Chemical Basis of Life: Elements and Compounds
1/66
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
67 Terms
Chemical Substance
A material with definite chemical composition.
Element
Substance that cannot be broken down further.
Compound
Substance of two or more elements in fixed ratio.
Trace Element
Essential element required in minute amounts.
Fluoride
Trace element added to reduce tooth decay.
Atom
Smallest unit of matter retaining element properties.
Subatomic Particles
Protons, neutrons, and electrons in an atom.
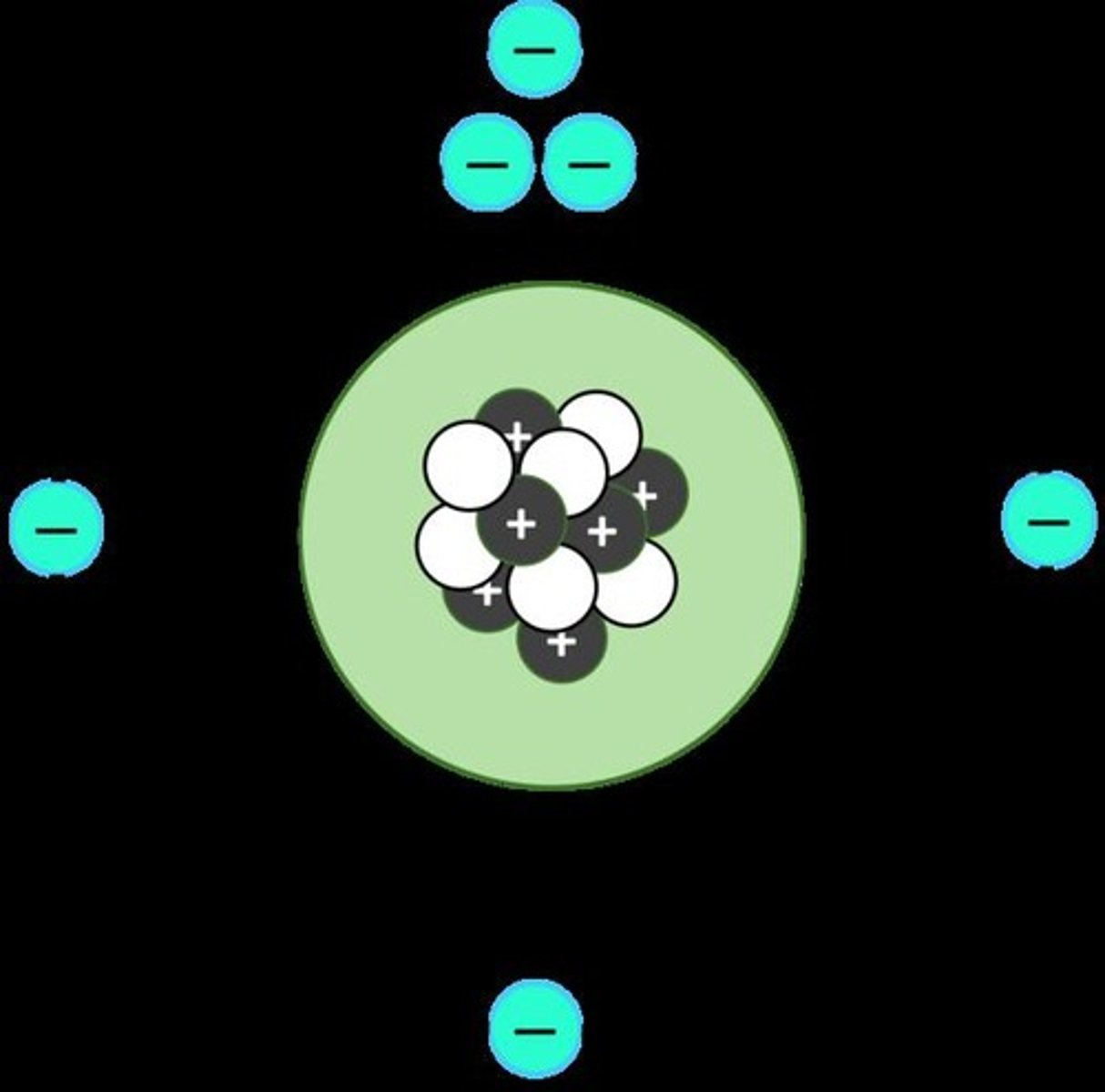
Nucleus
Dense center of an atom containing protons and neutrons.
Atomic Number
Number of protons in an atom's nucleus.
