Business - human resource management (sac2)
1/115
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
116 Terms
Human resource management
the effective management of the formal relationship between the employer and employees
Human resource manager
coordinates all the activities involved in acquiring, developing, maintaining and terminating employees from a business's human resources
Productivity
a measure of performance that indicates how many inputs (resources) it takes to produce an output (goods or services)
How human resource strategies can support business objectives
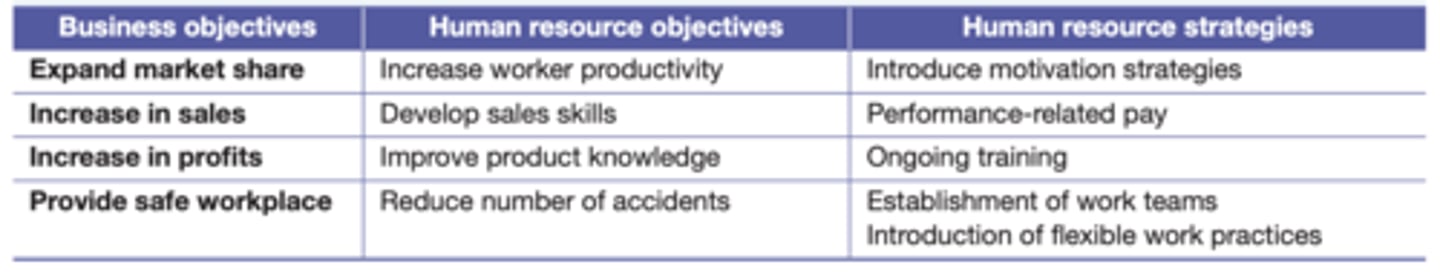
Relationships between human resource management and business objectives
employees play a key role in achieving business goals.
effective employee management strategies (like recruitment and training) boost performance and support objectives.
the HR department helps set and support business objectives across departments.
positive work relationships foster motivation, productivity, and goal achievement.
Motivation
the individual, internal process that directs, energises and sustains a person's behaviour
Need
a personal requirement
Hierarchy of needs
Maslow's sequence of human needs in the order of their importance
Maslow's hierarchy of needs in order
self-actualisation: need for development, creativity and growth.
esteem: need for self-esteem, power, control and recognition.
social: need for love, belonging and inclusion
safety: need for safety, shelter and stability
physiological: need for air, food, water and health
Workplace practices to satisfy these needs
self-actualisation: creative, interesting jobs opportunities for advancement
esteem: responsibility, promotion, recognition
social: teamwork, involvement in decision making, supportive management
safety: safe working conditions, job security
physiological: satisfactory pay for survival
Strengths of Maslow's hierarchy of needs
helps managers recognize that each employee has unique needs.
reminds managers that employees are at different development stages and require different motivational approaches.
simple and easy for both managers and employees to understand and apply.
Weaknesses of Maslow's hierarchy of needs
Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs lacks empirical evidence and may not apply to everyone.
managers may find it hard to pinpoint each employee's exact stage, making motivation strategies difficult to tailor.
overly simplistic, as one strategy can often meet multiple needs at once.
Locke and Latham's five principles of goal setting
clarity
challenge
commitment
feedback
task complexity
Clarity
clear, specific, and time-bound goals are more effective for motivation than vague instructions, as they provide measurable expectations and guide actionable steps.
Challenge
employees are most motivated by challenging yet achievable goals that are meaningful to the business and aligned with its objectives, offering appropriate rewards for success.
Commitment
employee commitment to a goal increases when they have input in setting it, making them more motivated and likely to achieve challenging goals that align with both their strengths and business objectives.
The importance of employee commitment to a goal
1. employee input into the goal
2. increased commitment from employee
3. goal can be made more challenging
4. increased rewards and motivation
Feedback
an effective goal program should include regular feedback to recognize progress, clarify expectations, and adjust goals if needed, with the format and frequency depending on the goal's complexity and duration.
Task complexity
goals should be challenging but achievable, with tasks that aren't overwhelming, supported by appropriate training and timelines to ensure employee motivation and business success.
Strengths of Locke and Latham's goal setting theory
clear, specific, and challenging goals motivate employees and enhance performance.
research supports that such goals, along with commitment and feedback, improve motivation.
employees perform to a higher standard, increasing productivity.
collaboration on goal-setting and feedback strengthens relationships between managers and employees.
Weaknesses of Locke and Latham's goal setting theory
vague, overly easy, or overwhelming goals can lead to poor performance and demotivation.
employee goals may conflict with each other or business objectives.
intense focus on goals might cause employees to neglect other job aspects.
focuses only on goal-setting, ignoring other performance factors.
failing to meet a goal can harm an employee's confidence.
