fetal skeleton
1/202
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
203 Terms
The skeleton initially appears as ____________.
Then, it will later undergo __________.
Cartilaginous
Ossification
Skeletal dysplasia describes abnormal (1)_______ and (2)_______ of cartilage that results in bones that appear (3)__________, (4)______, (5)_________, or fail to form at all.
Growth
Density
Shortened
Thin
Deformed
When the sonographer evaluates the long bones, these 4 questions should be asked:
Are the bones _________ correctly?
Are they all ________?
Are the bones _________?
Are the bones _____ or _________?
Mineralized
Present
Shortened
Bent, Fractured
Some skeletal dysplasias are lethal, meaning they are (1)____________ with life in their more (2)________ forms.
Incompatible
Severe
Nonlethal skeletal dysplasias tend to manifest in a ________ form.
Milder
Sometimes, abnormalities of the fetus can occur due to these 4 pathologies:
______hydramnios
Multiple _________
________ anomalies
___________________ syndrome
Oligohydramnios
Gestations
Uterine
Amniotic band
A patient whose fetus is at risk for skeletal dysplasia will be referred for what?
A targeted US
Many skeletal dysplasias are (1)_________, but can also be (2)________.
Genetic
Sporadic
List the 7 evaluation factors for skeletal dysplasia.
Assess limb shortening
Assess bone contour
Estimate degree of ossification
Evaluate thoracic circumference and shape
Survey for coexistent hand and foot anomalies
Evaluate face and profile
Survey for other associated anomalies (Heart defects and nonimmune hydrops)
When the sonographer is assessing limb shortening, all ______ bones should be measured.
Long
Skeletal dysplasia is suspected when limb length falls (1)________ than (2)___ standard deviations below the mean.
Greater
2
What 3 findings should be noted when assessing bone contour?
Thickness
Abnormal bowing or curvature
Fractures
What 2 factors can indicate hypomineralization?
Decreased attenuation of bones
Decreased shadowing
List 4 skeletal structures to pay close attention to.
Cranium
Spine
Ribs
Long bones
When evaluating thoracic circumference and shape, which 2 sonographic findings can indicate specific dysplasias?
Long, narrow chest
Bell-shaped chest
What is another term for bell shaped chest?
Champagne cork
When surveying hand and foot anomalies, which 2 pathologies should the sonographer look for?
Talipes (club foot)
Polydactyly
Why should the sonographer evaluate the face and profile?
To look for facial abnormalities
Rhizomelia is the (1)________ of the (2)________ segment of extremity.
Shortening
Proximal
Mesomelia is the (1)________ of the (2)________ segment of extremity.
Shortening
Middle
Acromelia is the (1)________ of the (2)________ segment of extremity.
Shortening
Distal
Micromelia is the (1)________ of the (2)________ limb of extremity.
Shortening
Entire
Phocomelia is the (1)________ of a (2)_______ of extremity.
Absence
Segment
Amelia is the (1)________ of the (2)_______ extremity.
Complete absence
Entire
Phocomelia will have either the _________ or _________ segment absent.
Proximal
Middle
What 2 structures are most commonly affected with rhizomelia?
Humerus
Femur
What 2 structures are most commonly affected with mesomelia?
Radius/Ulna
Tibia/Fibula
What 2 structures are most commonly affected with acromelia?
Hands
Feet
What 2 structures are most commonly affected with micromelia?
Entire arm
Entire leg
With phocomelia, the (1)__________ will be directly attached near the (2)_______.
Hands/Feet
Trunk
What 2 structures will be missing with amelia?
Arm
Leg
The shortening of the proximal segment (humerus/femur) of an extremity will be referred to as…
Rhizomelia
The shortening of the medial segment (radius/ulna, tibia/fibula) of an extremity will be referred to as…
Mesomelia
The shortening of the distal segment (hands/feet) of an extremity will be referred to as…
Acromelia
The shortening of the entire limb will be referred to as…
Micromelia
The absence of a segment of an extremity will be referred to as…
Phocomelia
The absence of an extremity will be referred to as…
Amelia

Is this image of the arm normal or abnormal?
If abnormal, what pathology is seen here?
Normal
Normal
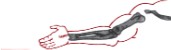
Is this image of the arm normal or abnormal?
If abnormal, what pathology is seen here?
Abnormal
Rhizomelia

Is this image of the arm normal or abnormal?
If abnormal, what pathology is seen here?
Abnormal
Mesomelia

Is this image of the arm normal or abnormal?
If abnormal, what pathology is seen here?
Abnormal
Micromelia
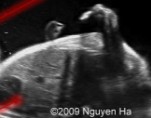
Is this image of the arms normal or abnormal?
