lab practical study guide 3
1/91
Earn XP
Description and Tags
animal biology
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
92 Terms
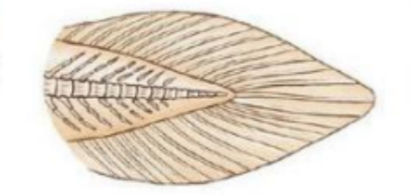
Label the fin type
Diphycercal
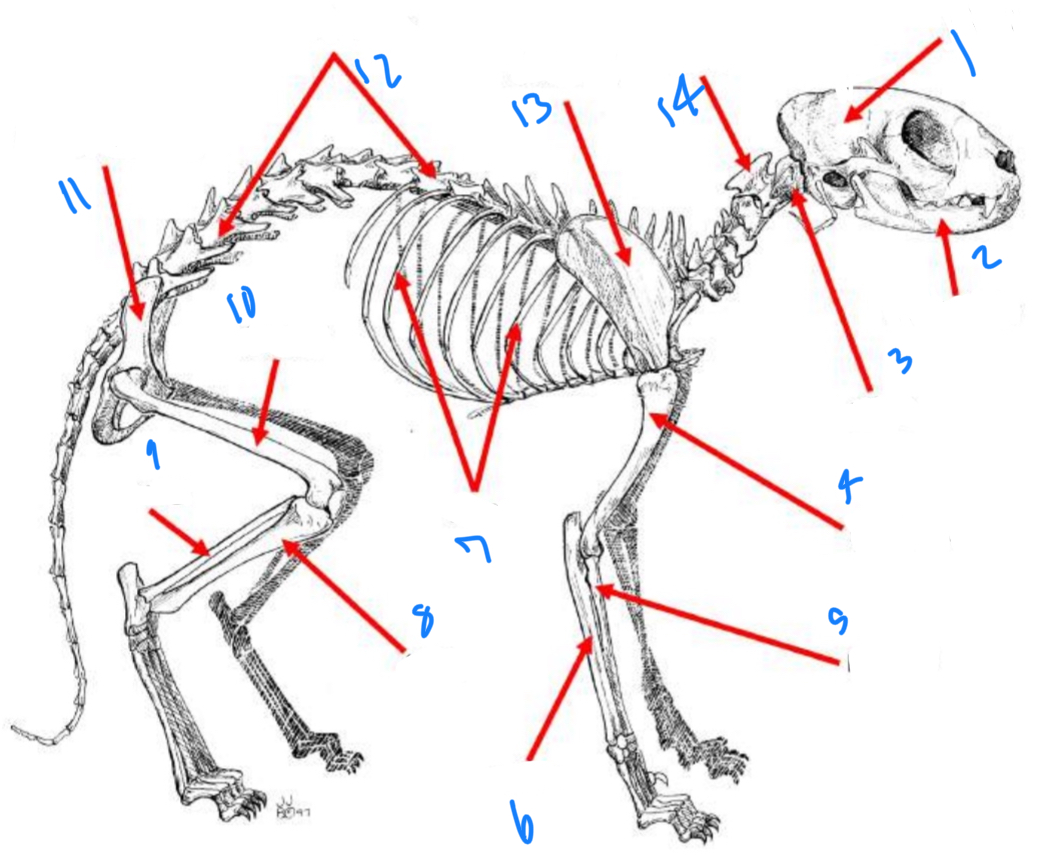
Label the anatomy starting at one
Skull, mandible, Atlas, humerus, radius, ulna, ribs, tibia, fibula, femur, hip, vertebrate, scapula, axis
List 2 key characteristics true of animals in subphylum Vertebrata
Cranium around brain and well developed head with paired sensory organs
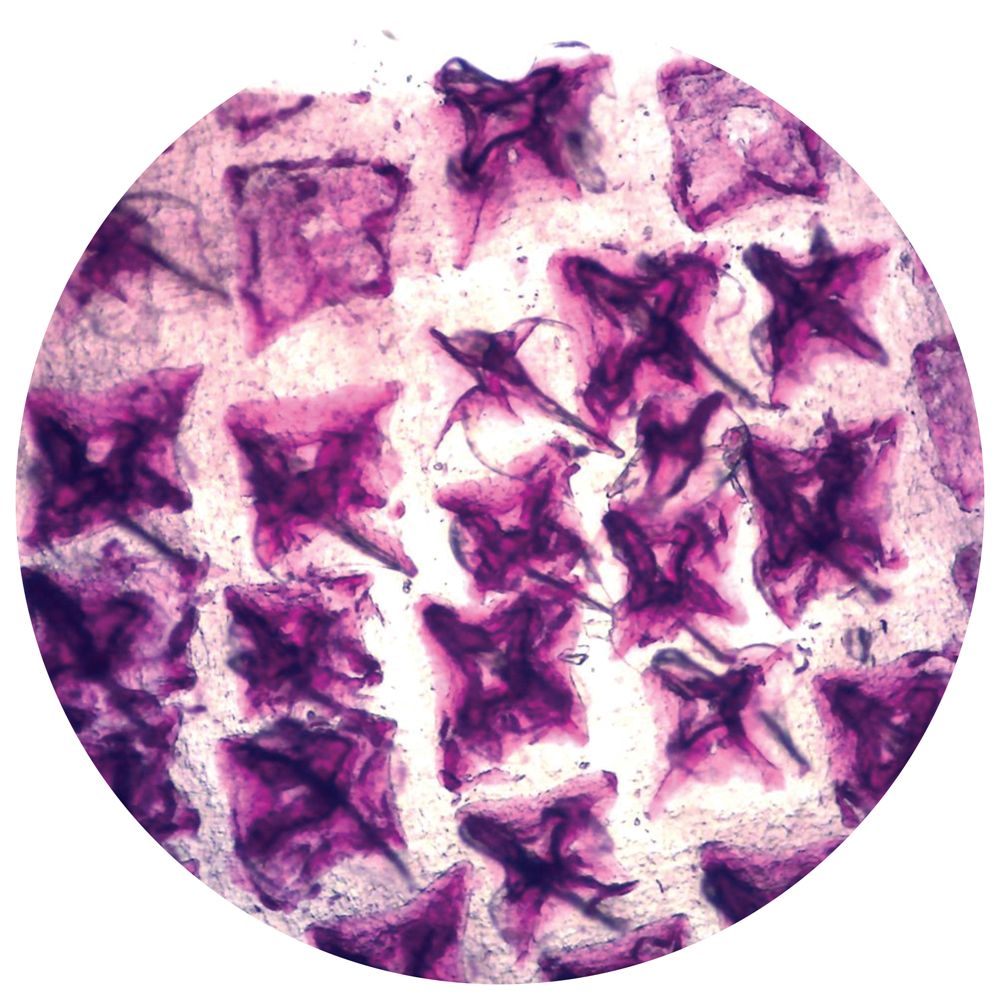
What type of scales are these
placoid (sharks)

What type of scales are these
ctenoid (teleost fishes)

