11 - Elbow
1/70
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
71 Terms
what are the 3 joints in the elbow?
humeroulnar, radioulnar, humeroradial
where is the humeroulnar joint? what is the angle of the humeral head?
between the trochlea of humerus and trochlear notch of ulna
posterior angle of 30-45º
what is the ulnar (medial) collateral ligament? when are the ulnar collateral ligaments tight?
runs obliquely
anterior fibers tight in extension, posterior fibers tight in flexion >90º
what is the radial (lateral) collateral ligament?
runs from the lateral epicondyle to the annular ligament, thickening of the capsule
what does the annular ligament do?
secures the proximal radioulnar joint
where is the origin and insertion of the lateral ulnar collateral ligament?
origin: lateral epicondyle
insertion: lateral olecranon
when is the interosseous membrane taut? what is its function?
5º of supination
prevents proximal displacement of the radius on the ulna
what is the function of the ulnar coronoid process? what provides varus/valgus stability at the elbow?
prevents posterior displacement
trochlea and ulnar fossa, in the last 30º of ext, the olecranon locks in the fossa providing valgus stability
T/F the joint capsule contains the humeroulnar and humeroradial joint and not the radioulnar joint
F, contains all 3 joints
what is the function of the anconeus?
is a dynamic stabilizer in response to varus stress and pronation/supination
initiates elbow ext but ineffective at full ext
what is the first muscle recruited with elbow flexion?
brachialis
which muscle is always active in elbow flexion?
brachialis
what muscle facilitates flexion in neutral forearm position?
brachioradialis
what muscle facilitates elbow flexion with forearm supinated?
biceps brachii
when is max elbow flex generated?
90º of flex
what position do triceps exert max torque?
90º of elbow flex
what are weak elbow flexors and pronators? (arise from medial epicondyle)
pronator teres, flexor carpi radialis, palmaris longus, flexor digitorum superficialis, flexor carpi ulnaris
what are weak elbow extensors and supinators? (arise from lateral epicondyle)
extensor carpi radialis longus and brevis, extensor digitorum, supinator, extensor digiti minimi, extensor carpi ulnaris
where is the olecranon bursa located?
posterior to the olecranon
T/F brachialis attaches to posterior capsule
F, attaches to anterior capsule
where does the ECRB originate?
lateral epicondyle but also annular ligament and radial collateral ligament
what are the peripheral nerves that cross the elbow?
ulnar, median, radial
what is the pathway of the ulnar nerve? what are common ulnar nerve injuries?
travels posterior to the medial epicondyle and through Arcade of Struthers (above elbow) and cubital tunnel
traction injuries with repeated elbow flexion, trauma, or cubitus valgus. vulnerable to compression in the cubital tunnel from hypertrophy of flexor carpi ulnaris and bony spurs
what is the pathway of the median nerve? what are common sites of compression?
courses through the two heads of the pronator teres
ligament of Struthers and pronator teres muscle can cause compression
what is the anterior interosseous nerve? what are common sites of compression?
motor nerve branch of the median nerve at pronator teres and travels deep in the forearm
can be compressed at pronator teres and deep forearm compartment leading to decreased FDP of index and middle, FPL and PQ
what is the pathway of the radial nerve? what branches from it? what are common radial nerve injuries?
travels from behind the humeral shaft around the lateral elbow into the supinator muscle and through the Arcade of Frohse
superficial branch of the radial nerve bifurcates here and contains only sensory nerve fibers
laceration or traction injury may occur with humeral shaft fractures. can also be compressed at the supinator muscle, Arcade of Frohse and ECRL
what is posterior interosseous nerve (PIN) syndrome?
the PIN is a branch of the radial nerve that provides motor innervation to the extensor compartment. it passes between the 2 heads of origin of the supinator muscle
PIN syndrome affects muscles it innervates. common extensors: ECRB, EDC, EDM, ECU, supinator, APL, EPB, EPL, EIP
has no cutaneous innervation
what are examples of functional outcome measures for UE?
