Biology topic 3
1/69
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
70 Terms
what are microorganisms
a group of tiny organisms including bacteria, viruses, protists and fungi.
do organisms cause problems
organisms don’t cause problems but a small group of them do and are called pathogens
what is a pathogen
microorganisms that enter the body and cause diseases. they cause communicable (infectious) diseases - diseases that can spread.
what are bacteria
type of organism
size
what they do
how they make you ill
single celled organisms
very small (1/100th) of body cells
they reproduce rapidly because of good food supply
make you feel ill by producing toxins (poisons) that can damage your cells and tissues
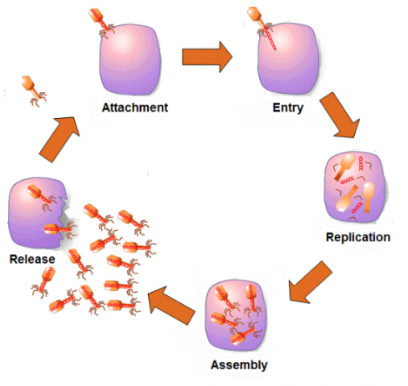
what are viruses
type of cells
size
what they do
how they make you feel ill
they are not cells and not living
they are tiny (1/100th of bacteria)
they reproduce rapidly inside your body
they live inside your cells and replicate themselves using cell machinery. the cell usually bursts releasing all new viruses that find new cells to take over. the cell damage is what makes you feel ill.
what are protists
type of cell
what parasites do
what parasites are transferred by
all eukaryotes and most are single-celled
some protists are parasites
parisites live on or inside other organisms and cause them damage.
often transferred to the organism by a vector - which doesn’t get the disease itself
what is fungi
type of cell
what hyphae can do
some fungi are single celled others have body made up of hyphae (thread like structure)
hyphae grow and penetrare human skin and the surface of plants causing disease
hyphae produce spores which can be spread to other plants/animals
how can pathogens be spread - 3 ways
water/food - some pathogens can be picked up by drinking or bathing in dirty water
air - pathogens can be carried in the air and then breathed in
direct contact - some pathogens can be picked up by touching contaminated surfaces including skin
measles
what type of disease is it
how it is spread
symptoms
how you can be protected
spread by droplets when infected person coughs / sneezes
causes red rash across body, fever
can be serious/ fatal but rare
people vaccinated against it when young
HIV
what type of disease is it
how it is spread
what it does
symptoms
Human Immunodeficiency Virus
spread by sexual contact or y exchanging bodily fluids like blood
can happen when people share needles when taking drugs
infects and destroys cells that normally help to defend the body against disease - makes people with HIV more likely to get ill from infection by other pathogens
initially causes flu like symptoms
HIV - what happens if they are not treated against it
after initial flu like symptoms, the person doesn’t experience any symptoms for several years
throughout that time the virus is doing more damage to your body
immune system weakens and you start to catch unusual invection and could develop cancers
if immune system is badly damaged, it can’t cope with any other infections or cancers
now the virus is known as late stage HIV infection or AID’s
how can HIV be controlled
by antiretroviral drugs
these stop the virus replicating in the body
tobacco mosaic virus (TMV)
what it affects
what it causes
symptoms
affects many species of plants (e.g. tobacco or tomato)
causes mosaic pattern on leaves of plants
parts of oeaves become discoloured
discolouration means plant can’t carry out photosynthesis affecting growth
hyphae
what are they
how they are spread
what they do to skin
what they produce
multi - cellular have long thread like structures
spread through the plants
penetrate skin (causes disease)
produces spores which spread and grow into new fungi
what are fungal disease
eukaryotic organisms - can be uni or multi-cellular
rose black spot
type of disease
what it causes
how the leaves react
how it spreads
causes purple or black spots to develop on the leaves of rose plants
leaves turn yellow and drop off
less photosynthesis can happen so the plant does not grow well
spreads in water or by wind
how can you treat rose black spots
use fungicides and strip the plant of affected leaves
leaves need to be destroyed so the fungus can’t spread to other rose plants
what is malaria
cause
transported how and by what