What type of scales are these
cycloid (teleost fishes)
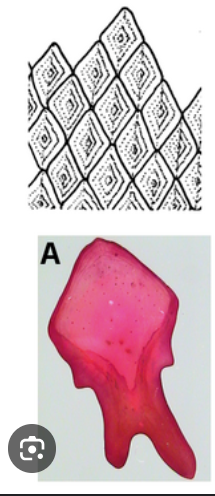
What type of scales are these
Ganoid (bony fish)
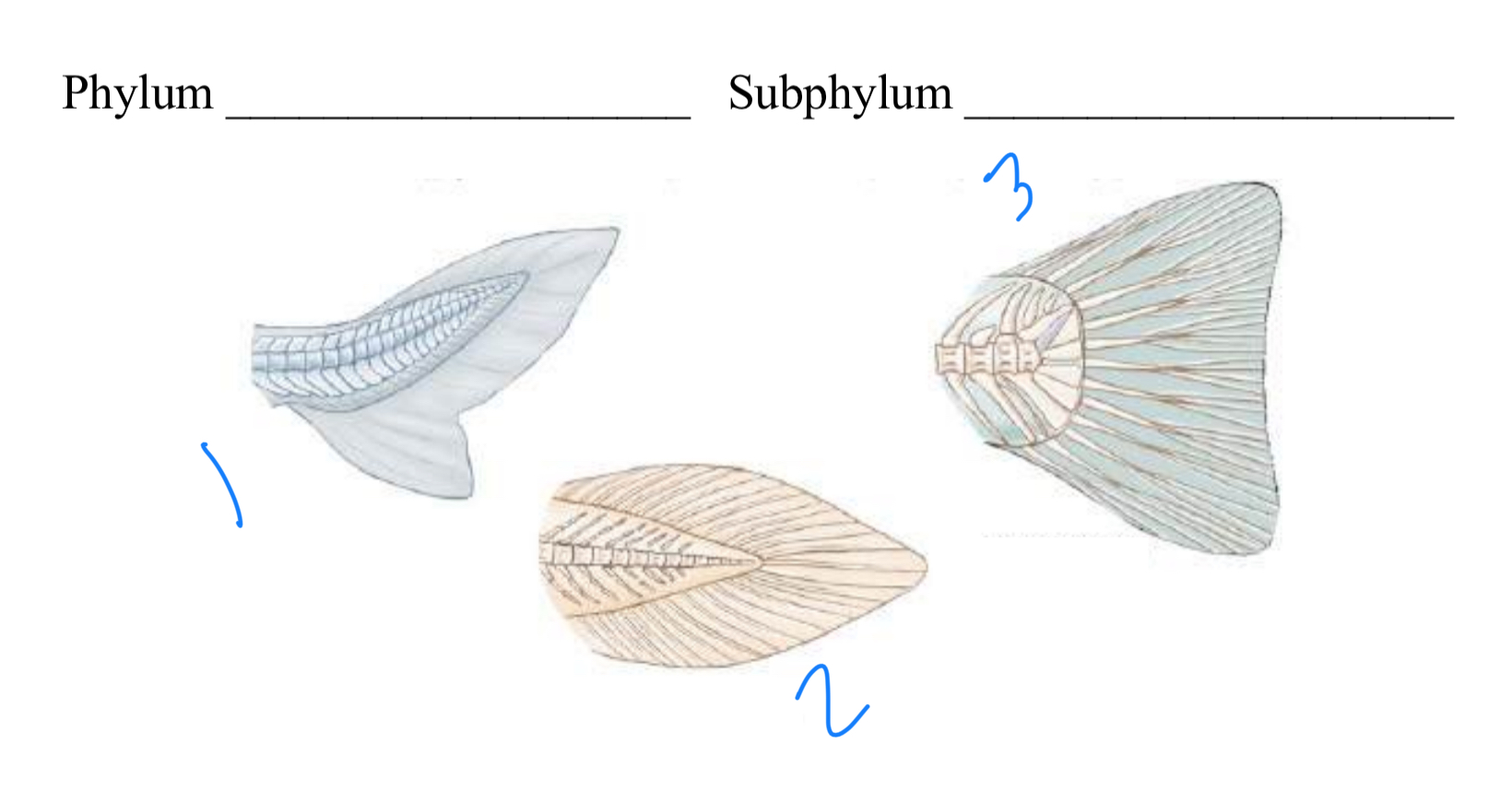
label the fin types starting at 1
heterocercal, diphycercal, homocercal
class of sharks
Chondrichthyes
Ampullae of Lorenzini function (sharks)
Electroreception to help catch prey
class of lampreys
Petromyzontida
Class of bony fish
Actinopterygii
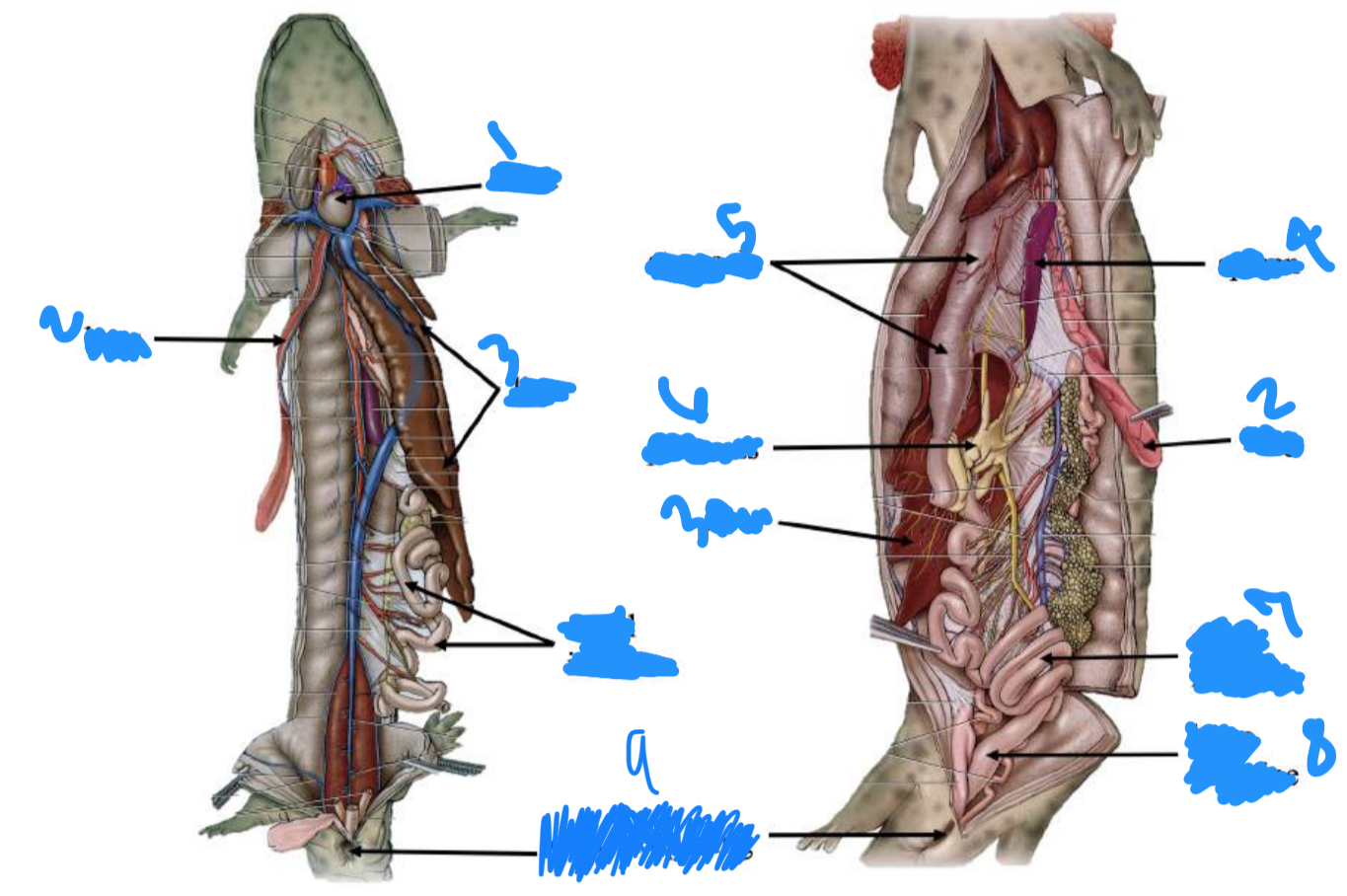
Label the anatomy starting with one
Heart, lung, liver, spleen, stomach, pancreas, small intestine, large intestine, cloacal opening
Label the Anatomy starting at one
Gills, gular fold, cloacal opening
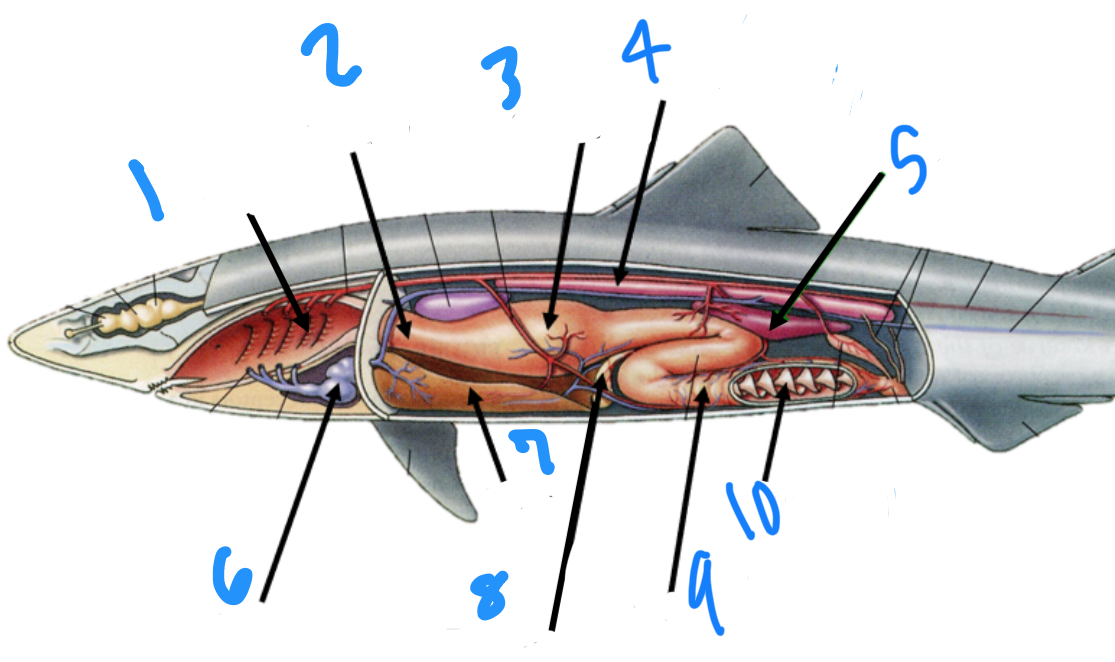
Label the internal structures of the shark starting at 1
Gills, esophagus, stomach, kidney, spleen, heart, liver, pancreas, valvular intestine/ileum, spiral valve
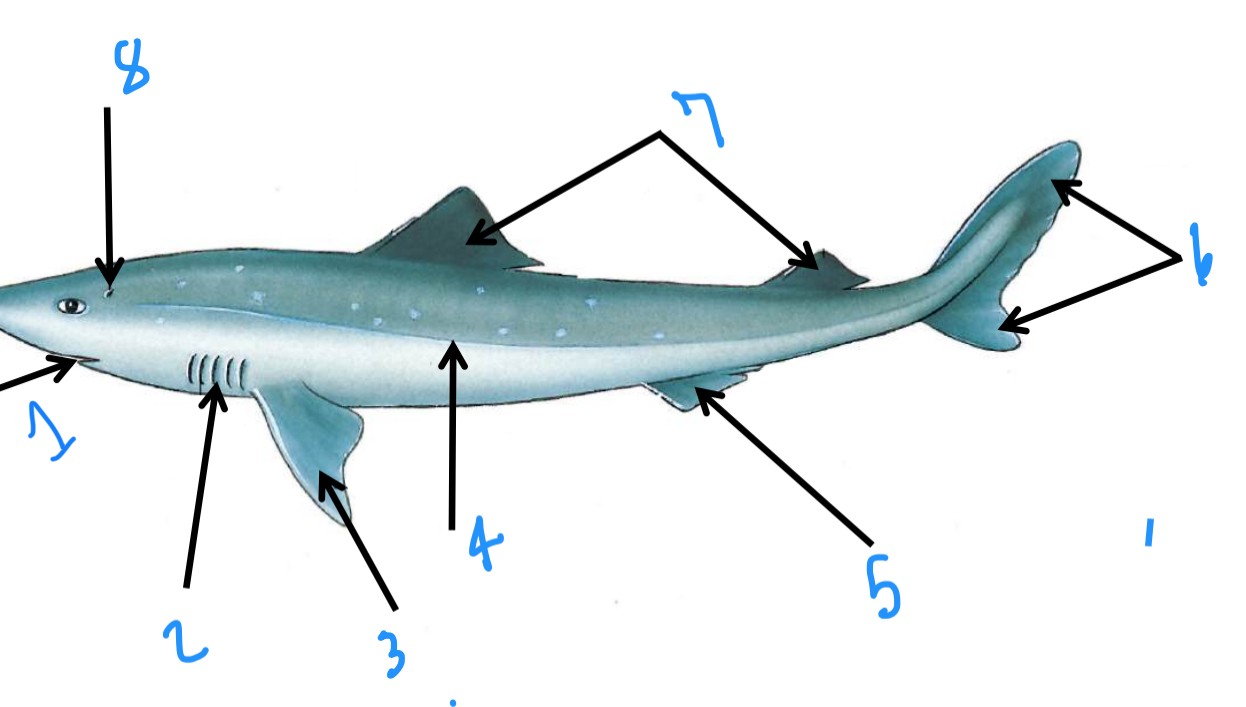
label the shark anatomy starting at 1
mouth, external gill slits, pectoral fin, lateral line, pelvic fin, caudal fin, dorsal fin, spiracle
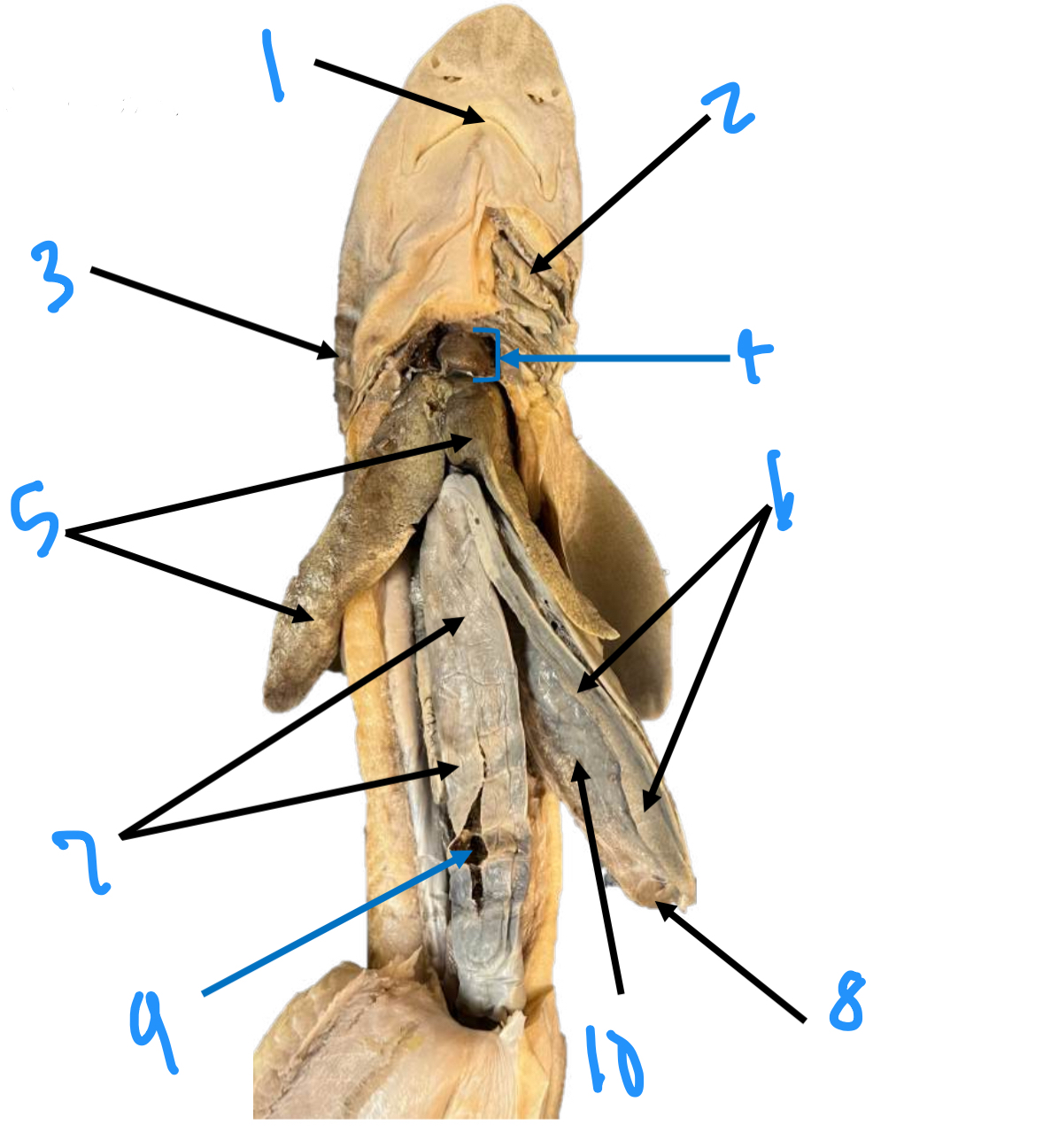
label the internal shark anatomy starting at 1
mouth, external gill slits, gills, heart, liver, stomach, valvular intestine, spleen, spiral valve, pancreas
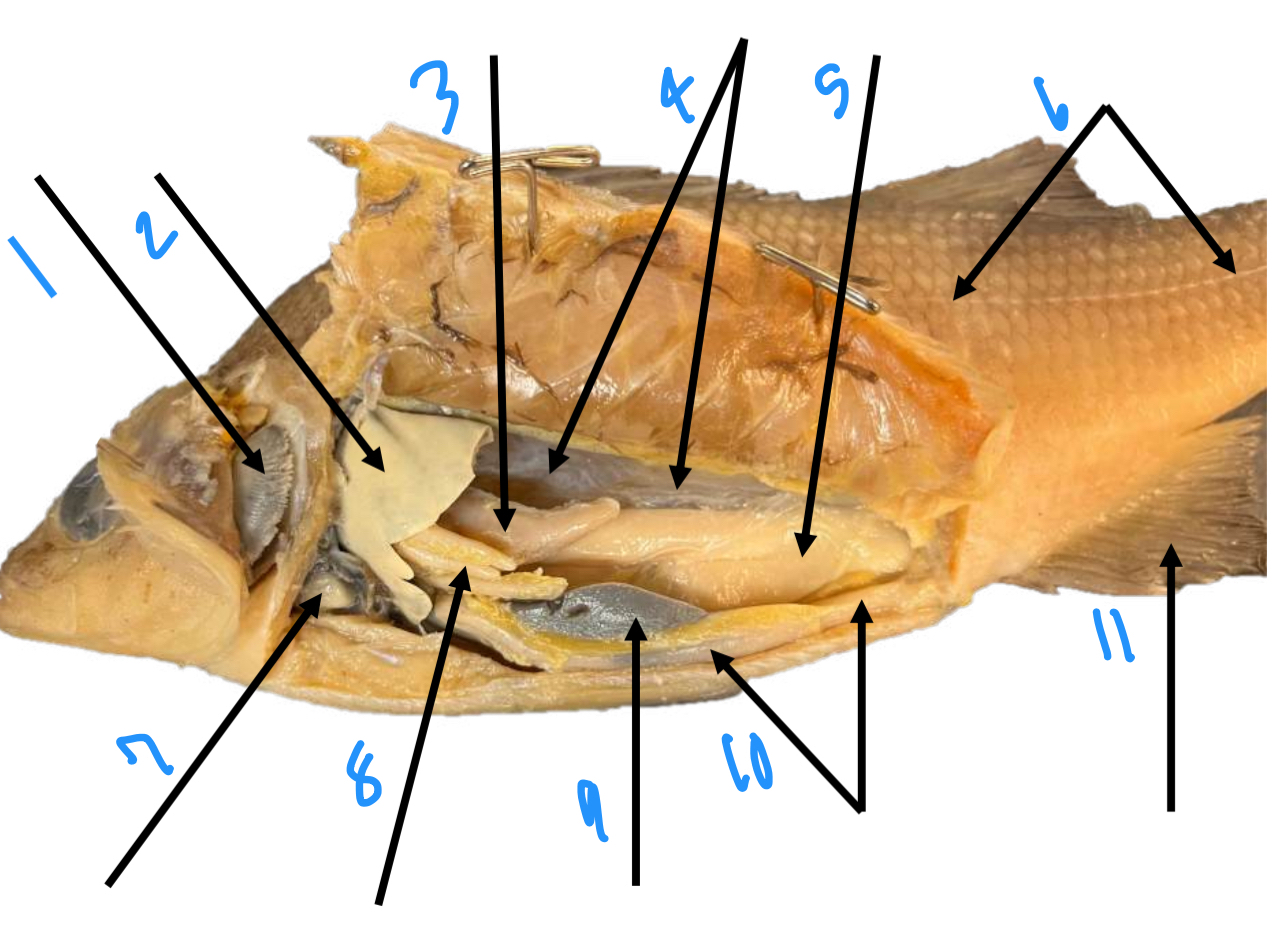
label the fish anatomy starting at 1
gills, liver, stomach, swim bladder, testis, lateral line, heart, pyloric ceca, spleen, intestine, anal fin
identify the class
Actinopterygii
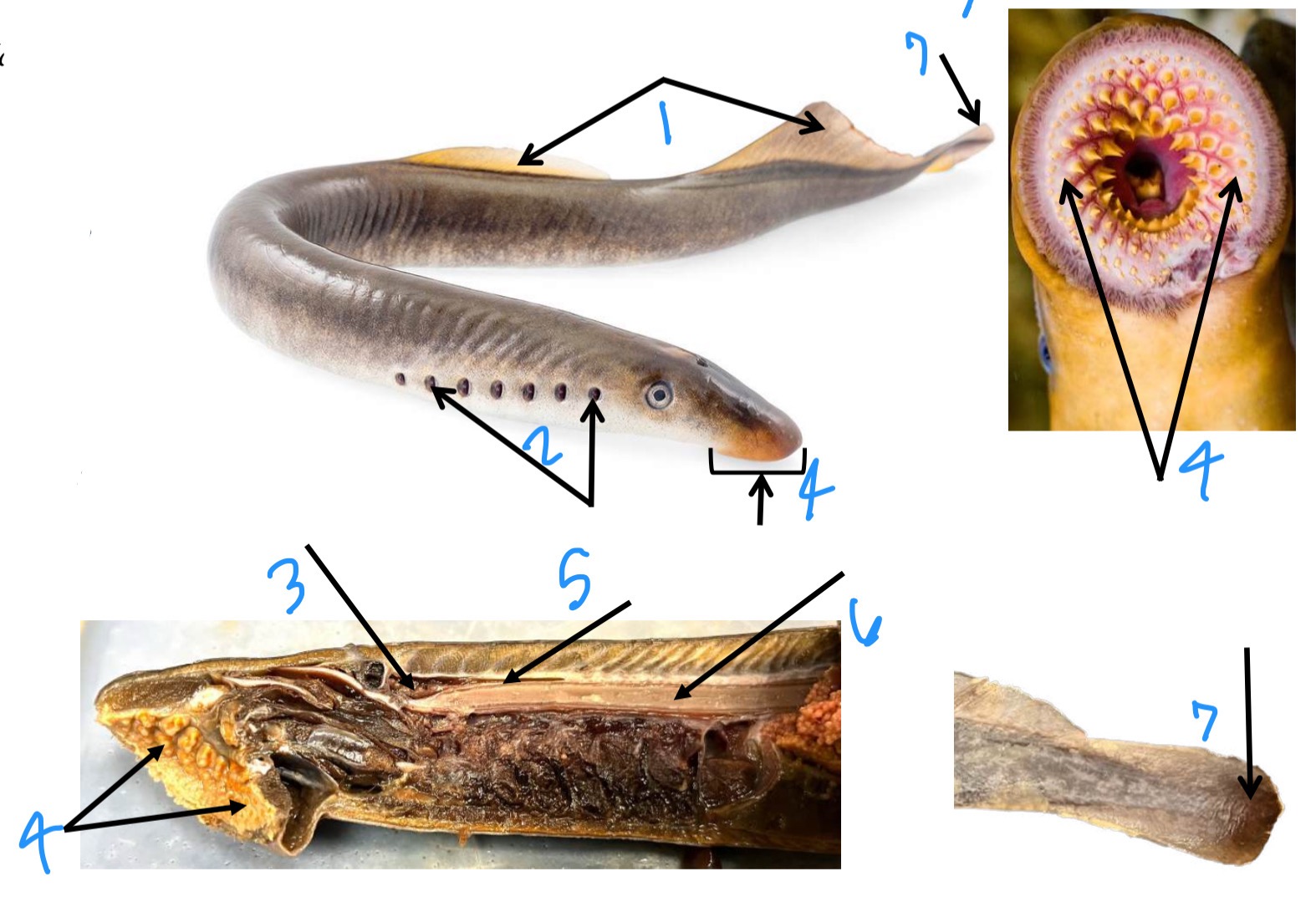
label the anatomy starting at 1
dorsal fins, gill slits, brain, buccal funnel, spinal cord, notochord, caudal fins
List at least two key characteristics for organisms in the subphylum Vertebrata
Well-developed head; bony skull around the brain
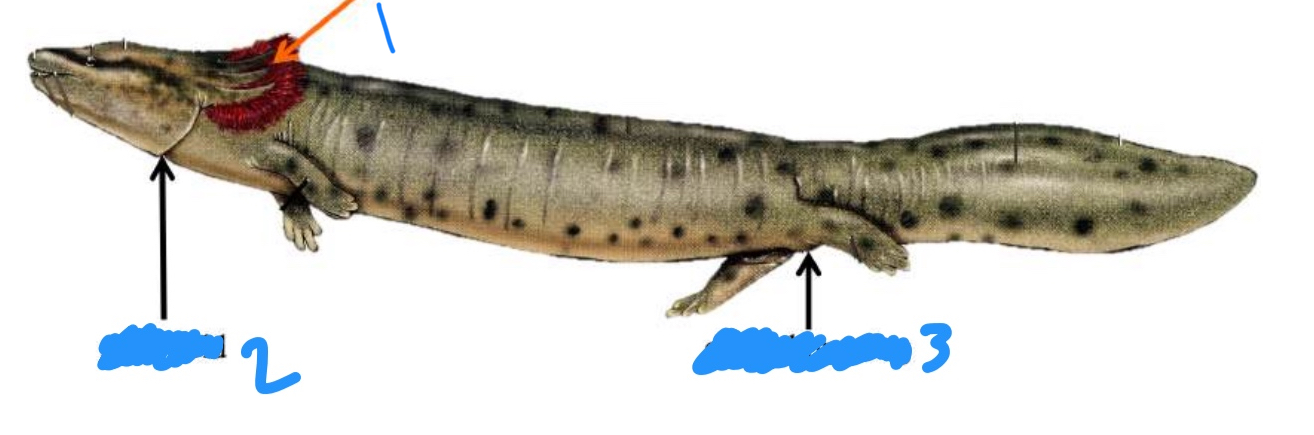
External gill slit (shark) function
Release water from shark’s body
Lateral line function
Sense vibrations
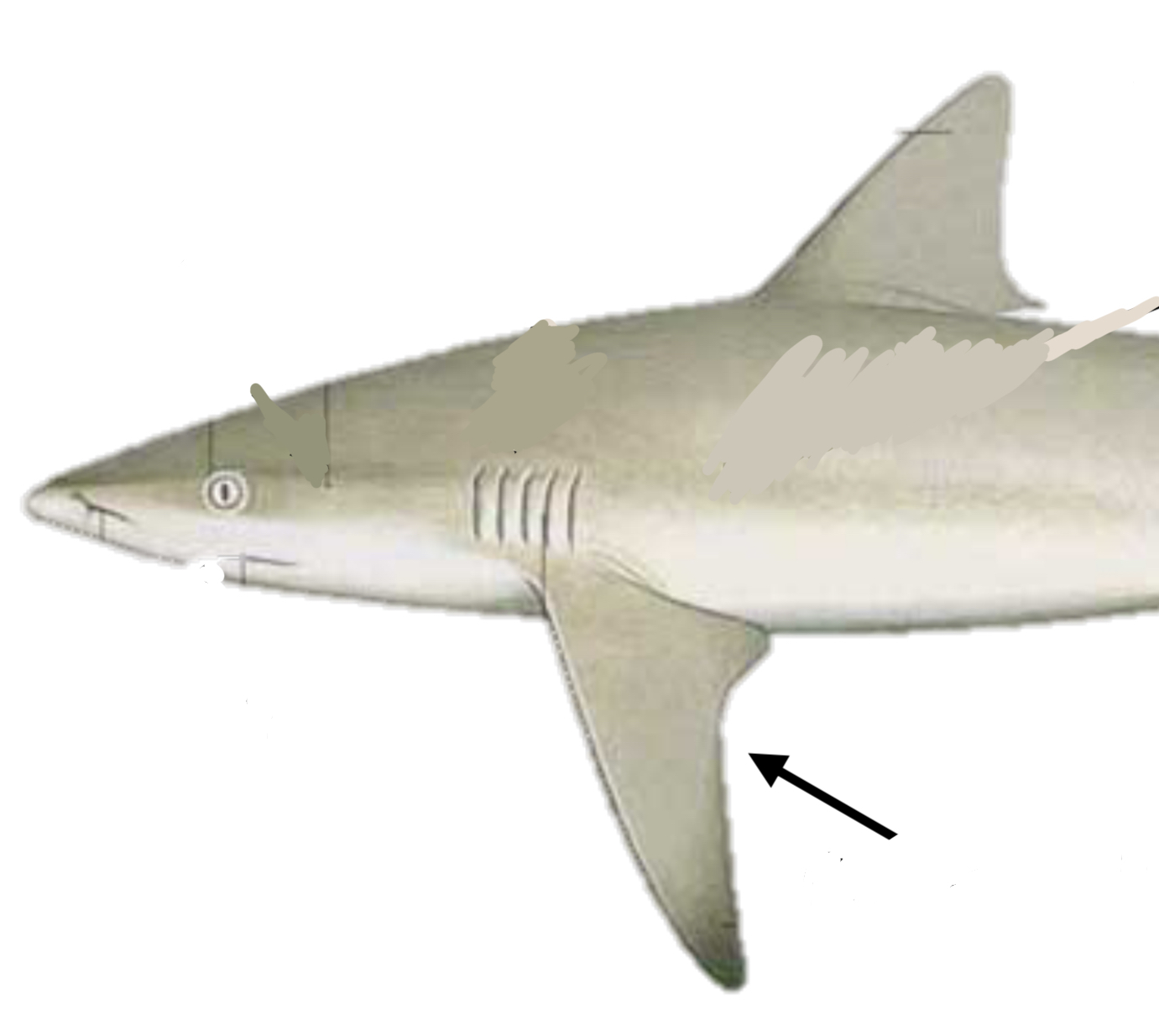
Identify the structure and its function
Pectoral fin; Steering
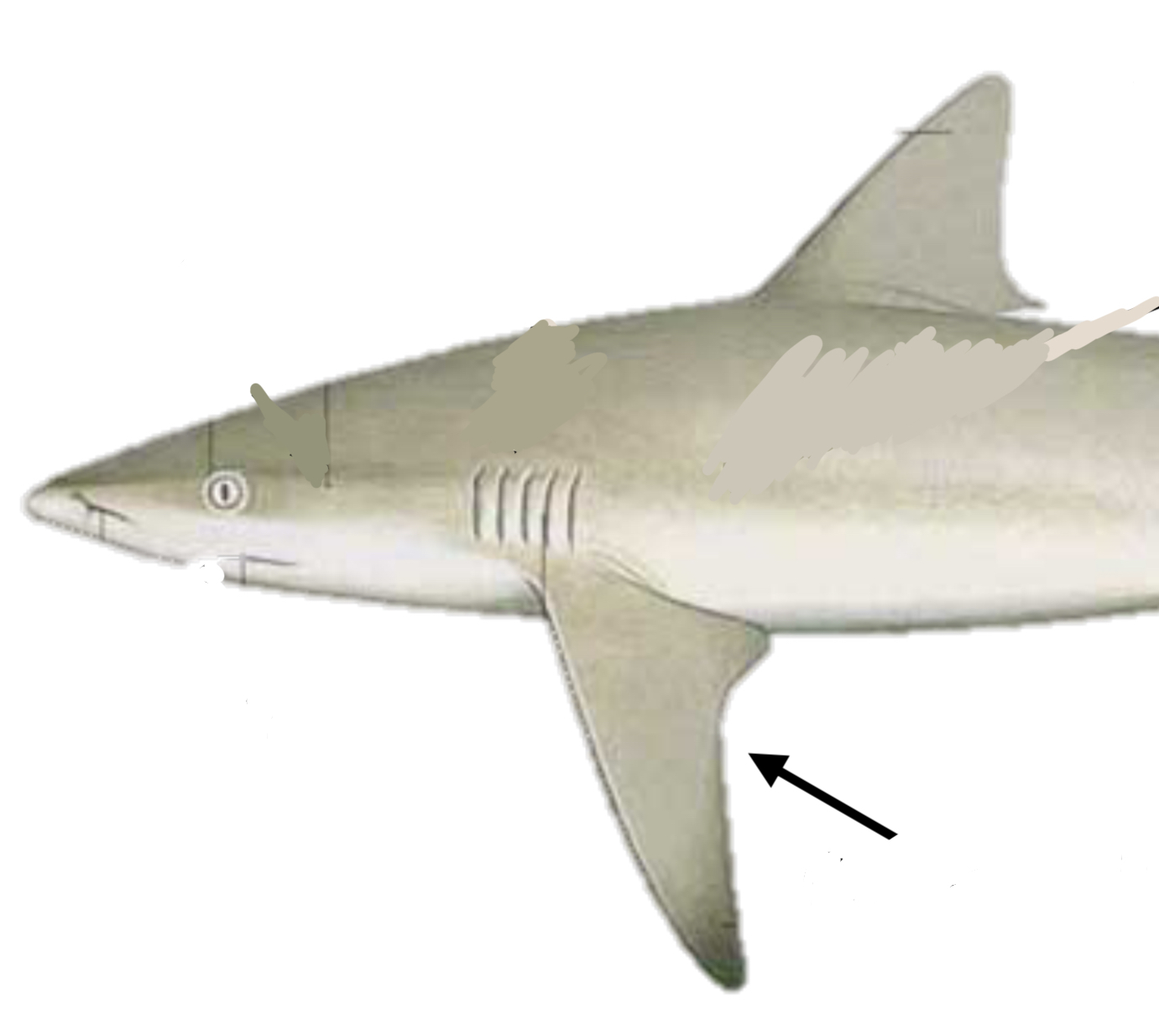
Pectoral fin function
Steering and braking

