Chapter 3 Mastery Training
1/32
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Chapter 3 - Perception
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
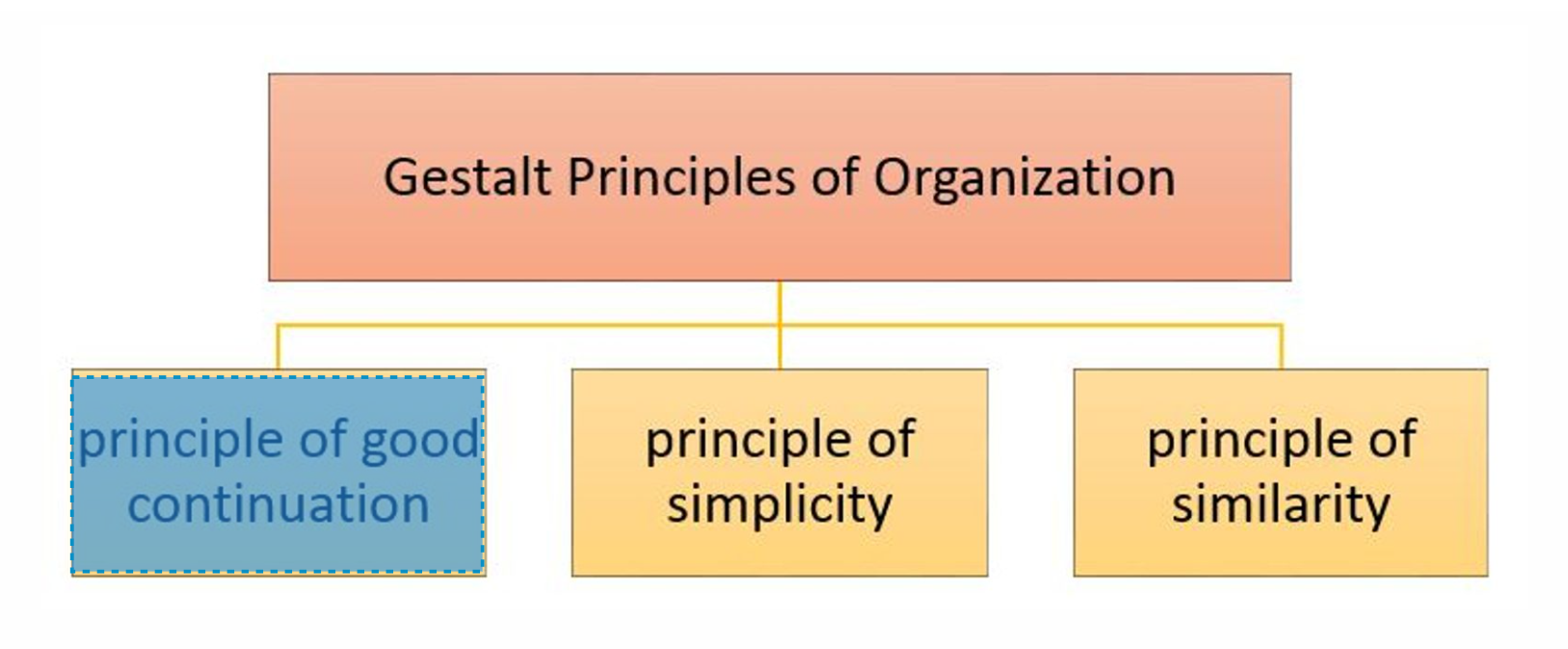
PRINCIPLE OF GOOD CONTINUATION
Idea that humans perceive two objects that overlap each as a single, uninterrupted object
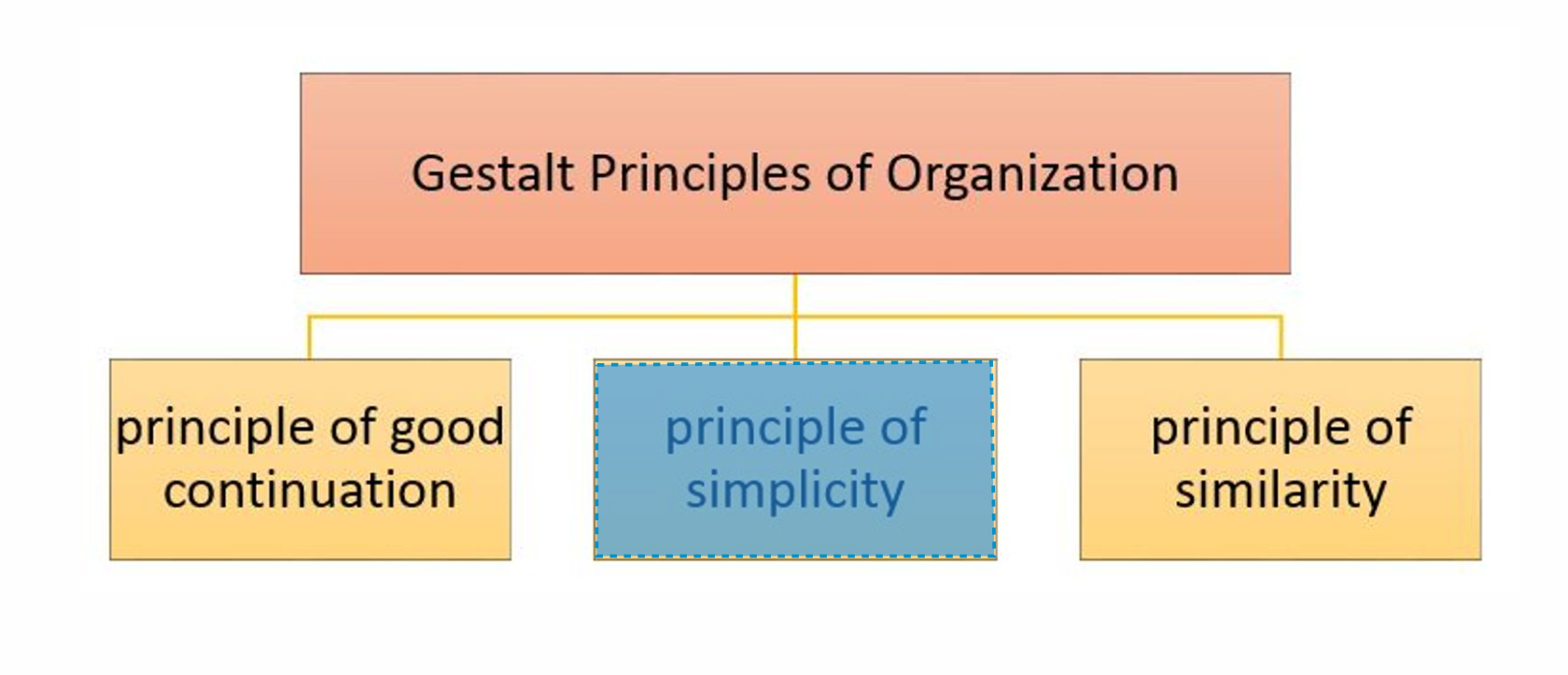
PRINCIPLE OF SIMPLICITY
Concept that every stimulus is perceived in its most uncomplicated form
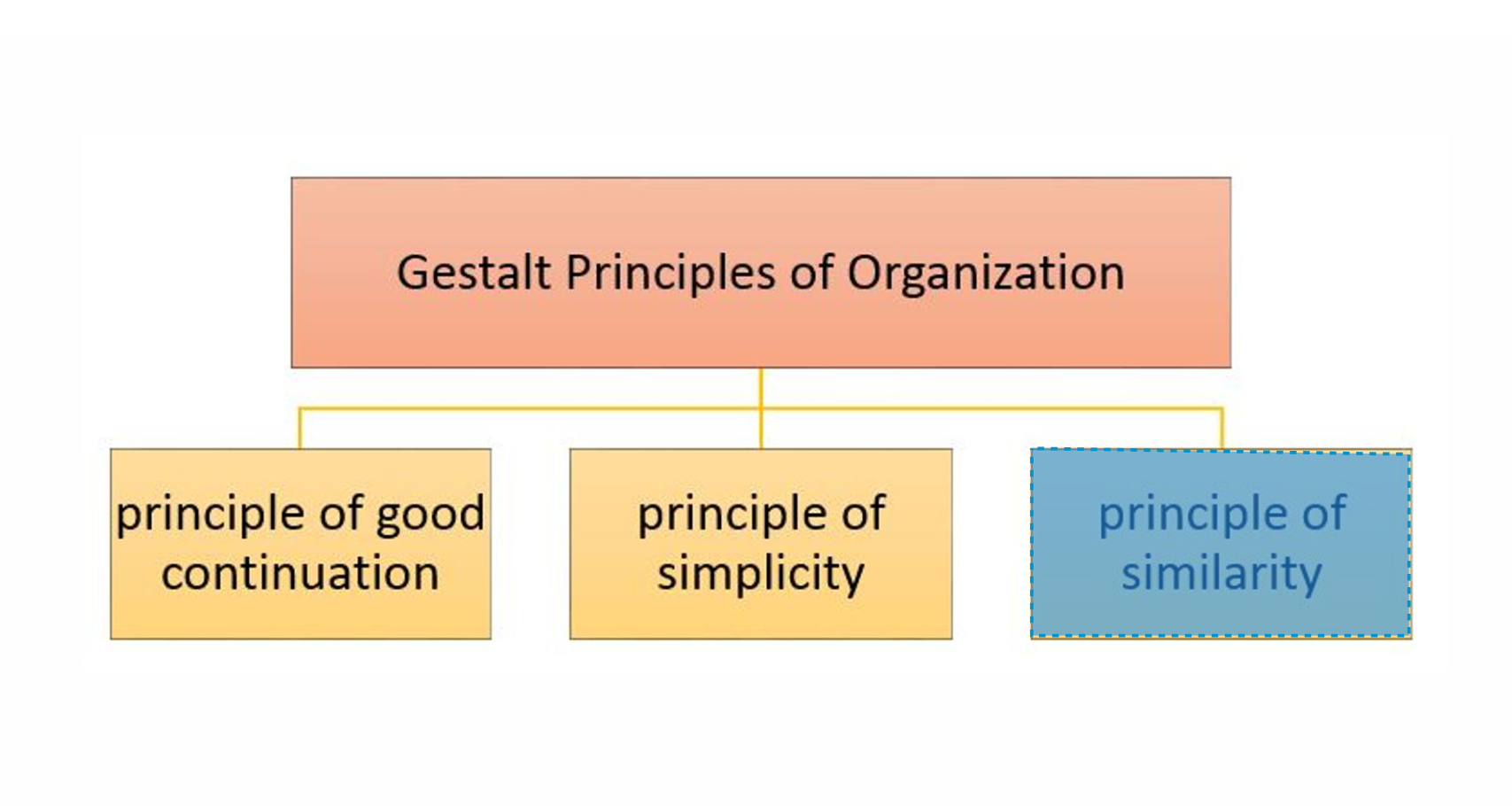
PRINCIPLE OF SIMILIARITY
Idea that things that resemble each other appear to be grouped together
PERCEPTION
Conscious experience that results from stimulation of the senses
INVERSE PROJECTION PROBLEM
