TV4101 - Bovine - Obstetrics 3
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
Dystocia due to multiple pregnancies
Can arise due to?
– Uterine inertia – overstretching of myometrium
– Simultaneous presentation of two or more foetuses. Usually one is presented cranially and the other caudally or both may present cranially or caudally
– Malposition of the first or subsequent foetuses
Dystocia due to multiple pregnancies
CX?
• Failure of birth to proceed normally
• Presentation of multiple limbs or heads
• Presentation of fore- and hindfeet in vaginal canal
• Birth or delivery of one foetus with death of 2nd
foetus → dystocia, retained placenta or postparturient ill cow as 2nd foetus decomposes
• With twins both foetuses are often smaller than normal but in some cases they will still be large foetuses
Dystocia due to multiple pregnancies
dx?
• Identify origin of each limb by carefully tracing back to foetal
body.
• Care is needed to differentiate from congenital abnormalities which can result in multiple heads and limbs
Dystocia due to multiple pregnancies
TX?
Foetal manipulation steps?
After deilvery?
Common sequeulae?
Repel one and deliver other by traction
Deliver most caudal foetus first or any foetus in caudal presentation as only hindlimbs need to be manipulated
Post devliery
Check for more foetuses
Oxytocin (20 IU IM) → uterine involution
Retained placenta, post partum metritis & delayed conception
Dystocia due to foetal malformation
Examples?
Head?
Fluid?
Spine flexion?
Hydrocephalus – enlarged cranium
Foetal ascites – abnormal distension of abdomen with fluid, passage of head, neck and thorax through vagina but abdomen will not pass
Foetal anasarca – Subcutaneous oedema (autosomal recessive in Ayrshire cattle)
Schistosoma reflexus – dorsoflexion of foetal spinal column with exposure of foetal viscera, common
Dystocia due to foetal malformation
Examples?
Joints?
Lumbar?
Monsters?
Mulitples?
Dwarves?
• Contortion and rigidity of joints, wry neck (rigidity of neck)
• Perosomus elumbus – agenesis of lumbosacral spine, normal cranial portion of foetus may traverse birth canal, but abnormal hind end with anklylosis of hindlimbs become impacted
• Chondrodystrophia foetalis (dwarf or bulldog calves)
• Acardiac monsters (headed, headless, amorphous – lack any external characteristics of a normal foetus)
• Multiplication/duplication of foetal parts

Dystocia due to foetal malformation - what this?
CX during delivery?
Cause?
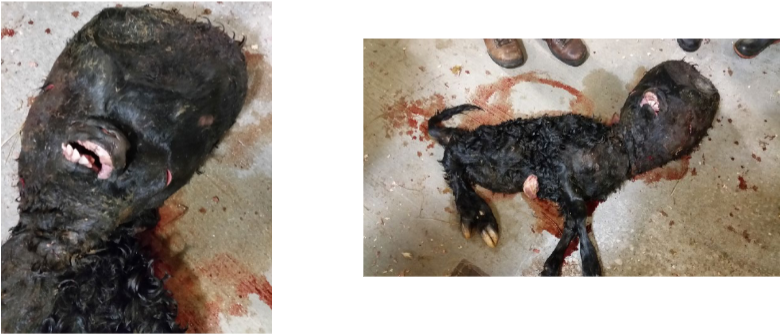
Perosomus elumbis
Cranial presentation - appears normal at first but is halted following delivery of thorax
Vaginal exploration may reveal abnormal lumbar and poor hind region, rigid HLs
Genetic cause potentially - agenesis of lumbosacral spine
What this?
CX?
TX?
Control?
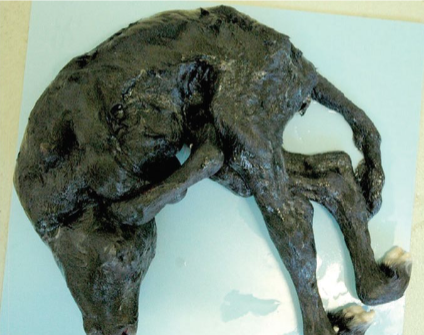
Neuropathic hydrocephalus – Angus cattle
Inherited, homozygous recessive disorder
Severe cranial enlargement from hydrocephalus, with dwarfism
• Affected calves may be aborted before the end of gestation
Collapse of hydrocephalic cranium or caesarean
Control: detection and culling of carriers
What this?
Describe it?