Identify the structure and name its function
Clasper; Deposit sperm in female reproductive tract
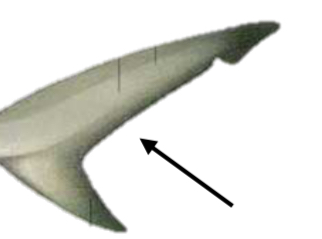
Identify the structure and its function
Caudal fin; Thrust while swimming
Cloaca function
Excretion
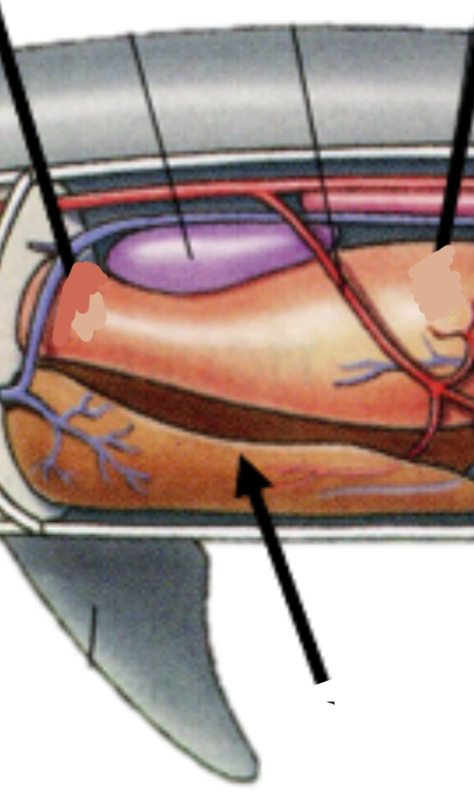
Identify the structure and the function
Liver; Stores oil to make shark more buoyant in water
Identify the structure and function
Spleen; Stores blood

Identify the function and the structure
Spiral valve; slows the passage of food through the intestines
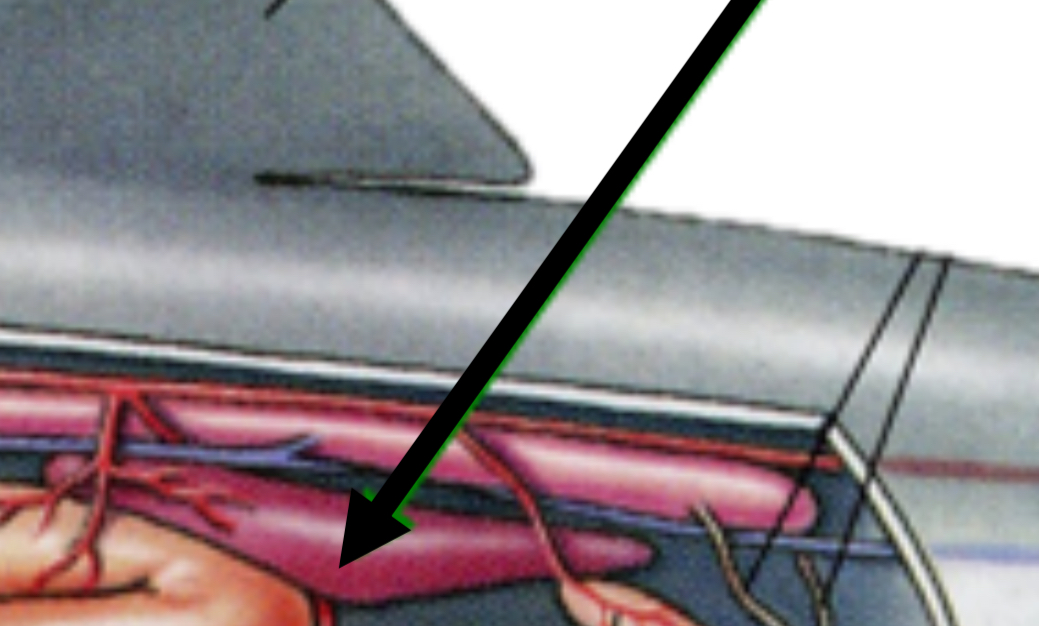
Kidney function
Filters metabolic waste out of the blood
Ampullae of lorenzini function
Electroreception to help catch prey
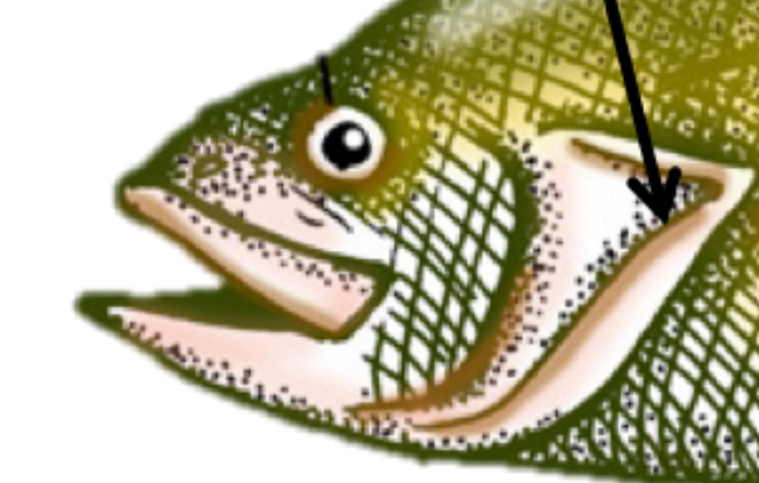

