Den 111 (chpt 1-2)
5.0(3)
Card Sorting
1/63
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
64 Terms
1
New cards
microbiology
1. the study of small life forms including bacteria, special fungi (mold and yeast), certain algae, protozoa, and viruses
2
New cards
bacteriology
study of bacteria
3
New cards
mycology
study of fungi
4
New cards
protozoology
study of protozoa
5
New cards
virology
study of viruses
6
New cards
infection control
preventing microbial contamination and infection
7
New cards
who first discovered microorganisms?
Antoni van Leeuwenhoek first observed microorganisms
8
New cards
pasteurization
destroying pathogens in milk or other fluids by heating it to 63 degrees Celsius for 30 minutes or to 72 degrees Celsius for 15 seconds
9
New cards
bacteriophages
viruses that lives within bacteria
phages = to devour
“bacteria eaters”
only attack bacteria
phages = to devour
“bacteria eaters”
only attack bacteria
10
New cards
where can bacteriophages be found
found in soil, sewage, waste and other places where bacteria live to keep bacteria at a minimum.
11
New cards
who recognized the use of heat to destroy vegetative bacteria and resistant bacterial spores
Louis Pasteur and John Tyndall
12
New cards
who first recognized the importance of handwashing to prevent the spread of disease agent?
ignaz semmelweis and Oliver Holmes
13
New cards
who is known as the father of oral microbiology
willoughby d miller and lord joseph lister
14
New cards
prion
proteins that able to induce abnormal folding of normal cellular prion proteins in the brain
15
New cards
beneficial activities of microbes
composting
probiotics for intestinal health
yeasts in baking
beer production
cheese, pickles, yogurt, sour cream
probiotics for intestinal health
yeasts in baking
beer production
cheese, pickles, yogurt, sour cream
16
New cards
bacteria that appear blue or purple are called
gram-positive
17
New cards
bacteria that appear pink or red are called
gram-negative
18
New cards
spherical bacteria cells
cocci
19
New cards
rod shaped bacteria cell
bacilli
20
New cards
curved or spiral bacteria cell
spirilla
21
New cards
metabolism
the physical and chemical changes that occur during bacterial growth (multiplication or increase number of cells)
22
New cards
enzymes
catalyst that chemically change a substance, such as breaking down proteins into amino acids
speeds up metabolic reactions
speeds up metabolic reactions
23
New cards
function/activity of cytoplasmic membrane
transport of nutrients
energy metabolism
secretion of waste
DNA synthesis
cell wall synthesis
surrounds the cytoplasm
energy metabolism
secretion of waste
DNA synthesis
cell wall synthesis
surrounds the cytoplasm
24
New cards
function/activity of cell
gives the cell its characteristic shape
protection from mechanical damage
protection from mechanical damage
25
New cards
function/activity of outer membrane (of gram-negative bacteria)
covers the cell wall
contains endotoxins
transport of nutrients
contains endotoxins
transport of nutrients
26
New cards
function/activity of capsule
protection from drying
antiphagocytic
attachment to surfaces
covers entire outer surface of the wall
antiphagocytic
attachment to surfaces
covers entire outer surface of the wall
27
New cards
function/activity of flagella
locomotion
used for transportation
used for transportation
28
New cards
function/activity of fimbriae (pili)
attachment to surfaces
transport of DNA between cells
transport of DNA between cells
29
New cards
function/activity of nucleoid
DNA control of cell activities
consists of DNA that contains most of genes controlling cell activities
consists of DNA that contains most of genes controlling cell activities
30
New cards
function/activity of endospore
protection against adverse conditions
makes a dense thick-walled structure.
most resistant forms of life against heat, drying, and chemicals
makes a dense thick-walled structure.
most resistant forms of life against heat, drying, and chemicals
31
New cards
Binary fission
cell divides into two daughter cells, in the next generation each of these daughter cells divides into two similar cells and this continues until the environmental conditions no longer support growth because of lack of nutrients, buildup toxic products, changes in pH, temperature and availability of oxygen.