Disability of Arm, Shoulder, Hand (DASH), quick DASH, Upper Extremity Functional Scale (UEFS), Patient Rated Wrist and Hand Evaluation (PRWHE)
what should your upper quarter scan consist of?
posture, ROM of cervical spine and shoulder complex, C-spine compression/distraction, neurological scan (reflexes, dermatomes, myotomes), special tests
what should you inspect about the skin around the elbow?
color, moisture (hyper/hypo hydrosis), wounds (location, size, color, drainage, odor), scars (flat, hypertrophic, hypersensitive, mobile, adherent, hyperemia)
what are other things you should inspect around the elbow?
deformities, muscle size (atrophy/hypertrophy), edema (measure circumference), bony prominences (medial and lateral humeral epicondyle, tip of olecranon), depression or infracondylar recesses (swelling if unable to see recess), carrying angle
what is normal carrying angle in men and women? how should you measure carrying angle?
men: 11-14º
women: 13-16º
should evaluate in full extension and full supination
what happens if you have exaggerated cubitus valgus and varus?
valgus: may cause traction neuropathy on ulnar nerve
varus: reversal of normal carrying angle (<5-10º)
what is normal elbow ROM? what is functional ROM?
ext/flex: 0-145º
pronation: 0-75º
supination: 0-80º
fxn ext/flex: 30-130º
fxn pron: 0-50º
fxn sup: 0-50º
T/F goni measurement for elbow and forearm ROM is highly reliable
T
what are factors to consider when assessing PROM?
pain - when it occurs in arc of motion
quality of motion: smooth, crepitus, clicking
end feel - flex: soft, ext: hard, sup/pron: firm
what position of elbow is ideal to test accessory motion and perform joint mobilizations on elbow?
loose pack position
what is LPP, CPP, and capsular pattern of humeroulnar joint?
LPP: 70º flex, 10º sup
CPP: ext and sup
capsular pattern: flexion > extension
what is LPP, CPP and capsular pattern of proximal humeroradial joint?
LPP: full ext and full sup
CPP: 90º flex, 5º sup
capsular pattern: flex>ext, sup>pron
what is LPP, CPP and capsular pattern of radioulnar joint?
LPP: 70º flex, 35º sup
CPP: 5º sup
capsular pattern: sup and pron equally limited
what are the different accessory motion tests at the elbow?
humeroulnar joint: distraction, medial-lateral tilt
radiohumeral joint: anterior-posterior glide
proximal radioulnar joint: anterior/posterior glide
distal radioulnar joint: anterior/posterior glide
how to MMT elbow flex and ext? how to differentiate extensors?
elbow should be at 90º
test with forearm supinated (biceps b.), pronated (brachialis)
wrist flexion and extension
ECRL and ECRB: resistance applied to 2nd and 3rd MC
ECU: resistance applied to 5th MC
ED: pt resists with fingers extended
what are ligamentous tests at the elbow?
valgus and varus instability test, lateral pivot shift test of elbow
how to perform valgus instability test? what is a positive test?
humerus in full ext rotation, elbow flexed 20-30º
abduction or valgus force applied
+ test is pain, excessive gapping, motion at medial elbow
how to perform varus instability test? what is a positive test?
humerus in full internal rotation, elbow flexed 20-30º, apply varus stress
tests radial collateral ligament (isolated injury is rare)
what is the most common lateral ligament injury?
