APHG: Unit 6 Cumulative Set, Services & Urban Development
1/134
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
135 Terms
inner cities
the regions just outside CBDs in North American cities
culture of poverty
a way of living that reflects a lack of income and accumulated wealth
- large % of income spent on housing
- possible homelessness
- lack of political power--attendance of inadequately funded schools
- living far from places with entry-level jobs (usually expensive to live near those places)
- difficulty getting credit
underclass
a group of people for whom poverty persists year after year and across generations
brownfields
contaminated industrial or commercial sites that may require environmental cleanup before they can be redeveloped or expanded
redlining
A process by which banks draw lines on a map and refuse to lend money to purchase or improve property within the boundaries.
Has been used as a method of racial discrimination in the past
urban development
renovating a site within a city by removing the existing landscape and rebuilding from the ground up
eminent domain
the right of a government or its agent to expropriate ("buy"/take) private property for public use, with payment of compensation
gentrification
the process of wealthier residents moving into neighborhoods and making them unaffordable for existing residents (increased housing quality)
- value increases and TAX VALUES increase; so does RENT
- makes it difficult for low-income residents and older people on fixed incomes to afford
EX: San Francisco, Chicago's Winter Park
rent control
a price ceiling placed on apartment rent (used in NYC and Denver)
housing projects
The Housing and Urban Development Act of 1965, part of the War on Poverty, channeled increased federal funds to public housing, but the low-cost developments ended up concentrating poverty and stimulating crime.
scattered site
site in which dwellings (low-cost housing projects) are dispersed throughout the city rather than clustered in a large project
homelessness
the condition of not having a permanent place to live
*Used to be primarily men in the US, but it affects a growing number of women and children*
food deserts
urban zones that lack food stores and contribute to health problems for poorer urban residents
racial segregation in housing
when people live in separate neighborhoods based on their ethnicity or race
blockbusting
people of one ethnic group, usually middle-class whites, would be frightened into selling their homes at low prices when they heard that a family of another group, usually African American or Hispanic, was moving into the neighborhood
- investors would profit by buying houses at low prices and reselling them for more money
- real estate agents would profit from a flurry of transactions
ghettos
areas of poverty occupied by a minority group as a result of discrimination
ethnic enclaves/urban colonies
locations with a high concentration of one specific ethnicity
EX: US cities called "Chinatown," "little Italy," and "Greektown"
groups most likely to gentrify
1. young urban professionals with spare &&& ("yuppies"--YUP= young, urban, professional)
2. older couples whose children have moved out ("empty nesters")
gated communities
fenced-in neighborhoods with controlled access gates for people and automobiles and rules for community aesthetics (looks--like housing, landscaping, etc.)
public transportation
buses, subways, light rail, and trains operated by a government agency
informal economy
the portion of the economy that is not taxed, managed, regulated by government.
shadow economy
the informal economy in more developed countries
urban canyons
Streets lined with tall buildings can channel and intensify wind. They also prevent natural sunlight form reaching the ground.
urban heat island
a portion of a city warmer than surrounding regions
urban wildlife
Rats, raccoons, and pigeons can thrive in cities, but they can spread diseases and be a nuisance to people.
rush hour
the commuting periods in early morning and in late afternoon or early evening when many people travel to and from work
urban sprawl
the rapid spread of development outward from the inner city
leapfrogging
when developers purchase land beyond the periphery of the city's built-up area
greenbelts
(in European cities) undeveloped area neighboring an urban area, often protected from development by planning law
smart growth
in the US, a set of polities to preserve farmland and other open, undeveloped areas near a city
New Urbanism
an urban planning movement invented to reduce sprawl, increase affordable housing, and create vibrant, livable neighborhoods--> largely walkable and mixed-use
- emerged in 1990s
- EX: Celebration, FL; Seacrest, FL

urban infill
the process of building up underused lands within a city
- opposite of leapfrogging
- cities have vacant areas of varying sizes
EX: Civita, CA
exurbanism/counter-urbanization/de-urbanization
the flow of residents moving from cities beyond the suburbs, usually to urban areas

three types of services
consumer, business, public
consumer services
- About 50% of all US jobs
-Businesses that provide services primarily to individual consumers, including retail services and education, health, and leisure services
business services
- 25% of all US jobs
- Services that primarily meet the needs of other businesses, including professional, financial, and transportation services
FIRE services
finance, insurance, real estate
public services
- About 10% of all US jobs
- Services offered by the government to provide security and protection for citizens and businesses.
