Cardiovascular System: Heart, Blood Vessels, and Circulation
1/129
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
130 Terms
What is the major function of the cardiovascular system?
To circulate substances throughout the body, supplying cells with oxygen and nutrients while removing wastes.
Where is the heart located in the body?
Within the mediastinum.
What is the approximate size and weight of an adult heart?
About the size of a closed fist and weighs approximately 300 grams.
What are the three membranes that cover the heart?
Serous pericardium- which includes fibrous, parietal, and visceral- and pericardial cavity.
What are the layers that compose the wall of the heart?
Epicardium, myocardium, and endocardium.
What are the upper chambers of the heart called?
Atria.
How do atria function in blood circulation?
They receive blood from veins passively.
What are the lower chambers of the heart called?
Ventricles.
How do ventricles function in blood circulation?
They pump blood from the heart into arteries actively.
What are the atrioventricular (AV) valves?
Valves that lie between the atria and ventricles, including the tricuspid and bicuspid (mitral) valves.
What is the function of chordae tendineae?
They connect the cusps of AV valves to the papillary muscles, preventing the valves from swinging back into the atria.
What are semilunar (SL) valves?
Valves located at the exit of the ventricles, including the pulmonary and aortic valves.
What is the role of arteries in the cardiovascular system?
To carry blood away from the heart, typically high in oxygen and low in carbon dioxide.
What is the role of veins in the cardiovascular system?
To carry blood toward the heart, typically high in carbon dioxide and low in oxygen.
What is the pathway of blood through the heart starting from the right atrium?
Right atrium → tricuspid valve → right ventricle → pulmonary SL valve → pulmonary trunk → pulmonary arteries → capillaries in lungs → pulmonary veins → left atrium → bicuspid valve → left ventricle → aortic SL valve → ascending aorta.
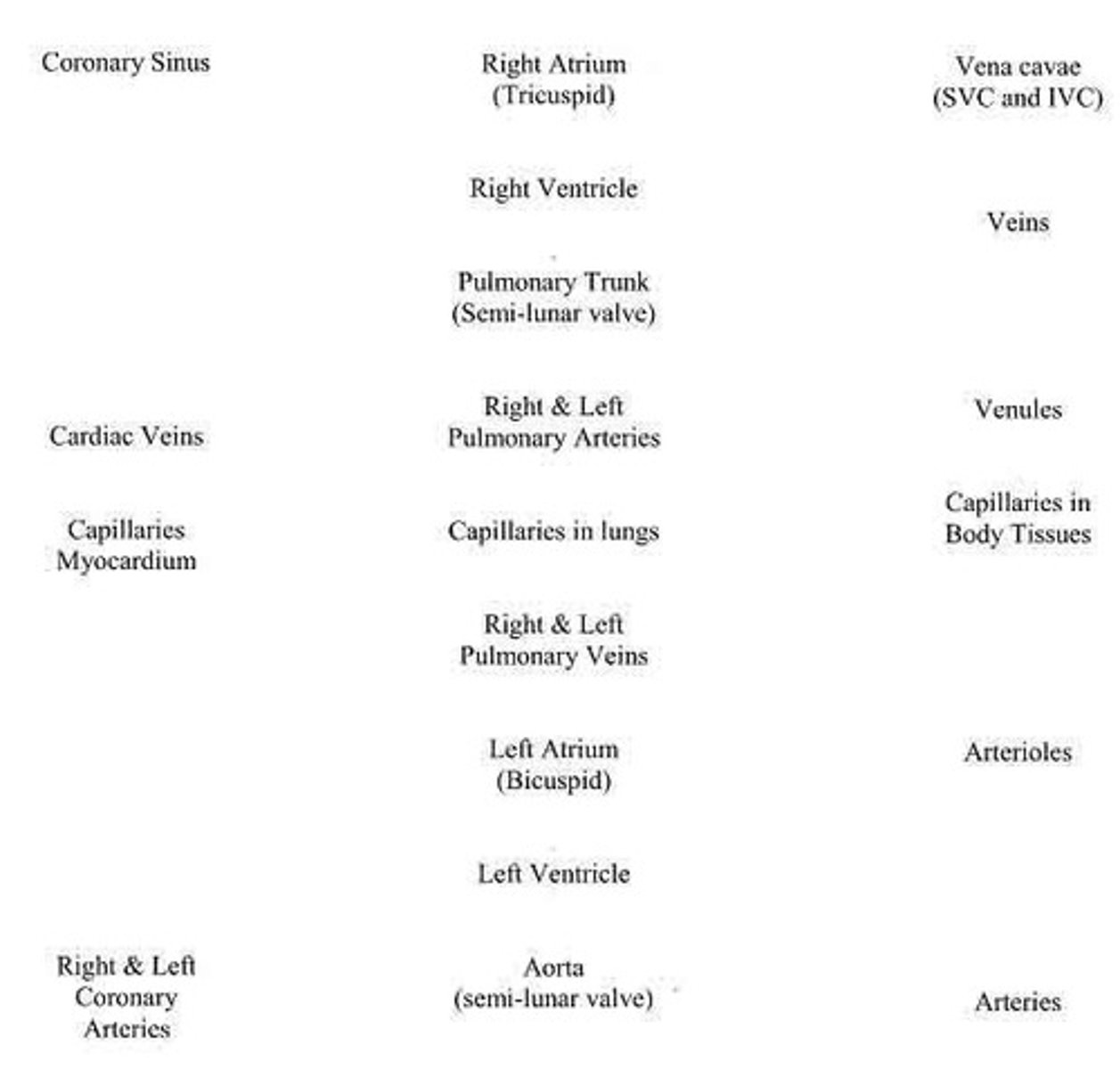
What is the significance of the ligamentum arteriosum?