lateral ulnar collateral ligament, injury results in posterolateral rotatory instability
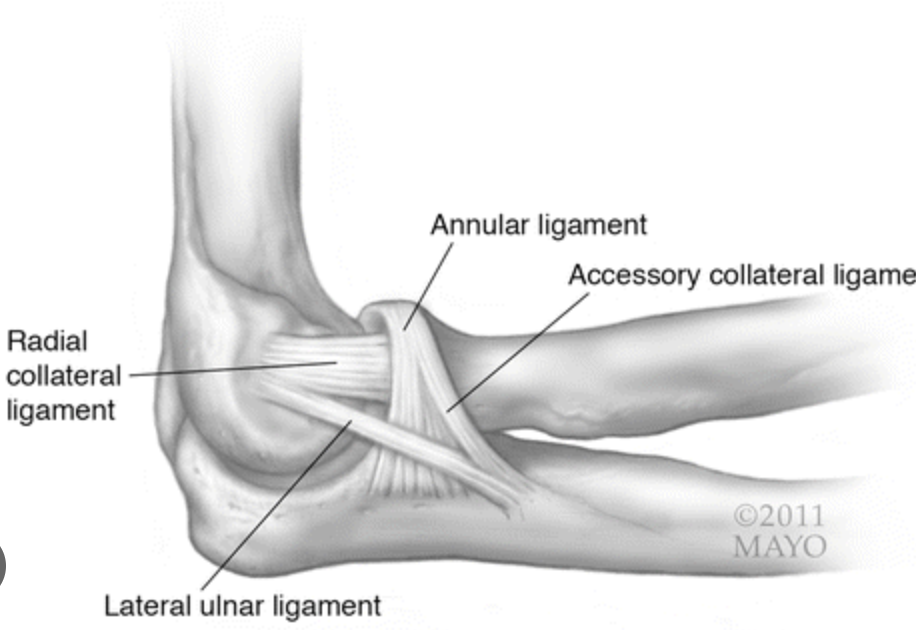
what does the lateral pivot shift test test for? what is a positive test?
indicates posterolateral rotatory instability due to lateral ulnar collateral ligament injury
pt lies supine with arm overhead, PT grasps pt wrist and forearm with elbow extended in full supination and applies valgus stress and axial compressive force while gradually flexing the elbow in supination
+ test: 40-60º there is a sudden reduction (clunk)
what is the Tinel sign?
indicates level of neuritis and nerve regeneration
+ if tingling and parasthesias along nerve distribution
what does the elbow flexion test used for? what is a positive test?
indicates Cubital Tunnel Syndrome
+ if produces paresthesias in ulnar nerve distribution, 15% of asymptomatic people are +
what is the pronator teres syndrome test? what is a postive test?
resist pronation and passively extend elbow to compress the median nerve even more (because it runs through the 2 heads of the pronator teres)
+ is reproduction of paresthesias in median nerve distribution
what is middle finger extension test? what is a positive test?
tests radial tunnel syndrome
+ if pain in radial tunnel
what is the tennis elbow test? what is a positive test?
tests for lateral epicondylitis
method 1: pt forearm at 90º pronated, resist wrist extension
method 2: PT passively pronates forearm, flexes wrist, extends elbow
+ is pain at lateral epicondyle and/or common extensor muscle insertion
what is the medial epicondylitis test? what is a positive test?
tests for Golfer’s elbow
PT passively supinates forearm and extends pt’s elbow and wrist
+ is pain over medial epicondyle
what is lateral epicondylitis (Tennis Elbow)? causes? sx?
def: a lesion affecting the origin of the muscles that extend the wrist (ECRL/ECRB, ED)
sx: overuse, repeated forceful pronation and supination, heavy lifting or hammering
s/sx: tenderness with palpation over ECRB at lateral epicondyle, pain with resisted wrist ext and radial deviation, pain with wrist radial deviation combined with active gripping, pain with passive wrist flexion and forearm pronation and full elbow extension; tenderness on outside of common extensor origin, pain over lateral elbow with gripping activities
what is medial epicondylitis? s/sx?
def: aka Golfer’s Elbow
s/sx: inflammation of the flexor mass of the medial condyle insertion, tenderness over medial humeral epicondyle, + medial epicondylitis test (pain with resisted wrist flexion when elbow is in full ext and supination); pain over medial elbow with wrist flex and forearm pronation
what is olecranon bursitis? causes?
inflammation of bursae between olecranon and the skin
usually caused by a single episode of trauma or repeated WBing, may or may not be painful
infection must be ruled out before dx
what causes bicep tendon rupture? s/sx?