service sector...
triggered recession in 2008
speculation
An involvement in risky business transactions in an effort to make a quick or large profit.
recession
a period of temporary economic decline during which trade and industrial activity are reduced, generally identified by a fall in GDP in two successive quarters.
Central Place Theory (Christaller)
A theory that explains the distribution of services, based on the fact that settlements serve as centers of market areas for services; larger settlements are fewer and farther apart than smaller settlements and provide services for a larger number of people who are willing to travel farther.
Brian Berry
geographer who noticed central place theory occuring in the US Midwest
central place (node)
A market center for the exchange of services by people attracted from the surrounding area.
market area (hinterland)
The area surrounding a central place, from which people are attracted to use the place's goods and services.
range
The maximum distance people are willing to travel to use a service.
levels of market area
hamlet, village, town, city
periodic markets
When small vendors from all around meet up at a certain location to sell goods sometimes weekly and sometimes annually (Farmers Market)
offshore financial services
Offer low tax rates and privacy laws for wealthy corporations and individuals

business-process outsourcing
relocating an entire business function to an independent service provider--> insurance claims processing, payroll management, transcription work, billing of credit cards, shipments, technical inquiries like repairs
Former colonies frequently used for business process outsourcing
- India, Malaysia, Phillippines
- Because of ability to speak English due to history of British and American colonial rule
Chicago, Los Angeles, NYC, San Francisco
specialize in general business
Boston and San Jose
2 examples of computing and data processing services specializing areas in the U.S.
Austin, Orlando, and Raleigh-Durham
specialize in high-tech industries and support services
Alburquerque, Colorado Springs, Huntsville, Knoxville, and Norfolk
specialize in military activity and support services
Washington, DC
specializes in management-consulting services
Richard Florida
Said that talent clusters in cities based on cultural factors, not economic factors.
two types of rural settlement distributions
1. clustered
2. dispersed
clustered rural settlement types
1. circular
2. linear (French long-lot)
Latin America
Typically, the more urbanized a region, the more developed it is. The exception to this rule is _______________________________________.
Wirth's 3 characteristics of urban life
1. large size
2. high density
3. socially heterogeneous people
social heterogeneity
(AKA diversity); VARIETY of people in urban settlements means more individual freedom for inhabitants (ex/unusual professions, sexual orientations, cultural interests are more tolerated in urban areas)
functional zonation
division of a city into different regions or zones for certain purposes or functions
Central Business District (CBD)
the commercial heart of a city; often located near the physical center of a city or the crossroads where the city was founded
bid-rent
An economic theory that refers to how the price and demand on real estate changes as the distance towards the Central Business District (CBD) increases.