Lawrence and Nohria's four drive theory
drive to acquire: includes the desire to own material goods, and encompasses the desire for status, power and influence.
drive to bond: the strong need to form relationships with other individuals and groups.
drive to learn: includes our desire to satisfy our curiosity, to learn new skills and to explore the world around us.
drive to defend: desire to remove threats to our safety and security and to protect what we regard as 'ours'.
Strengths of Lawrence and Nohria's four drive theory
the drives work independently, offering flexibility in behavior and strategy choices.
adaptable to complex environments or situations.
the four drives translate into effort that enhances behavior, improving business performance and achieving objectives.
Weaknesses of Lawrence and Nohria's four drive theory
other drives beyond the four outlined by Lawrence and Nohria may also influence motivation.
workplace competition can negatively impact cooperation and information sharing.
Similarities between hierarchy of needs and goal setting theory
Locke and Latham's goal achievement is similar to Maslow's esteem and self-actualization needs.
both theories emphasize the importance of recognition, feedback, and job satisfaction as motivators.
both focus on achieving one objective at a time.
Differences between hierarchy of needs and goal setting theory
Maslow's theory is long-term, while Locke and Latham's is short-term with new goals after each achievement.
Locke and Latham focus on individual goals, while Maslow encourages company-wide progression.
Maslow focuses on internal needs, while Locke and Latham align external goals with business objectives.
employees are key in Locke and Latham's theory, while managers play a larger role in Maslow's.
Similarities between goal setting theory and four drive theory
Locke and Latham's goal rewards align with Lawrence and Nohria's drive to acquire.
both theories emphasize managers understanding employee needs.
both focus on employees, with Locke and Latham involving them in goal-setting and Lawrence and Nohria focusing on their drives.
cooperation is key in both, with Locke and Latham focusing on goal-setting and feedback, and Lawrence and Nohria on understanding drives.
Differences between goal setting theory and four drive theory
Lawrence and Nohria's theory focuses on internal drives, while Locke and Latham's on external goals.
Locke and Latham focus on one goal, while Lawrence and Nohria address all four drives simultaneously.
goal Setting Theory aligns with business objectives, four drive theory with internal motivation.
Similarities between hierarchy of needs and four drive theory
both theories were originally designed to explain human behavior and later adapted for workplace motivation.
both emphasize employee satisfaction: Maslow focuses on esteem and self-actualization, while Lawrence and Nohria focus on the four drives.
the drive to acquire aligns with Maslow's physiological needs.
the drive to bond corresponds to Maslow's social needs.
the drive to learn is similar to satisfying self-actualization needs.
Differences between hierarchy of needs and four drive theory
Maslow's theory has five hierarchical levels, while Lawrence and Nohria's four drives are of equal importance.
Maslow's theory follows a sequential progression, while the four drives can be satisfied simultaneously.
the drive to defend focuses on minimizing negatives, unlike Maslow's hierarchy, which emphasizes positive motivators.
5 motivation strategies
performance related pay
career advancement
support
sanction
investment in training
Performance related pay
the monetary compensation provided to employees relative to how their performance is assessed according to set standards
Short term effect of performance related pay
performance-related pay, including bonuses and commissions, has a short-term motivational effect but can provide longer-term motivation when used consistently as employees anticipate regular rewards for their efforts.
Long term effect of performance related pay
share plans, profit sharing, and gainsharing provide longer-term motivation as rewards take time to materialize, requiring employees to adopt a long-term perspective on business success.
Advantages of performance related pay
provides financial rewards tied to improved performance.
aims to boost productivity, engagement, and commitment.
Rewards are predictable and easily calculated.
applies only when there is actual performance improvement.
Disadvantages of performance related pay
similar rewards may create jealousy and conflict among employees with differing performance.
businesses may struggle to afford performance-related pay.
If rewards are not increased yearly, employee dissatisfaction may arise.
low base pay can lead to high turnover if employees don't earn enough.
not all employees are motivated by pay.
Career advancement
the assignment of more responsibilities/authority to employees or the promotion of employees to positions that bring rewards, such as increased salary, fringe benefits and increased responsibilities
Short term effects of career advancement
moving into a more challenging position with supervisory or managerial responsibilities can provide a pay rise and greater job security, satisfying low-order needs on Maslow's hierarchy and offering motivation to perform well.
