Lesson 6 - Latent Print Development
1/153
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
154 Terms
Powder
What process involves the application of finely divided particles that physically adhere to the aqueous and oily components in latent print residue on nonporous surfaces?
Powder
What is one of the oldest and most common methods of latent print detection, having been used as early as 1891?
Latent print powder has an affinity for moisture and preferentially clings to the residue deposited by friction ridge skin.
How does latent print powder work?
Adhesion
The mechanical attraction between the particles of latent print powder and the moisture and oily components in a print causes _____.
Pigment and binder
Commercial powders rely on two elements to provide adhesion to latent print residue without “painting” the substrate: _____ and _____.
Pigment
What element of latent print powder provides for effective visualization, offering contrast and definition against the background surface?
Binder
What element of latent print powder provides for maximum and preferential adhesion to latent print residue?
Background painting
Occurs when an undesirable amount of powder adheres to the substrate as well as the latent print, hindering detection
Reflected light, absorbed light, luminescence
Visualization of powder-developed prints will occur via _____ _____ (light powders), _____ _____ (dark powders), and _____ (fluorescent powders).
Bichromatic powder
Powder that uses highly reflective aluminum powder mixed with black powder to achieve visualization on both light and dark surfaces
Carbon black
What is one of the most common latent print powders?
Aluminum
What is the most common metal flake powder?
Stearic acid
Addition of _____ _____, intended to influence flake morphology during milling, increases the adhesion value of flake powder.
Nonporous, soft brush
Powders are typically applied to _____ surfaces with a _____ _____.
Animal hair, fiberglass filaments, feathers
Conventional brushes are typically made with _____ _____, _____ _____, or sometimes _____.
Loading
The process of lightly dipping the filament tips of a brush into a sterile, wide-mouth container that holds a small amount of powder
Magnetic powder
Powder that utilizes the ferromagnetic properties of iron powder mixed with pigment powder, allowing for application with a magnetized rod that has no bristles
Lifting and photography in situ
What are the two ways to record or preserve a powdered impression?
Lifting
Process by which tape is placed onto the surface bearing a powdered impression, rubbed to remove air bubbles and to ensure good adhesion to the prints, and removed and placed on a backing card that contrasts with the color of the powder
Hinge lifters
An adhesive square is attached to a backing card by a hinge
Fluorescent powders
Powders that rely on the principle of luminescence to provide contrast between fingerprint and background and are created by adding a laser dye in solution to a binder and allowing the mixture to evaporate
Small particle reagent
Uses molybdenum disulfide in suspension for developing fingerprints on wet, nonporous surfaces
Sticky-side powder
A fingerprint powder suspension used to develop prints on the adhesive side of tape
DFO (1,8-diazafluoeren-9-one), 1,2-indanedione, 5-MTN (5-methylthioninhydrin)
What are the three most common ninhydrin analogues?
Ruhemann’s purple
What is the product of the reaction between ninhydrin and amino acids?
14
At least ___ amino acids may be present in fingerprint residues; thus, the ideal reagent must be nonspecific to a particular amino acid.
Water
Development of ninhydrin in a high-humidity environment is of utmost importance because _____ is a necessary reactant.
Light, oxygen
Ruhemann’s purple is known to degrade in the presence of _____ and _____.
Zinc chloride
A post-treatment with _____ _____ has been described for enhancing weak ninhydrin prints by using the light of an argon ion laser.
Metal-salt, 490, 510
Formation of a ____-____ complex alters the color of Ruhemann’s purple from deep violet to red or orange; the lighter hue may provide a greater contrast against a dark-colored background, especially when observed at ____-____ nm.
Polar, nonpolar
Ninhydrin solutions are typically prepared in two steps: A stock solution is prepared that has a high proportion of _____ solvent to facilitate the stability of the mixture, and a portion of the stock solution is diluted with a _____ carrier solvent to produce a reagent suitable for application to evidential items.
Dipping, spraying, brushing
Application of ninhydrin working solutions can be performed by _____, _____, or _____.
80
Development of ninhydrin may be accelerated in a specialized humidity-controlled oven; heat should not exceed ___ degrees Celsius.
Paper, porous
Ninhydrin is most suited to _____, although any _____ substrate may give visible results.
Fuming (sublimation)
Grinding in a mortar and pestle to form a fine powder and applying directly with a fingerprint brush (suitable for heat- or solvent-sensitive paper)
What are two alternative methods for ninhydrin application?
