purposes. Water is acting as a base because of its relatively higher pKa to the species, which would make our species the acid in this case.
If pKa > 7.0, we consider the species to be a base. Water’s pKa is 7 for our purposes. Our species is acting as a base because of its relatively higher pKa to water, which would make our species the base in this case.
Let’s list some common acids we’ll be seeing in biochemistry, yeah? Give me their pKa.
H2CO3 (carbonic acid).
CH3COOH (acetic acid).
H2PO4- (dihydrogen phosphate).
NH4+ (ammonium).
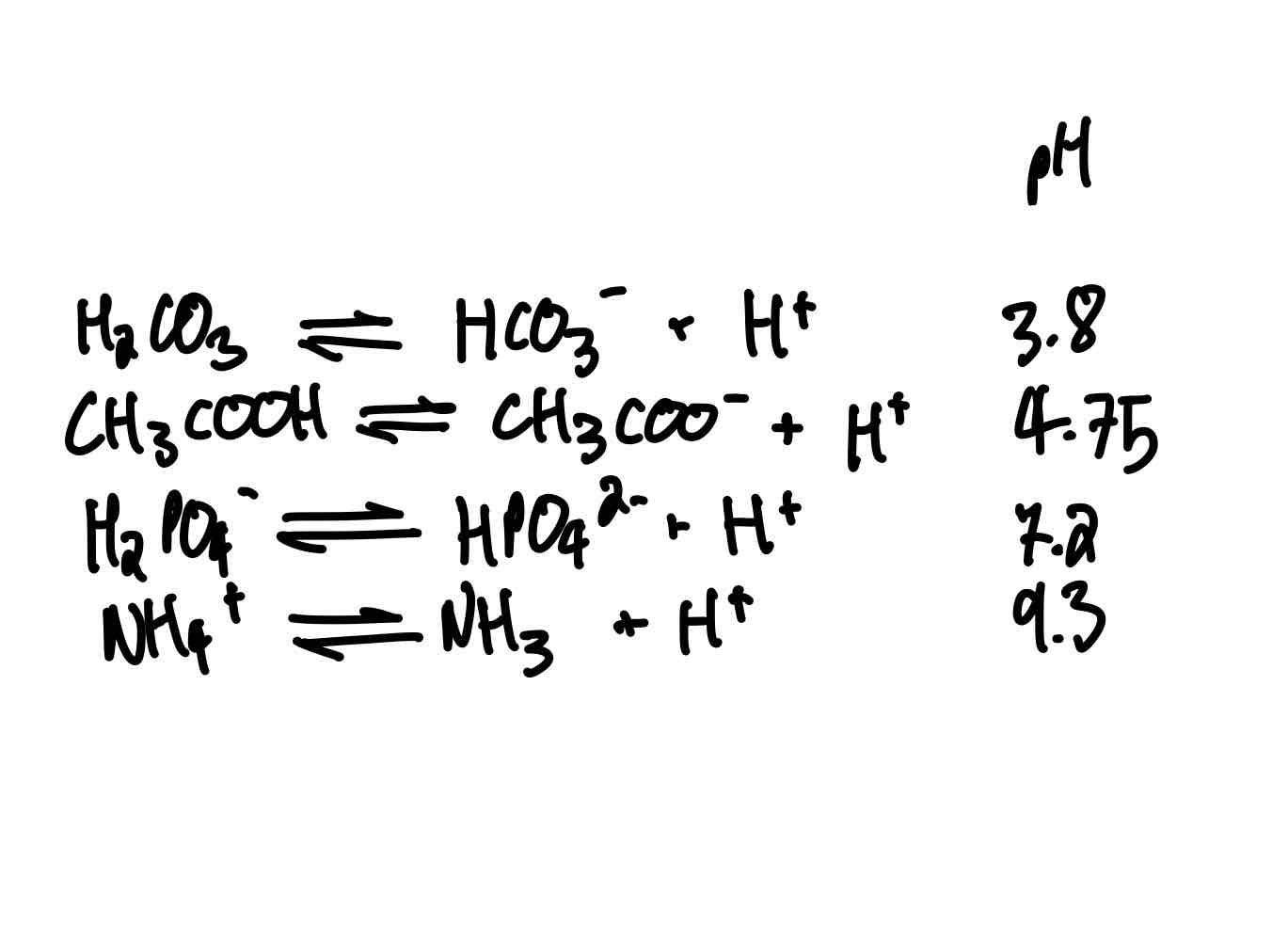
Contrast pH and pKa. What does each tell you?
pH tells you weather your solution is acidic or basic.
pKa tells you whether an acid is strong or weak.
Talk to me ‘bout buffers.
What’s a buffer? What does it do?
What does it contain?
What is the main buffer in our cells?
Buffer = chemical system resisting ∆pH by neutralizing added acid or added base.
Buffer contains significant amounts of a weak acid and its conjugate base.
The main buffer system found is the phosphate buffer system, with dihydrogen phosphate as the weak acid and hydrogen phosphate as the conjugate base.
What does the buffer’s weak acid neutralize? What does the buffer’s conjugate base neutralize?
The weak acid neutralizes the added base, e.g. hydroxide ions.
The conjugate base neutralizes the added acid, e.g. hydronium ions.
Talk to me ‘bout titration curves.
What does a titration curve show you?
What does the buffer zone in a titration curve shows you?
In a titration curve, at what pH will the buffer start to “buffer” or does it duty?
