JW 5 & 6 Heterocycles, 5-membered rings with 1 heteroatom
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
12 Terms
What is a heterocycle?
Heterocycles are cyclic compounds containing one or more different atoms than carbon
Carbocycles are cyclic compounds that are only contain carbon like cyclohexane or benzene
Heterocycles can be aromatic or non-aromatic
a non-aromatic heterocycle will behave similarly to an open chain compound
What are some examples of aromatic heterocycles? What causes their unique chemistries?
The properties of each one will depend on ring size and the number of heteroatoms
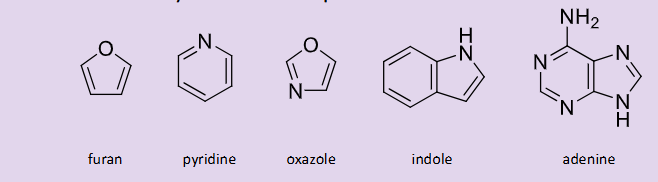
Do pyrrole, furan and thiophene comply with the rules of aromaticity?
yes
They have 4n + 2pi electrons, they are planar for orbital overlap and they are fully conjugated
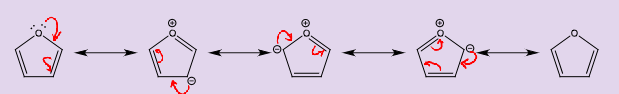
What is the difference between tautomerisation and resonance?
Resonance is the movement of electrons only and does not create real or different compounds, it is instantaneous and signified by a double headed arrow.
Tautomerisation is the movement of electrons and hydrogens, it makes real and different compounds and is not instantaneous and is show by equilibrium arrows.
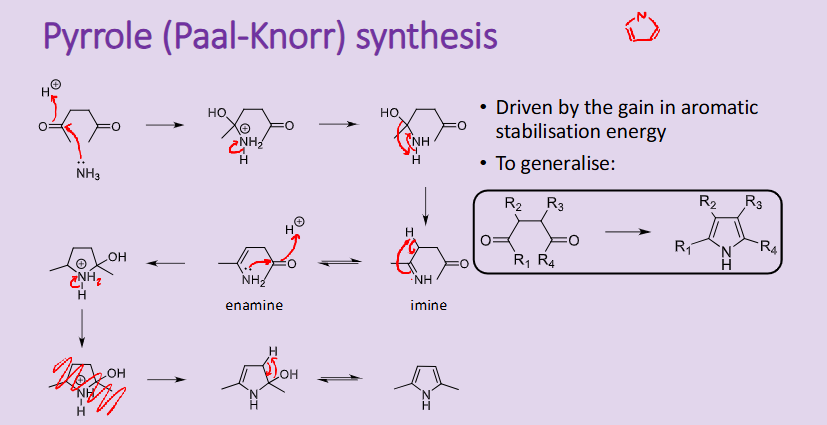
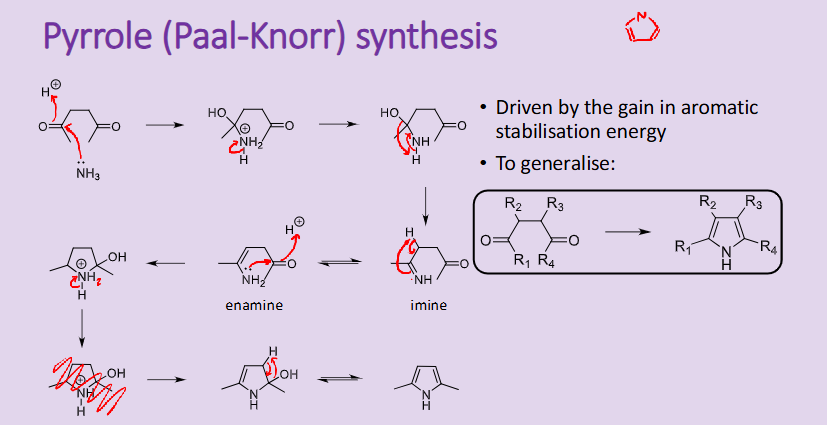
Outline the reaction, conditions and the mechanism for the Pyrrole Paal Knorr synthesis
reaction driven by the aromatic stabilisation energy
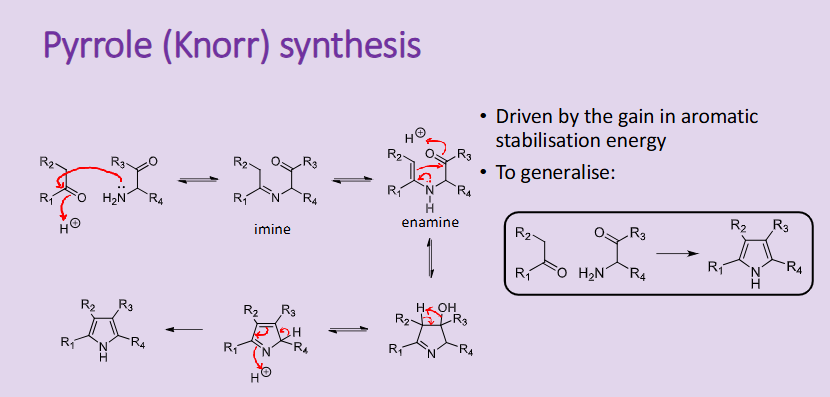
Outline the reaction, conditions and the mechanism for the Pyrrole Knorr synthesis
driven by the gain in aromatic stabilisation energy
How is pyrroles basicity assessed?
