MH Lecture 5 - Substance-Related Addictive Disorders
1/8
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
9 Terms
Substance-Related Addictive Disorders Diagnostic Criteria
excessive use of drug
persistent desire/unsuccessful effort to control usage (distress)
excessive time devoted to drug seeking behaviours
strong cravings
dysfunction in work, school, home, or social life related to drug use
drug use in hazardous situations (e.g. driving)
drug use despite aversive outcomes
tolerance (leading to escalating use)
withdrawal symptoms
Substances that qualify for SRD
alcohol
caffeine
cannabis
hallucinogens
inhalants
opioids
sedatives/hypnotics/anxiolytics
stimulants
tobacco
other
+ gambling disorder — operates on the same brain mechanism as substance use disorder
Substance Use Continuum
total abstinence
rare/social use
heavy social use/early problems
heavy problem use/early addiction
clear addiction/dependency
Is Addiction a habit
stage 1 — voluntary use
stage 2 — habitual use
stage 3 — compulsive use
What is a habit
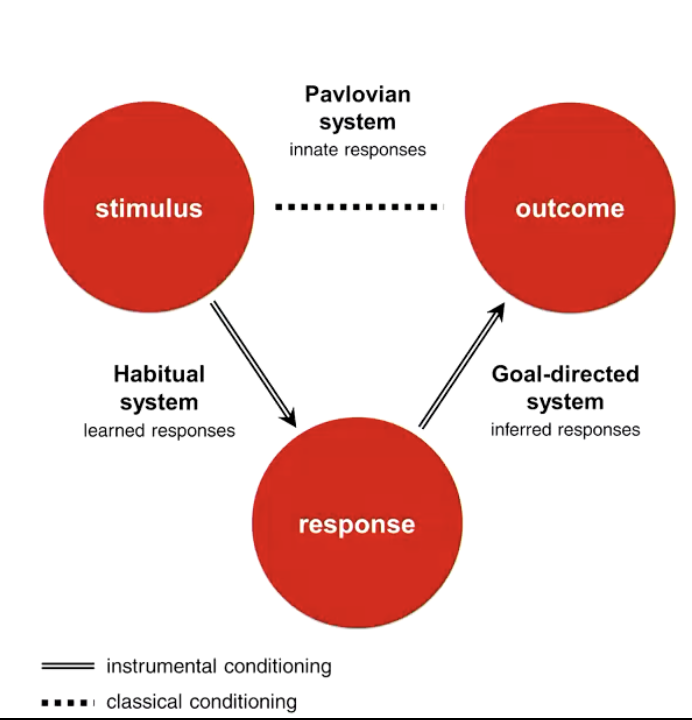
stimulus-response learning
inflexible patter of thought/behaviour
sensitive to triggers/cues
Dark Side of Addiction
CRF — increased by drug withdrawal symptoms (increases stress response)
Initial drug seeking is motivated by rewarding aspects of the drug
goal = feel happy
once dependence is formed — drug seeking motivated by stress of withdrawal
goal = feel normal
Trouble with treating addiction
drugs of abuse have wildly different mechanisms
impact neuroplasticity in different ways
no one size fits all solution
only common component is the behavioural pattern of addiction formation
Treatment Approaches
Exposure therapy
breaking associations between drug related cues and drug seeking behaviour
Attentional bias retraining
redirecting focus from drug related cues
Counterconditioning
e.g. disulfiram (antabuse) — causes instant hangover
Other pharmacological approaches
e.g. CRF antagonists
dark side of love
blocking CRF activity supresses the effects of ‘hearbreak’
when humans form pair bond — level of CRF in brain skyrockets — particularly in areas to do w anxiety — ready for incoming anxiousness and depression
the threat of separation is stressful
drugs and pair bonding interact in a lot of similar ways