Atomic Mass
Sum of protons and neutrons in nucleus.
Isotope
Atoms with same protons, different neutrons.
Carbon-14
Radioactive isotope used for carbon dating.
Radioactive Isotope
Unstable isotope that decays and releases energy.
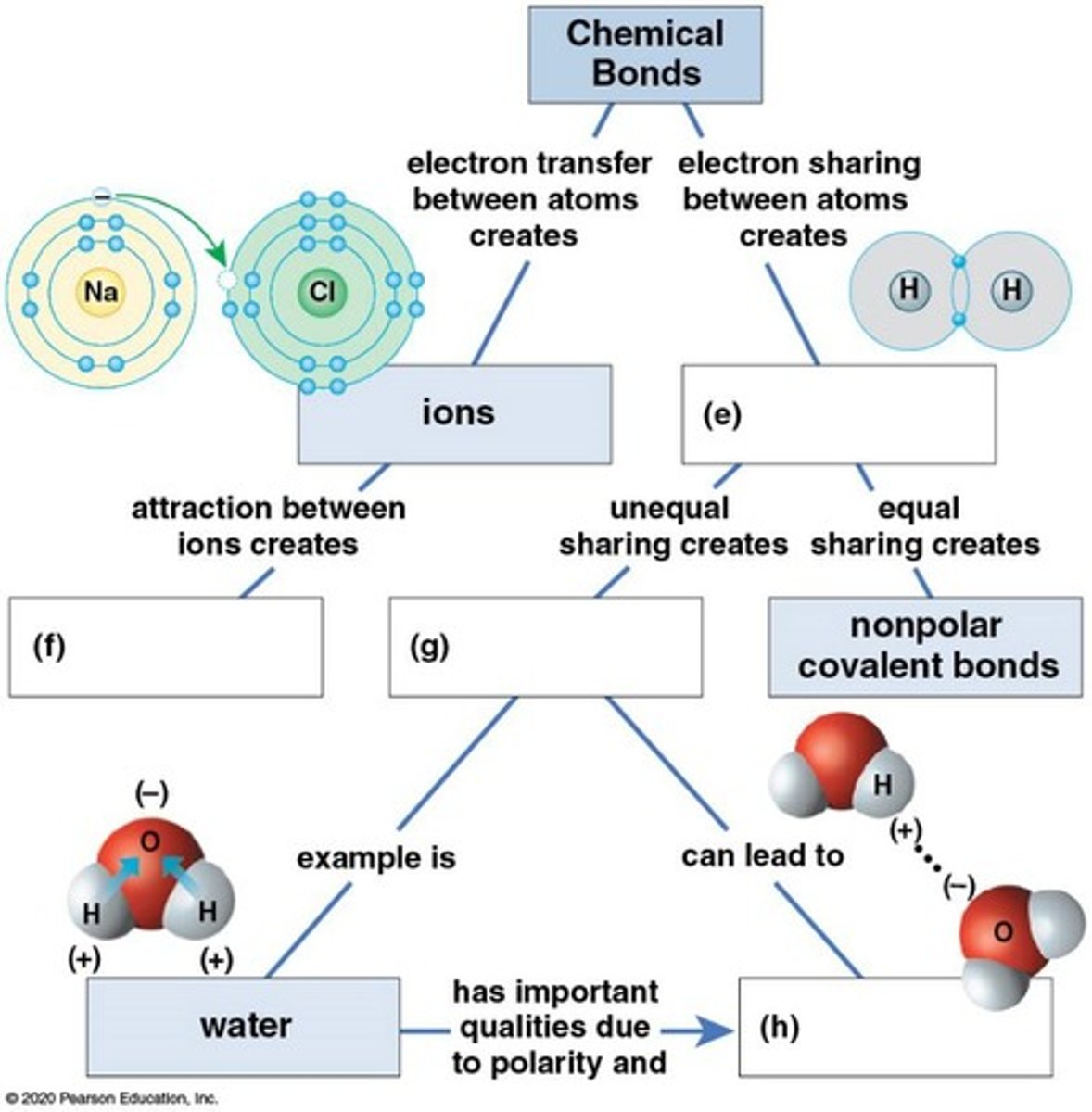
Chemical Bond
Attraction between atoms due to electron interactions.
Electron Shell
Region around nucleus where electrons are found.
Goiter
Thyroid enlargement due to iodine deficiency.
Proton
Positively charged particle in an atom's nucleus.
Neutron
Neutral particle in an atom's nucleus.
