Unit 9 Chemistry - Thermochemistry
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
49 Terms
Thermochemistry
Study of heat transfer (thermal energy). All physical and chemical changes require a change in energy, either absorbed or released.
Law of Conservation of Energy
Energy cannot be created nor destroyed but is conserved
Heat
Energy transferred between 2 objects due to temperature differences
Which direction does heat flow?
Always flows from hot to cold
When does heat transfer stop?
When thermal equilibrium is reached
How is heat measured?
Measured indirectly through temperature changes
Conduction
Transfer of heat by direct contact between objects
Convection
Transfer of heat by bulk movement of matter in liquids or gases
Radiation
Transfer of heat by electromagnetic waves (light)
Temperature
Measures average kinetic energy of particles
How is temperature measures?
Measures in C or Kelvin (K) (K = C + 273)
Specific Heat
Amount of energy required to raise the temperature of 1g of a substance by 1 C (or 1 K)
What is the unit of measurement for specific heat?
J/g C or J/g•K
Insulator
Transfers heat and energy slowly/poorly. High specific heat values. (Wood, cotton, fiberglass, rubber)
Conductor
Transfers heat and energy easily/more quickly. Low specific heat value. (Copper, steel, iron)
Chemical Potential Energy
Energy is stored in chemical bonds
Energy is absorbed when bonds broken
Energy is released when bonds formed
Enthalpy
Amount of energy lost or gained during a chemical or physical change, abbreviated as ΔH, measured in kj/mol
Endothermic
Process where bonds are broken, which requires energy to be absorbed (+ΔH)
Exothermic
Process where bonds are formed, releasing energy (-ΔH)
Endothermic temperature
In an endothermic reaction, heat flows from the surroundings to the system, making the container cold
Exothermic temperature
In an exothermic reaction, heat flows from the system to its surroundings, making the container warm
System (energy transfer)
Process being studied
Surroundings (energy transfer)
Things & conditions around the system
Universe
System + surroundings
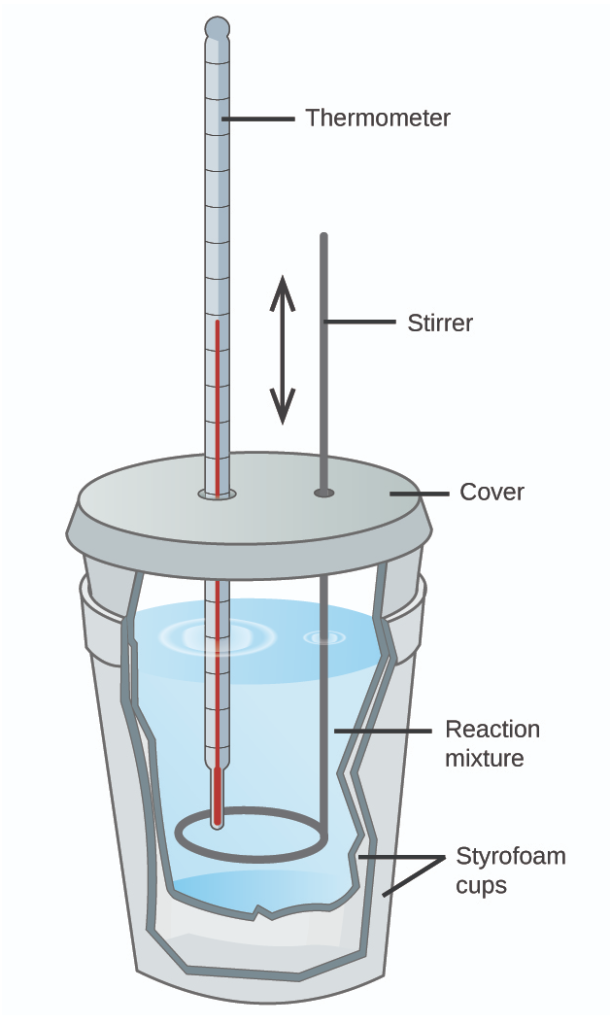
Calorimeter
Insulated container that is used to study heat changes in physical and chemical processes
Hess’s Law
The enthalpy change for a reaction is a sum of its parts
Kinetic Molecular Theory
Matter is composed of tiny particles
particles are in constant random motion
Particles interact w/ each other through attractions and repulsions
Solid intramolecular forces
Dominated by strong intramolecular forces (ionic or metallic)
Solids volume, density, & shape
Definite volume, high density, & shape
Liquid intermolecular forces
Covalent with strong IMF
Liquids volume, density, and shape
Definite volume, medium density, and indefinite shape
Gas intramolecular forces
Dominated by weak intramolecular forces (covalent and weak IMF)
Gas volume, density, and shape
Indefinite volume and shape, low density
Phase changes
Energy is used to change the state by breaking or forming intermolecular forces between molecules
Melting
Solid→Liquid, Endothermic
Energy required is heat of fusion Δ𝐻𝑓
Freezing
Liquid→Solid, Exothermic
Heat of solidification Δ𝐻solid
Vaporization
Liquid→Gas, Endothermic
Enthalpy of vaporization Δ𝐻vap
Condensation
Gas→Liquid, Exothermic
Heat of condensation, Δ𝐻cond
Sublimation
Solid→Gas, Endothermic
Deposition
Gas→Solid, Exothermic
Does endothermic absorb or release energy?
Absorbs
Does exothermic absorb or release energy?
Releases
What is Activation Energy?
The sufficient amount of energy for a reaction to occur, minimum # required
Transition State/Activated Complex
Unstable arrangement of atoms that exists at the peak of activation energy, half way b/w products and reactants
Catalyst
Provides an alternate pathway with a lower activation energy to speed up the process
What is entropy?
Measure of the molecule randomness/disorder of a system, based on freedom of movement w particles
Gibbs Free Energy
Measures how favorable a process is based on thermodynamic conditions (enthalpy, entropy, and temperature)
Thermodynamically favored
Process occurs w/o external intervention
Thermodynamically unfavored
Process does not occur under the current conditons