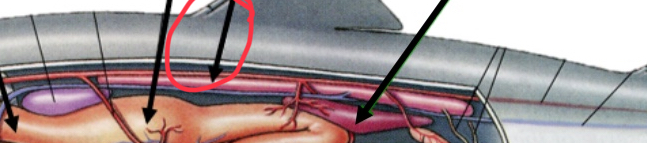
operculum function
Pump water across gills
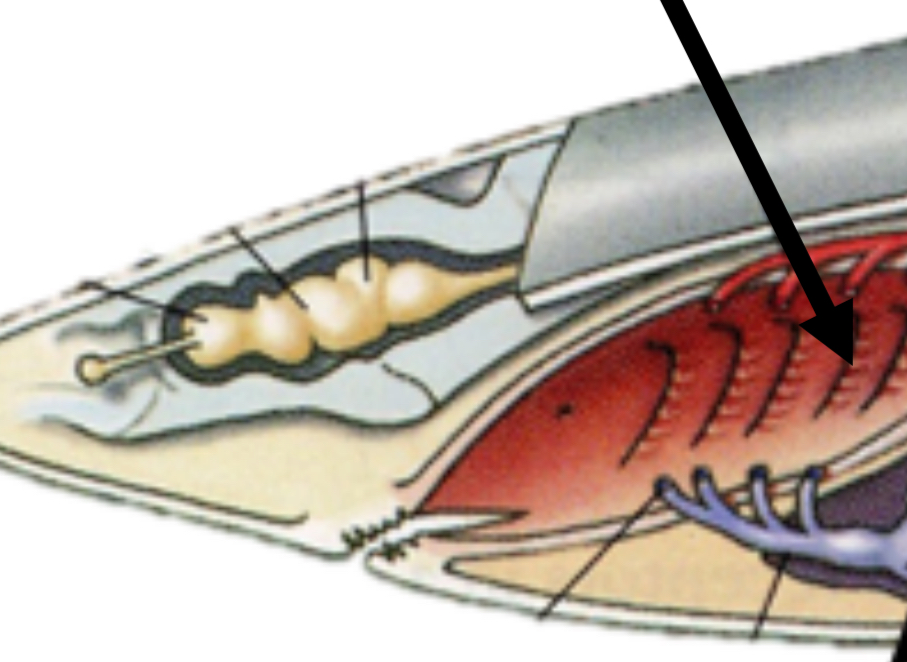
gills function
Respiration
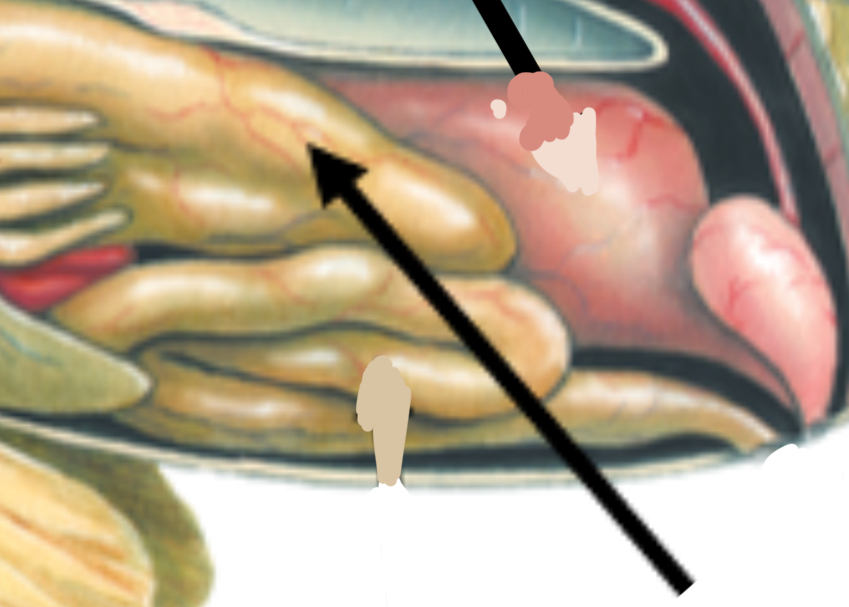
Identify the structure and function
Stomach; Digestion
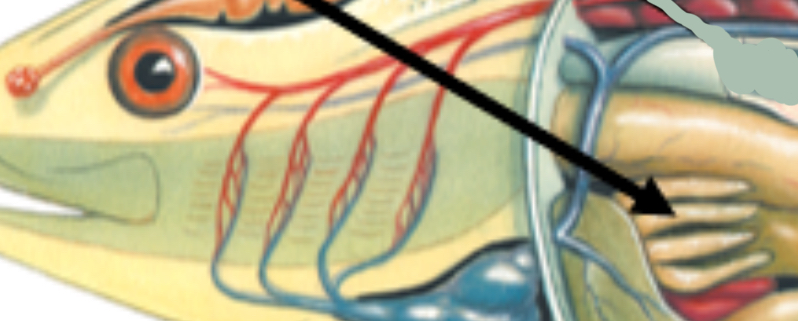
Identify the structure and function
Pyloric ceca; Pouch that increases surface area for digestion
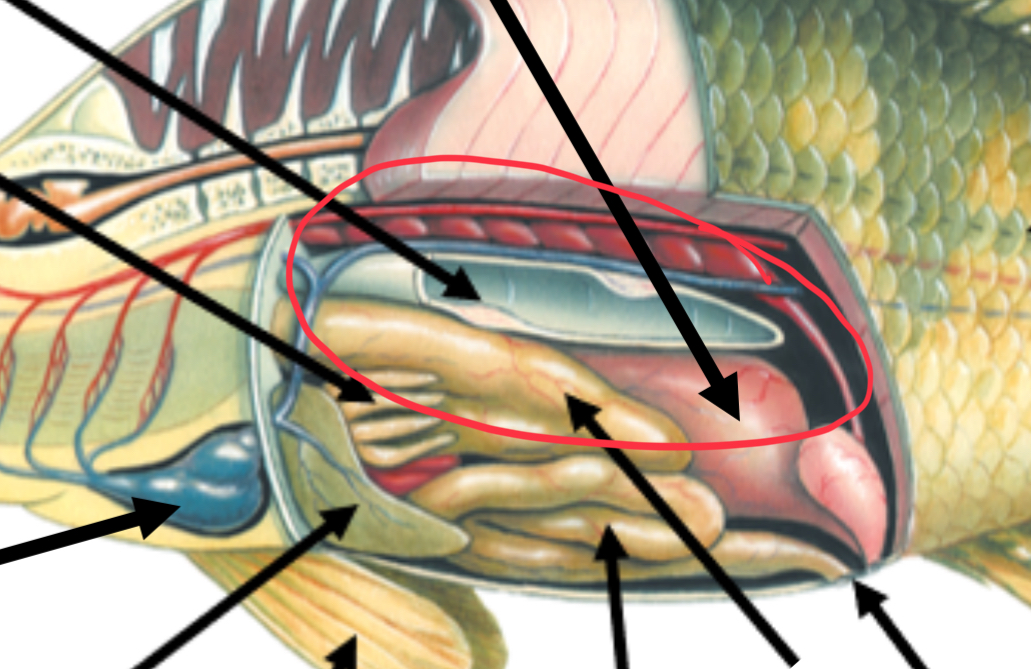
Swim bladder function
Maintains buoyancy
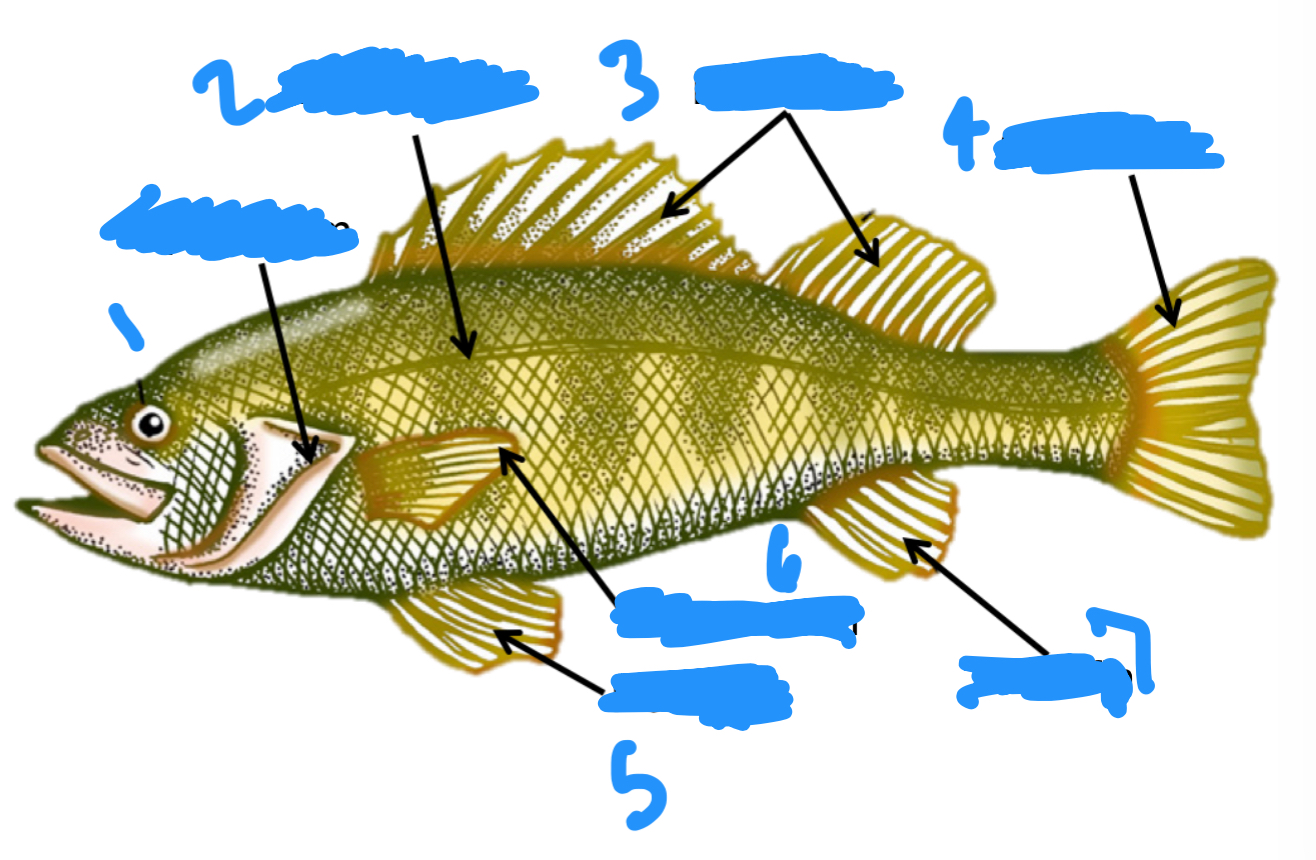
Label the perch anatomy starting at one
Operculum, Lateral line, Dorsal fins, caudal fin, Pelvic fin, Pectoral fins, anal fin
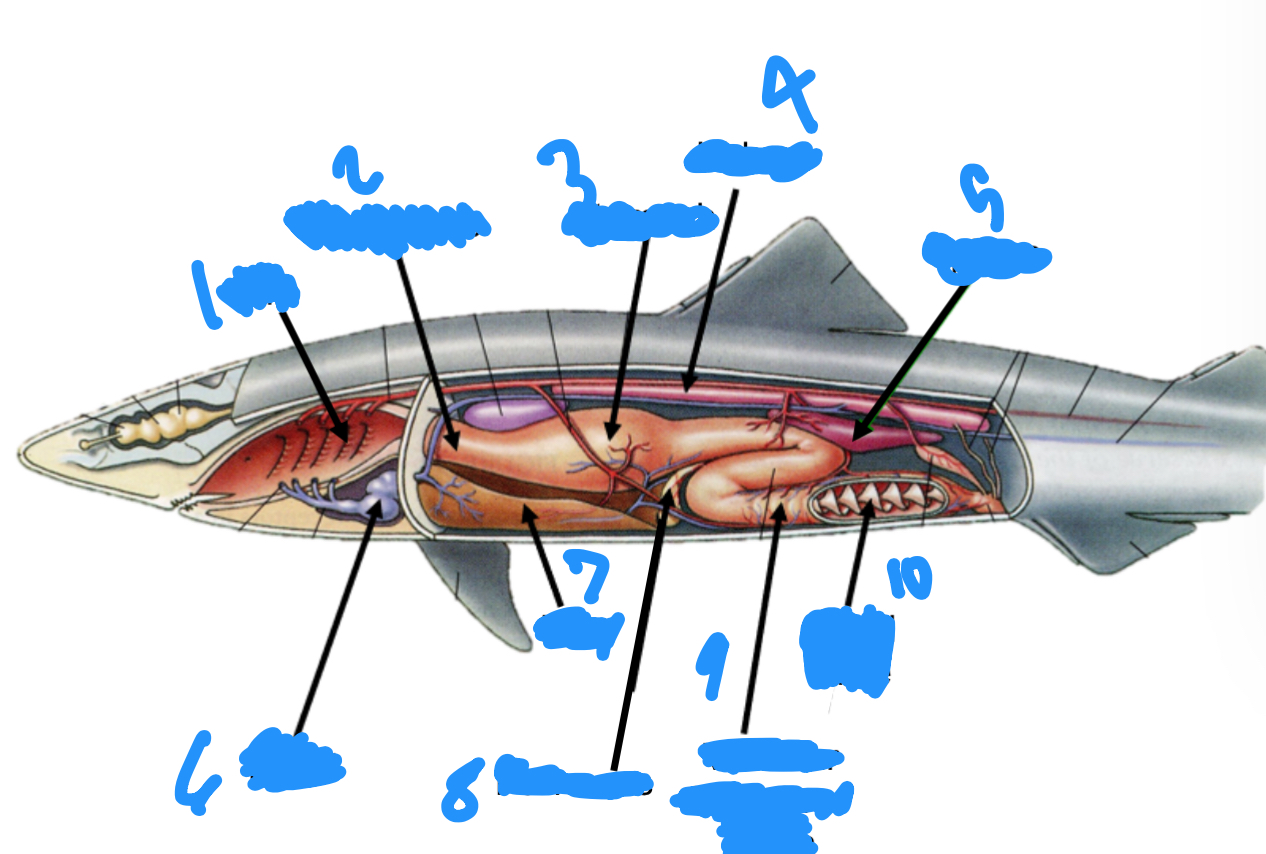
Label the internal shark anatomy starting at one
Gills, Esophagus, Stomach, Kidney, Spleen, Heart, Liver, Pancreas, ileum, Spiral valve
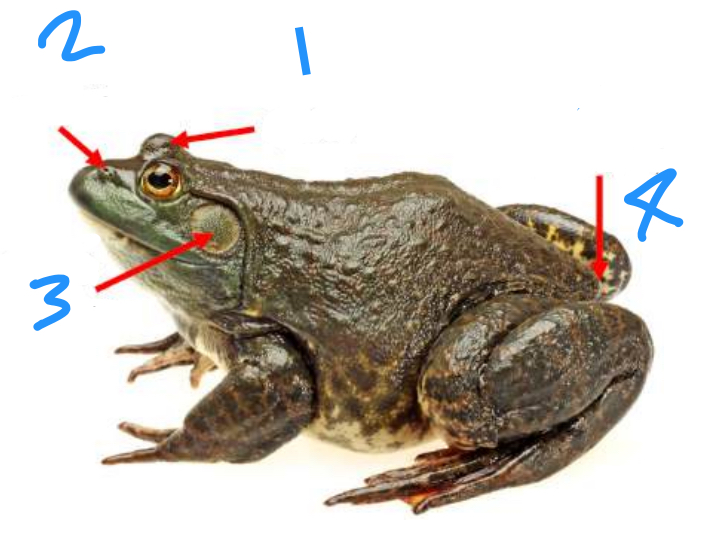
Label the structures starting at 1
Eyelid, nostril, tympanic membrane, cloacal opening
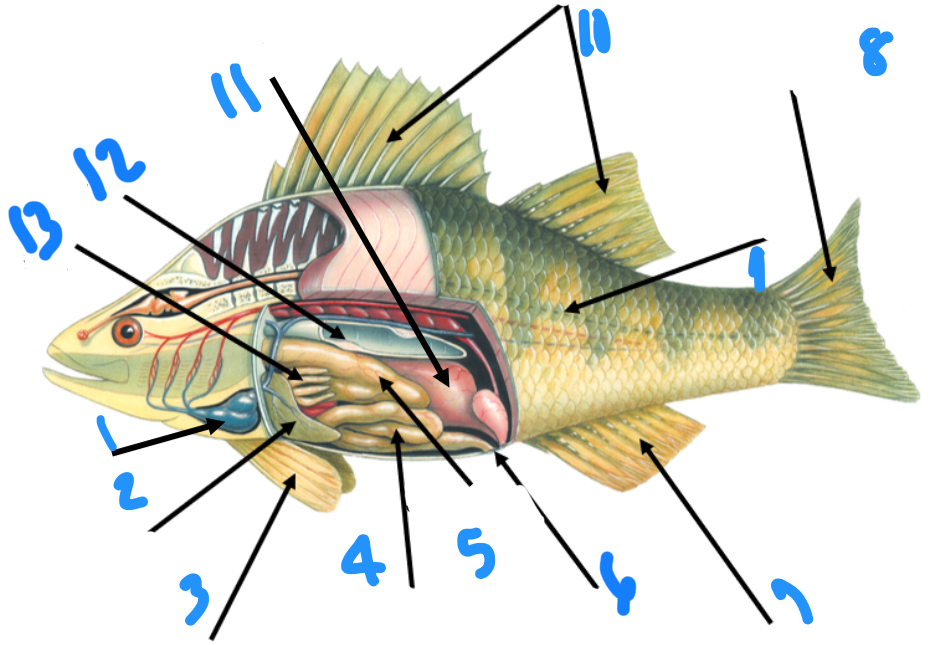
Label the anatomy starting at one
Heart, liver, pectoral fin, intestine, stomach, anus, anal fin, caudal fin, lateral line, dorsal fins, ovary or testis, swim bladder, pyloric ceca
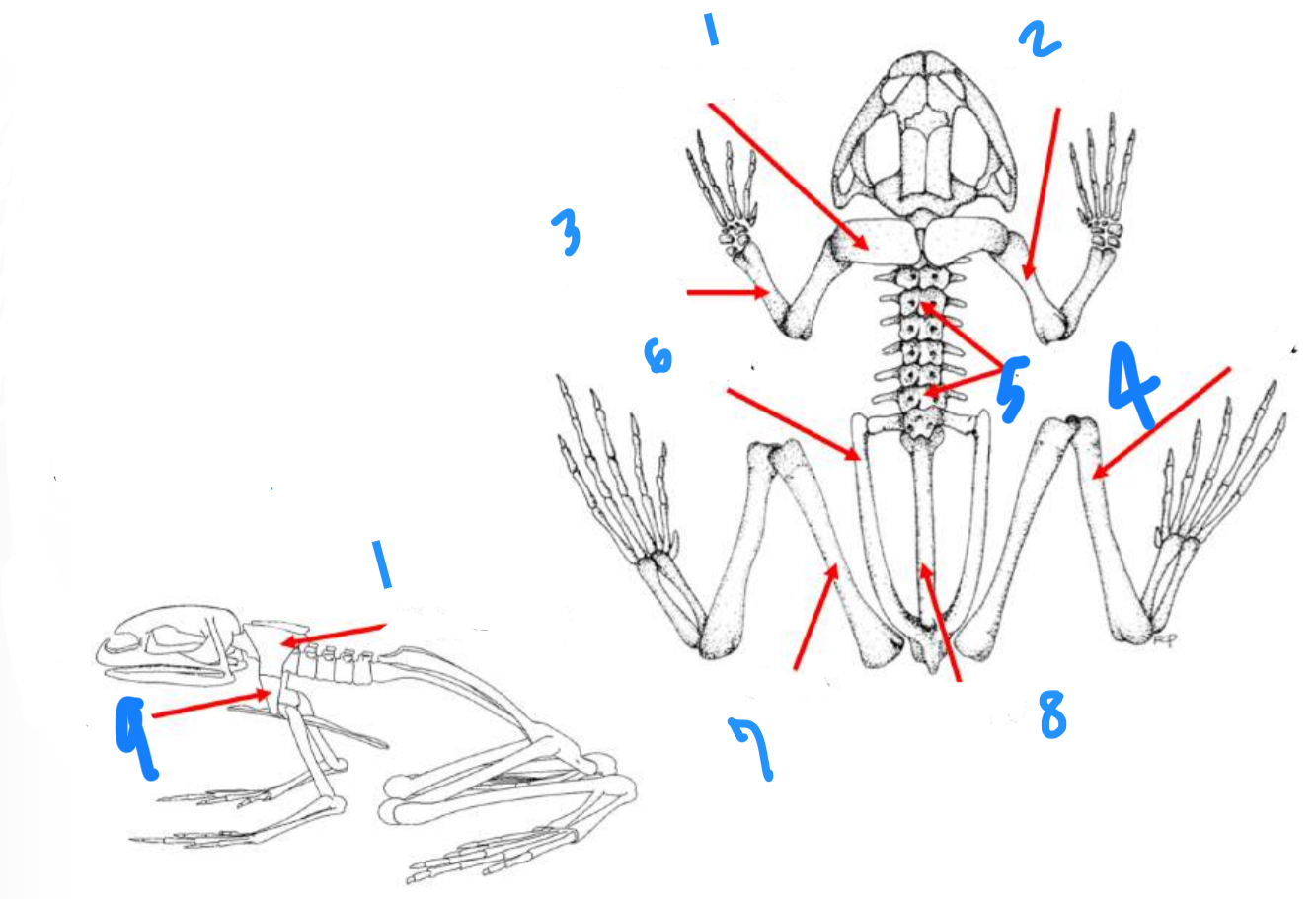
Label the structures starting at 1
Suprascapula, humerus, radioulna, tibiofibula, vertebrae, ilium, femur, urostyle, scapula
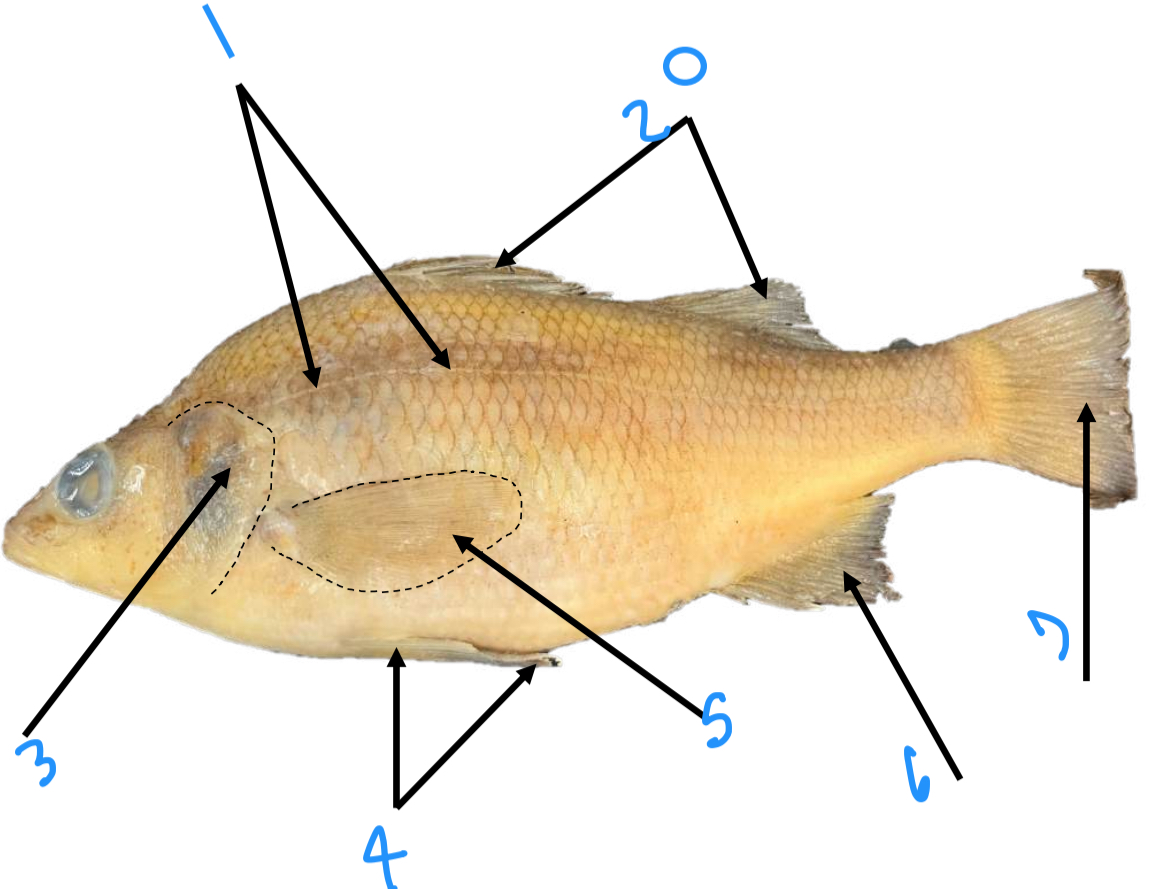
Label the anatomy starting with one
Lateral line, dorsal fin, operculum, pelvic fin, pectoral fin, anal fin, caudal fin
Phylum and Subphylum of frogs
Chordata and Vertebrata
Class and order of frogs
Amphibia and Anura
List 2 key characteristics true of class Amphibia
Skin is usually moist with no scales, larvae are usually aquatic
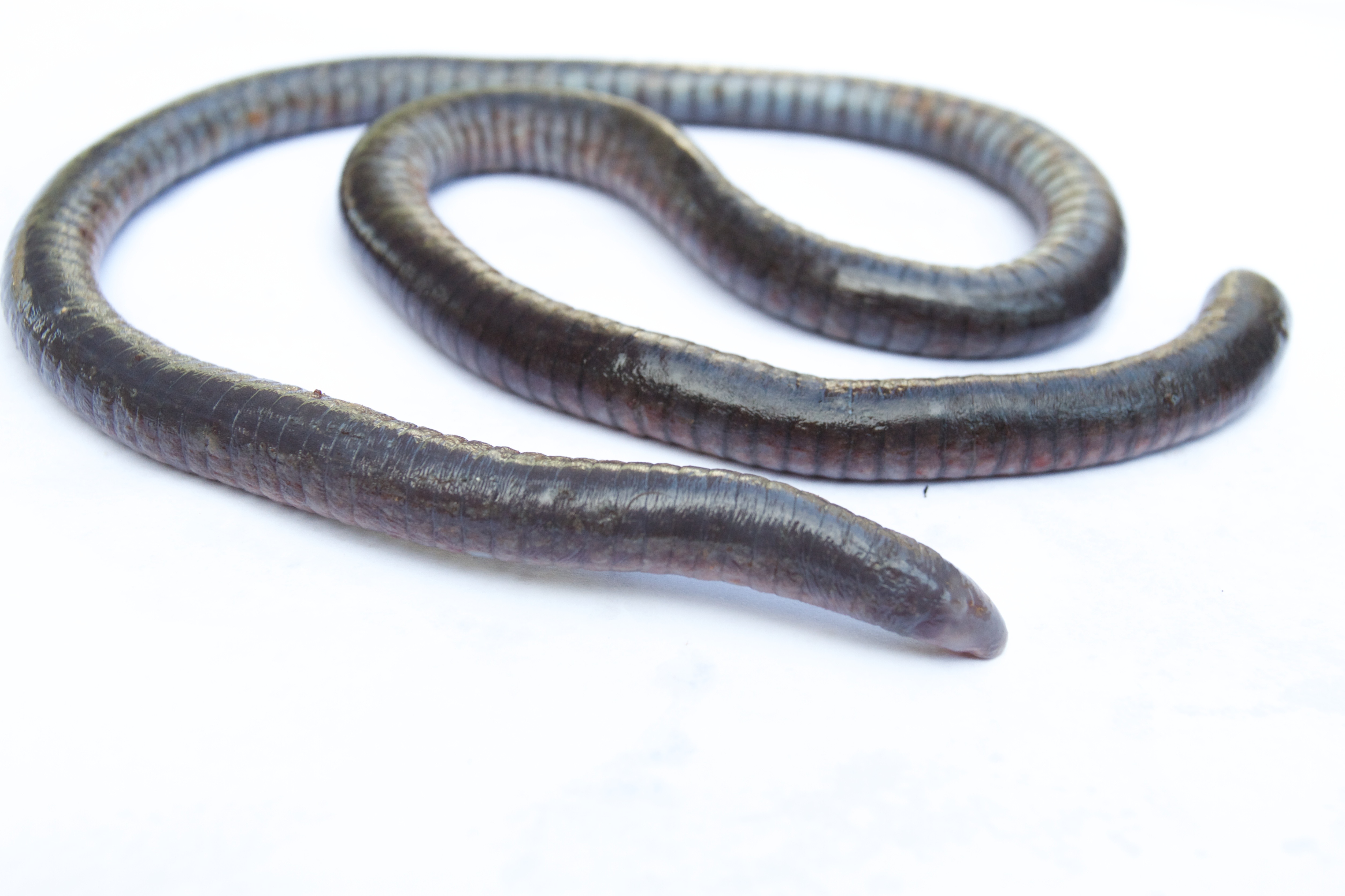