Task of determining the object that caused a particular image on the retina
VIEWPOINT INVARIANCE
Ability to recognize an object seen from different outlooks
BOTTOM-UP PROCESSING
Sequence of events that starts with information received by the receptors
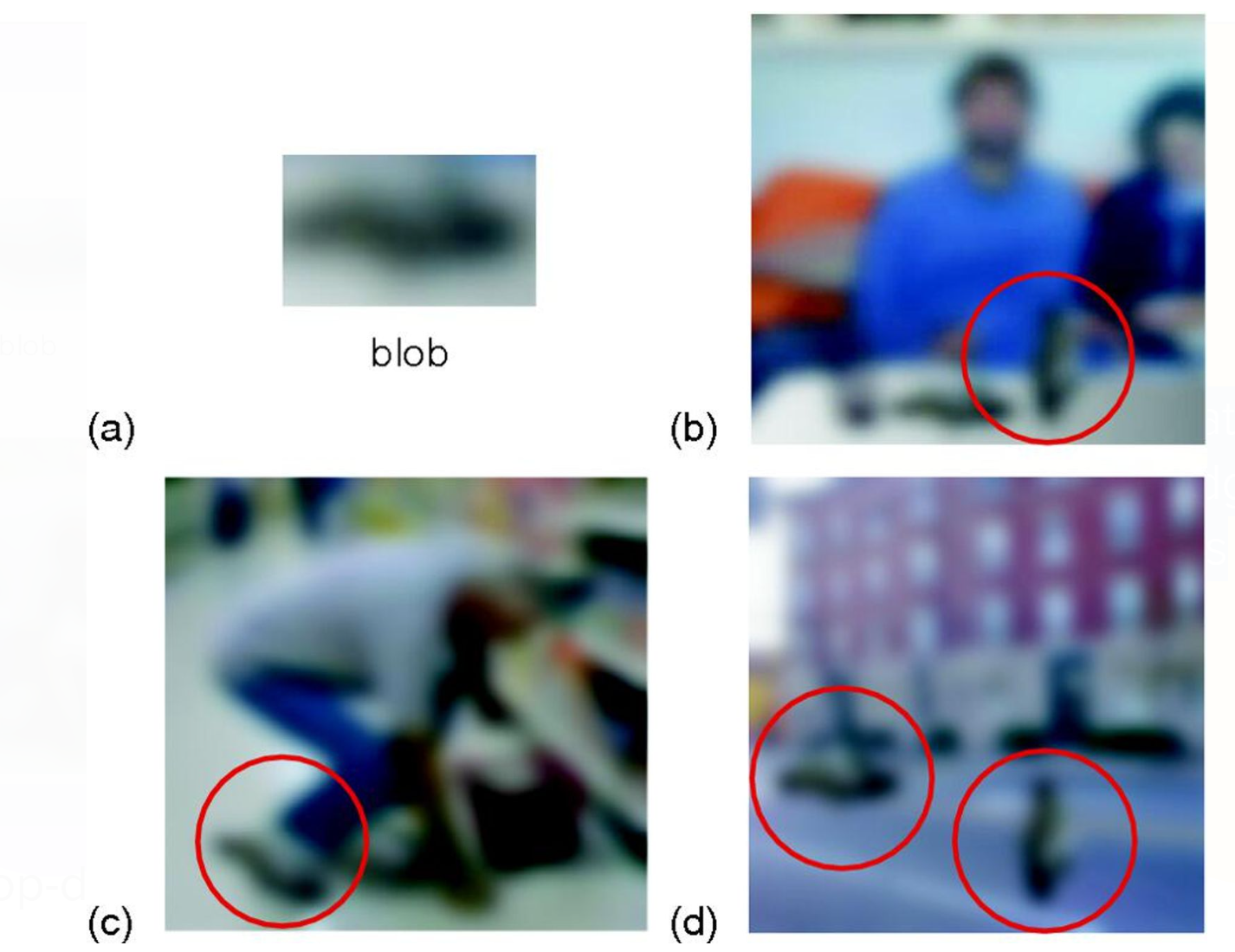
TOP-DOWN PROCESSING
Sequence of events that involves a person's knowledge or expectations
SPEECH SEGMENTATION
Process of perceiving individual words within the continuous flow of the language signal
TRANSITIONAL PROBABILITIES
Likelihood that one speech sound will follow another within a word
LIKELIHOOD PRINCIPLE
Perception of the object that is expected to have caused the pattern of stimuli received
UNCONSCIOUS INFERENCE