CBD Characteristics
1. skyscrapers and underground cities that might include shopping, parking, rapid transit (US and Canada)
2. Located in the historic heart of the city where buildings are lower but services are still concentrated (Europe)
3. Manufacturing activities are rare because land value is so high
4. high-density housing in residential areas--high-rise apts, usually expensive
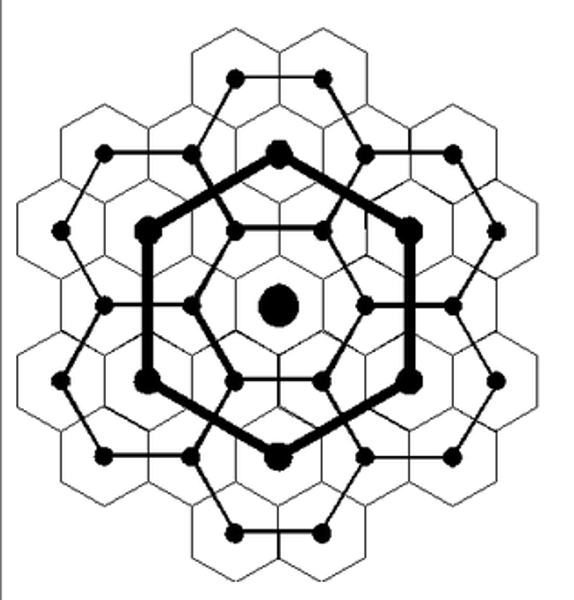
Concentric Zone Model (Burgess Model)
- series of rings that surrounds a CBD
- proposed by _______ in the 1920s to describe Chicago
- series of rings that surrounds a CBD
- first ring around CBD--zone of transition (industrial uses mixed with poorer quality housing)
- Second ring= low-cost residential ("working class" housing)
- Third ring=moderate-cost residential (higher quality housing)
- Fourth ring= commuters' zone (larger homes and lots in suburban areas on the edge of the city)
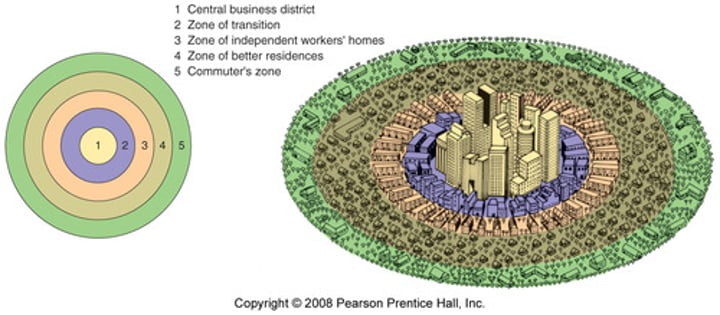
Sector Model (Hoyt Model)
- Proposed by _______ in the 1930s to describe Chicago
-Described how different types of land use and housing were all located near the CBD early in a city's history. Each grew outward as the city expanded, creating wedges (sectors) of land use rather than rings
- Describes sectors of low, medium, and high income housing.
- Notes a sector for transportation extending from the edge to the center of the city.
- Places low-income housing next to industrial/transport zones
- Places high-income housing in a wedge extending away from other zones along with a wide tree-lined boulevard or on higher ground (hill, etc.)
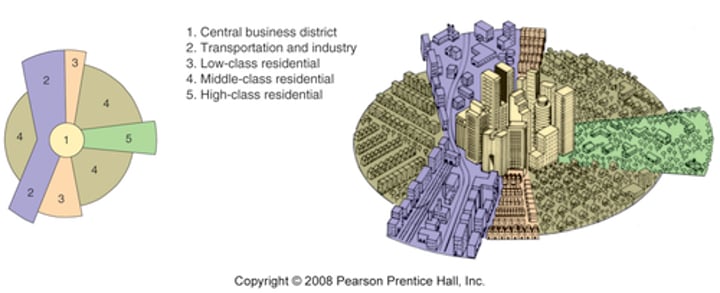
Multiple Nuclei Model (Harris & Ullman
Proposed by _________________ in the 1940s to describe Chicago.
- Suggested that functional zonation occurred around multiple centers or nodes
- Each node either attracted or repelled certain types of activities.