Electron
Negatively charged particle orbiting the nucleus.
Mass Number
Total number of protons and neutrons.
PET Scan
Imaging technique using radioactive isotopes.
Chemical Properties
Characteristics determined by electron distribution.
Living Organisms
Composed of matter made from chemical elements.
Ionic Bond
Attraction between oppositely charged ions.
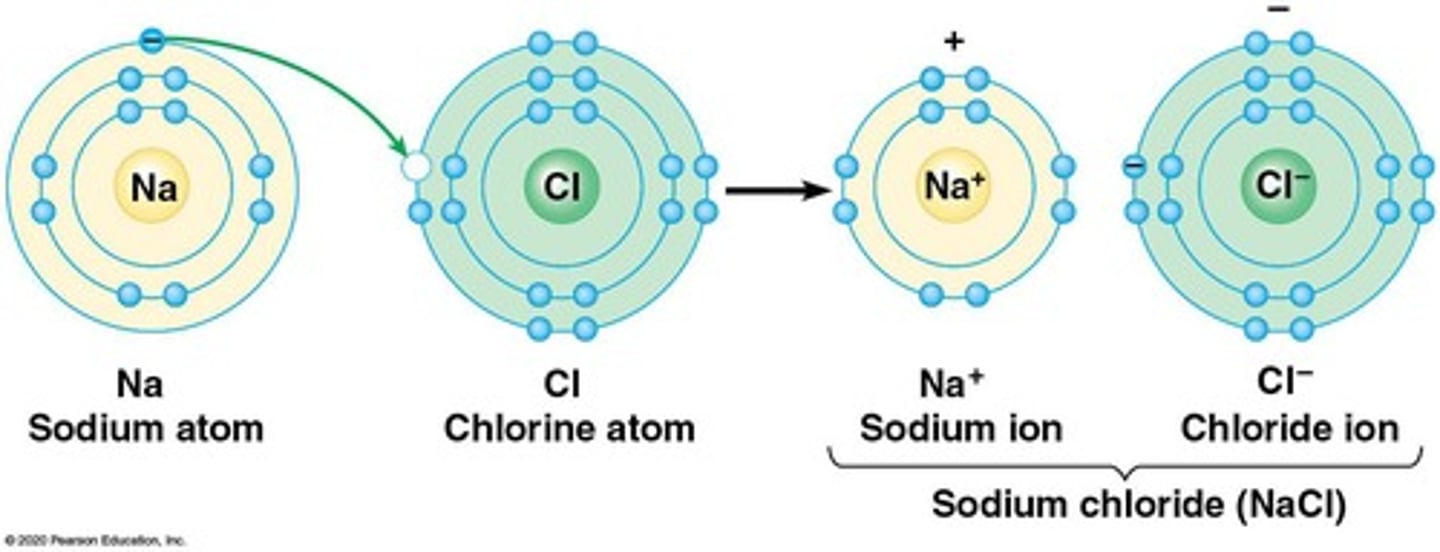
Ion
Atom or molecule with an electrical charge.
Covalent Bond
Atoms share electrons instead of transferring.
Valence Shell
Outer shell of an atom containing electrons.
Polar Covalent Bond
Unequal sharing of electrons between atoms.
Nonpolar Covalent Bond
Equal sharing of electrons due to similar electronegativity.