Idea that some of our perceptions result from unmindful assumptions we make about the environment

APPARENT MOVEMENT
Illusion of motion perception when stimuli in different locations are flashed one after another
PRINCIPLES OF PERCEPTUAL ORGANIZATION
Proposal that explains how small elements of a scene become perceptually grouped to form larger units
LIGHT-FROM-ABOVE ASSUMPTION
Belief that light usually comes from a higher level
OBLIQUE EFFECT
Finding that vertical and horizontal orientations can be perceived more easily than other orientations

PHYSICAL REGULARITY
Commonly occurring property of the environment
SEMANTIC REGULARITY
Characteristic associated with the functions carried out in different types of scenes
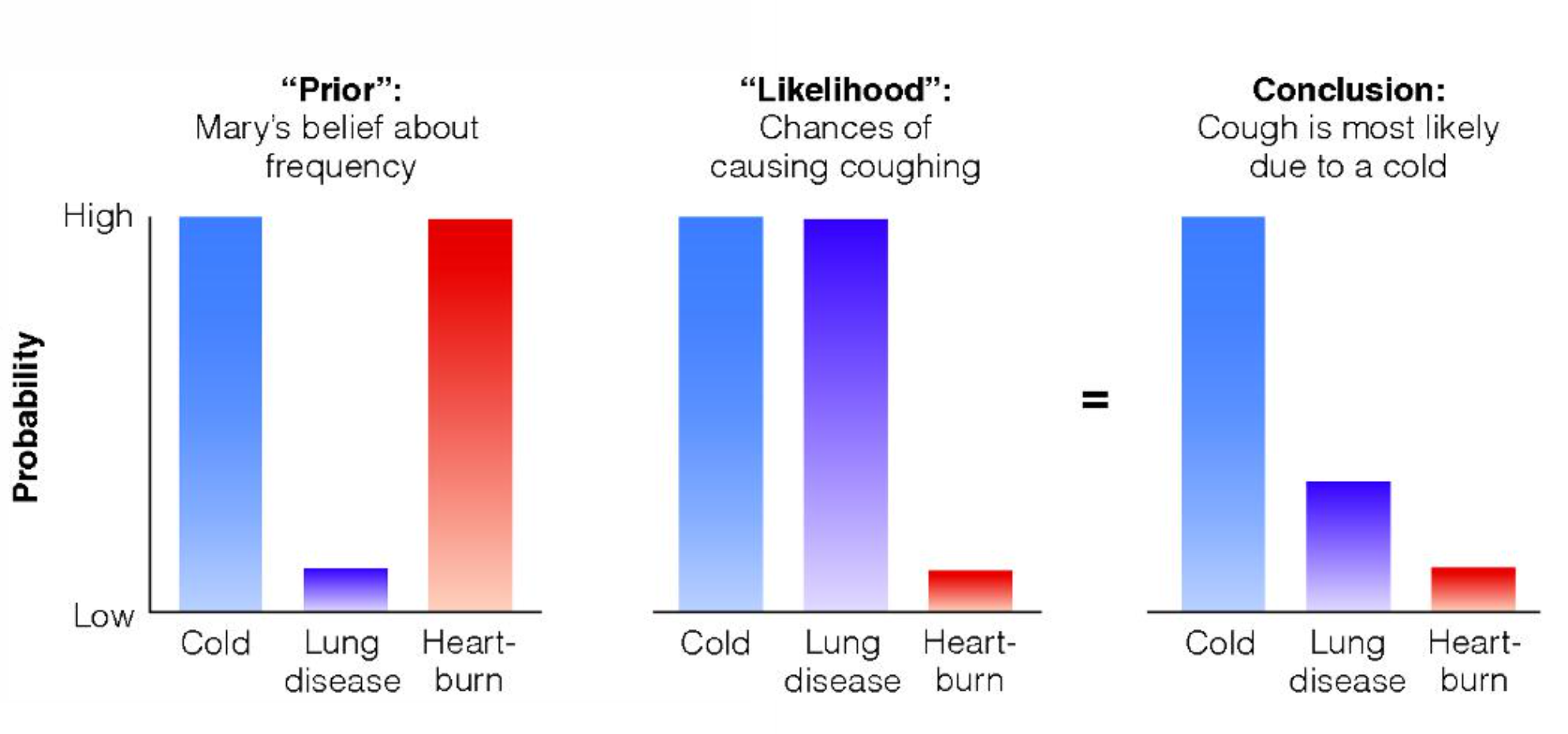
BAYESIAN INFERENCE