the N lone pair is involved in resonance but not readily available so this makes the assumption pyrrole is not very basic
protonated pyrrole has a very low pKa of 0.4 which shows that as it is very low, pyrrole is acidic and wants to lose a proton
Therefore pyrrole is NOT basic
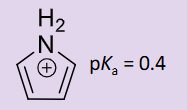
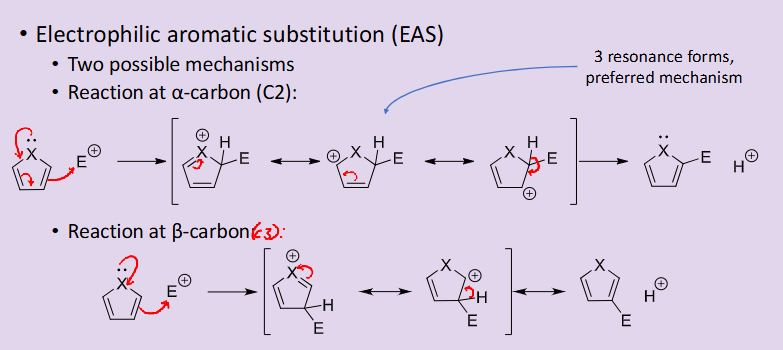
Outline the two general potential mechanisms for an electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction
What are some common electrophiles for electrophilic aromatic substitution?
Br+ - sourced from Br2
NO2+ - sourced from acetyl nitrate
RC+=O - sourced from RCOCl and AlCl3
SO3H+ - sourced from molecule in image
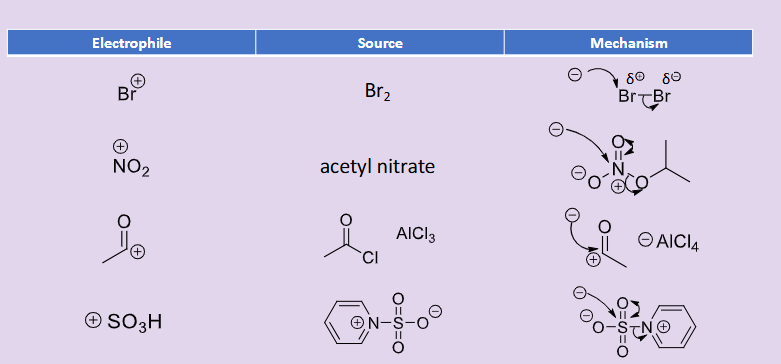
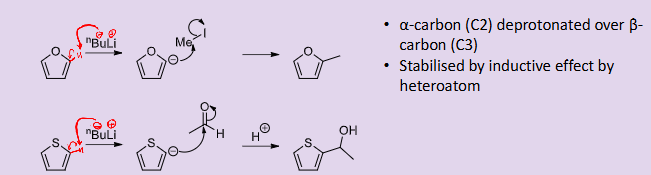
What is the order of reactivity for the 5-membered 1-heteroatom heterocycles
Most to least reactive: pyrrole > furan > thiophene > benzene
How can anionic substitution occur in pyrrole?
it can occur on the Nitrogen and on the alpha carbon atom
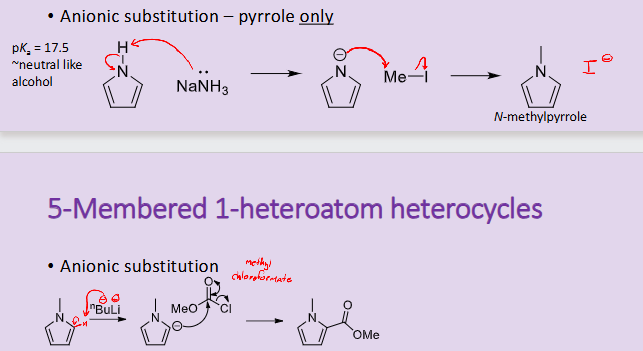
How does anionic substitution occur for furan and thiophene?
it can only occur on the alpha carbon and not on the heteroatom like pyrrole