Cause?
Control?
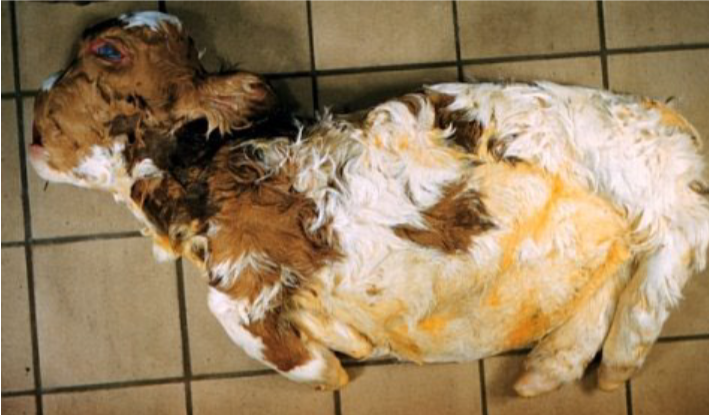
Arthrogryposis multiplex. ‘Curly calf syndrome’
• Congenital limb fixation
• Mild hydrocephalus
Same chromosome affected as neuropathic hydrocephalus
DNA test is now available and carriers are being detected and eliminated
What this?
Achondroplasia (bulldog calf)

What this?
Describe it?
Causes?
TX?
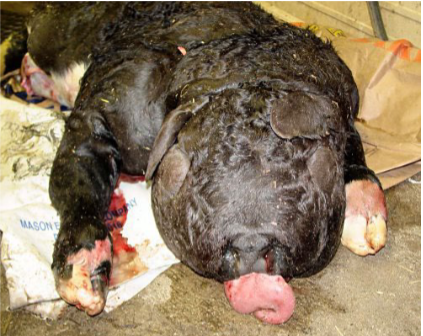
Foetal ascites & anasarca (hydrops foetalis)
Abnormal accumulation of fluid characterized by an accumulation of fluid, in at least two foetal compartments
e.g. oedema of foetus and placenta, ascites, pleural effusions and/or pericardial effusions
Myriad congenital anomalies can cause this (results in passive venous congestion) eg pulmonary, cardiac, liver anomalies
Draining fluid filled compartment with a palm knife
• Foetotomy
• C-section
What this?
Pulmonary Hypoplasia Anasarca (hydrops foetalis)
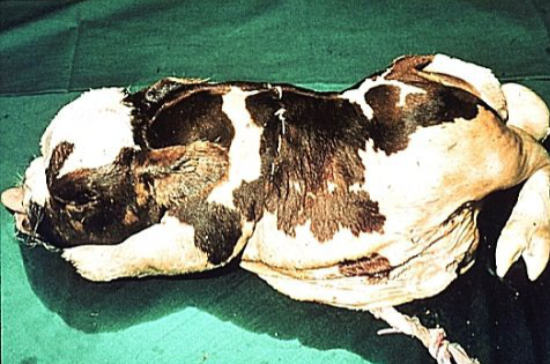
What is this?
Describe it
Caused by?

What this?
How does it work?
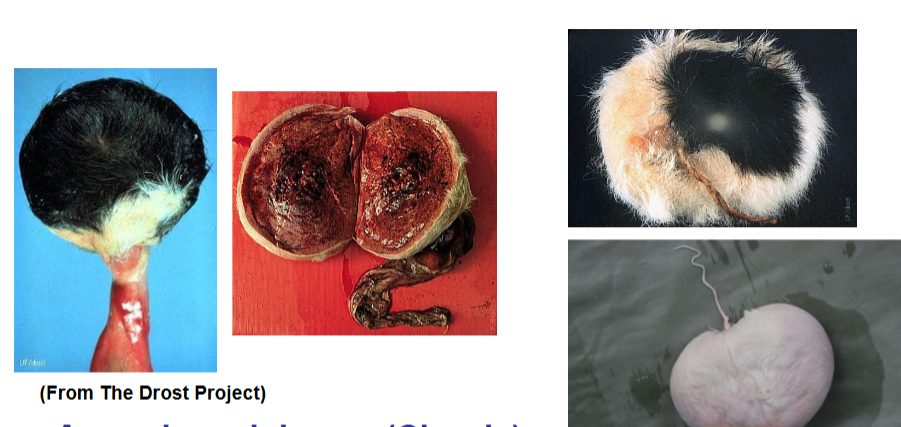
Amorphus globosus (Classic)
Incomplete twin (with all 3 layers, ectoderm, mesoderm and endoderm) connected vascularly to twin placenta
May be different sex to normal twin but no freemartin risk as no gonadal tissue
What this?