Identify the class and order
Amphibia and Apoda

Identify the class and order
Amphibia; Urodela

Identify the class and order
Amphibia; Anura
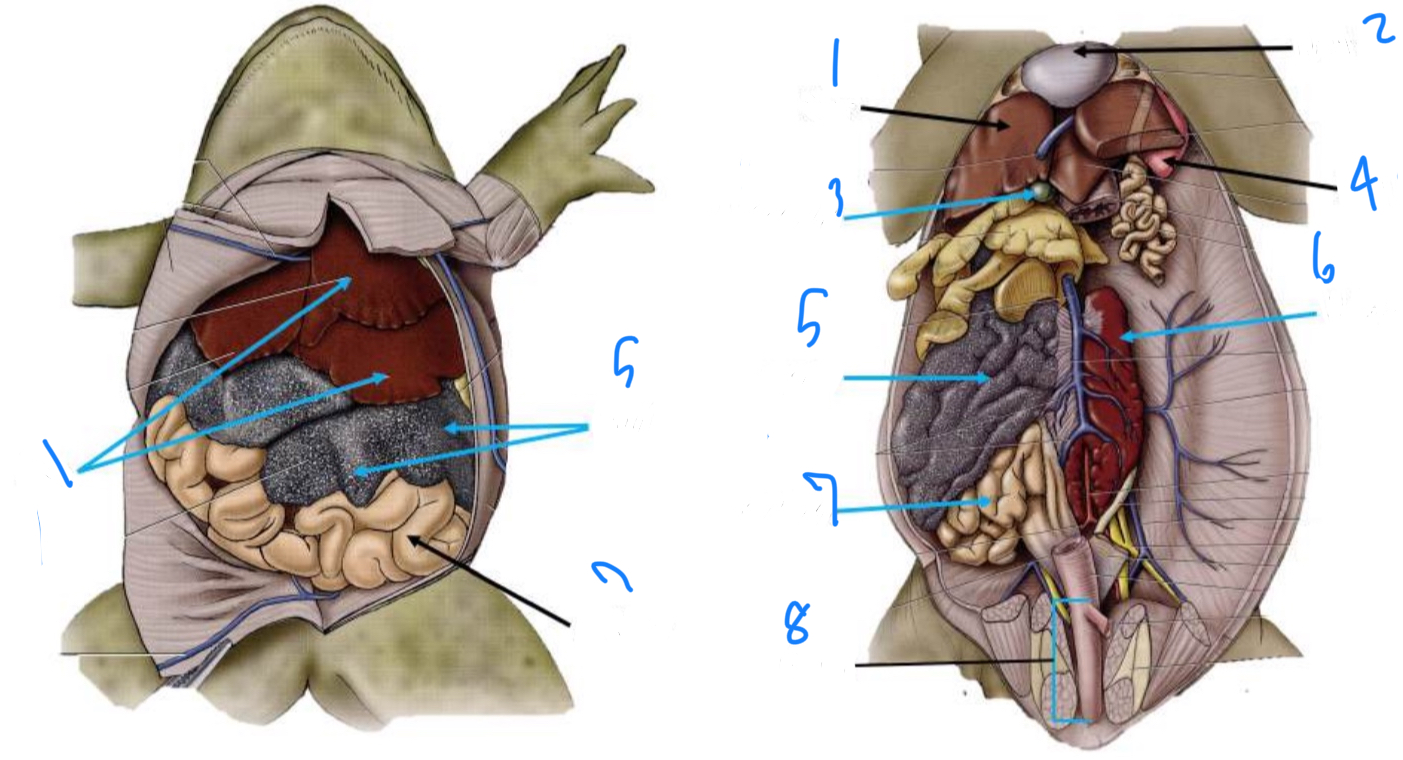
Label the internal frog anatomy starting at 1
Liver, heart, gallbladder, lung, ovaries, kidney, oviducts, cloaca
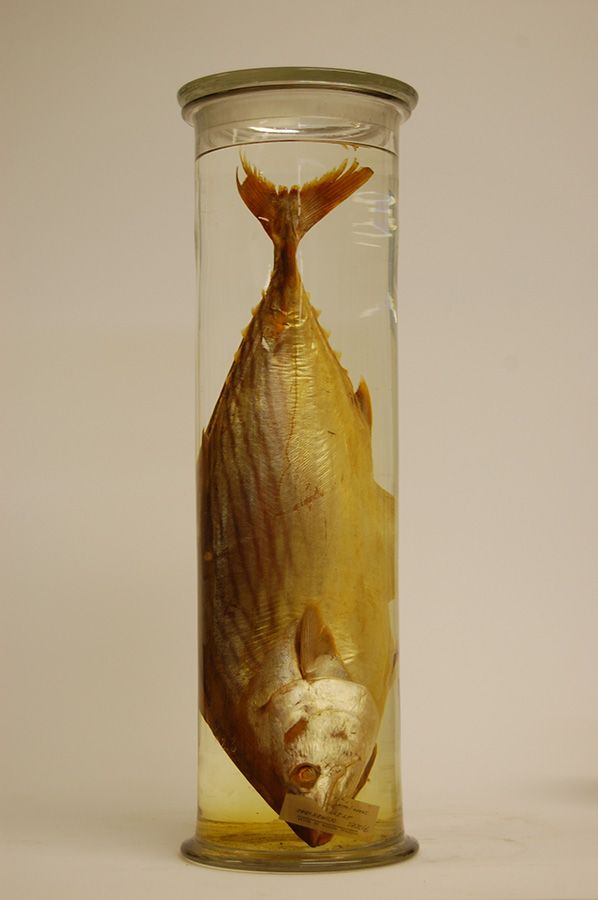

Identify the phylum and subphylum
Chordata; Vertebrata
Class of lizard, snakes, turtles, and crocodilians
Reptilia
List two characteristics true of class Reptilia
Dry skin with scales and respiration via lungs
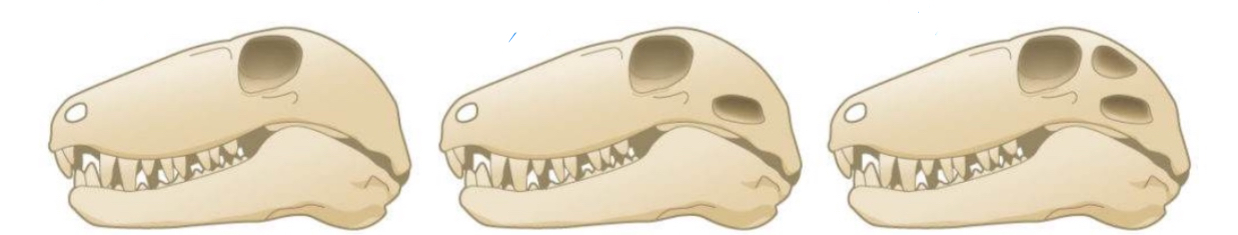
Identify the skull types starting at 1
Anapsid, synapsid, diapsid
Class and Order of turtles and tortoises
Reptilia; Testudines
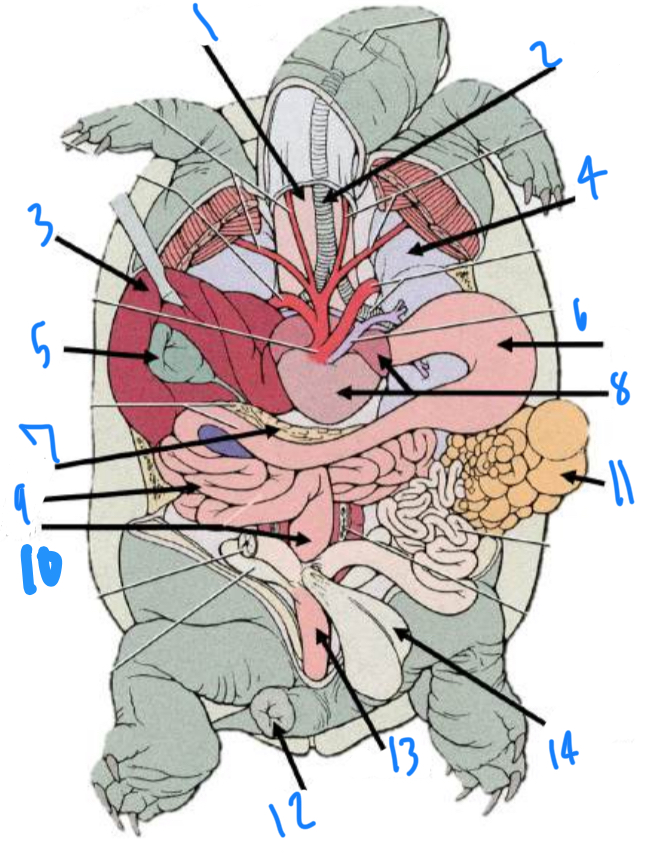
Identify the internal turtle anatomy starting at 1
Esophagus, trachea, liver, lung, gallbladder, stomach, pancreas, heart, small intestine, large intestine, ovaries, cloacal opening, cloaca, urinary bladder
Phylum and Order of lizards and snakes
Chordata; Squamata
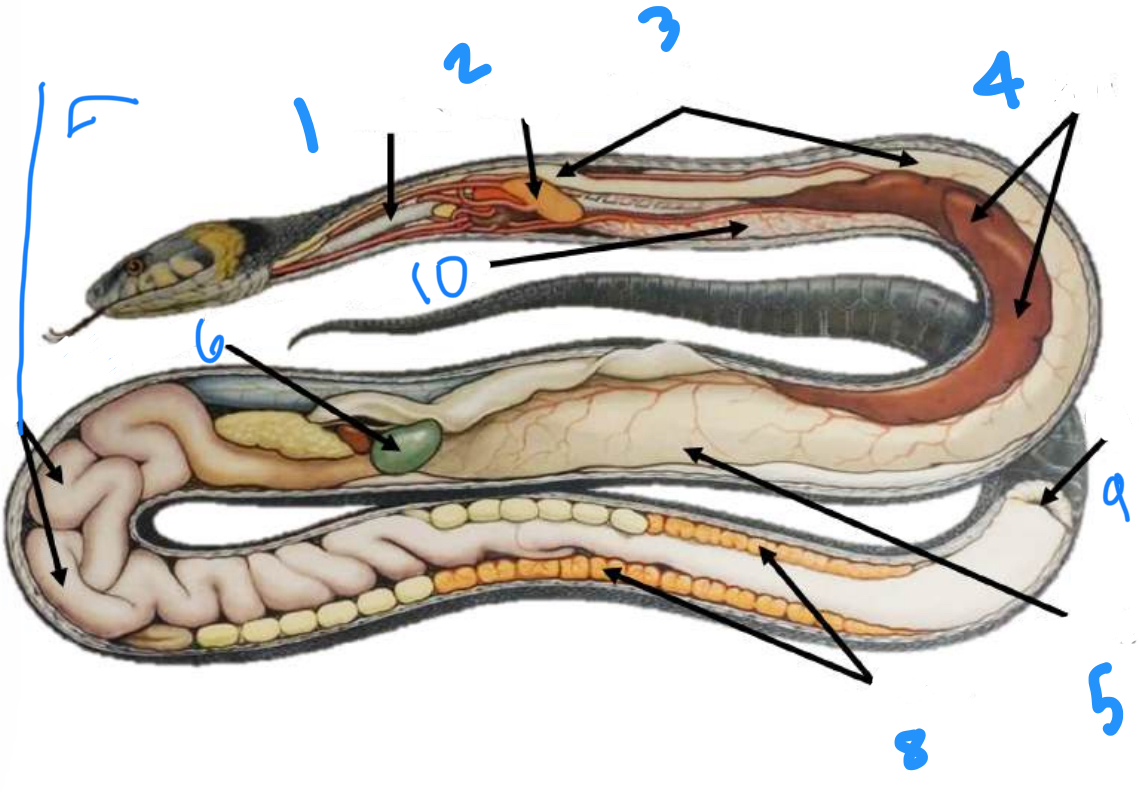
Label the internal snake anatomy starting at 1
Trachea, heart, esophagus, liver, stomach, gallbladder, intestine, kidneys, cloaca, right lung
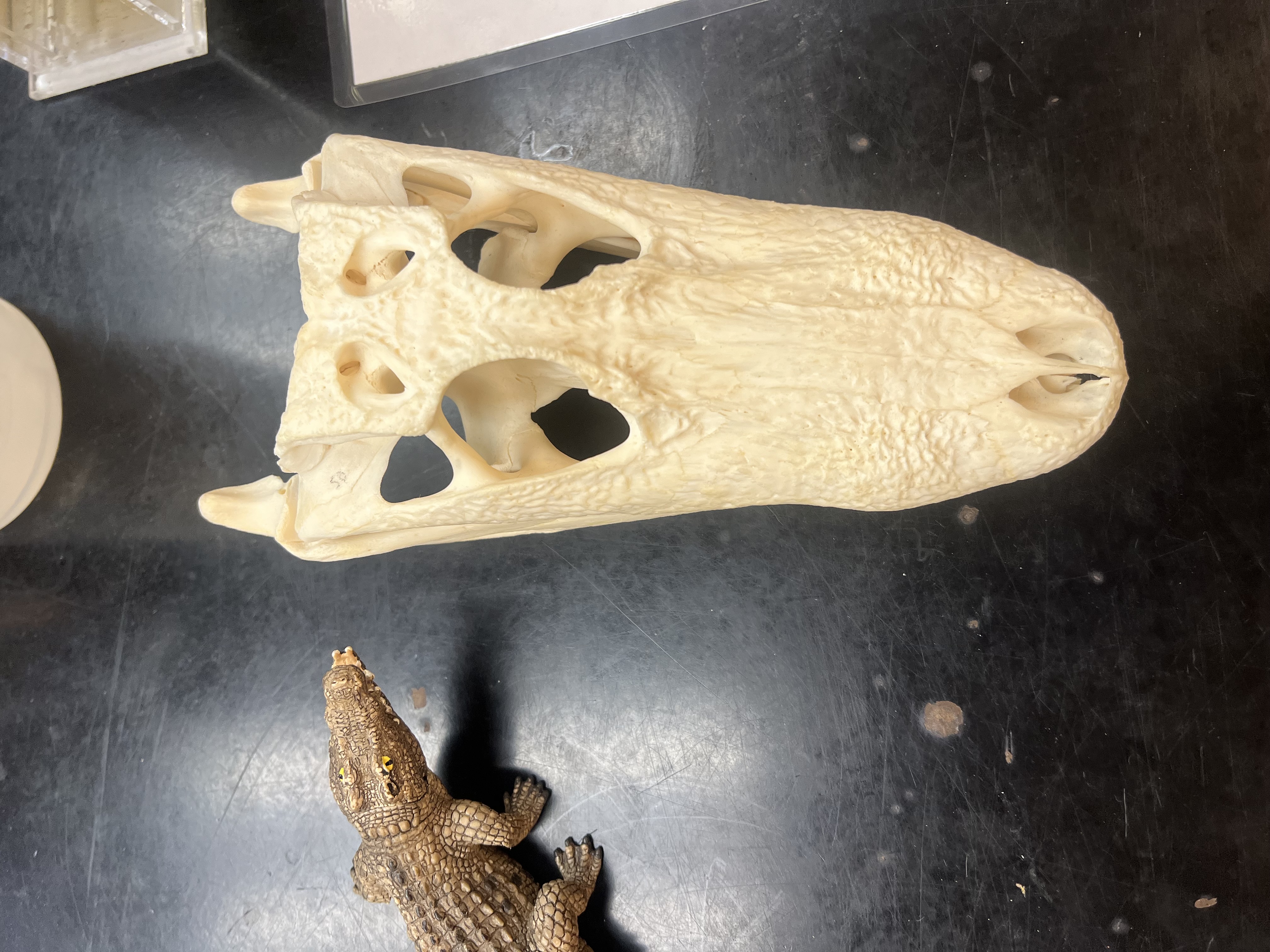