Long term effects of career advancement
career advancement satisfies higher-level needs in Maslow's hierarchy, including social, esteem, and self-actualization needs, while also fulfilling drives such as achievement, status, bonding, and learning, encouraging employees to stay with the organization.
Advantages of career advancement
helps retain valuable employees.
rewards past performance and encourages future contributions.
promoted employees feel they can contribute more, boosting productivity, engagement, and commitment.
satisfies employees seeking achievement or additional responsibility.
Disadvantages of career advancement
promotion positions must have a clear purpose, not just be created.
limited promotion opportunities may lead to rivalries and conflict.
promotions can cause resentment if others feel they deserve the position.
employees may be promoted beyond their capacity.
Support
the assistance or services (such as counselling and mentoring) provided by the business to help employees cope with difficulties that may impede their work performance
Short term effects of support
providing support and encouragement for good performance or after a mistake can motivate employees to improve and learn from their experiences.
Long term effects of support
a supportive workplace fosters loyalty and long-term motivation, encouraging employees to remain committed to the work environment.
Advantages of support
many forms of support, like encouragement, have little to no cost.
services like counseling and mentoring help develop meaningful professional relationships.
support and encouragement positively influence employee attitudes, boosting confidence and motivation.
Disadvantages of support
it can be challenging to find reasons to support and encourage some employees.
employees may become overly dependent on support services or the person providing them.
a positive corporate culture is necessary for effective support and encouragement.
Sanction
a form of penalty or discipline imposed on an employee for poor performance
Short term effects of sanction
fear of sanctions can motivate employees by addressing lower-order needs, such as physiological and safety needs, and the defense drive, but only impacts short-term motivation.
Long term effects of sanction
this approach has limited value in fostering long-term commitment to the business, as it does not encourage sustained employee engagement.
Advantages of sanction
sanctions for poor behavior can motivate employees to improve performance.
sanctions may quickly stop inappropriate behavior in some employees.
Disadvantages of sanction
excessive focus on sanctions can reduce employees' sense of belonging, negatively impacting motivation.
sanctions may cause resentment, leading to conflict between management and staff.
sanctions are typically a short-term motivator.
Investment in training
the direction of finances, or resources such as time, into the teaching of skills to employees
Short term effects of investment in training
providing additional skills increases job satisfaction and short-term motivation, as employees seek higher-paying jobs through training opportunities.
Long term effects of investment in training
training supports long-term motivation by fulfilling esteem and self-actualization needs, aligning with Locke and Latham's Goal Setting Theory and Lawrence and Nohria's drives, enhancing employee skills and contributing to business objectives.
Advantages of investment in training
shows employees they are valued and supported in career growth.
enhances skills, boosting confidence, productivity, and business performance.
satisfies higher-level needs, aligns with goal-setting theory, and meets some drives.
improves retention by increasing loyalty and motivation.
Disadvantages of investment in training
training may be ineffective if there are insufficient higher-level skill jobs available.
the business may struggle with the costs of training.
training investment can be lost if employees leave for other opportunities.
poor systems, facilities, or mismatched job roles can prevent training from motivating employees.
Training
the process of teaching staff how to do their job more efficiently and effectively by boosting their knowledge and skills
Benefits of training - employees
opportunity for promotion and self-improvement Improved job satisfaction through better job performance
a challenge means the chance to learn new things adaptability means greater ability to adapt to and cope with changes
Benefits of training - business
higher productivity through better job performance and more efficient use of human resources Goals and objectives more effectively met
reduced costs due to less labour turnover and absenteeism, and fewer errors and accidents
a more capable, 'mobile' workforce
Training options
on the job training
off the job training
On the job training
involves employees learning specific skills for tasks within the workplace, using the equipment and resources available in that environment.
Advantages of on the job training
cost-effective as there are no travel or additional expenses.
employees remain productive while training.
trainees use the actual equipment needed for the job.
employees train in a familiar environment with familiar colleagues.
immediate feedback from experienced colleagues is available.
Disadvantages of on the job training
trainer quality may vary, and not everyone can teach effectively.
older staff may pass on bad habits to newer employees.
the learning environment may be noisy and distracting.
using real tools and equipment for training can disrupt production.
trainers may need to leave their own duties to conduct training.
Off the job training
off-the-job training involves employees learning skills at an external location, typically through specialised institutions like universities or TAFE colleges.
Advantages of off the job training
offers a wider range of skills and qualifications than in-house training.
provides access to outside experts and broader experiences.
more structured with clear assessment processes.
may lead to formally recognised qualifications.
allows focused, distraction-free learning for both trainer and trainee.