caused by parisitic protists - needs a host to survive
transported by mosquitoes
they suck up parasites hwen they feed on an infected animal
every time the mosquito feeds on another animal it infects it by inserting the protist in the animal blood vessel and protist spreads to new host
malaria
symptoms
how spread of malaria can be reduced
causes repeating episodes of fever
can be fatal
destroy breeding sites (they can breed in water so get rid of water source)
killing with insecticides
mosquito nets
mosquito repellent
salmonella food poisoning - bacterial disease
how it can be caught
symptoms & how they are cause
example
caught by any food contaminated with the bacteria
people can suffer from fever, stomach cramps, vomiting, diarrhoea
symptoms caused by the toxins that the bacteria produce
passes by itself in a week
e.g. eating chicken that caught the disease when alive, eating food that has been contaminated by being prepared in hygienic conditions
gonorrhoea
what it is
how it is passed on
symptoms
avoid how
sexually transmitted disease (STD)
STD’s passed on by sexual contact e.g. unprotected sex
pain when urinating, thick yellow or green discharge from vagina or penis
avoid unsafe sex, use barrier methods of contraception (condoms)
gonorrhoea treatment and why it is not so good
penicillin - gonorrhoea strains (different types) become resistant to penicillin
rarer and more expensive antibiotics have been needed
people can be treated with other antibiotics
reducing and preventing spread of disease - 4 things
being hygienic - washing hands or cleaning cooking items
destroying vectors - by getting rid of these this prevents the disease from being passed on, also could use insecticides
isolating infected individuals - prevents isolated person from passing it on
vaccination - can’t develop the infection and then pass it on
difference between communicable and non - communicable disease
communicable disease can be spread from person-person and non-communicable can’t
features human body has stopping pathogens from entering the body - physical barriers
skin, kills pathogens
hair, mucus in your nose trap particles that could contain pathogens
trachea and cronchi lined with cilia - hair like structures that waft mucus up to back of throat where it can be swallowed
features human body has stopping pathogens from entering the body - chemical barriers
stomach produces hydrochloric acid - kills pathogens that make it that far from mouth
what does the immune system do
if pathogens make it in your body the immune system kicks in to destroy them. most important type of immune system is white blood cells. they travel around your body and crawl in every part of you patrolling microbes.
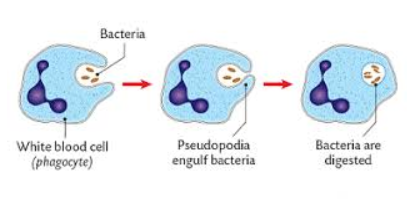
1 way the white blood cells destroy pathogens - phagocytosis
tracking pathogens
binding to them
engulf foreign cells and digesting them
1 way the white blood cells destroy pathogens - antitoxins
pathogens produce toxins that can kill cells
antitoxins produce - counteract toxins produced by the invading bacteria
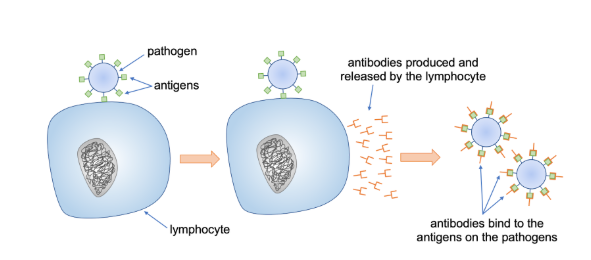
1 way the white blood cells destroy pathogens - antibodies
antigens - invading (foreign) pathogens have unique molecules on its surface
when you white blood cells come across a foreign antigen, they will start to produce proteins called antibodies to lock onto invading cells so they can be found and destroyed by other white blood cells
the antibodies produced are specific to that type of antigen - won’t lock on to others
antibodies are produced rapidly and carried arounf body to find silmilar bacteria or viruses
what happens if the person is infected with the same pathogen - white blood cells
white blood cells rapidly produce antibodies to kill pathogen
the person is naturally immune to that pathogen as they have already had it and won’t get ill
what do vaccinations involve
involve injecting small amounts of weakened, dead or inactive pathogens
they carry antigens which cause your white blood cells to produce antiodies to attack them - even though the are harmless
what do vaccines work on
bacteria or viruses
what happens if pathogens of the same type appear at a later date
white blood cells can rapidly mass produce antobodies to kill off the pathogen.