Describe it
Holoacardius Amorphus aka Anidean monster
An embryonic anideus is a blastoderm in which no embryonic axis develops

What this?
Importance?

General principles for managing foetal monstrosities
DX?
Traction?
Placenta?
Limbs?
Abnormalities may be detected on vaginal examination or progress of foetus fails to occur or is halted during application of traction
Small foetus? Traction no no
Placenta may be abnormal - oedematous
Detection of abnormal limb, head and/or neck postures that cannot be corrected (eg arthrogrypotic limb)
General principles for managing foetal monstrosities
TX
Fluid?
Traction?
Foetotomy?
Draining swollen or oedematous regions with single or multiple incisions with a palm knife eg hydrocephalus, foetal ascites, foetal anasarca
Traction where abnormality still enables passage through the birth canal safely with mild traction or abnormality can be corrected or reduced in size
Foetotomy to reduce size of abnormal part, remove abnormal part(s) or transect foetal body to reduce foetal size
General principles for managing foetal monstrosities
TX
Hydrocephalus?
Anything?
• Hydrocephalus – a transverse cut with wire passed behind the ears and the head of the foetotome positioned in the mouth should remove the dorsal half of the foetal head
• Caesarean section
What this?
Occurs in who?
Twin aspect?
Caused by?
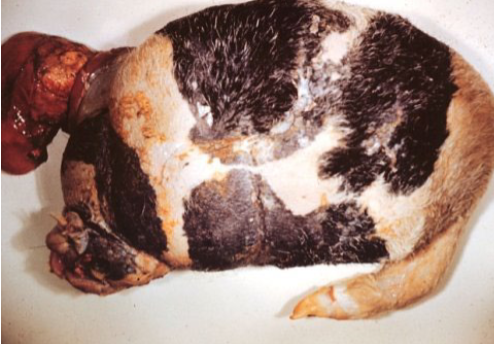
Schistosomus reflexus
Occurs in ruminants, pigs, horses
An affected foetus can be cotwinned with a normal or
freemartin foetus
A genetic cause (autosomal recessive is suspected) - Higher in Holsteins and Jerseys
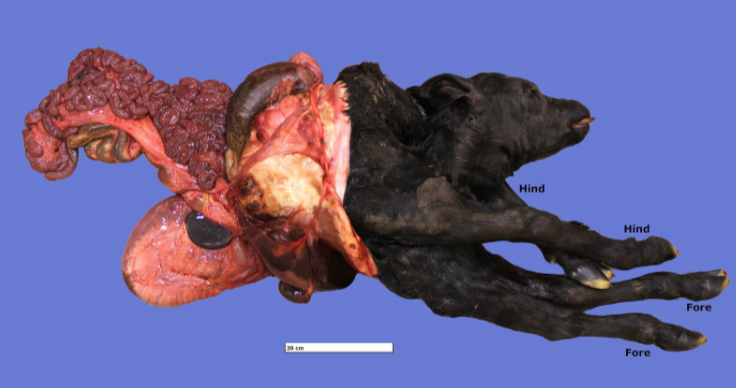
Schistosomus reflexus
What change happens to foetal body?
