FPSYC3400: Decision-Making & Critical Incident Management
1/46
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Lecture 10
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
47 Terms
Examples of Critical Incidents
•Armed intruders
•Hostage taking
•Barricaded persons
•Bomb threats & suspicious packages
•Being operated on the wrong side/site
•Suicide or murder of a co-worker
•Workplace violence
•Natural disasters (e.g., earthquakes, floods, tornados)
•Major disasters (e.g., plane crash; train derailments; oil spills; nuclear; fire)
•Invasion & War
•Murder of Sammy Yatim (2013)
•Unmarked Graves of Indigenous Peoples, Residential Schools
•Nova Scotia Mass Casualty event (2020)
•Toronto Van attack (2018)
•G20 Summit, Toronto (2010)
Critical Incident Management (CIM) Cycle
preparing for critical incidents
managing critical incidents
restoring public confidence
Traditional Decision Making (TDM) is related to which theory?
Classical Decision Theory
According to the Classical Decision Theory what characteristic do decision makers have?
• Are objective
• Have complete information
• Consider all possible alternatives & their consequences
• Select the optimal solution
Traditional Decision Making (TDM) Criticisms
rarely possible to consider all alternatives
impractical to consider all consequences
estimation process costs time & effort
does not allow for an optimal or extensive exhuastive comprehensive search
information is rarely complete and/or accurate
individual lack mental capacity to process all the information
What is Naturalistic Decision Making (NDM) concerned with?
with how individuals and teams use their experience to assess, make meaningful decisions and take action in dynamic, uncertain, and time-pressured situations
With regard to Naturalistic Decision Making (NDM) blank is an important variable to consider
experience
Features of Naturalistic Decision Making (NDM)
• Ill-defined goals & ill-structured task
• Uncertainty, ambiguity, & missing data
• Shifting & competing gals
• Dynamic & continually changing conditions
• Action-feedback loops (real-time reactions to changed conditions)
• Time stress
• High stakes
• Multiple players
• Organizational goals & norms
• Experienced decision-makers
Essential Characteristics of Naturalistic Decision Making (NDM)
proficient decision makers
relevant experience and knowledge to rely on their experiences
process orientation
does not making an attempt to predict which options will be implemented but tries to describe the cognitive processes of proficient decision makers
situation-action matching decisions rules
matching isn’t a generic label; for decisions with the basic structure because it is appropriate for the situation, which means that any options are evaluated one at a time
when presented with several options, no by comparing them against each other
matching relies on pattern matching and informal reasoning rather than anayliztial
context-bound informal modelling
Driven by experience and knowledge
exert knowledge is dominant and contact specific and decision makers asense tive smeantive indicating that individuals work as well as the suyantiv contexct
the structure of language
empirical-based prescription
actions are baed on experience; options that are optimal in some formal sense but when they cannot be implemented they are considered worthless
Hydra is blank based training?
simulation
Hydra: Simulation-Based Training enables?
the monitoring of group dynamics, real-time leadership, and naturalistic decision-making in critical incidents
Hydra: Simulation-Based Training - Benefits
• Scenarios are immersive & often replicate real-life conditions
• Allow the person to gain experience in a safe learning environment
• Participants get experience working as a team in high-pressure environments
• Allows for formative assessments of knowledge and decision-making skills of participants
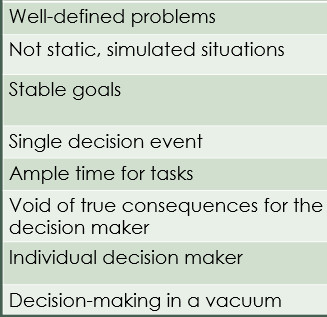
Which decision-making is related to these features?
Traditional

Which decision-making is related to these features?
Naturalistic
Which decision making cannot use all the information that is available all of the time?
Heuristics & Decision-Making
Heuristics & Decision-Making can lead to blank in decision making
biases
When is Recognition-Primed Decision-Making (RPD) model used?
complex and uncertain situations
Recognition-Primed Decision-Making (RPD) 2 processes
situation assessment
evaluation using mental simulation
Slide 16
Done
Key Features of Recognition-Primed Decision-Making (RPD)
Blend of intuition (pattern recognition) and analysis (mental simulation)
NOT just intuition
First option is usually workable
NOT random generation
Satisficing
NOT optimizing
Evaluation through mental simulation
NOT Rational Choice
Focus on elaborating and improving options
NOT choosing between options
Focus on situation awareness
NOT courses of action
Decision maker primed to act
NOT waiting to complete the analysis
What example in lecture is used?