In a titration curve, at what pH will the buffer stop “buffering” or give up?
What does it mean when pH = pKa?
A titration curve graph that shows the change in pH of a solution as a titrant (acid or base) is added.
Titration curves have a buffer zone that shows you the slow change in the pH due to the performance of the acid.
At pH = pKa - 1, it starts to buffer or resist pH.
At pH = pKa + 1, it stops buffering and gives up resisting to pH changes.
At pH = pKa, there is equal amount of [HA] and [A-], i.e. 50% weak acid and 50% conjugate base.
Show me mathematical proof that, when a buffer’s weak acid is half neutralized, you get pH = pKa. Hint: Use the pH and pKa equations.
*
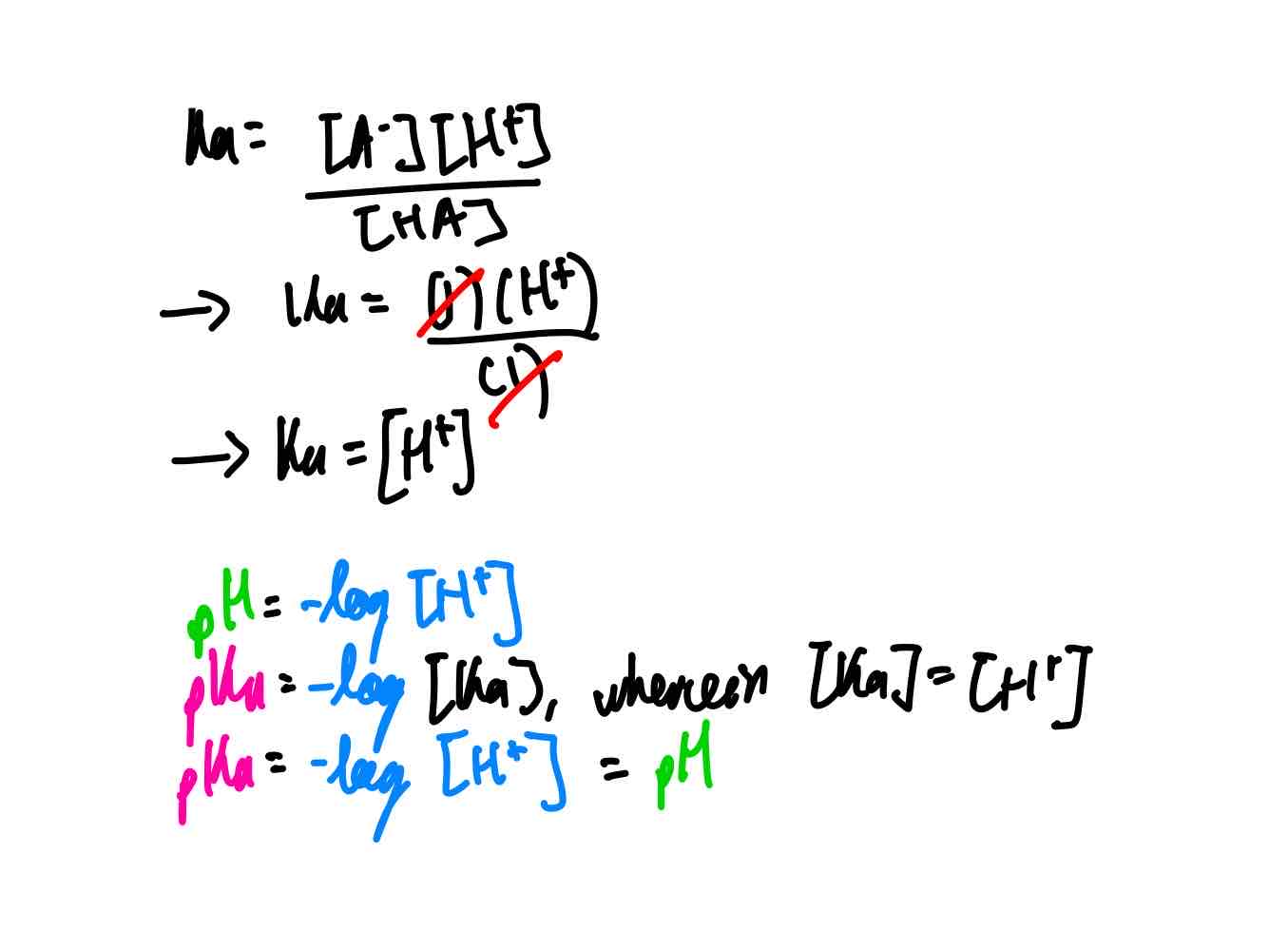
If you add a strong acid to a buffer, will the buffer’s weak acid increase or decrease? Will the buffer’s conjugate base increase or decrease?
If you add base to a buffer, will the buffer’s weak acid increase or decrease? Will the buffer’s conjugate base increase or decrease?
If you add a strong acid to a buffer, you get more weak acid and less conjugate base.
If you add a strong base to a buffer, you get less weak acid and more conjugate base.
What is the Henderson-Hasselbalch (HH) equation? What does it calculate for you?
This calculates the pH of the weak acid-conjugate base pair of our buffer.
What are the three situations you will be placed in, in regard to the HH equation?
All in one form, wherein the pH is MORE than one unit above the pKa or wherein the pH is LESS than one unit below the pKa.
Both in equal amounts, wherein pH = pKa.
pH is WITHIN one unit below or above the pKa and not equalling the pKa.