Disadvantages of off the job training
can be too theoretical without hands-on experience.
more costly due to fees and travel expenses.
results in lost productivity during employee absence.
qualified employees may leave for better opportunities.
training may not directly match workplace skill needs.
Development
the process of preparing employees to take on more responsibilities in the future, acquiring better knowledge and skills, and gaining more experience
Performance management
a focus on improving both business and individual performance through relating business performance objectives to individual employee performance objectives
4 performance management strategies
management by objectives
performance appraisals
self-evaluation
employee observation
Management by objectives
a process by which management and employees agree on a set of goals for each employee, with these goals all contributing to the objectives of the business as a whole
Advantages of management by objectives
involving employees in goal setting boosts productivity and responsibility.
clarifies expectations for both managers and employees.
identifies training needs, supporting career development.
enhances communication and awareness of business objectives.
Disadvantages of management by objectives
can be time consuming since meetings and reports required can add to the responsibilities and burden of both management and employees. This can also add to expenses. management by objectives is not always useful for all types of employees.
failure to meet objectives could become demoralising for some employees, resulting in a lack of motivation.
staff who meet objectives may expect a pay rise or promotion this can be expensive for a business.
Appraisal
the formal assessment of how efficiently and effectively an employee is performing their role in the business
Advantages of appraisal
encourages communication and strengthens manager-employee relationships.
provides feedback to help employees improve performance.
supports decisions on pay, promotions, and dismissals.
Disadvantages of appraisal
time-consuming, especially with frequent appraisals.
can cause stress for both managers and employees.
meeting performance standards may lead to costly expectations for rewards.
Self-evaluation
a process whereby employees carry out self-assessment, based on a set of agreed criteria
Advantages of self-evaluation
encourages employee involvement and understanding of their role.
helps employees assess their own strengths, weaknesses, and performance.
gives the business insight into employee self-perception and development needs.
identifies training needs and allows employees to request support.
Disadvantages of self-evaluation
employees may exaggerate or be dishonest in self-evaluations.
managers still need to monitor and address performance issues.
some employees may lack confidence in assessing themselves.
training needs identified may increase business costs.
Employee observation
a strategy where a variety of opinions on the performance of employees is sought with the aim of arriving at a more comprehensive picture of past and current performance
Advantages of employee observation
provides well-rounded feedback from multiple sources for a complete view of performance.
helps identify strengths, weaknesses, and key soft skills like teamwork and leadership.
encourages employees to learn from high-performing peers.
peer feedback may be more impactful if employees value their colleagues' opinions.
Disadvantages of employee observation
observation can cause employee stress and may not accurately assess technical skills.
requires a high level of trust to avoid biased or harmful feedback.
positive feedback might lead to costly expectations for rewards.
Voluntary termination
retirement
resignation
redundancy
Involuntary termination
dismissal
redundancy
Termination
the ending of the employment of an employee
Retirement
occurs when an employee decides to give up fulltime or part-time work and no longer be part of the labour force
Resignation
the voluntary ending of employment by the employee 'quitting' their job
Redundancy
occurs when a person's job no longer exists, usually due to technological changes, a business restructure, or a merger or acquisition
Dismissal
occurs when the behaviour of an employee is unacceptable and a business terminates their employment
Unfair dismissal
when an employee is dismissed because the employer has discriminated against them in some way, such as firing someone because she is pregnant
Entitlement considerations
the rights to benefits that employees have when leaving the workplace, either on a voluntary or an involuntary basis
Transition considerations
issues relating to the process of changing from one job to another or from one set of circumstances to another
Workplace relations
it is the process of communication and negotiation between employers and employees (or their representatives) to establish working conditions that satisfy both employee needs and business objectives.
Participants in the workplace
human resource managers
employees
employer associations
unions
fair work commission
Role of human resource manager
negotiation of employment agreements with employees and their representatives
training of staff and other managers
implementation of the agreement
dealing with disputes
Trade unions
organisations formed by employees in an industry, trade or occupation to represent them in efforts to improve wages and the working conditions of their members
Employer associations
organisations that represent and assist employer groups
Log of claims
a list of demands made by workers, typically through their union, regarding wages and conditions, with employers potentially responding with a counter-list of claims.
Fair work commission
Australia's national workplace tribunal that has a number of responsibilities under the Fair Work Act 2009
Award
a legally binding document determined by the Fair Work Commission that sets out minimum wages and conditions for whole industries or occupations
Advantages of awards
less costly for the business
less time spent determining terms and conditions
less work for management as allowances are pre-determined
employees have limited input
provides a stable and secure safety net for employees