Topic 5 - The Working Cell
1/52
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
53 Terms
plasma membrane
a phospholipid bilayer that selectively allows (semipermeable) for the diffusion of small, nonpolar molecules (e.g. oxygen, carbon dioxide) and lipid molecules
What's embedded within the plasma membrane?
cholesterol, proteins (peripheral & integral), glycoproteins, glycolipids
What is the fluid mosaic model?
a model that represents the cell membrane as a fluid “mosaic” of components
What properties affect membrane fluidity?
phospholipid type (saturated v. unsaturated fatty acids), cholesterol, temperature
passive transport
cell doesn’t expend energy for this, specifically, relying on diffusion
diffusion
a form of passive transport that represents molecular movement from a region of high concentration to low concentration (requires a concentration gradient)
active transport
cell must expend energy
bulk transport
involves membranous vesicles moving large substances
endocytosis
when a cell takes in materials from its outside environment into their membrane by engulfing them in the plasma membrane, forming a vesicle.

exocytosis
where a cell expels large molecules and/or waste products by fusing a vesicle with the plasma membrane
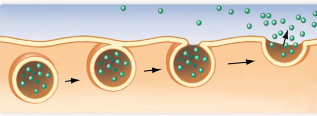
What cannot pass through the hydrophobic core of the plasma membrane?
polar and charged molecules
Facilitated passive transport
requires integral proteins aka “transport proteins”
Channel Proteins
specific to the transported substance which are sometimes open all the time and sometimes only open when a signal is received (e.g. aquaporin)
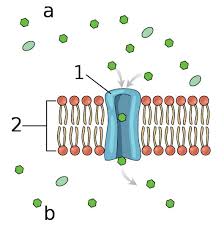
Carrier Proteins
specific to the transported substance and some are used in active transport (e.g. GLUT)
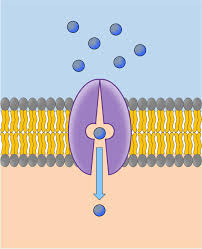
Osmosis
the diffusion of water across a semi-permeable membrane (molecular movement moves from high solvent to an area of low solvent concentration)
Water moves from…
an area of low osmolarity to an area of high osmolarity
osmolarity
describes the solution’s total solute concentration
hypertonic solution
net movement of water OUT of the cell, leading to cell shrinking
hypotonic solution
net movement of water INTO the cell, leading to cell swelling and burst due to excessive water intake
isotonic solution
no net movement IN or OUT of the cell due to equal solute concentration
Active transport
utilizes energy to move substances from low to high concentration, requiring the using integral carrier proteins known as pumps
What are the 3 types of carrier proteins used for active transport?
uniporters, symporters, and antiporters
Uniporters
move a SINGLE type of molecule/ion down a concentration gradient
Symporter
moves TWO types of molecules/ions in the SAME direction
Antiporter
moves TWO types of molecules/ions in OPPOSITE directions
Primary Active Transport
energy is directly provided by ATP hydrolysis
Secondary Active Transport
energy stored in electrochemical gradient that relies on the flow of another ion to provide energy to move another molecule against its gradient
energy
the capacity to do work
kinetic energy
energy in motion
potential energy
stored energy
How can PE be transformed into KE?
as energy conversion generates heat byproduct
What type of energy do hydrocarbons contain?
chemical energy
How does the structure & function of ATP allow for it to function as a battery?
stores energy obtained from food and releases it later as needed
Metabolism
sum of all chemical reactions within an organism
Anabolism
process that assemble/build larger molecules from smaller ones (requires energy)

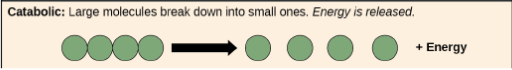
Catabolism
process that break down larger molecules to smaller ones (requires energy)
What is the change in G (available energy) in exergonic reactions?
delta G < 0

What is the change in G in endergonic reactions?
delta G > 0
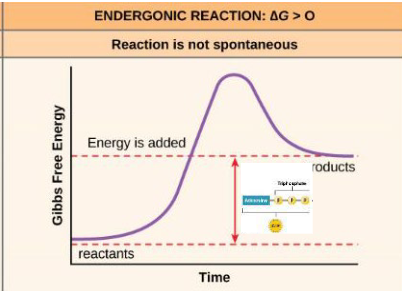
Enzymes
proteins that function as biological catalysts by decreasing activation energy
Enzyme-Substrate Complex
enzymes have a highly specific active site to fit the shape + chemistry of a substrate (the entry of a substrate enables shape change of the enzyme to further perfect the fit in which products are released afterwards)
Enzyme Inhibitor
molecules that binds to an enzyme and reduces the rate of enzymatic reactions
Competitive Inhibition
compete with substrates to bind at an enzyme’s active site
Noncompetitive Inhibition
bind at the allosteric site of an enzyme
What are forms of enzyme regulation?”
enzyme inhibitor, allosteric regulators
Allosteric Regulator
molecule that binds at a site other than an enzyme’s active site that leads to a change in the active site
How do cells communicate with each other?
signaling molecules, receptor proteins, signal transduction pathway
Membrane Proteins
proteins embedded in the cell membrane that receive external signals like hormones and neurotransmitters
Receptor Proteins
a specialized class of proteins that recognize and bind to a specific ligand
Signal Transduction Pathway
a sequence of chemical reactions that lead to cellular response
What are 3 types of membrane receptors?
G-Protein coupled receptor, enzyme-linked, ion channel gated receptor
What are the 3 types of signaling molecules?
hormones, neurotransmitters, pheromones (can be hydrophobic or hydrophilic)
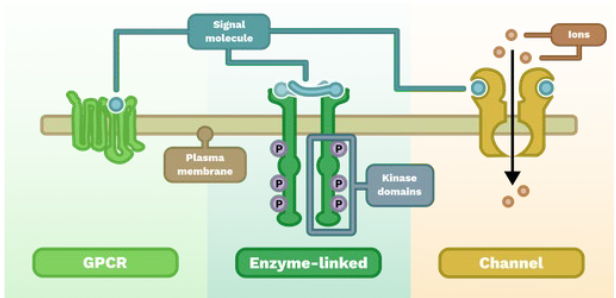
How doe membrane receptors receive signaling molecules to start the process of cellular response?
a signaling molecule attaches to the receptor protein and the receptor protein accelerates the creation of product from substrate (signaling molecule), upon reaction completion, the signaling molecule upon creating necessary products