- RESULT: A city with a patchwork of land uses, each with its own center or nucleus (possibly multiple CBDs)
CBD and related functions continued to exist
- Were joined by smaller business districts that emerged in the suburbs
- Zone of industry→ variety of possible locations
- University or business park: attract nearby restaurants, theaters, other amenities; people might create a district of student housing or high-quality homes nearby
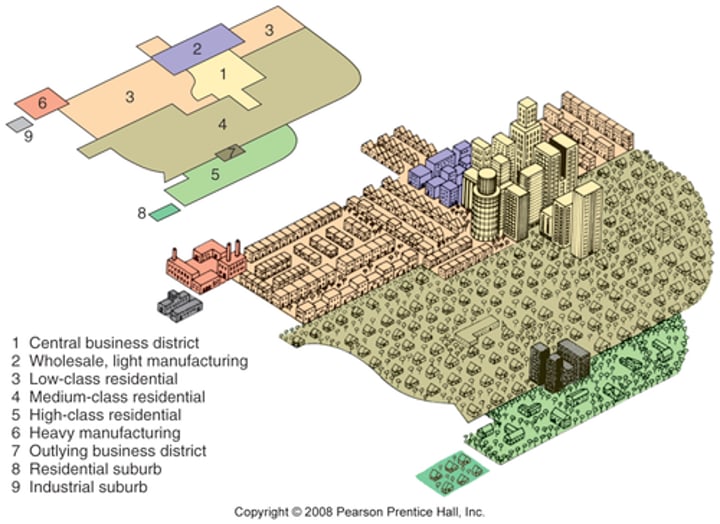
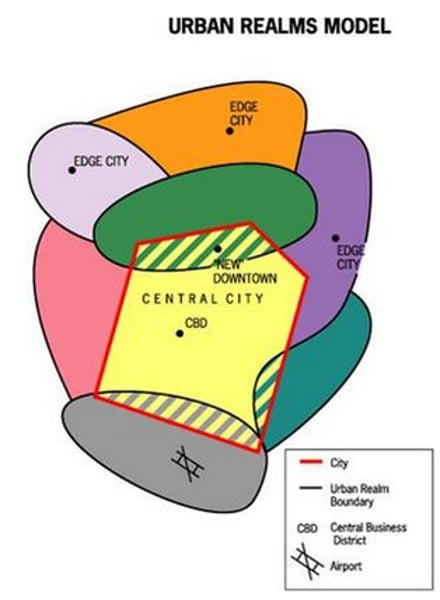
Galactic City Model (Chauncey Harris)
- Proposed in 1950s by ___________ to describe Detroit
- Created after suburban growth skyrocketed as governments built highways that improved transportation in and out of cities
- Describes the spread of US cities outward from the CBD to the suburbs leaving a declining inner city
- Developes EDGE CITIES: Nodes of economic activity that have developed in the periphery of large cities. They usually have tall office buildings, a concentration of retail shops, relatively few residents, and are located at the junction of major transportation routes: mini-downtowns
edge cities
nodes of economic activity that have developed in the periphery of large cities
*ALSO DEVELOP IN URBAN REALMS MODEL*
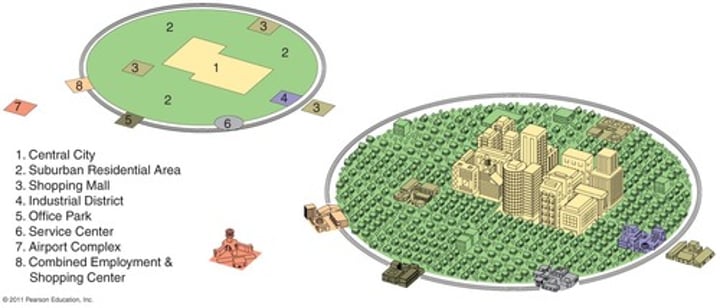
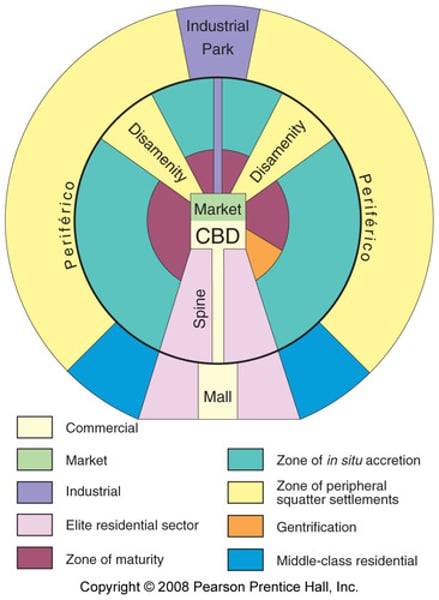