Liquid nitrogen
Fluorescence may be induced in ninhydrin-developed prints by submerging the article in _____ _____ and exciting the treated fingerprint with 490-510 nm of light.
Pink, red, 560
The product of the DFO-amino acid reaction is ____ to ____ in color with an absorption maximum at a wavelength of approximately ___ nm.
High, low
The DFO reaction requires a ____-temperature, ____-humidity environment.
True
True/False: The combination of DFO followed by ninhydrin develops more fingerprints than DFO or ninhydrin alone.
530, 590, 555, 610
DFO-developed prints can be observed using ___ nm excitation light and a ___ nm barrier filter or ___ nm excitation light and a ___ nm barrier filter.
Pink
1,2-Indanedione produces a faint ____-colored product that fluoresces brightly at room temperature.
520, 590
Fluorescence of indanedione-developed prints can be observed under ___ nm illumination and viewed through a ___ nm filter.
False
True/False: 1,2-Indanedione develops fewer fingerprints than DFO, ninhydrin, or the DFO-ninhydrin sequence combined.
The thermal paper can be soaked repeatedly in acetone until the ink and thermal coating are completely removed.
Blotter or filter paper can be soaked in a solution of ninhydrin dissolved in acetone and allowed to dry. An exhibit can then be placed between two sheets of the impregnated paper and sealed in a plastic bag in dark conditions for at least 48 hours and up to 7 days.
How can thermal paper be processed with ninhydrin to prevent blackening and discoloration of the paper?
80 degrees Celsius at 65% RH
What are the temperature and humidity conditions for ninhydrin?
85 degrees Celsius at 60% RH
What are the temperature and humidity conditions for indanedione?
100 degrees Celsius for 40 minutes
What are the temperature and time conditions for DFO?
Fumes of CA ester monomers bond with initiators in print residue.
The monomer on the residue reacts with another monomer in the vapor phase to form a dimer on the print. This reacts with another monomer, and so on and so forth, eventually forming a polymer.
The polymer chain reaction is terminated in the final phase.
What are the three stages of polymer growth in super glue fuming?
The age of the print, residue composition, and environmental conditions
CA ester polymer morphologies are affected by what three things?
Overfuming
_____ will leave prints appearing “frosty” with a lack of edge detail, making them difficult to differentiate from a background also coated with CA polymer.
To warm a small amount of liquid glue in an aluminum evaporation dish on a heating block in a special chamber with a circulation fan and temperature and humidity controls.
What is a common approach to the volatilization of CA?
Cardboard boxes, frames with clear plastic sheeting, large tents, a vehicle interior, and even entire rooms
What can be used to create makeshift chambers for super glue fuming?
Size of the chamber
Quantity of glue
Temp of heat source
Nature of substrate and latent print residue
Super glue fuming times depend on what four things?
Oblique, axial, reflected, transmitted lighting techniques, and UVA reflection (longwave)
How can super glue-developed prints be enhanced optically?
With fluorescent dye stains
How can super glue-developed prints be enhanced chemically?
With the application of fingerprint powder
How can super glue-developed prints be enhanced physically?
It is thought that dye-staining polymerized prints works like a molecular sieve, where the dye molecules get stuck in the polymer by filling voids in the compound.
How does fluorescent dye staining of super glue-developed prints work?
When the energy of the photon exactly matches the difference in energy between two of the energy levels of the molecules of the surface substance
When is a photon of light absorbed by a surface?
The colors of light that are reflected, not the color corresponding to the wavelengths of light that are absorbed.
What makes up the color of a surface?
After a molecule absorbs light and is raised to a higher energy level, it relaxes back to ground state by giving off energy in the form of light; emission is immediate.
What is fluorescence?
“Red-shifted”
Fluorescence is _____, meaning that it is to the red side of the electromagnetic spectrum in relation to the incident light from the forensic light source.
Barrier
When using fluorescence to view a fingerprint, the _____ filter blocks the reflected wavelengths of light from the light source while allowing the fluorescent wavelengths to pass through.
Native constituents in latent print residue
Foreign substances picked up by the hand and transferred through deposition
Intentional chemical enhancement
Substrate fluorescence
Fingerprint examinations may produce fluorescence from four sources:
Yellow
What color filters are used for incident light wavelengths from UV to 445 nm?
Orange
What color filters are used for incident light wavelengths from 445 to 515 nm?