the vaccinated person is now immune to that pathogen and won’t get ill
vaccination pros
protection from diseases
controls common diseases (polio, measles, whooping cough)
prevent outbreak (epidemics) - kills lots of people
herd immunity, lots of people vaccinated even if 1 person gets disease the pathogen won’t spread to others easily
vaccination cons
don’t always work - sometimes don’t give you immunity
sometime have reaction to vaccine (fever) but bad reactions are rae (seizures)
balancing the risks
deciding whether to have a vaccination means balancing risks - risk of catching disease if you don’t have a vaccine against the risk of having a reaction if you do.
what are painkillers and what do they do
example - aspirin
drugs that relive pain
they don’t actually tackle the cause of the disease they just help reduce the symptoms
antibiotics what they do
example - penicillin
kill (or prevent growth of) the bacteria causing the problem without killing your own body cells
different antibiotics kill different bacteria so important to be treated with right one
what do antibiotics not destroy
they don’t destroy viruses (e.g. flu or cold)
viruses reproduce using their own body cells making it difficult to develop drugs that destroy just the virus without killing the body cells
even if antibiotics could fight viruses they wouldn’t be able to find them as viruses hide within our body cells making it impossible to kill them without killing our body cells to
how can bacteria become resistant
bacteria can mutate
sometimes the mutations cause them to be resistant (not killed by) an antibiotic
if you have an infection some of the bacteria may be resistant to antibiotics
when you treat the infection only the non-resistant strains of bacteria will be killed
the individual resistant bacteria will survive and reproduce and population of resistant strain will increase. this is e.g. of natural selection
the resistant strain could cause a serious infection that can’t be treated by antibiotics

slowing down the development of antibiotic resistance
to slow down the rate of development of resistant strains it is important doctors don’t overprescribe antibiotics
it is also important you finish the whole course of antibiotics and don’t just stop when your better
what is aspirin and how was it developed
used as a painkiller and to lower fever
developed from a chemical found in willow
what is digitalis and how was it developed
used to trat heart conditions
developed from a chemical found in foxgloves
how was penicillin discorvered
alexandra Flemming returned from a lab and noticed bacteria growing in a petri dish
he found the fungus produced a substance that was able to kill the bacteria
because the gene of the fungus is penillium it is called penicillin
how do you prepare the work area for the aseptic technique (procedure carried out to prevent the contamination of pure cultures of microorganisms) petri dish prac
clear the work space of all non- essential items
clean the workspace with disinfectant
kills all unwanted bacteria and so decreases the chance of agar plate becoming contaminated
preparing the agar plates for growth of bacteria
glass petri dish and agar gel must be sterilised before use by using an autoclave or pre sterilised plastic petri dishes can be bought
reason - kills any unwanted bacteria that are present in the solution or on petri dishes
pour agar into sterile petri dishes and allow to set fully
reason - provides the selected bacterium with all the nutrients needed to grow
plating the bacteria (putting bacteria on agar gel) steps
everything should be done beside a blue bunsen flame
reason - stop the agar getting contaminated with unwanted bacteria from air
swirl the bacteria to make sure the bacteria culture is well mixed
reason - make sure the bacteria aren’t all at the bottom of the container
sterilise the inoculating loop by heating it in bunsen. or sterlise by putting it in alcohol for few seconds
reason - kills any unwanted bacteria present in the loop
remove lid of bacteria bottle and put mouth of bottle in bunsen flame
kill off any unwanted bacteria that could be on bottle
dip inoculation loop in micro organism solution and make streaks on surface of agar plate
reason - allows bacteria to spread out to grow in individual colonies on agar plate
secure the lid with tape
reason - lid stops additional unwanted bacteria from air contaminating the plate. don’t fully seal lid as will stop oxygen reaching bacterium
incubate at a max temp 25 degrees
reduces chance of growing harmful pathogen that would grow at 37 degrees in human body
clearing up petri dish practical
all contaminated materials disposed
all work surfaces disinfected and ensure hands washed with soapy water
why is drug testing done
to make sure the drugs are safe and effective
stage 1 of preclinical testing
cells and tissues
drugs tested on human cells and tissues in the lab
you can’t use them to test drugs that affect whol organs or entire organisms
cheaply test lots of substances
stage 2 preclinical testing
live animals
test of live animals to test effiancy (whether drug works and produces affect looking for) and to find out about toxicity (how harmful) and to find best dosage (concentration that should be given and how often its given)
what does the law say about stage 2 preclinical testing
law in britain states any new drug must be tested on 2 different live mammals
what do some people think about testing on animals
people think it’s cruel to test on animals, but others believe this is the safest way to make sure a drug isn’t dangerous before it's given to humans.