“A hungry donkey stands between two identical hay piles. The donkey always chooses whichever hay is closest to him. Both piles are exactly the same distance apart, one on his right, one on his left, and they are identical in every way. Which pile of hay will the donkey choose to eat?
Why is Critical Incident & Decision-Making research important?
There is a need to incorporate some form of judgement/decision-making theory into existing training curriculums
Knowing where uncertainty comes from allows more focused advice and recommendations to improve training
• Without prior knowledge, training, or frequent exposure, the response is generally one of stress, confusion, frustration, and fear
Result à mistakes!
How do we make decisions?
brain is capable of processing only for a limited of time
1-9 pieces
deciding which information is important
people spontaneously try to make sense of complex information
memory operates in a away that predisposes us to account for information in terms of stories or narratives
blank plays a central role in investigators decision-making
narratives
When does endogenous uncertainty exist?
when situational information is:
sparse
overwhelming
contradictory
novel
Which Critical Incident feature is harder to manage?
endogenous
Where do exogenous uncertainties derive from?
confusion over the expectation of one’s own and other behaviours
comrpomise the effectiveness with which teams plan and execute decisions and action
blank can reduce confidence and self efficacy and cause problems for dynamic decision making
poor role understanding
Exogenous uncertainty can derail teamwork by?
affecting team cohesion and reducing team members willingness to share/seek information with others
Strength of Traditional Decision Making
has a repertoire of sophisticated research designs and methods of quantifying decision outcomes
allow for strictly controlled studies of isolated events in the investigative decision making process
Naturalistic Decision Making favours?
studies of group processes and teamwork which can provide insight to the concept such as team situation awareness shared, problem assessment and them mind and shared mental models
What example was used in lecture with regard to NDM?
firefighters
What is more important expert performance or precision knowledge?
expert performance
What example in the lecture with regard to field studies?
Professor Scott - University of Liverpool
football - hoolignanism
how fans interacted with each other
Critical Decision Making Interview - Single Incident
provides a method of collecting in retrospect insight into different decision makers, decision making processes
very specific
allows researchers to identify critical decision points throughout he deciiuons making prcss in that individent
providece indiations of cues an dpatterns that maybe that experts perceve those kind of rule of thunb theuve devised for making decisons these spcifici situtations
Limits of Field Studies, Simulations & Laboratory Techniques
can’t introduce or interpose the real level or emotional or risk related factors inherent in police decision making
can’t prepare officers the routine or unanticipated conditions that may encounter
Field studies: can’t go in the middle of incident and try and manage the incident
blank act has a halfway point between laboratory and field based approaches in order to maximize the strengths of both methods and minimize limitations
simulation based technologies
Why are simulation based technologies useful?
for synthesizing contrasting traditional and naturalistic decision making approaches because it allows both observation and testing of both these theories at the same time.
Heuristics should be viewed as?
adaptive tools that help us navigate in complex environments and make quick and fairly accurate judgements based on limited information
How can error occur using availability heuristic?
if an event is available because of something other than actual frequency
maybe a recent similar event, recent strong associated emotional experiences to that event
blank is a naturalistic decision making
Recognition-Primed Decision-Making (RPD)
Recognition-Primed Decision-Making (RPD) is based on?
cognitive processes of situation assessment, which is about how decision makers make sense of situations guide action as well as mental simulation evaluation
RPD: Fundamental Scenarios
varying degrees of operator recognition can simplify large proportions of decision processes
Level 1: Simple Match
Level 2: Diagnose the Situation
Level 3: Evaluate Course of Action
What happens in RPD Model: Orient, when Expectancies are violated?
maybe you identified the situation and now we move to decide
blank occurs between the option generation and option evaluation stages of decision making and involves an active engaged effort to decidee
decision inertia
When are decision maker most likely to become inert?
faced with decisions that are least-worst decisions
those in which all choices offer a potentially negative outcome and are high risk
What separated decision inertia in a negative outcome for more general decision or avoidance which can be positive?
if events hasty o reckless decisions; despite the individuals motivation or act they struggle to make a choice either cognitively or behaviourally