Latin American City Model (Griffin-Ford Model)
- Two-part CBD at the center of the city (Traditional market center next to modern high-rise center)
- High-quality housing (starts next to CBD, extends outward from urban core)
- Spine of commercial development (goes through the middle of the high-quality housing area;
theaters, restaurants parks, and other amenities; ends in a growing secondary center or "mall")
- As distance from city center increases, housing quality decreases (public transportation, urban water supply, access to electricity→ decrease)
- Outer ring of the city: periferico (poverty, lack of infrastructure, areas of poorly built housing: shantytowns: Residents are often recent migrants)
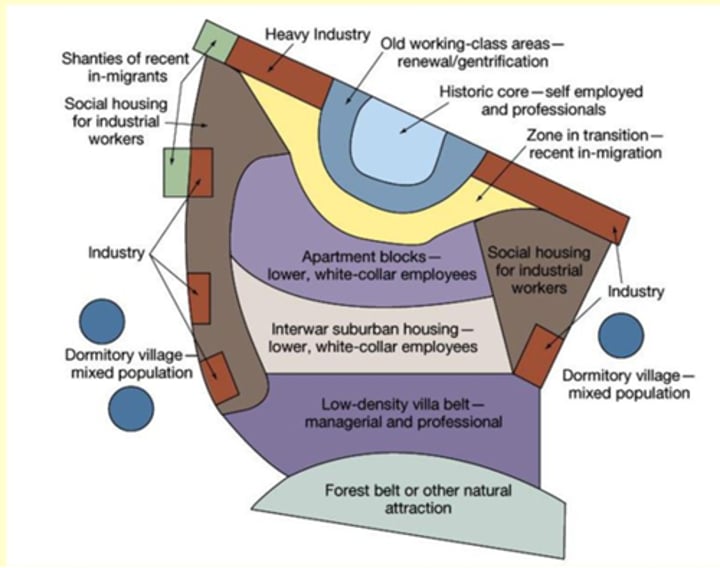
European Cities Model
- Descendents of medieval & preindustrial cities
- City walls for protection→ restrained growth
- Grew very slowly for centuries→ very little planning
- Dense mix of commercial and residential land use
- Narrow, winding streets
- Difficult to find distinct land-use zones
- Later urban renovations
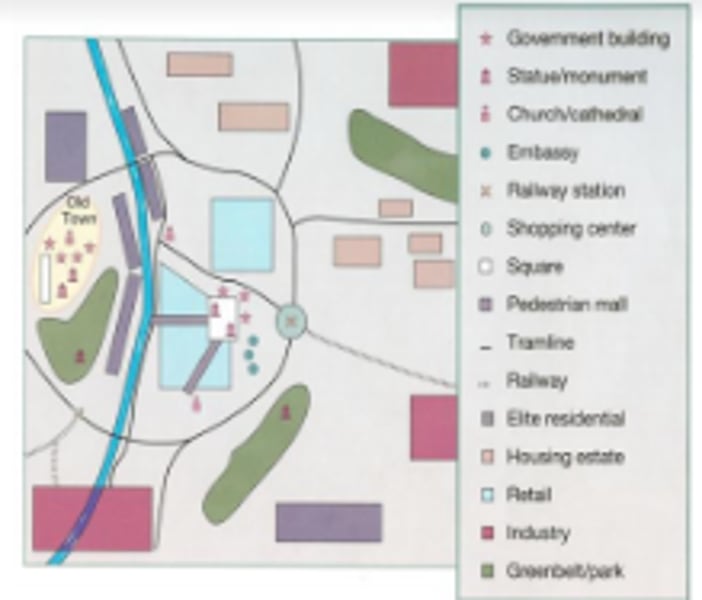
Eastern European City Model
- A historic center that is fairly unchanged with elite residential and industrial centers around the periphery of the city.
- Retail centers near the historic center help expand the city centers role as a tourist destination.