Failure of the abdominal muscles to fuse medially → abdominal fissure and the development of a spinal inversion
Head and tail curving dorsally in relation to the long axis of the foetus
The viscera are located externally within the amnion and the limbs and spinal column are usually ankylosed
Schistosoma reflexus – Clinical signs
Dystocia with palpation of foetal viscera within the vaginal canal or visible externally
Foetal visceral loops of intestine smaller than dam (DDX uterine rupture)
Palpation of multiple limbs within the vaginal canal with ankylosis of limbs and vertebral canal
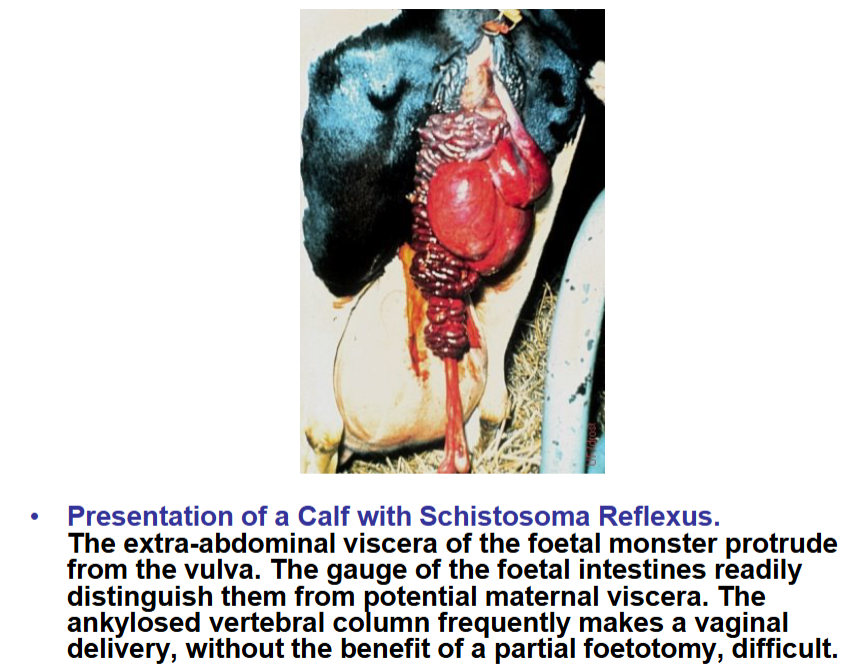
Schistosoma reflexus
Presentation options
– Visceral (transverse ventral) presentation – most amendable to foetotomy
– Presented by extremities (transverse dorsal) – more difficult
to reduce with foetotomy
Schistosoma reflexus – Treatment
Steps?
Foetotomy done first usually as long incision may be needed for c-section
Bisection following passage of a wire introducer
around the foetal trunk can enable sufficient reduction in foetal size to enable delivery by traction
Easier for transverse ventral (viscera presented) than transverse dorsal (limbs presented) presentation (C-section easier in latter)
In case of visceral presentation, remove viscera first, if still alive, break umbilical cord first
Frequency of treatments applied to correct dystocias arising from cases involving a schistosomas reflexus
Freq from most to least used
Why wouldn’t you do these?
Most cases foetotomy, then C-section, the simple traction
Case is hopeless as cow is severely exposed to toxic decomposing emphysematous foetus
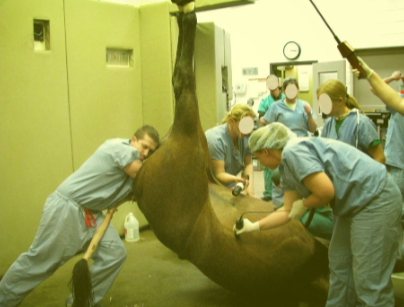
Equine dystocia – general principles
Foal surviability?
C-section?
Risks?
Look out for?
Most foals presented dead as equine placenta separates from endometrium rapidly during foaling
Caesarean section may be indicated where correction cannot be achieved relatively quickly, atraumatically and foal is alive
Risks of cervical laceration, uterine trauma and perforation are high with manipulation of the foetus and foetotomy
Look out for flexural deformities, contracted tendons, wry neck which can complicate
Equine dystocia – general principles
What can assist delivery?
Straining?
Tail?
Presentation?