Other people think that animals are so different from humans that testing on animals is pointless
stage 3 clincal trials
tested on human volunteers
first drug tested on healthy volunteers to make sure it doesn’t have any harmful side effect when the body is working normally
very low dose of drug is given and is slowly increased to find maximum dosage without side effects
what happens if the drug is good when tested on healthy volunteers
if the results are good the drug is tested on suffering people with the illness. the optimum dose is found - dose of drug that is most effective with few side effects
what is a placebo and why is it done
patients put in 2 group
1 drug given to 1 and other given a placebo - substance like the drug but does nothing
so the doctor can see the difference the drug makes - allws for the placebo effect (patient expects teatment to work so feels better even though treatment does nothing)
why are the results of drug testing and trial not published until they have been through peer review
prevents false claims
what are blind and double blind trials
clinical trials are blind - patient in study doesn’t know whether they are getting drug/placebo
often they are double blind - niether patient nor doctor know until results gathered
this is so the doctor monitering the patients and analysing the results aren’t subconciously influenced by their knowledge / biased
why is it important drugs are tested
make sure they are safe
what can plants catch diseases from
from microorganisms (fungi, viruses, bacteria) , larger organisms (insects) or deficiency diseases
what is a deficiency disease
Plants need mineral ions from soil.
If there aren’t enough, plants suffer deficiency symptoms
Nitrates needed to make proteins and therefore for growth. Lack of nitrates causes stunted growth
Magnesium ions needed for making chlorophyll which is needed for photosynthesis.
Plants without enough magnesium suffer from chlorosis (not enough chlorophyll made) and have yellow leaves
what are diseases caused by pathogens
Infestation with pests - Plants can also be infested and damaged by insects.
Aphids are an insect that can cause damage to plants. Infestations of pests are easy to spot - you should be able to see them on plants
signs to detect plant diseases
Stunted growth
Spots on the leaves
Patches of decay (rot)
Abnormal growths, e.g. lumps
Malformed stems or leaves
Discolouration
what is crown gall
bacterial disease that causes growths on plants
how can you identify plant diseases
Looking up the signs in a gardening manual or on a gardening website
Taking the infected plant to a lab and scientists can identify the pathogen
Using testing kits that identify the pathogen using monoclonal antibodies
what defences do plants have
Plants have physical, chemical and mechanical defences against pests and pathogens
what are physical plant defences
waxy cuticle, which provide a barrier to stop pathogens entering
cell walls made from cellulose, these form a physical barrier against pathogens that make it past the waxy cuticle
Plants have layers of dead cells around their stems, the outer part of bark on trees. These act as barriers to stop pathogens from entering
what are chemical plant defences
antibacterial chemicals which kill bacteria, the mint plant and witch hazel
poisons which can deter herbivores (organisms that eat plants) e.g. tobacco plants, foxglove and deadly nightshade
what are mechanical plant defences
thorns and hairs, these stop animals from touching and eating them
leaves that droop or curl when something touches them. This means that they can prevent themselves from being eaten by knocking insects off themselves and moving away from things
mimic other organisms, the passion flower has bright yellow spots on its leaves which look like butterfly eggs. This stops other butterflies from laying their eggs there. Several species of plant in the ‘ice plant family’ in southern Africa look like stones and pebbles. This tricks other organisms into not eating them