rare, if so often from radial head dislocation. caused by unexpected extension force to elbow
s/sx: acute onset of swelling, pain, ecchymosis, decreased strength, increased discomfort
T/F biceps and tricep ruptures are rare
T
what are nerves that are likely to be involved with an elbow problem?
cervical nerve roots (radiculopathy)
brachial plexus
ulnar n
median n → anterior interosseous n
radial n → posterior interosseous n and radial sensory n
what is cubital tunnel syndrome? causes? s/sx?
ulnar n entrapment
causes: entrapment in Arcade of Struthers, hypertrophied FCU, or trauma, cubitus valgus, bony spurs, tumors
s/sx: pain - vague dull aching in forearm, weak/atrophied FCU, FDP, interossei and lumbricals of 4th and 5th (Ulnar Claw deformity), hypothenar muscles and adductor pollicis (Froment’s) and deep head of flexor pollicis brevis, decreased sensation and paresthesia in ulnar nerve distribution; positive Tinel sign over cubital tunnel and elbow flexion test, Wartenberg’s sign (abduction of the small fingers)
what is pronator teres syndrome? s/sx?
compression of the median nerve as it dives through 2 heads of pronator teres in prox forearm (where AIN divides from MN and dives deeper into forearm)
s/sx: pain in anterior aspect of elbow and forearm, numbness and tingling in the MN distribution, motor weakness in MN distribution of wrist and hand, pain exacerbated by wrist flexion combined with elbow flexion and forearm pronation; positive pronator teres test, pain in volar 1/3 of forearm, paresthesias in median n. distribution, motor weakness in FCR, FDS, lumbricals of index and middle fingers, pronator teres
s/sx of anterior interosseous n syndrome?
no sensory symptoms, motor weakness in FPL, FDP to index and middle, can be identified by a positive “OK” sign, pronator quadratus weakness in forearm pronation tested with elbow in full extension
common with compartment syndrome
where is the radial nerve vulnerable to injury proximal to the elbow?
lateral upper arm - mid-humeral shaft fx, wrist drop/”Saturday night palsy”
axilla - compression over brachial plexus from crutches, wrist drop
what is radial tunnel syndrome? s/sx?
compression of the radial sensory nerve (5 cm distal to elbow in radial tunnel)
s/sx: constant pain but no motor weakness or paresis, pain increases with pronation and wrist flexion, tender distal to common extensor muscle mass insertion, positive middle finger extension test, pain with resisted supination with elbow extended (tunnel closed in supination)
what is posterior interosseous nerve syndrome? s/sx?
compression of posterior interosseous nerve as it passes through the 2 heads of supinator in the Arcade of Frohse
s/sx: same as radial tunnel but also with motor weakness, weakness in ED, EDM, EIP, EPB, EPL, APL, radial drift of wrist with active wrist extension due to weakness in ECU, possible weakness of supinator
radial tunnel syndrome vs posterior interosseous syndrome?
radial tunnel: involves pain without motor weakness
PIN: involves pain and motor weakness
what types of vascular lesions might affect the elbow?
brachial artery laceration - mx emergency
compartment syndrome - mx emergency
forearm compartment syndrome
rapid, excessive swelling which may impede or obliterate the blood flow
Volkmann’s contractures may result from prolonged intracompartmental pressure → nerve and muscle tissue death, needs immediate surgery
what fx are common around the elbow?