General anaesthesia and elevation of mare’s hindlimbs
To control straining – can insert a stomach tube through the glottis into trachea of the mare
Wrap tail
Most delivered in cranial presentation
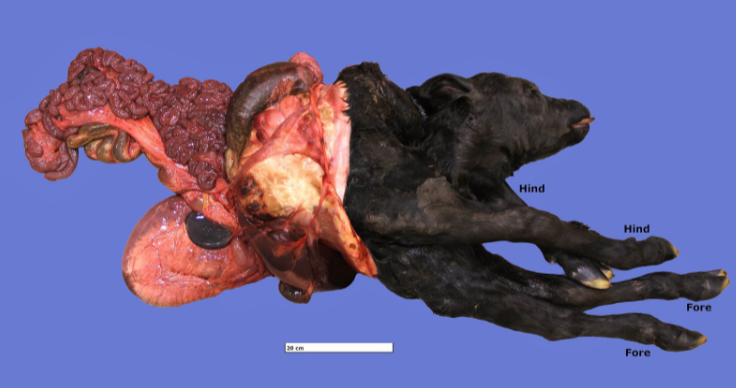
schistosoma reflexus calf
Foetotomy diagrams
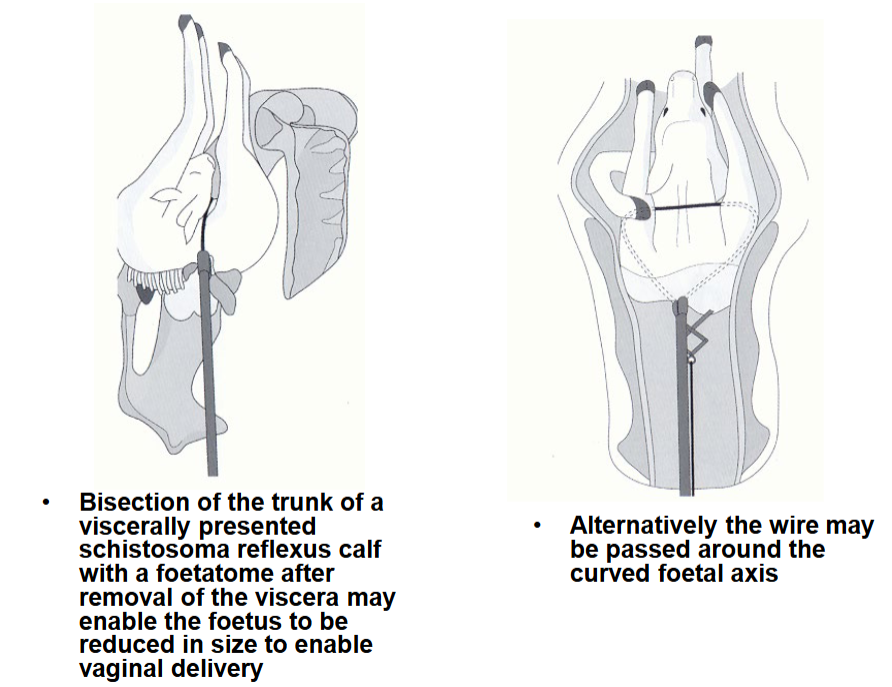
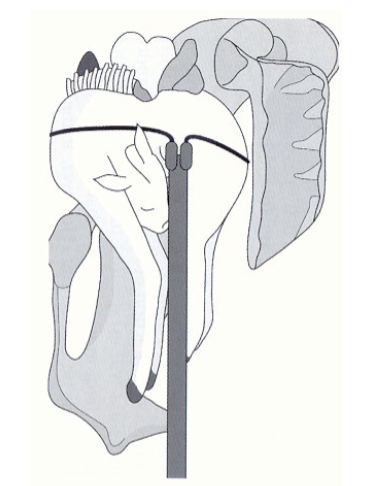
Description?

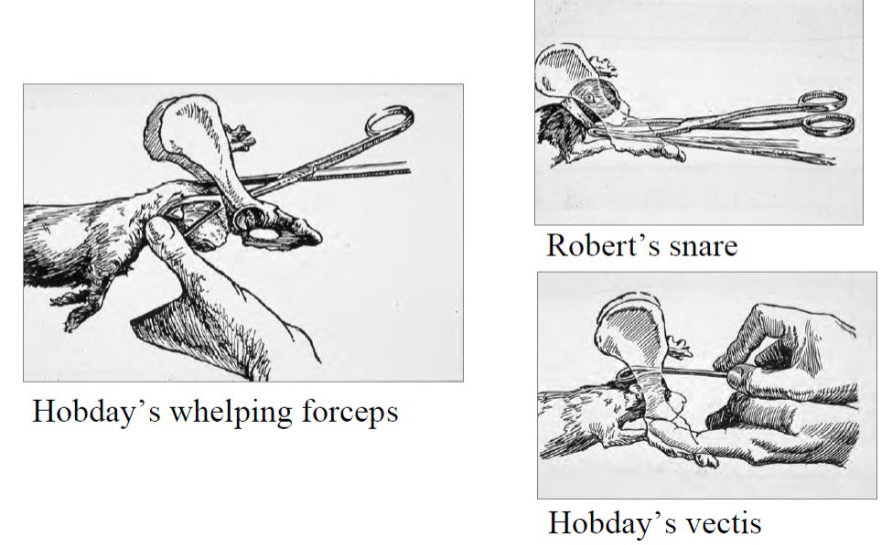
Equipment for companion animals
What is this?