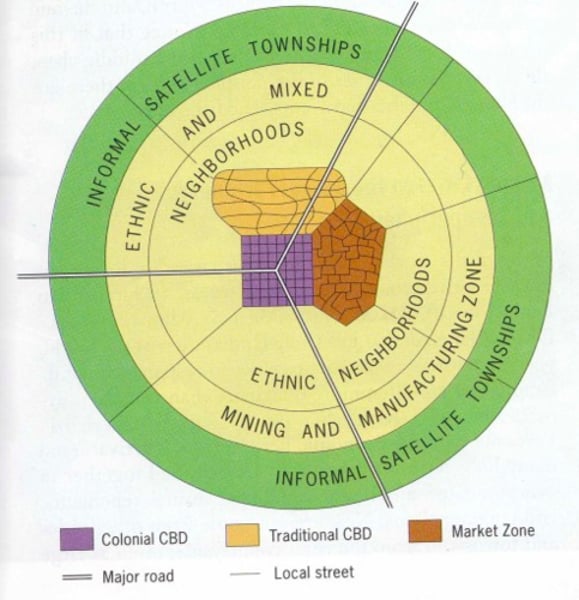
African City Model
- Rare to have large cities until 19th century European colonization
- Growing rapidly in recent decades
- Identifiable zones
1. Traditional CBD
2. Colonial CBD
3. Informal economy zone
4. Zone of mining and manufacturing
5. Residential zones: often based on ethnicity
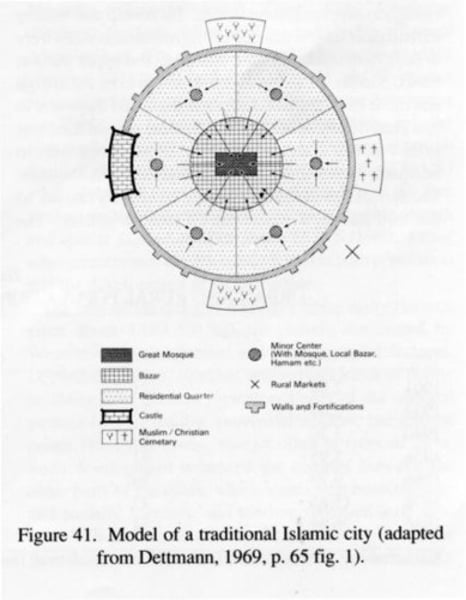
Middle Eastern and Islamic City Model (North Africa, parts of Spain & E Africa and a bit of SE Asia)
- Shaped by the spread of Islam
- Central mosque
- Defensive citadel: a fort designed to protect the city with its palace and barracks for soldiers
- Residential Neighborhoods: Reflect differences in ethnicity, tribe, or branch of Islam
Three features of neighborhoods
Streets and alleys twisting with frequent dead-ends
Homes have central courtyards rather than front or back yards
Windows are small and located above eye level
THESE ALL CREATE SHADE (hot regions) & PRIVACY (Islamic culture)
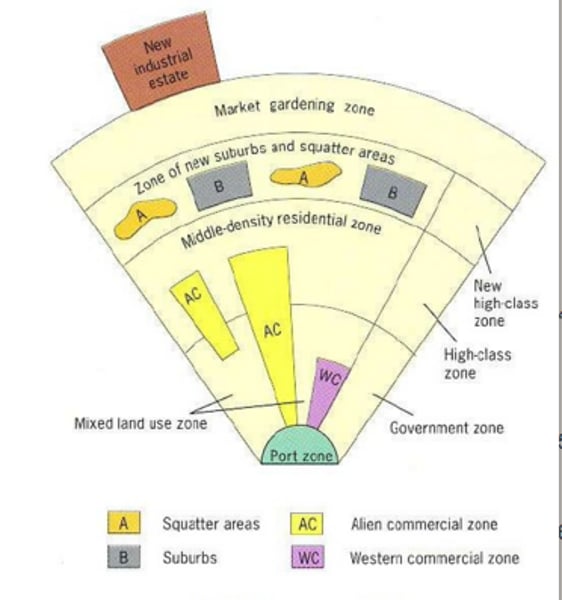
Southeast Asian City Model (McGee Model)
- Describes the land use in many of the larger cities in SE Asia
- Former colonial port zone
- Might include a governmental zone
- Commercial zone dominated by foreign merchants and ambassadors (if a capital)
- Belt of market gardening surrounds the city
*History of Chinese immigration--huge Chinese influence*
urban planning
a process of promoting growth and controlling change in land use
zoning laws
laws in a city or town that designate certain areas, or zones, for residential and business use
residential zones
the areas of a city devoted to where people live rather than to commercial or industrial functions
McMansions
Homes referred to as such because of their "super size" and similarity in appearance to other such homes; homes often built in place of tear-downs in American suburbs.