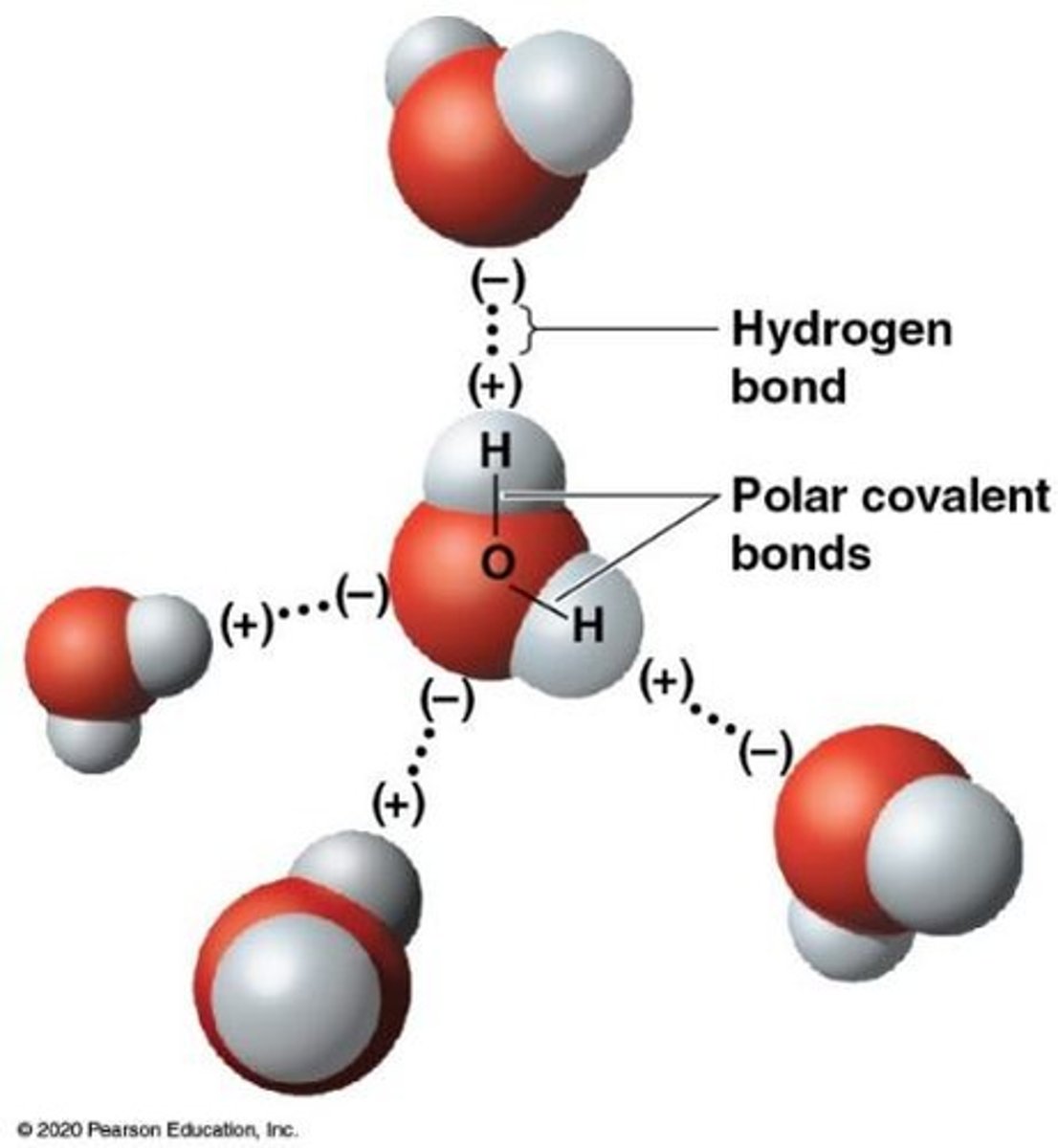
Hydrogen Bond
Weak bond between polar molecules, notably water.
Cohesion
Molecules of the same kind stick together.
Adhesion
Clinging of one substance to another.
Surface Tension
Measure of difficulty to break a liquid's surface.
Chemical Reaction
Process of making and breaking chemical bonds.
Reactants
Substances that undergo change in a chemical reaction.
Products
Substances formed as a result of a chemical reaction.
Electronegativity
Ability of an atom to attract electrons.
Water Molecule
Composed of two hydrogen and one oxygen atom.

Crystal of Table Salt
Ionic compound formed by sodium and chloride ions.
Thermal Energy
Energy associated with random movement of atoms.
Chemical Composition
Arrangement of atoms in a substance.
Molecule
Two or more atoms bonded together.
Cohesion in Water
Causes surface tension and droplet formation.
Hydrogen Bonding in Water
Enables water's unique properties and interactions.
Electron Transfer
Movement of electrons between atoms forming ionic bonds.
Polar Molecule
Molecule with an unequal distribution of charges.
Heat
Thermal energy transfer from warm to cool bodies.
Temperature
Measure of heat intensity in a substance.
Hydrogen Bonds
Strong interactions that stabilize water's temperature.
Evaporative Cooling
Cooling effect when a liquid evaporates.
Density of Ice
Ice is less dense than liquid water.
Aqueous Solutions
Uniform mixtures of water with solutes.
pH Scale
Measures acidity or basicity of a solution.