32
New cards
what do bacteria need for growth
temperature
acidity
nutrients
oxygen metabolism
water
acidity
nutrients
oxygen metabolism
water
33
New cards
thermophiles
grow best at 56 degrees celsius
34
New cards
mesophiles
grow at a temp ranging from 22 degrees Celsius to 45 degrees celsisus
bacteria that grow and survive in the human body including those that cause infectious diseases (dental caries, periodontal disease, tuberculosis, bacterial pneumonia, tetanus)
bacteria that grow and survive in the human body including those that cause infectious diseases (dental caries, periodontal disease, tuberculosis, bacterial pneumonia, tetanus)
35
New cards
psychrophiles
grow at temps from 1 degree Celsius to 22 degrees Celsius
bacteria that are present in the ocean and that spoil food stored in a refrigerator
bacteria that are present in the ocean and that spoil food stored in a refrigerator
36
New cards
acidogenic
bacteria that produce acids during growth
37
New cards
aciduric
bacteria that live in highly acidic environments
38
New cards
trace elements
iron - transports oxygen
iodine - formation of thyroid hormones
copper - responsible for function of RBC and bone and connective tissue
zinc - formation of enzymes, helps blood clot. important in immune function
chromium - function of insulin
selenium - antioxidant
iodine - formation of thyroid hormones
copper - responsible for function of RBC and bone and connective tissue
zinc - formation of enzymes, helps blood clot. important in immune function
chromium - function of insulin
selenium - antioxidant
39
New cards
water
all life forms require water. it dissolves nutrients and facilitates entrance or transport of nutrients into the cell.
40
New cards
proteases
enzymes released into the environment that break down proteins into amino acids that can enter the cell
41
New cards
obligate aerobes
require the presence of oxygen
42
New cards
microaerophiles
can tolerate conditions at low oxygen concentrations
43
New cards
obligate anaerobes
cannot tolerate oxygen and only grow in its absence
44
New cards
facultative anaerobes
can grow either in the presence of absence or oxygen.
45
New cards
culturing bacteria
culturing = growing
can be liquid (broth) or semi-solid (agar)
can be liquid (broth) or semi-solid (agar)
46
New cards
agar
seaweed derivative with added nutrients
47
New cards
catabolism
breakdown of nutrients into smaller molecules
48
New cards
anabolism
simple molecules that combine to generate complex molecules
49
New cards
fermentation
an anaerobic process that usually involves the breakdown of sugars with end products of organic acids or alcohols
50
New cards
bacterial metabolism (fermentation)
enzyme breaks down sugar molecule into pyruvic acid
pyruvic acid is converted into lactic acid
lactic acid is then released from the bacterial cell as waste product
that lactic acid waste is what causes the teeth to decay
pyruvic acid is converted into lactic acid
lactic acid is then released from the bacterial cell as waste product
that lactic acid waste is what causes the teeth to decay
51
New cards
preventing growth
changing or eliminating a physical or nutritional requirement for growth or by using a chemical agent that interferes with cell division
52
New cards
bacteriostatic
agents or conditions that prevent bacterial growth without killing them
53
New cards
killing bacteria
accomplished by physical or chemical means and is an important aspect of disease prevention and infection control
54
New cards
bactericidal
killing bacteria
55
New cards
virucidal
killing viruses
56
New cards
fungicidal
kills fungi
57
New cards
structure of viruses
smaller than bacteria
structure consists of nucleic acid spore, capsid (surrounded by a protein coat), some also have an envelope (outer structure of lipids, proteins and polysaccharides), and host cell attachment sites (portion of the virus that binds to human cells)
\
structure consists of nucleic acid spore, capsid (surrounded by a protein coat), some also have an envelope (outer structure of lipids, proteins and polysaccharides), and host cell attachment sites (portion of the virus that binds to human cells)
\
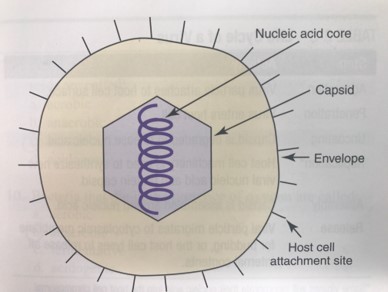
58
New cards
virus life cycle
not free living
need host to survive
need host to survive
59
New cards
Viral lytic cycle
1. virus attaches to a cell
2. virus penetrates cell membrane and inject nucleic acid into cell
3. viral nucleic acid replicates using host cellular machinery
4. new viral nucliec acids are packaged into viral particles and released from the cell. host cell may be destroyed in the process
60
New cards
persistant viral infections
latent (dormant/hidden), chronic, or slow
examples: herpes simplex, hepatitis B
examples: herpes simplex, hepatitis B
61
New cards
host cell transformation
some viruses infect host cells and affect the properties of cells without causing lysis
new properties may result in uncontrolled cell growth (tumors, cancer)
new properties may result in uncontrolled cell growth (tumors, cancer)
62
New cards
apotosis
programmed cell death
63
New cards
fungi
include mushrooms, mold, yeasts
64
New cards
most important fungus in dentistry
oral candidiasis (thrush or denture stomatitis)