Energy systems
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
Energy =
capacity or ability to perform work
Features of ATP
stored in our cells
Only useable form of energy in the body
2-3 second store must be resynthesised
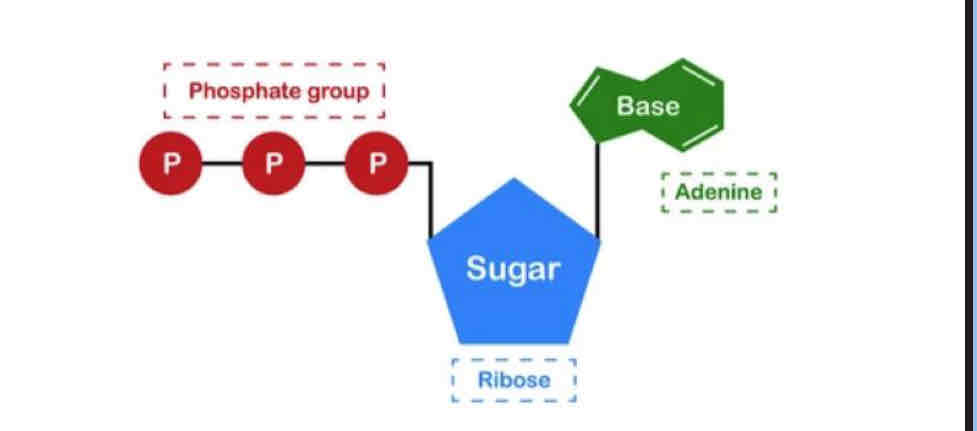
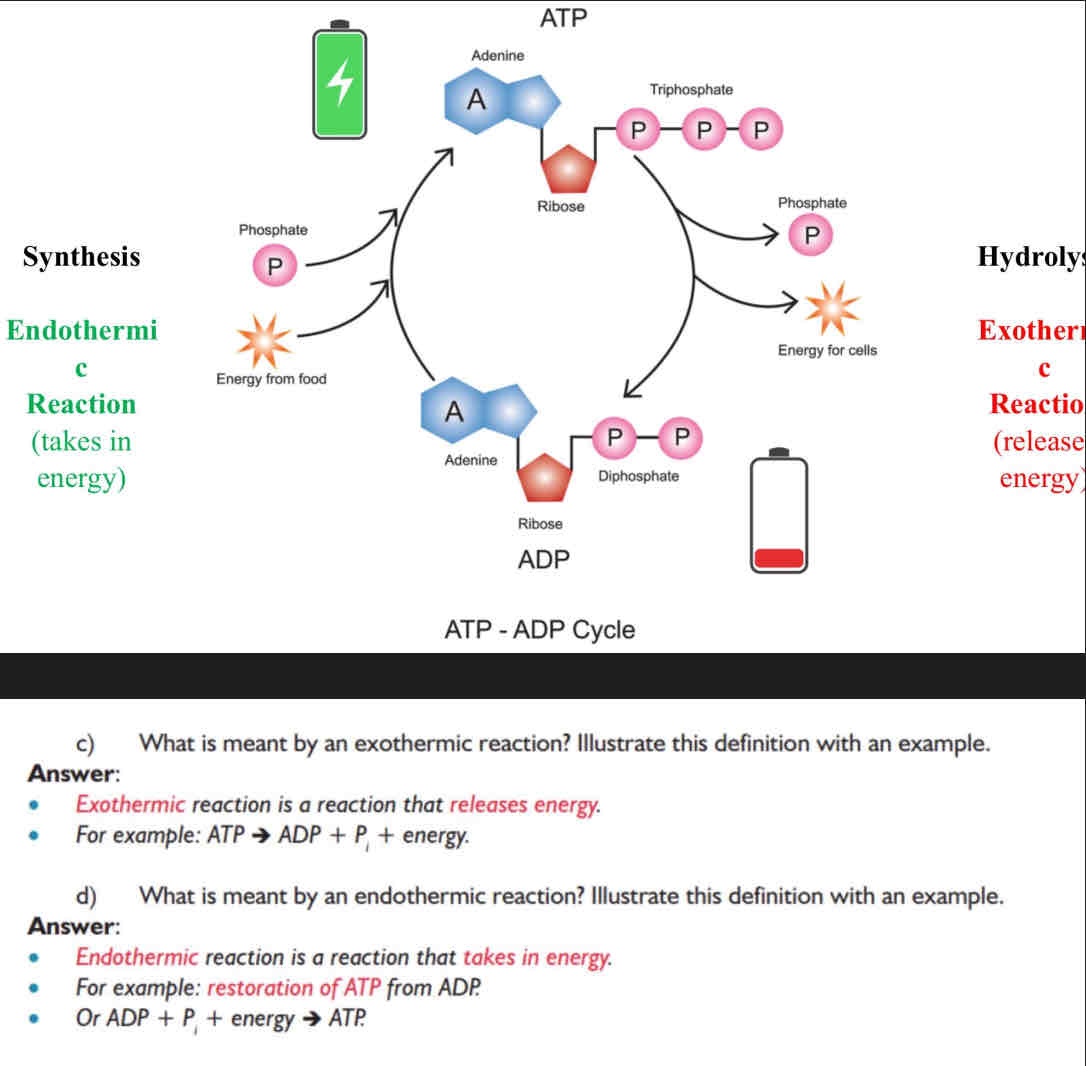
How is ATP broken down and resynthesised
What are the equations for this
what is mechanical energy
Give an example
The ability to carry out work
A cricket player swings their bat, the bat has mechanical energy through the arms kinetic energy
What is electrical energy
Give an example
Energy that is stored and released by charged particles
The human body used electrical energy to pass impulses through nervous system allowing muscular contraction
What is Potential energy
Give an example
Energy stored within an object
Set position in starting blocks for 100m sprinters
What is chemical energy
Give an example
Energy stored in the bonds from compounds
Eg: an athlete eating food and transferring this into energy
What is kinetic energy
Give an example
Energy stored in a moving object
Eg: running
What are the three energy systems
Phosphocreatine system
Glycolytic system
Aerobic system
Features of phosphocreatine system
Store of phosphocreatine is broken down by creatine kinase (enzyme) and releases energy. This is used to turn ADP to ATP
it takes place in cell
It lasts 10 seconds
System is anaerobic
Used for fast powerful bursts of energy
Features of glycolytic system
Takes place in sarcoplasm
Glucose is broken down into pyruvic acid
If no oxygen is present pyruvate is converted into lactic acid
System is anaerobic
Features of the aerobic system
In glycolysis glucose is turned into pyruvate
In link reaction/ Krebs cycle Pyruvate forms acetyl coenzyme A
Has co2 and hydrogen as bi products
In electron transport chain Hydrogen ions are transferred over membrane forming ATP, water is formed as bi product
34 molecules of ATP are made
Takes place in mitochondria
What is the energy continuum
describes type of energy pathway used by the body during exercise
And helps to identify which energy system is predominant
Allows athletes to target training specifically to a given energy pathway
What are thresholds
Transition point between two energy systems
What is aerobic threshold
Where lactate in blood rises and anaerobic pathways have to help with energy production
What is anaerobic threshold
The point of exercise where Lactate builds up in the body faster than the body can remove it
What is fatigue
Reduction of muscular performance and inability to maintain power
Factors affecting fatigue
Dehydration
Reduced levels of calcium
Reduced levels of acetylcholine
Reduced rate of ATP synthesis
Lactic acid build up
Glycogen depletion
Ways to combat fatigue after event
2 Hour window of opportunity for protein and glucose
Hypotonic, hypertonic and hypotonic drinks