Order of crocodiles
Crocodilia
Class of birds
Aves
2 characteristics of birds
Light, hollow bones and forelimbs adapted into wings for flight
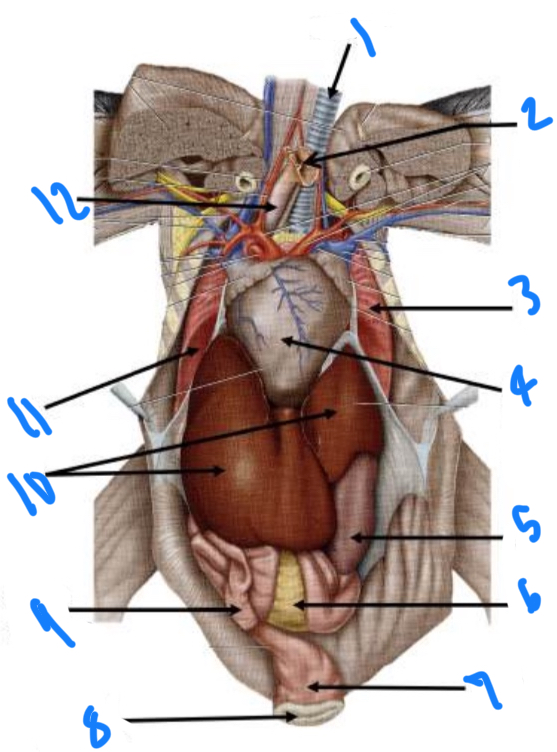
Identify the external structures on the bird starting at 1
Trachea, crop (removed), lung, heart, gizzard, pancreas, cloaca, cloacal opening, small intestine, liver, lung, esophagus

Trachea function
Move air to and from lungs for respiration
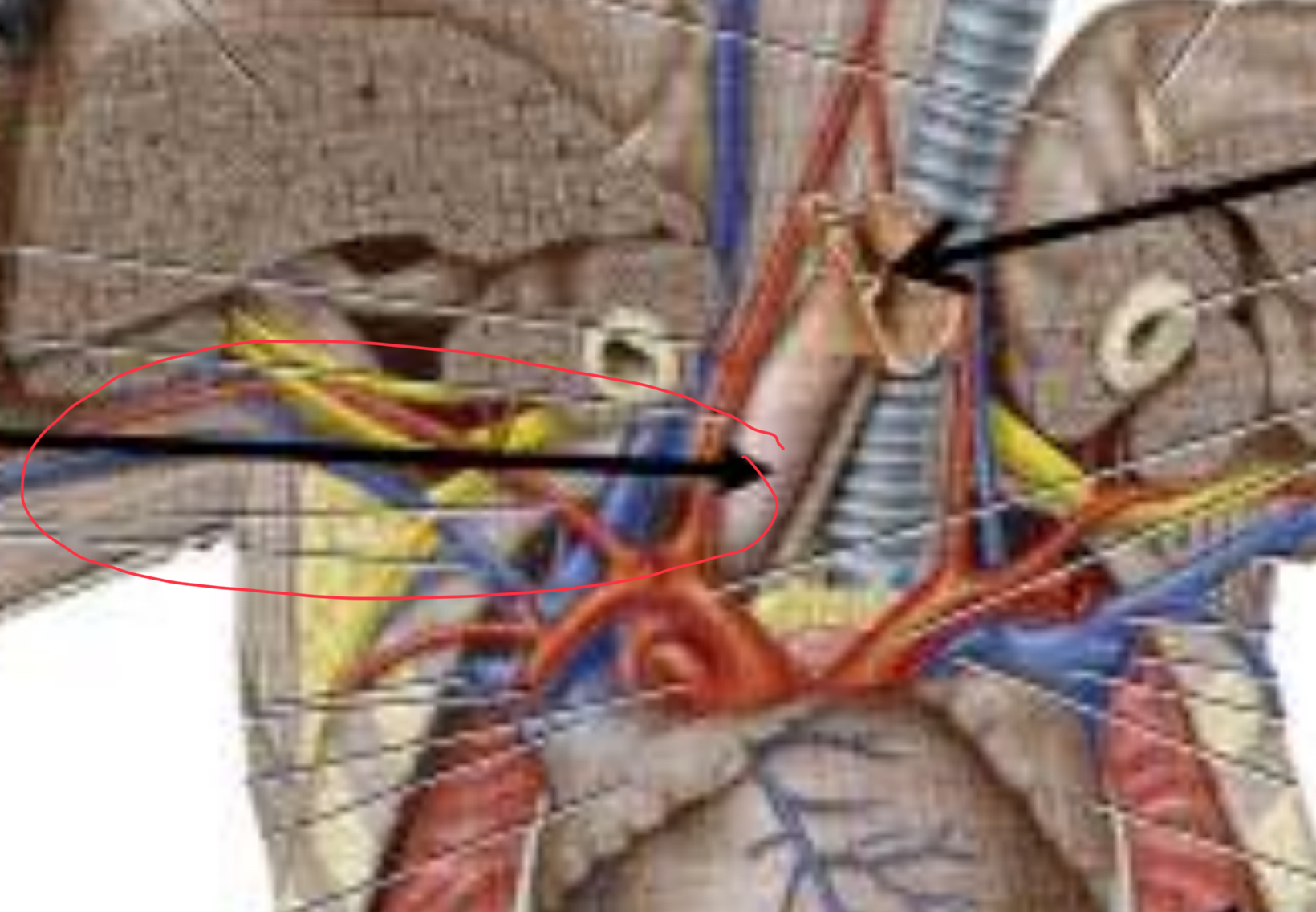
Structure and function (birds)
Esophagus; Move swallowed food to the crop
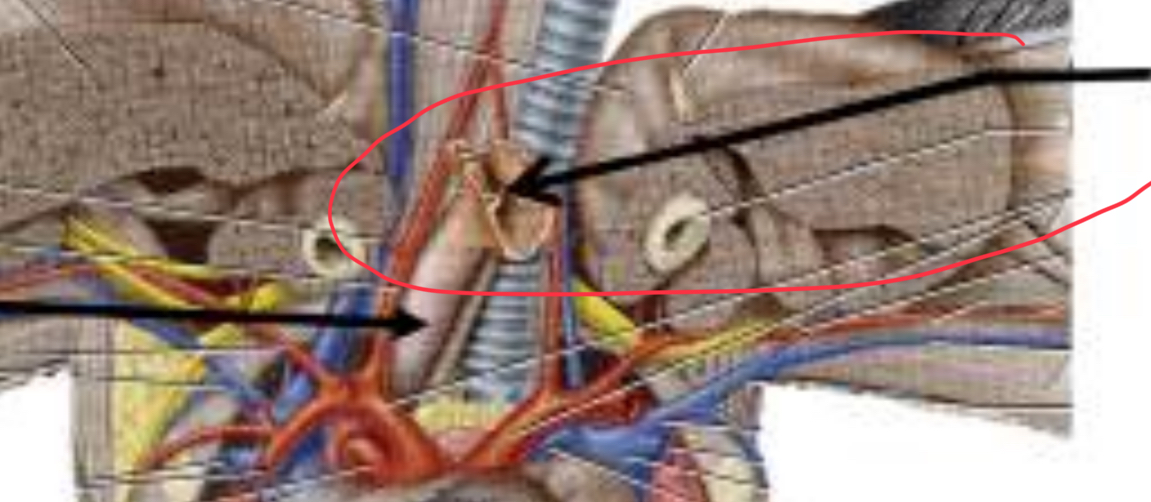
Structure and function
Crop; Temporarily store food
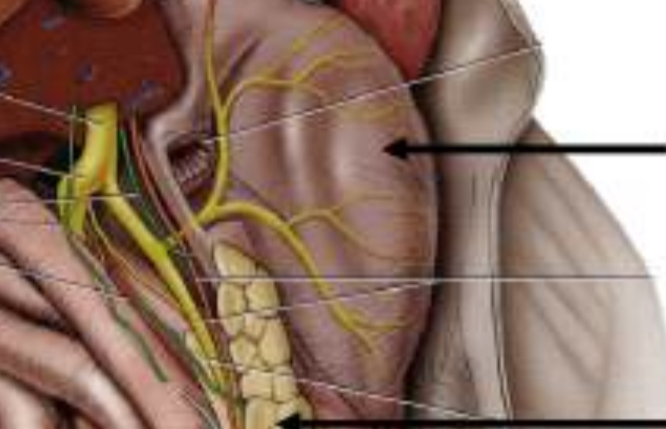
Label the structure and function
Gizzard; Grinds food
Uropygial gland (birds) function
Secretes oil to coat feathers and make them waterproof
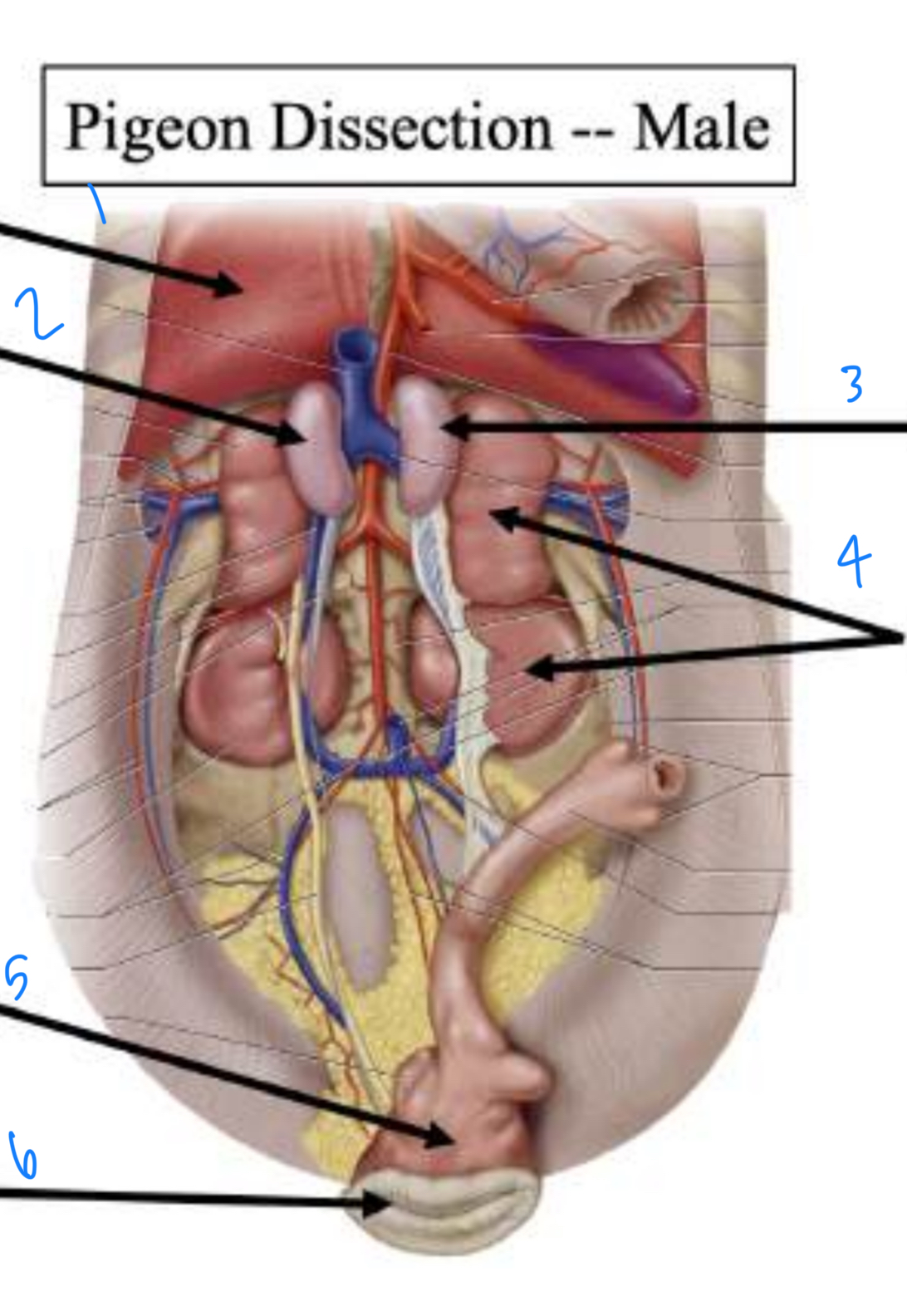
Label the male pigeon anatomy starting at 1
Lung, testis, testis, kidneys, cloaca, cloacal opening
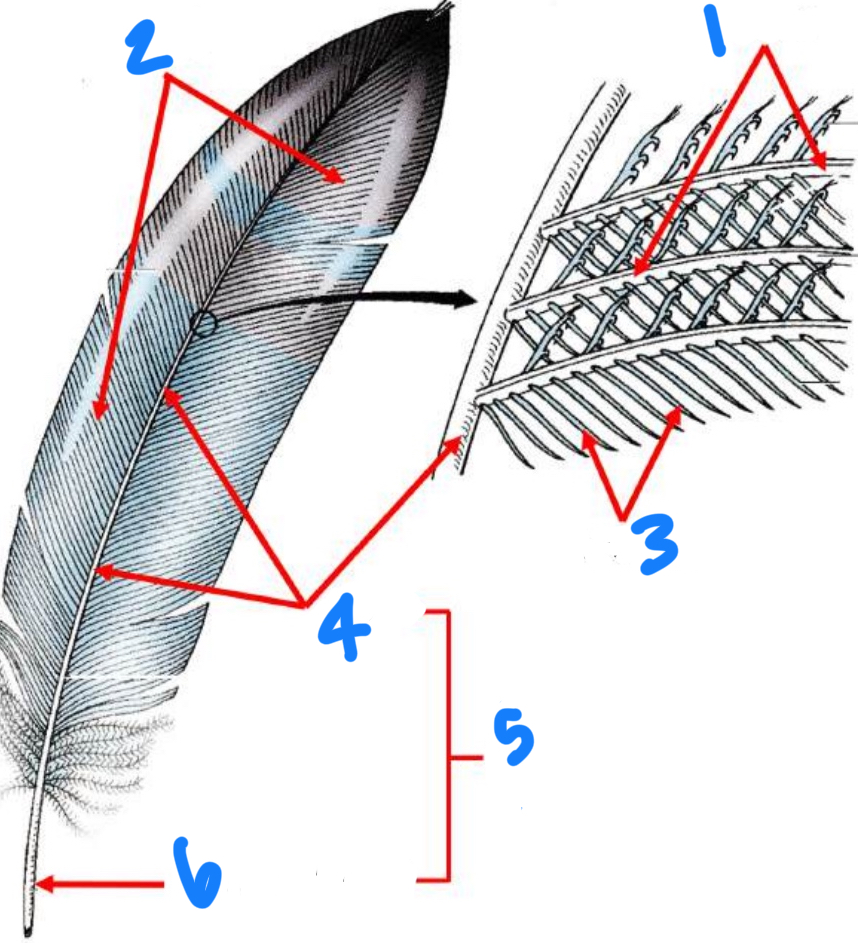
Identify the parts of the feather starting with 1
Barbs, vane, barbules, rachis, shaft, quill
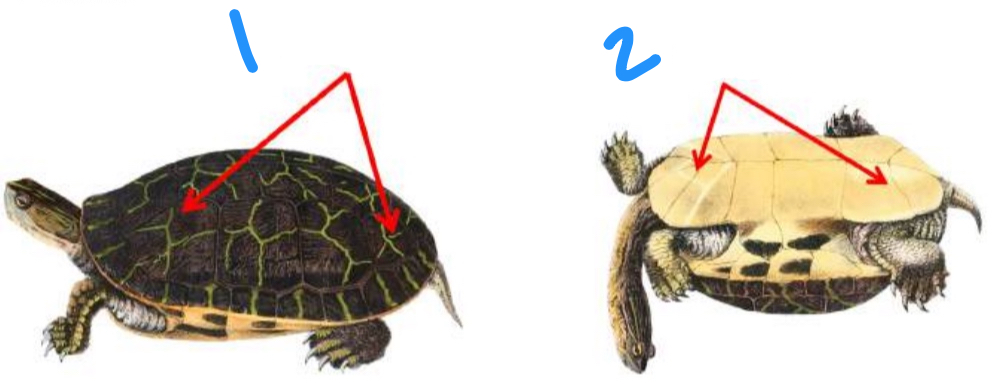
Label the turtle structures starting at one
Carapace and plastron