It is a remnant of the fetal ductus arteriosus.
What occurs during the cardiac cycle?
The heart undergoes a sequence of events including contraction (systole) and relaxation (diastole) to pump blood.
What does an ECG pattern represent?
electrical activity of the heart, indicating the timing of heartbeats.
What are the pressure and volume changes during a cardiac cycle?
Pressure increases during contraction and decreases during relaxation, while volume decreases during contraction and increases during relaxation.
What mechanisms aid in returning venous (deoxygenated) blood to the heart?
Muscle contractions, respiratory movements, and valves in veins
What distinguishes the pulmonary circulation from systemic circulation?
Pulmonary circulation carries deoxygenated blood from the heart to the lungs, while systemic circulation carries oxygenated blood from the heart to the rest of the body.
What is the function of the coronary arteries?
To supply blood to the myocardium (heart muscle).
What is the role of the aorta?
To carry oxygenated blood from the left ventricle to the body.
What is the function of the superior and inferior vena cava?
To bring deoxygenated blood from the body back to the right atrium.
What changes occur in the cardiovascular system with aging?
decreased elasticity of blood vessels, increased blood pressure, and changes in heart function.
What is the first chamber of the heart that receives deoxygenated blood?
Right atrium
What valve is located between the right atrium and right ventricle?
Tricuspid valve
What structure carries deoxygenated blood from the right ventricle to the lungs?
Pulmonary trunk
What is the role of pulmonary veins in the circulatory system?
They carry oxygenated blood from the lungs to the left atrium.
Which valve is located between the left atrium and left ventricle?
Bicuspid or Mitral valve
What is the function of the aortic semi-lunar valve?
It opens to allow blood to flow from the left ventricle into the ascending aorta.
What are the coronary arteries responsible for?
Supplying oxygenated blood to the heart muscle.
What is an anastomosis in the context of coronary circulation?
Connections between two or more branches of arteries that supply the same region with blood.
What is the significance of the cardiac cycle?
It includes all events associated with one heartbeat, involving contraction and relaxation of the heart.
What occurs during ventricular systole?
The ventricles contract and pump blood into the arteries.
What is the role of the sinoatrial (SA) node?
It acts as the pacemaker, initiating cardiac impulses and controlling heart rhythm.
What is the function of the atrioventricular (AV) node?
It serves as a delay signal that allows for ventricular filling.
What does the electrocardiogram (ECG) record?
The electrical changes that occur in the myocardium during the cardiac cycle.
What does the term 'lubb' refer to in heart sounds?
The sound produced by the closing of the AV valves during ventricular systole.
What does the term 'dupp' refer to in heart sounds?
The sound produced by the closing of the semi-lunar valves during ventricular diastole.
What is the purpose of cardiac muscle fibers forming a functional syncytium?
To allow the entire structure to contract as a unit when stimulated.
What are Purkinje fibers responsible for?
Conducting the cardiac impulse into the mass of muscle tissue in the ventricles.
What happens to blood pressure during atrial systole?
Atrial pressure is high, which pumps blood into the ventricles.
What is the significance of the cardiac conduction system (CCS)?
It coordinates the events of the cardiac cycle, making the heart an effective pump.
What is the role of cardiac veins?
To carry deoxygenated blood from the myocardium back to the right atrium.
What is the ascending aorta's function?
To carry oxygenated blood from the left ventricle to the body.
What occurs during ventricular relaxation (diastole)?
The ventricles fill with blood as pressure decreases.
What can an ECG help determine?
If the conduction pathway is normal, if the heart is enlarged, or if certain regions are damaged.
What is the function of capillaries in the myocardium?
To facilitate the exchange of gases.
What is a murmur in heart sounds?