filtering
a process of change in the use of a house, from single-family owner occupancy to abandonment
- usually involves splitting a larger, grand house into apartments
suburbanization of business
the movement of commerce out of cities to suburbs where rents are cheaper and commutes for employees are shorter
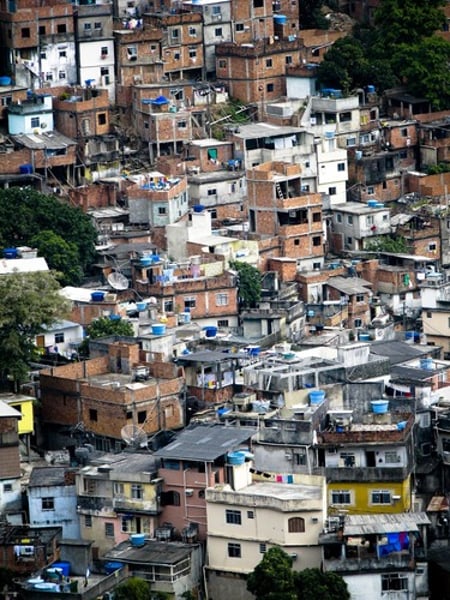
favelas
huge slums that surround some Brazilian cities (or other cities in Latin America)

consolidation
a solution to the legal fragmentation of many metro areas in which certain areas of government are handled jointly, across numerous separate municipalities, while other elements of local government continue to be handled by individual municipalities
special districts
a governmental area created to attempt to solve a specific need, such as for public transportation over a large region
EX: Colorado has created a regional transportation ____________, or authority, that includes Denver and surrounding areas to facilitate mass transit for the multiple communities of the region
unincorporated areas
populated regions that do not fall within the legal boundary of any city or municipality
annexation
Legally adding land area to a city in the United States
census tract
An area deliniated by the us beureau of the census for which statisitcs are published; in urbanized areas, census tracts correspond roughly to neighborhoods (4,000-12,000 people)
census block
An area bounded on all sides by visible (roads, rivers, etc.) and/or invisible (county, state boundaries) features that is the smallest geographic entity for which census data are available.
Urban Realms Model
A spatial generalization of the large, late-twentieth-century city in the United States. It is shown to be a widely dispersed, multicentered metropolis consisting of increasingly independent zones or realms, each focused on its own suburban downtown; the only exception is the shrunken central realm, which is focused on the Central Business District (CBD).
ecumene
The portion of Earth's surface occupied by permanent human settlement.
settlement
a place with a permanent human population
characteristics that allowed the development of cities
1. agricultural surplus
2. social stratification
3. job specialization
urbanization
an ongoing process that does not end once a city is formed; involves the causes and effects of existing cities that are growing ever larger
percent urban
an indicator of the proportion of the population that lives in cities and towns as compared to those that live in rural areas
suburb
a largely residential area adjacent to an urban area
suburbanization
the process of people moving, usually from cities to residential areas on the outskirts of cities
Causes of suburbanization
1. economic expansion--easier to get a home loan
2. greater purchasing power for many families ($$)
3. growth of car-centered lifestyle
4. government's construction of vast system of new highways (getting to and from work got easier)
5. US Federal Housing Administration--loans for houses in suburbs and newly-zoned single family housing there
6. GI Bill--made easier for returning veterans to get home loans and college educations
7. racial tensions (white flight)
8. pre-fabricated houses=cheaper construction
reurbanization
process in which some suburbanites return to live in the city