Skull type of turtle
Anapsid
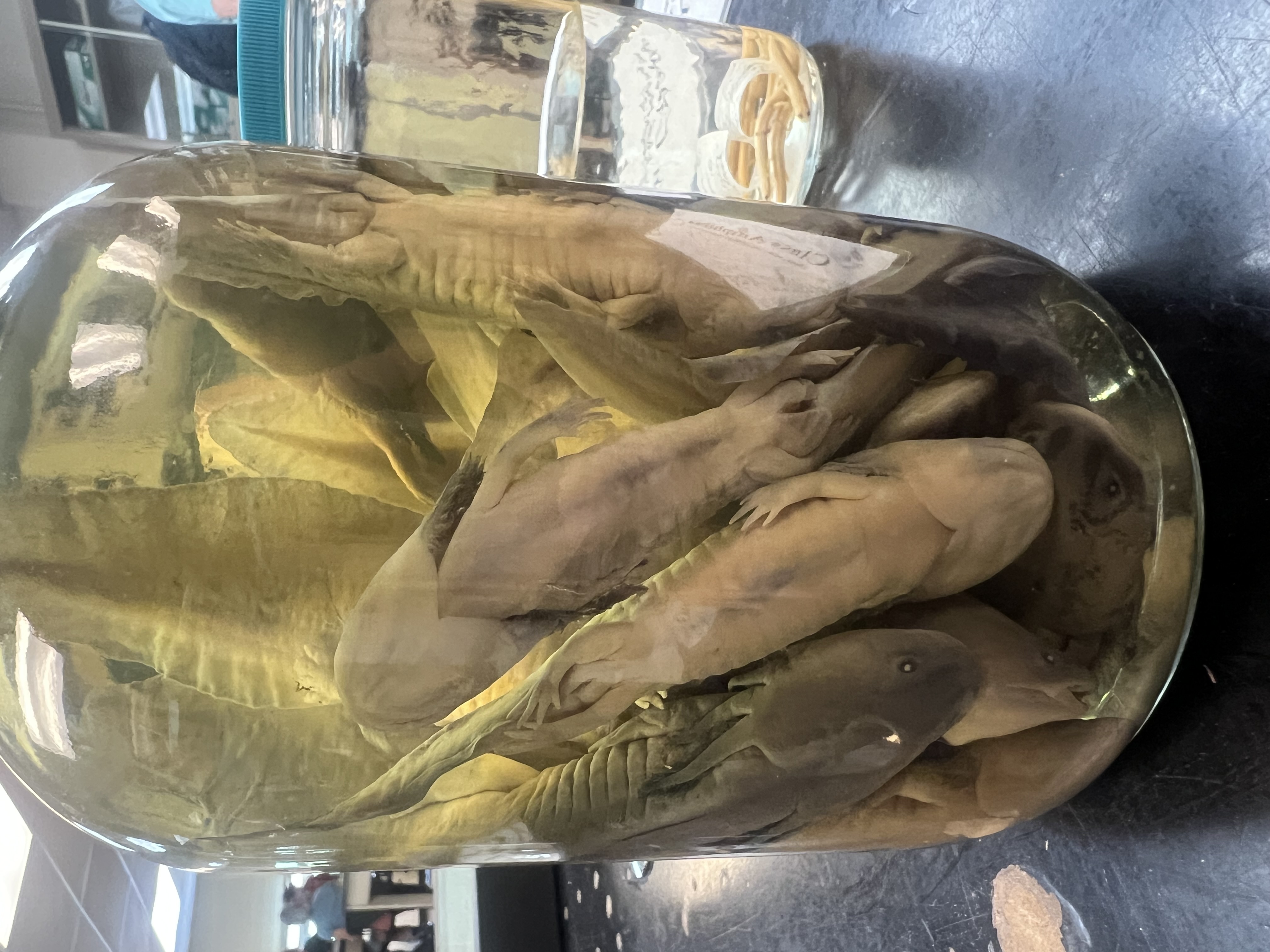

Identify the order
Urodela
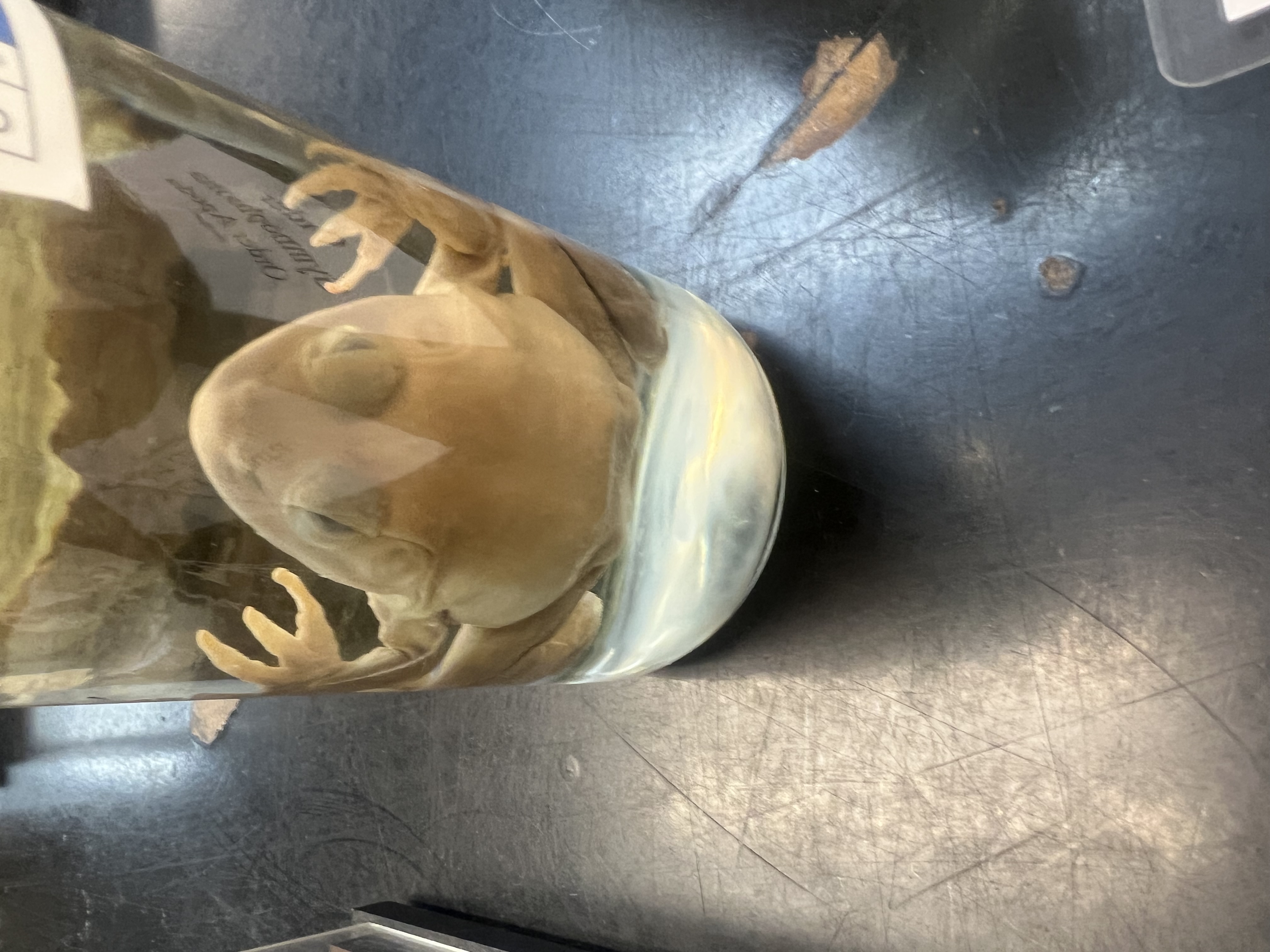
Idenitfy the subphylum and order
Vertebrata and Anura
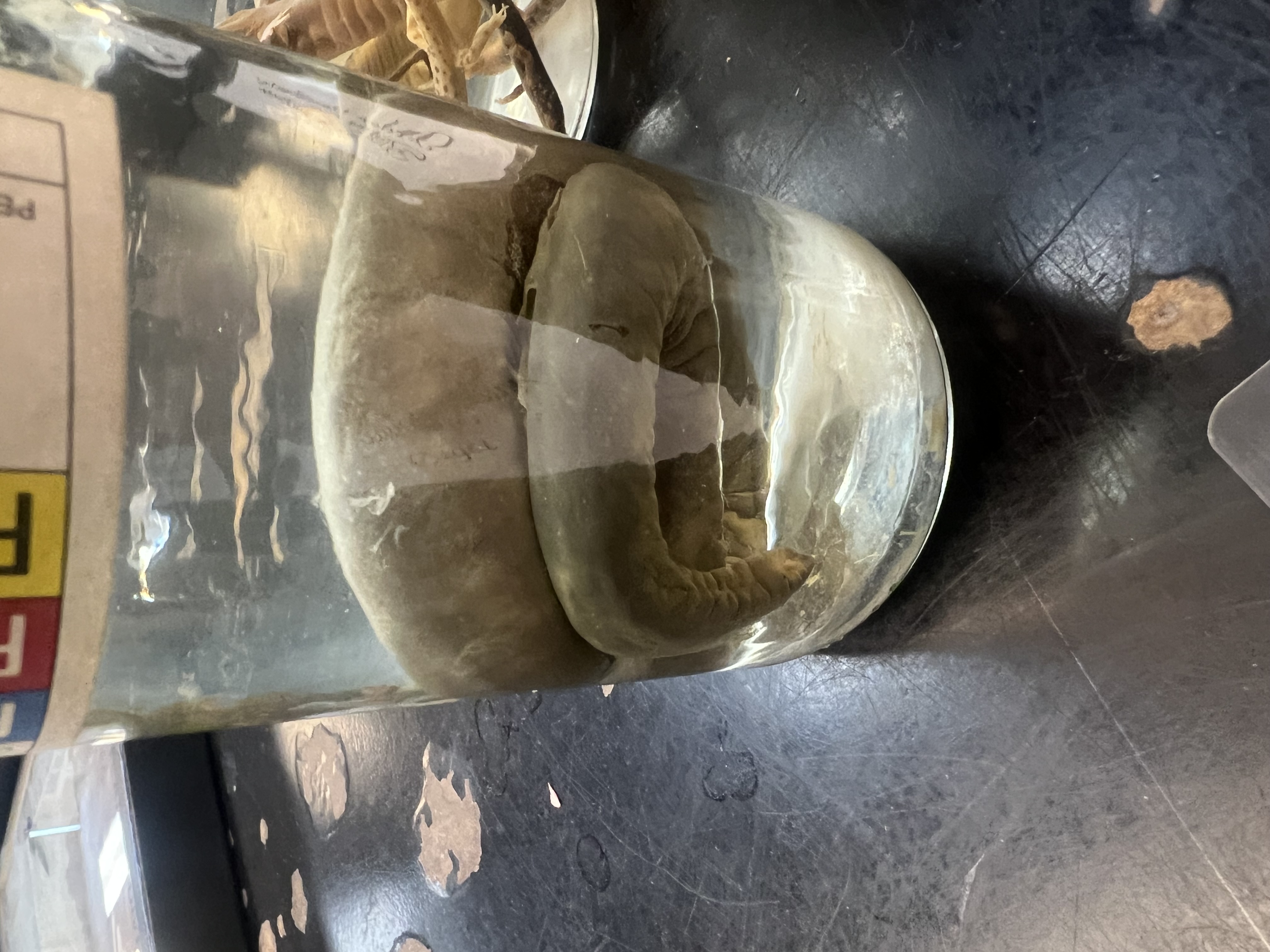

Identify the phylum and order
Chordata and Apoda
3 orders under Class Amphibia
Urodela (salamanders), Anura (frogs), Apoda (caecilians)

Skull type of mammals
Synapsid
Class of mammals
Mammalia
2 subclasses of class mammalia
Prototheria and Theria
Animals of subclass Protothoria
Anteaters, platypus, egg-laying and nipple lacking mammals
Animals of subclass Theria
All other viviparous (live birth) animals
2 infraclasses of subclass Theria
Metatheria and Eutheria
Metatheria animals
Opossums, kangaroos,koalas
Eutheria animals
Rodents, whales, bats, elephants, felids, humans, canids, etc
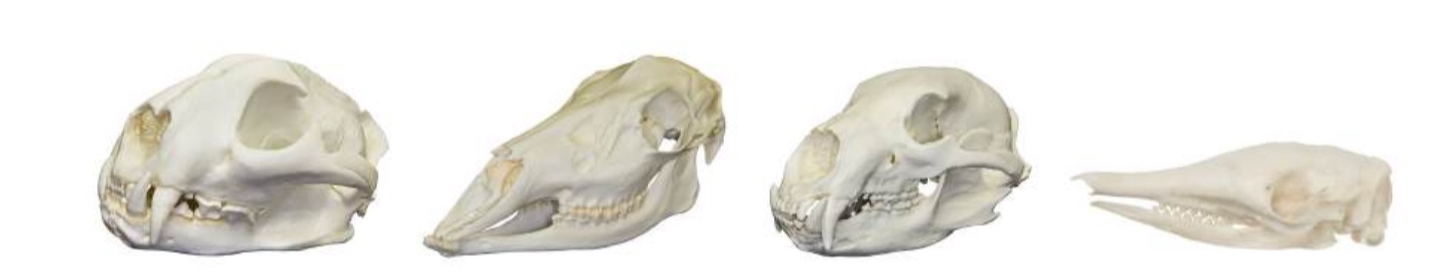
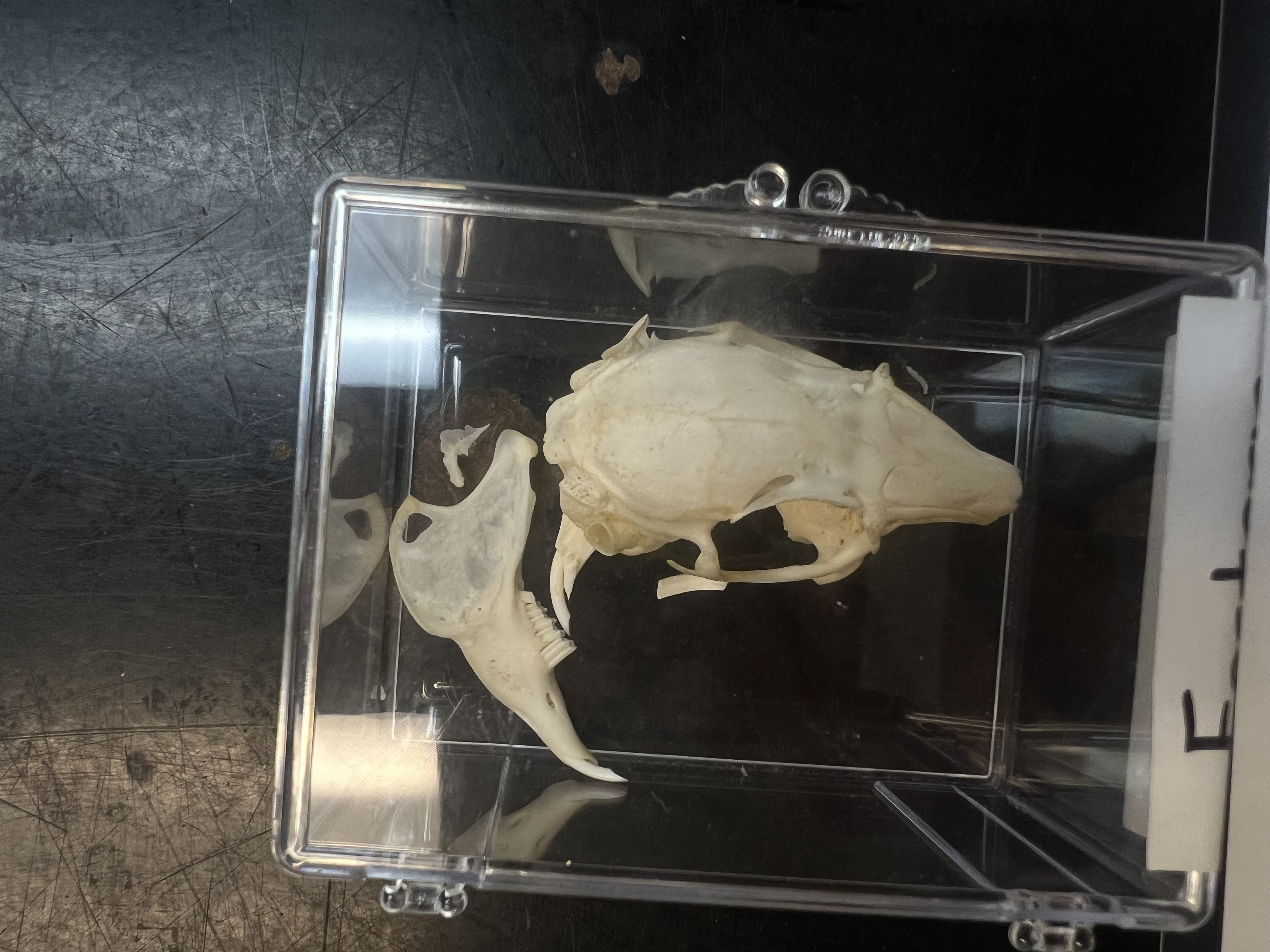
Label the skull types starting at 1
Carnivore, herbivore, omnivore, insectivore
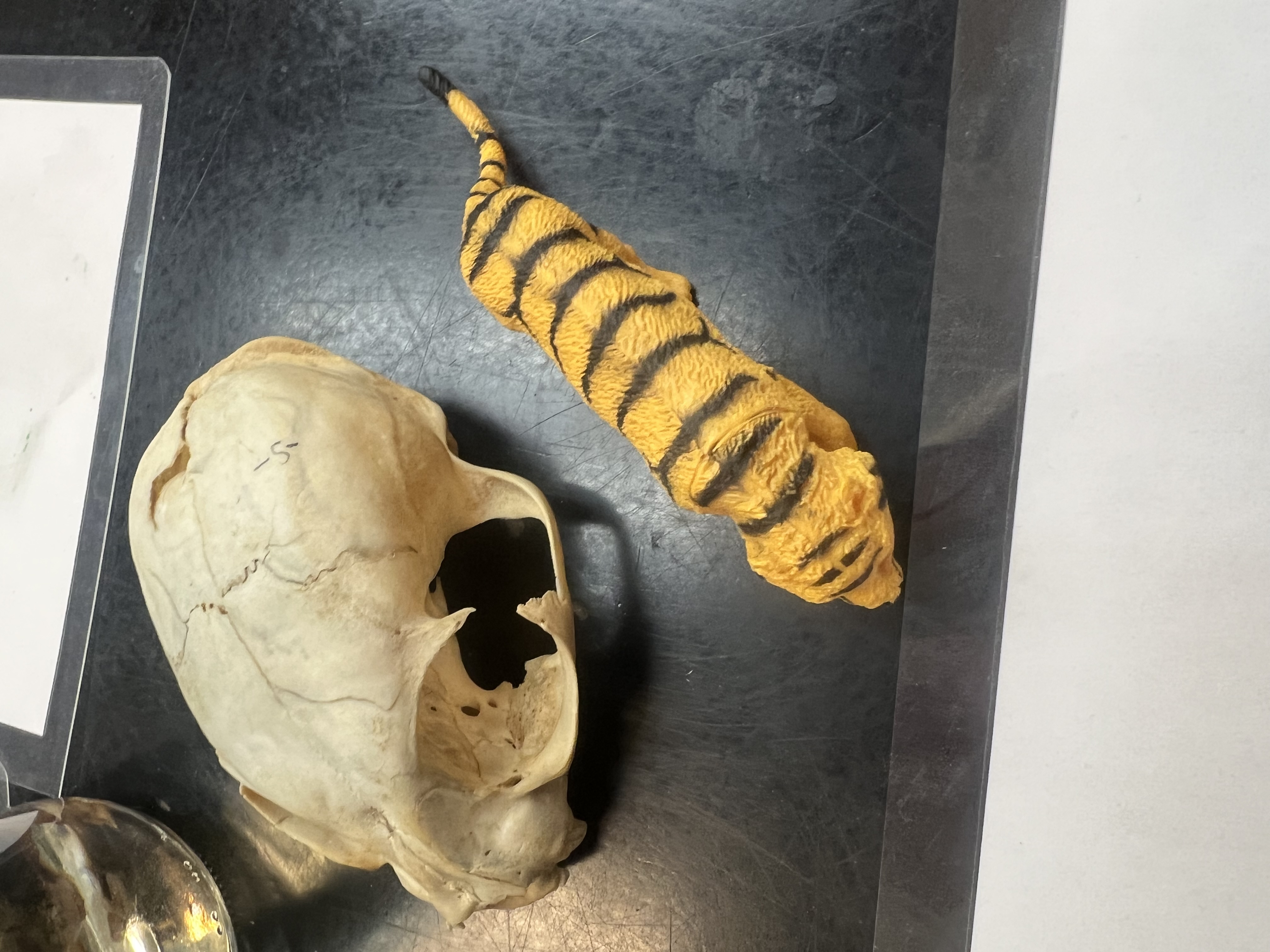

