Organic Chemistry Vocabulary - Page 1
1/14
Earn XP
Description and Tags
A set of 15 vocabulary flashcards covering common organic functional groups from Page 1 notes.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
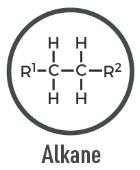
Alkane
A saturated hydrocarbon with only single bonds between carbon atoms; general formula CnH2n+2.
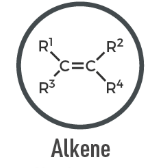
Alkene
A hydrocarbon containing at least one carbon–carbon double bond (C=C); unsaturated.
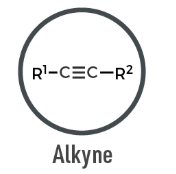
Alkyne
A hydrocarbon containing at least one carbon–carbon triple bond (C≡C); highly unsaturated.
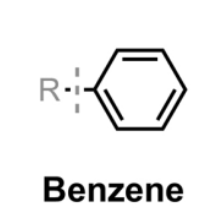
Benzene
An aromatic ring (C6H6) with a conjugated system and resonance, typically represented as a hexagon with alternating double bonds.
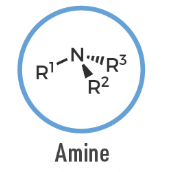
Amine
An organic compound containing a nitrogen atom bonded to one or more carbon substituents (R–NR'R''); general formula for amines.
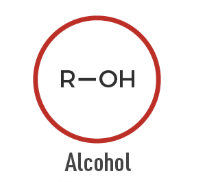
Alcohol
An organic compound containing a hydroxyl group (-OH) attached to carbon.
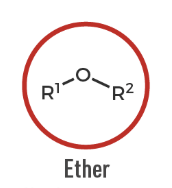
Ether
An organic compound with an oxygen atom connected to two carbon substituents (R–O–R').
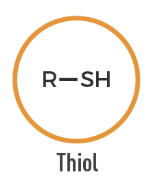
Thiol
An organic compound containing a sulfhydryl group (-SH) attached to carbon.
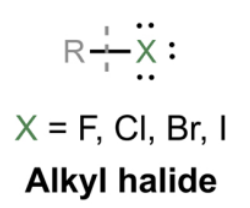
Alkyl halide
A compound with a carbon chain bonded to a halogen atom (X = F, Cl, Br, I).
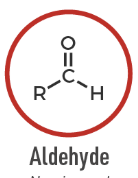
Aldehyde
A carbonyl-containing compound with the formyl group: R–CHO.
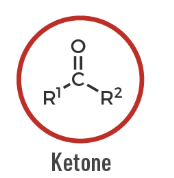
Ketone
A carbonyl-containing compound where the carbonyl carbon is bonded to two carbon groups: R–CO–R'.
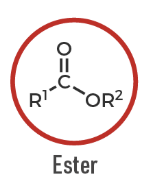
Ester
A carbonyl compound with an OR' group: R–CO–OR'.
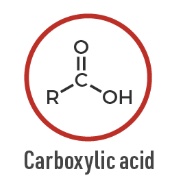
Carboxylic acid
A functional group with a carbonyl and hydroxyl: R–COOH.
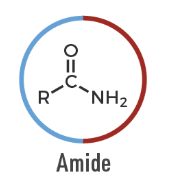
Amide
A carbonyl compound bonded to nitrogen: R–CONR'R''.
Nitrile
A functional group with a carbon triple-bonded to nitrogen: R–CN.