A sound that occurs when the closing of the valve cusps is incomplete, causing blood to leak back.
What does an ECG help determine?
if the conduction pathway is normal, if the heart is enlarged, and if certain regions are damaged.
What precedes contraction in the heart?
Depolarization
What precedes relaxation in the heart?
Repolarization
What does the P wave represent in an ECG?
small upward wave that represents atrial systole (depolarization).
What occurs 0.1 seconds after the P wave begins?
The atria contract.
What does the QRS complex indicate?
the onset of ventricular depolarization.
What happens shortly after the QRS complex begins?
The ventricles start to contract.
What does the T wave represent?
ventricular repolarization.
What is indicated by an enlarged P wave?
It may indicate enlargement of an atrium, possibly due to mitral stenosis.
What does an enlarged Q wave signify?
may indicate a myocardial infarction (MI).
What does an enlarged R wave suggest?
ventricular hypertrophy.
What role does the autonomic nervous system play in heart regulation?
It regulates the cardiac cycle through the cardiovascular center located in the medulla of the brainstem.
How does the parasympathetic nervous system affect heart rate?
It decreases the cardioinhibitor reflex center.
How does the sympathetic nervous system affect heart rate?
It increases the cardioacceleratory reflex center.
What effect do hormones like epinephrine have on the heart?
increases heart rate and contractility.
What is the function of arterioles?
deliver blood to capillaries and regulate blood flow and blood pressure.
What is the structure of arteries?
three layers: tunica interna, tunica media, and tunica externa.
What is the primary function of capillaries?
permit the exchange of gases, nutrients, and wastes between blood and tissues.
What type of capillaries have small openings between endothelial cells?
Continuous capillaries.
What type of capillaries contain pores?
Fenestrated capillaries.
What are sinusoids?
capillaries with large openings and incomplete basement membranes, found in the liver and spleen.
What regulates blood entry into capillary beds?
Precapillary sphincters
What happens to capillary blood flow when metabolic needs are met?
Precapillary sphincters close
What is the net effect of fluid movement in capillaries?
Fluid is lost at the beginning of the capillary bed but most is regained by the end.
What percentage of blood is found in systemic veins and venules?
60-70%
What is the composition of blood in the heart?
8-11%
What is blood pressure?
The pressure exerted by blood on the wall of a blood vessel.
What is pulse?
The pressure wave that travels through arteries following left ventricular systole.
What is the normal range for pulse?
60-100 beats per minute (bpm).
What instrument is used to measure blood pressure?
Sphygmomanometer.
What is the typical blood pressure reading for a normal adult at rest?
120 mm Hg / 80 mm Hg.
What factors influence arterial blood pressure?
Heart action, blood volume, resistance to flow, and blood viscosity.
What is cardiac output (CO)?
The volume of blood pumped by each ventricle each minute, calculated as CO = heart rate (HR) x stroke volume (SV).
What is the normal cardiac output for an adult?
Approximately 5 liters per minute.
What is peripheral resistance (PR)?
The opposition to blood flow primarily due to friction, influenced by blood viscosity, total blood vessel length, and blood vessel radius.
How does blood vessel radius affect blood pressure?
An increase in radius decreases peripheral resistance and therefore lowers blood pressure.
What is the Frank-Starling Law of the Heart?
The strength of heart contraction increases as venous return (preload) increases.
What is the role of baroreceptors?
They detect changes in blood pressure in the aorta and carotid arteries and send impulses to the cardiovascular center.
What happens when blood pressure is too high?
Baroreceptors send signals to decrease heart rate and cause vasodilation to lower blood pressure.
What hormones increase blood pressure?
Epinephrine, norepinephrine, antidiuretic hormone (ADH), angiotensin II, and aldosterone.
What is the function of atrial natriuretic peptide (ANP)?
It decreases blood pressure by causing vasodilation and promoting salt and water loss in urine.
What assists venous blood flow?
Skeletal muscle contractions, one-way valves, and respiratory movements.
What is central venous pressure?
The pressure of blood in the right atrium, which can increase if the heart is weak.
What are the two major circuits of blood circulation?
The pulmonary circuit and the systemic circuit.
What does the pulmonary circuit do?
Carries blood from the right ventricle to the lungs and returns oxygenated blood to the left atrium.
What is the arterial system responsible for?
Carrying blood from the heart to body cells.
What is the venous system responsible for?
Carrying blood from body cells back to the heart.
What is the relationship between blood volume and blood pressure?
There is a direct relationship; an increase in blood volume leads to an increase in blood pressure.
What is the significance of blood viscosity in relation to blood pressure?
Higher blood viscosity (thickness) increases peripheral resistance, which raises blood pressure.
What is the effect of increased total blood vessel length on blood pressure?
raises peripheral resistance and subsequently increases blood pressure.