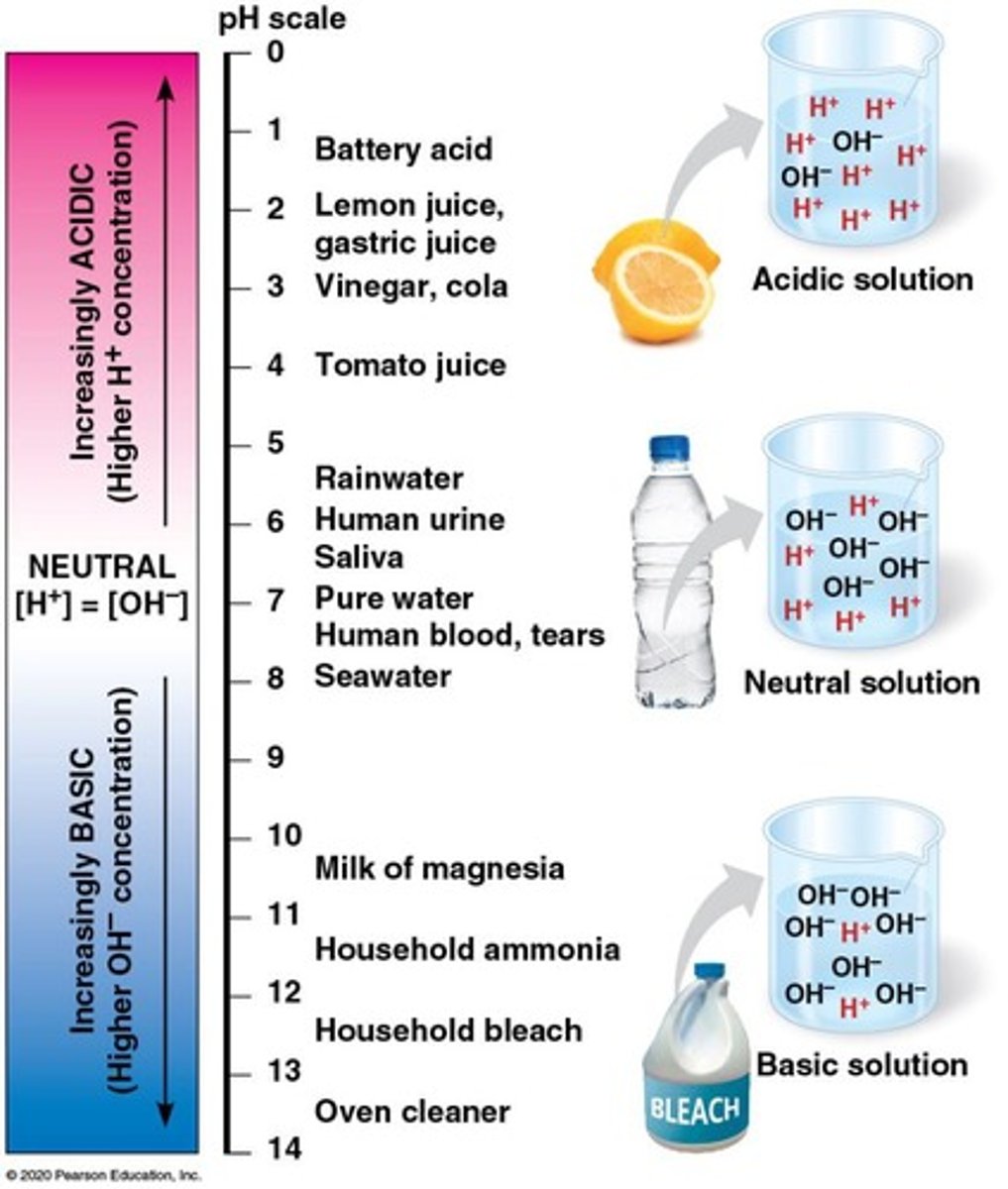
Acids
Substances that lower pH by adding H+ ions.
Buffers
Minimize pH changes by regulating H+ ions.

Chemical Elements
Fundamental substances essential for life.
Subatomic Particles
Protons, neutrons, and electrons in atoms.
Isotopes
Atoms with the same element but different mass.
Ionic Bonds
Electrostatic attraction between oppositely charged ions.
Covalent Bonds
Sharing of electron pairs between atoms.
Hydrogen Bonds
Weak attractions between polar molecules.
Chemical Reaction
Process that alters the composition of matter.
Polar Covalent Bonds
Unequal sharing of electrons between atoms.
Nonpolar Covalent Bonds
Equal sharing of electrons between atoms.
Reactivity of Elements
Determined by electron configuration and bonds.
Solvent of Life
Water's ability to dissolve many substances.
Life-Supporting Properties
Unique characteristics of water essential for life.