If abnormal, what pathology is seen here?
Abnormal
Phocomelia
What pathology is seen in this image?
Amelia
A small thoracic circumference can indicate ________________ thorax.
Bell-shaped
List the 4 common sonographic features seen in fetal skeletal dysplasias.
Severe micromelia
Small thoracic circumference
Short ribs
Poor ossification
List the 7 lethal skeletal dysplasias learned in this lecture.
Thanatophoric dysplasia
Short-rib polydactyly syndrome
Homozygous achondraplasia
Achondrogenesis
Osteogenesis imperfecta II
Congenital hypophosphatasia
Campomelic dysplasia
Short-rib polydactyly syndrome will be ___% lethal.
70%
List the 5 non-lethal skeletal dysplasias learned in this lecture.
Heterozygous achondroplasia
Osteogenesis imperfecta I
Osteogenesis imperfecta III
Osteogenesis imperfecta IV
Arthrogryposis
What is the most common lethal skeletal dysplasia?
Thanatophoric Dysplasia
Thanatophoric dysplasia is _________ in occurrence.
Sporadic
List the 5 US findings of Thanatophoric dysplasia.
Severe micromelia
Kleeblattschadel (clover leaf skull)
Platyspondyly
Narrow thorax with shortened ribs and protuberant abdomen
Large head with prominent forehead (frontal bossing)
Thanatophoric dysplasia will see severe micromelia, meaning the femur will be shaped how?
Like a telephone
What is another term for kleeblattschadel?
Cloverleaf skull
What is another term for cloverleaf skull?
Kleeblattschadel
Kleeblattschadel (cloverleaf skull) occurs as a result of what other pathology?
Premature craniosynostosis
What does platyspondyly mean?
Flattened vertebral bodies
How does platyspondyly appear on US? (2)
Flat vertebral bodies
Increased intervertebral disc space
Which 2 chest shape pathologies can be found with thanatophoric dysplasia?
Bell shaped
Champagne cork
What is the medical term for ‘large head with prominent forehead’?
Frontal bossing
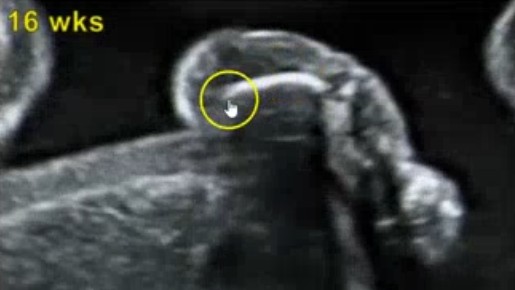
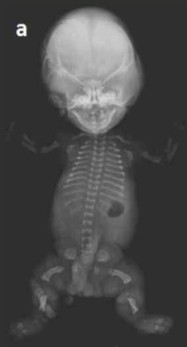
What is abnormal about this image if the femur is telephone shaped?
This image can be an US finding of what pathology?
Severe micromelia
Thanatophoric dysplasia
What is abnormal about this image?
Micromelia
What is abnormal about this image?
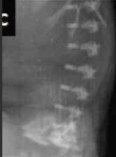
This finding can be associated with what pathology?
Platyspondyly
Thanatophoric dysplasia
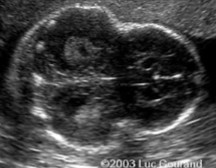
What is abnormal about this image?
This finding can be associated with what pathology?
Kleeblattschadel (Cloverleaf skull)
Thanatophoric dysplasia
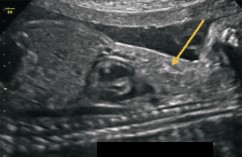
What is abnormal about this image?
This finding can be associated with what pathologies?
Bell shaped thorax
Thanatophoric dysplasia
Osteogenesis Imperfecta Type 2
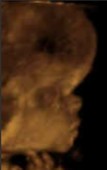
What is abnormal about this image?
This finding can be associated with what pathology?
Frontal bossing
Thanatophoric dysplasia
Achondroplasia
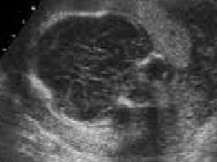
What is abnormal about this image?
This finding can be associated with what pathologies?
Kleeblattschadel (Cloverleaf skull)
Thanatophoric dysplasia
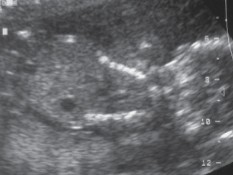
What is abnormal about this image?
Champagne cork thorax
Short rib polydactyly syndrome is a ________ skeletal dysplasia.