Idea that estimation of the probability of an outcome is determined by prior probability and likelihood
LIKELIHOOD
In Bayesian inference, the extent to which the available evidence is consistent with the outcome
PRIOR
Person's initial belief about the probability of an outcome
SCENE SCHEMA
Person's knowledge about what is likely to be contained in a particular setting
THEORY OF NATURAL SELECTION
Characteristics that enhance an animal's ability to survive and reproduce will be passed on
BRAIN ABLATION
Removing part of the cerebrum
LANDMARK DISCRIMINATION PROBLEM
Task of remembering an object's location and choosing that location after a delay
OBJECT DISCRIMINATION PROBLEM
Task of remembering something based on shape and choosing it when presented with another item
WHAT PATHWAY
Part of the brain associated with perceiving or recognizing objects
WHERE PATHWAY
Part of the brain associated with neural processing that occurs when people locate objects in space
DORSAL PATHWAY
Part of the brain that extends from the visual cortex in the occipital lobe to the parietal lobe
VENTRAL PATHWAY
Lower part of the brain that goes from the visual cortex in the occipital lobe to the temporal lobe
ACTION PATHWAY
Neural tract extending from the visual cortex to the parietal lobe
PERCEPTION PATHWAY
Neural tract extending from the visual cortex to the temporal lobe
MIRROR NEURON
Brain cell that responds both when an activity is observed and when it is performed