What are some ways a coach can maximise recovery opportunities in a match
Substitutions
Sports gels/sports drinks
Time outs
Ensure physio is available at half time
Cooling aids
Gamesmanship to slow play
Effective warm up
Change of tactics
What is EPOC
Aim of EPOC?
Excess post exercise oxygen - The volume of oxygen consumed during recovery above normal resting rate
Restore body to pre exercise state or homeostasis
Also replenish fuels used in exercise and prevent injury in future
What happens to the body during EPOC
Phosphocreatine is replenished and brings level back to normal
Lactic acid id removed to bring body back to correct levels
Removal of hydrogen ions to remove acidity
Rehydration allows body to return to homeostasis
Thermoregulation = cools down body temp
Resaturation of myoglobin allow oxygen to be transported into the muscle
ReSynthesis of protein brings levels back to normal
Glycogen stores are restored for future use
Oxygen delivery remains high for recovery
Ventilation and heart rate increase to increase oxygen delivery
2 stages of EPOC
Fast component (alactacid)
Slow component (lactacid)
Explain What the fast component of recovery is
Called alactacid component
Uses one extra oxygen to help with replenishment
Occurs in first 3 minutes
Resynthesis of ATP AND PC
Restoration of myoglobin
Reduction in cardiac output and ventilation
Conversion of glycogen to glucose
Phosphagen replenishment
Body temperature reduced
Restoration can take as little as 30 seconds
Explain what the slow component of recovery is
Called the lactacid component
Breaks up and removes lactic acid built up in exercise
Occurs after first 3 minutes of peak exercise after (fast component)
Removal of lactate and hydrogen ions
Protein repairs damaged muscle fibres
Replenishment of energy stores
Rehydration
Restoration of glycogen and carbohydrates
Return temperature to resting levels
Restoration of myoglobin
What is priming in priming exercise
The manipulation of the intensity of the exercise of the pulse raiser of the warmup to speed up how quickly the aerobic system starts at onset of exercise
Why do athletes prime
Reduce recovery time
Improve overall performance
Improve efficiency and performance of energy systems
How does priming target each energy system
Phosphocreatine system = do polymeric and 10m sprints
Glycolytic = fast jogging for 100m followed by 50m sprint
Aerobic = long low intensity running
other positives of priming
Increased body temp and increased ROM
Negatives of priming
If too high it can cause onset of fatigue if not managed carefully
How does the body respond to priming
Enzyme activity increases to aid glycolysis
Glycogen breakdown to produce energy faster
Cardiac output increases to provide more oxygen to muscles
Faster sweat production (thermoregulation) to prevent overheating
Capillaries open more for vascular shunt
Body temp increases do more force production
Pyruvate breaks down to aid aerobic system