Lethal
Short rib polydactyly syndrome is characterized by what 4 factors?
Short ribs
Narrow thorax
Short limbs (micromelia)
Polydactyly
Infants with short rib polydactyly syndrome die due to what pathology?
Pulmonary hypoplasia
These 5 findings can be associated with short rib polydactyly syndrome:
______ anomalies
____________ system anomalies
__________ anomalies
_______ anomalies
_____hydramnios
CNS
Cardiovascular
GU tract
Face
Polyhydramnios
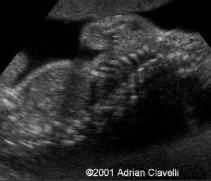
What is abnormal about this image?
Short ribs
Narrow thorax
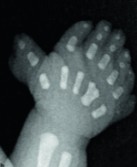
What is abnormal about this image?
This finding can be associated with what pathology?
Polydactyly
Short rib polydactyly syndrome
Ellis-Ven Creveld Syndrome
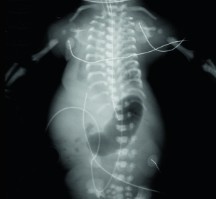
What is abnormal about this image? List each one.
This finding can be associated with what pathology?
Short ribs, narrow thorax, and short limbs (micromelia)
Short rib polydactyly syndrome
Achondrogenesis
Dwarfism refers to a ___________ and ______ stature.
Disproportionately
Short
Achondroplasia is associated with…
Dwarfism
Achondroplasia produces ________ and _______ bones.
Short
Squatty
List the 2 types of achondroplasia.
Heterozygous achondroplasia
Homozygous achondroplasia
Which form of achondroplasia occurs 80% of the time?
Heterozygous achondroplasia
Which form of achondroplasia occurs 20% of the time?
Homozygous achondroplasia
What is the name of the most common nonlethal skeletal dysplasia?
Heterozygous achondroplasia
Which form of achondroplasia has a good survival rate, normal intelligence, and a normal life span?
Heterozygous achondroplasia
Which form of achondroplasia is considered lethal?
Homozygous achondroplasia
What are the 2 main sonographic findings of homozygous achondroplasia?
Severely narrow thorax
Rhizomelia
Most infants with homozygous achondroplasia will die shortly after birth due to ____________ complications.
Respiratory
List the 4 US findings of achondroplasia.
Rhizomelia
Trident hands
Frontal bossing
Macrocephaly
Define trident hands.
Increased space between the 3rd and 4th digits

What is abnormal about this image?
This finding can be associated with what pathology?
Trident hands
Achondroplasia
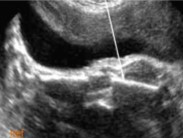
The femur is at a shortened length in this image. What is that referred to as?
This finding can be associated with what pathology?
Rhizomelia
Achondroplasia
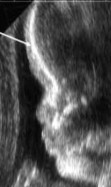
What is abnormal about this image?
This finding can be associated with what pathologies?
Frontal bossing
Achondroplasia
Thanatophoric dysplasia
Achondrogenesis is a rare, _______ skeletal dysplasia.
Lethal
Infants suffering from achondrogenesis will either be (1)_________ or (2)_____ shortly after birth from (3)_____________________.
Stillborn
Die
Pulmonary hypoplasia
What is achondrogenesis caused from?
What 2 pathologies will achondrogenesis result in?
Cartilage abnormalities
Abnormal bone formation
Hypomineralization
List the 6 US findings of achondrogenesis.
Decreased or absent ossification of spine
Severe micromelia
Decreased cranial ossification
Short thorax and short ribs
Micrognathia
Polyhydramnios
Define micrognathia.
Abnormally small jaw
Decreased cranial ossification will be seen because the sonographer will be able to ________ the skull.
Compress
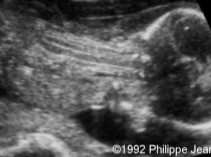
What is abnormal about this image?
This finding can be associated with what pathologies?
Decreased or absent ossification of the spine
Achondrogenesis
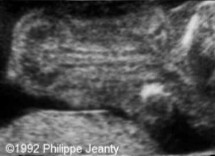
What is abnormal about this image?
This finding can be associated with what pathologies?
Decreased or absent ossification of the spine
Achondrogenesis
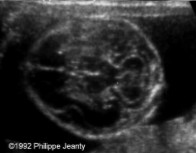
What is abnormal about this image?
This finding can be associated with what pathologies?
Decreased cranial ossification
Achondrogenesis
Osteogenesis Imperfecta Type II
Osteogenesis imperfecta is a rare disorder of (1)________ production leading to which 2 pathologies?
Collagen
Brittle bones
Blue sclera