Red
What color filters are used for incident light wavelengths from 515 to 550 nm?
UV lamps, alternate light sources (filtered lamps), and lasers
What are the three types of light sources available for visual/fluorescence examination?
Long-pass, short-pass, band-pass
What are the three types of filters used in alternate light sources?
Lasers
_____ have in the past been less portable and affordable but generated considerably more power than filtered lamps.
Bloody
_____ impressions are a good example of enhancement through absorption at a discrete wavelength.
420
The maximum absorption wavelength for dried blood is approximately ___ nm; illumination at this wavelength makes the blood-stained ridges appear darker.
RAM
Dye stain that is a combination of rhodamine 6G, Ardrox, and MBD
560 nm
What is the absorption maximum for DFO?
515 nm
What is the absorption maximum for 1,2-indanedione?
380 nm
What is the absorption maximum for Ardrox?
440-445 nm
What is the absorption maximum for Basic Yellow 40?
465 nm
What is the absorption maximum for MBD?
490-530 nm
What is the absorption maximum for Rhodamine 6G?
Time-resolved imaging
A technique that takes advantage of the difference between the time of emission of the substrate and the fluorescing fingerprint; if the background fluorescence decays faster than the fluorescence of the chemical on the latent fingerprint, the background can be eliminated by adjusting the delay time between excitation and detection
Those that use the heme grouping to prove or infer the presence of blood
Those that react with proteins or their breakdown products
What are the two types of chemical blood enhancement methods?
Crystal tests and catalytic tests
What are the two kinds of tests that use the heme group in hemoglobin?
Luminol
Heme test that relies on the peroxidase activity of the heme group but uses sodium perborate instead of hydrogen peroxide
Acid dyes
Protein dyes that are often characterized by the presence of one or more sulphonate groups, usually the sodium salt
Hydrogen bonding, van der Waals
_____ _____ and other physical forces, such as ___ ___ _____, may play a part in the affinity of acid dyes to protein molecules.
Fixing, dyeing, washing
What are the three processing stages required for acid dyes?
The fixing stage prevents ridge detail in blood from diffusing or being completely washed away
Why is the fixing stage required for acid dyes?
5-Sulphosalicylic acid and methanol
What are the most effective fixing agents for acid dyes?
This stage removes excess dye on nonporous surfaces and acts as a destainer on porous surfaces
Why is the washing stage required for acid dyes?
Acid yellow 7, Acid violet 17, and amido black
What are the three most common acid dyes?
Sudan black
Dye stain used for the detection of sebaceous components of friction ridge skin on nonporous and some semiporous substrates that produces a blue-black product; also detects ridge detail where the friction ridge skin or substrate has been contaminated with grease, food residue, or dried deposits of soda or sweetened drinks
Transparent tape lifters, hinge lifters, rubber-gelatin lifters, lifting sheets, casting material
What are the different types of lifters?
Nonporous
These surfaces are not permeable to water, other liquids, and air. Examples are glass, many hard and soft plastics, metals, ceramics, and painted metals.
Porous
These surfaces are composed of materials that absorb water and other liquids. Examples are paper, card, cardboard, and untreated wood.
Semi-porous
This is a broad category of surfaces which includes both materials of truly semi-porous nature, such as leather and some painted surfaces, and those with regions of porous nature interspersed with nonporous regions, such as heavily printed paper or cardboard.
Optical processes should be used at the beginning of any processing sequence (and after each process as required)
Liquid-free processes should be used before any liquid-containing processes
Organic solvent-based processes should be used before water-based processes.
Water-based processes should be used at the end of any processing sequence.
What are the four rules of sequential processing?
Long-pass filters
Allow only light longer than a certain cut-on wavelength to pass through. Shorter wavelengths are blocked.
Short-pass filters
Allow only light shorter than a certain cut-off wavelength to pass through. Longer wavelengths are blocked.
Band-pass filters
Allow only a narrow range (band) of wavelengths to pass through; longer and shorter wavelengths cannot. All other wavelengths are blocked.
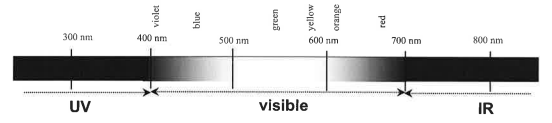
Electromagnetic Spectrum
The entire collection of all possible wavelengths of light
KAPAK packaging
What object that is readily accessible in the lab is an effective mask that can be used to protect adhesive surfaces?