order of these animals
Carnivora
Order of bats
Chiroptera

Order of these animals (rabbits, hares)
Lagomorpha
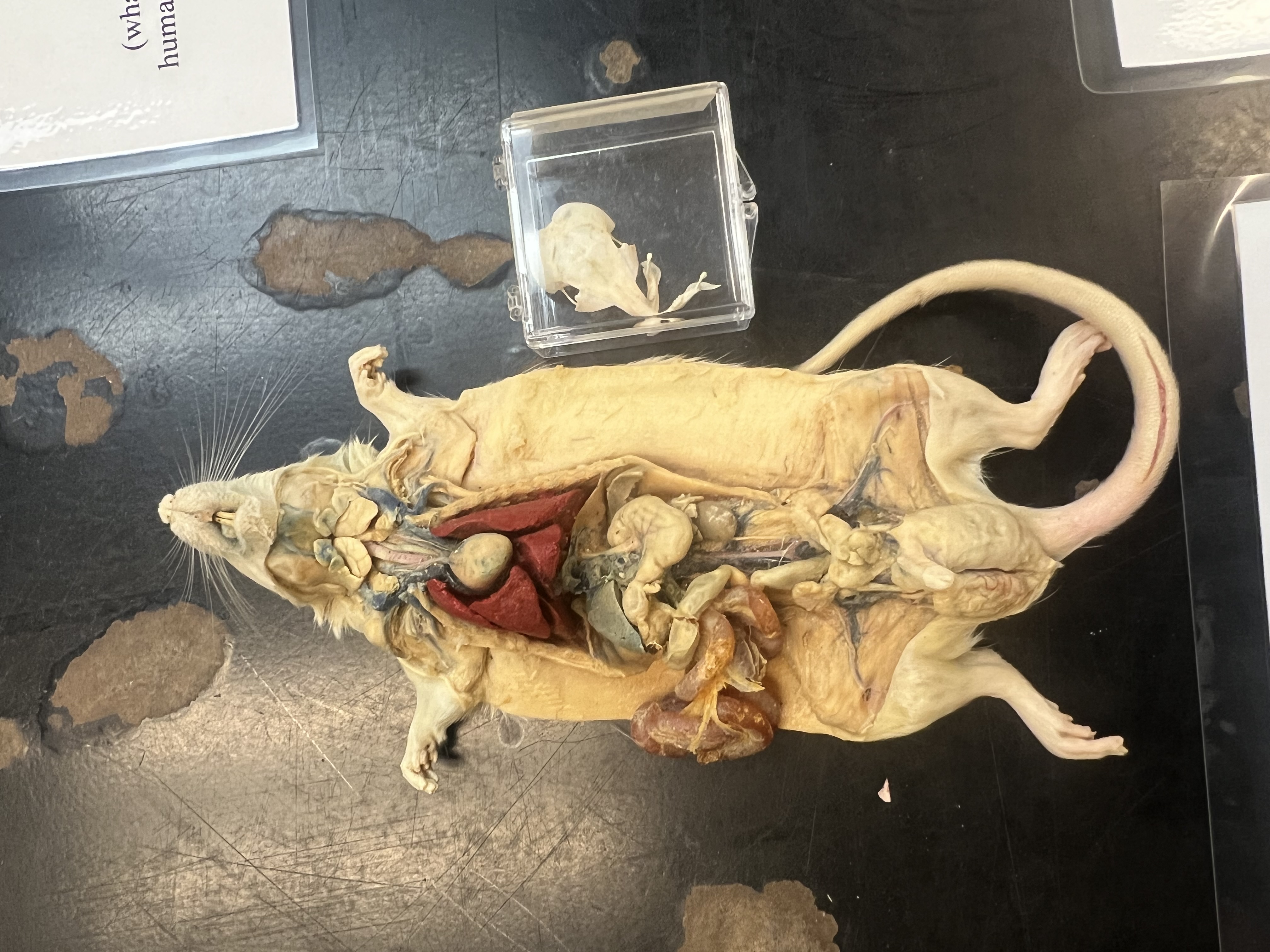
Order of rodents
Rodentia
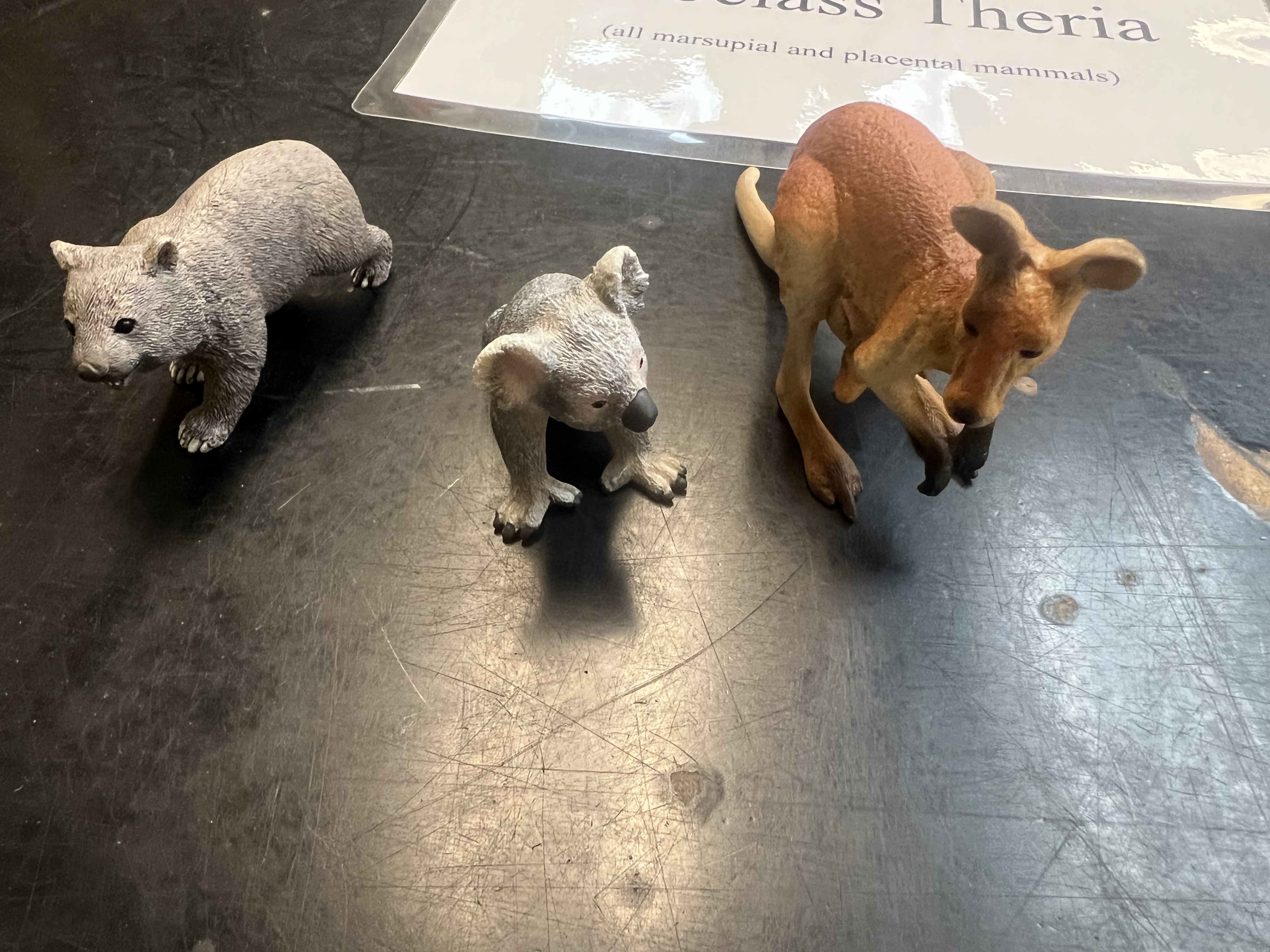

Infraclass of these animals
Metatheria
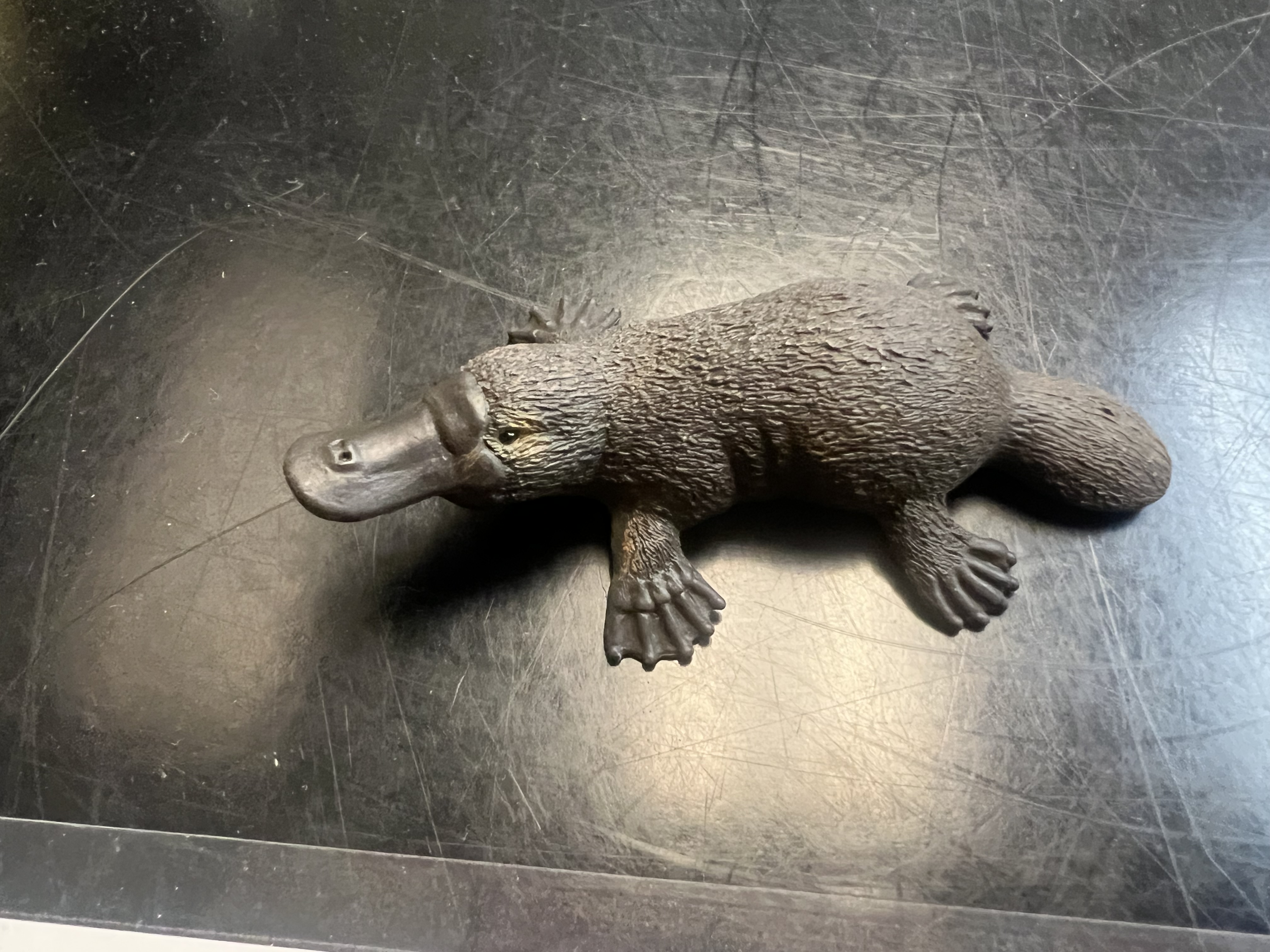

Identify the subclass
Prototheria
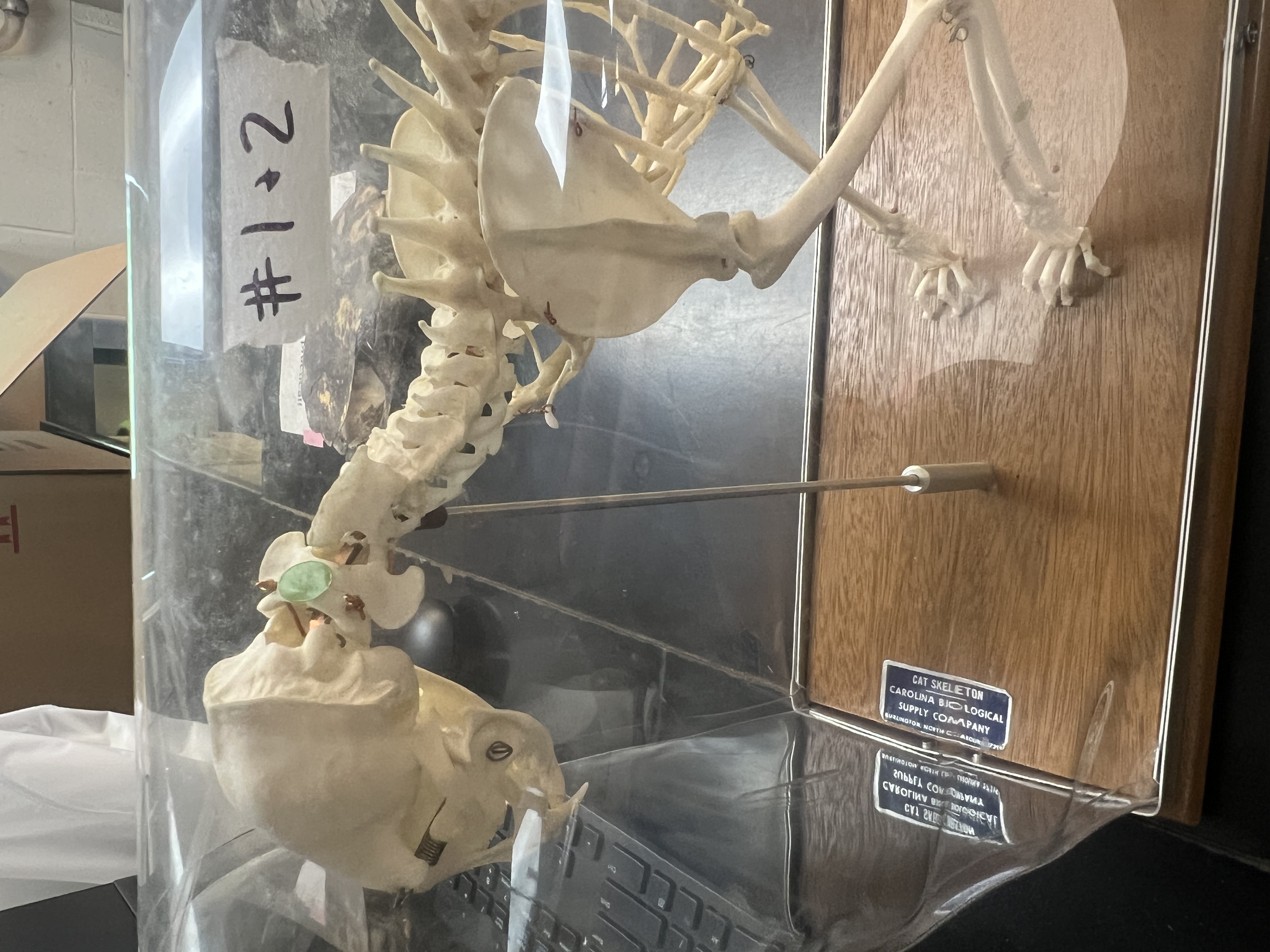

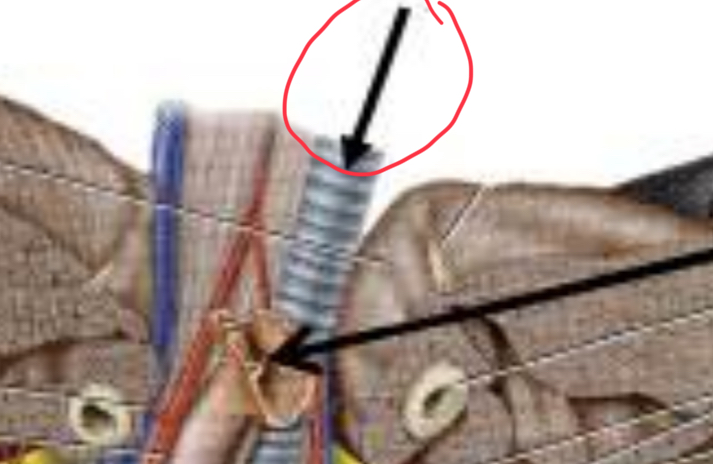
Identify the anatomy of the green dot
atlas