distal humerus - usually high impact injury
olecranon - fall on posterior elbow
radial head
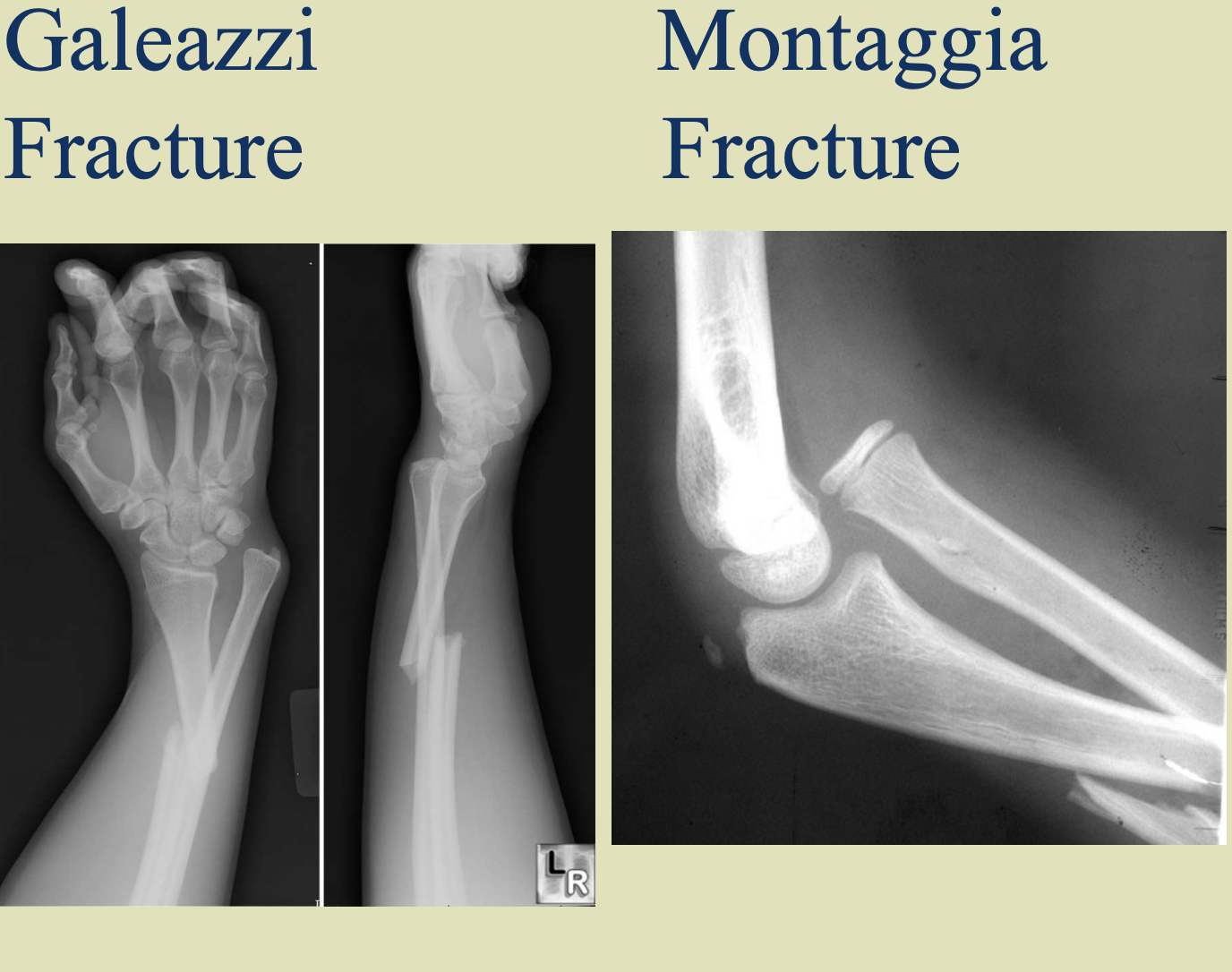
monteggia - ulna fx with radial head dislocation at the elbow
galeozzi - radius fx with ulna dislocation at the wrist
elbow dislocation and joint pathology
radius/ulna - FOOSH - frequently associated with ulna fx, make sure to check for ulnar n dysfunction
radial head - common in adults, reduction is imperative
pulled elbow syndrome - radial head dislocation in children
what is stiff elbow? types?
Proximity of brachialis and triceps to the joint and the complexity of the 3 bone articulation give the elbow the propensity for stiffness
Myositis ossificans - ossification of the muscles, will see decrease in ROM and increase in pain
Heterotrophic ossification - formation of organized bone within and about the elbow joint
Common with open injuries, fracture dislocation- require aggressive PROM