Lecture 12: Vesicular Transport within Golgi and Endosome
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
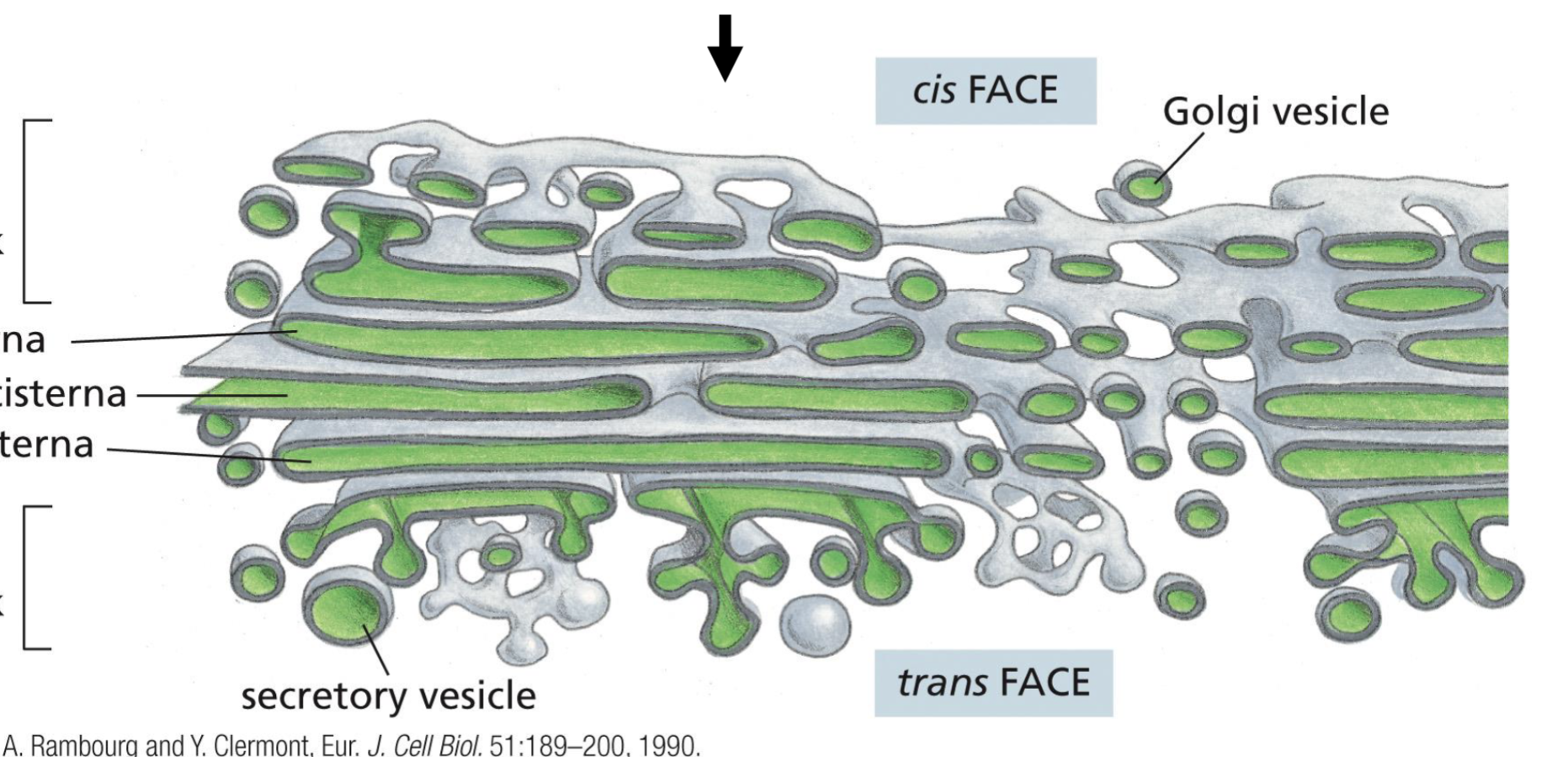
Structure of Golgi Apparatus
cis Side - ER facing side, trans Side - plasma membrane facing side
cis Golgi network (CGN)
cis cisterna, medial cisterna, trans cisterna
trans Golgi network (TGN)
what does exit signal do?
Cargo that needs to be transported has exit signals. Exit signal proteins are often packaged into vesicle to be transported
Which protein bound by cargo receptor?
soluble proteins bound by cargo receptors, which binds to adaptor protein of the inner COPII coat
What binds the transmembrane protein?
bound by COPII coat
How does cargo without an exit signal get packaged into vesicle?
diffusion - if concentration is high, can be pushed in
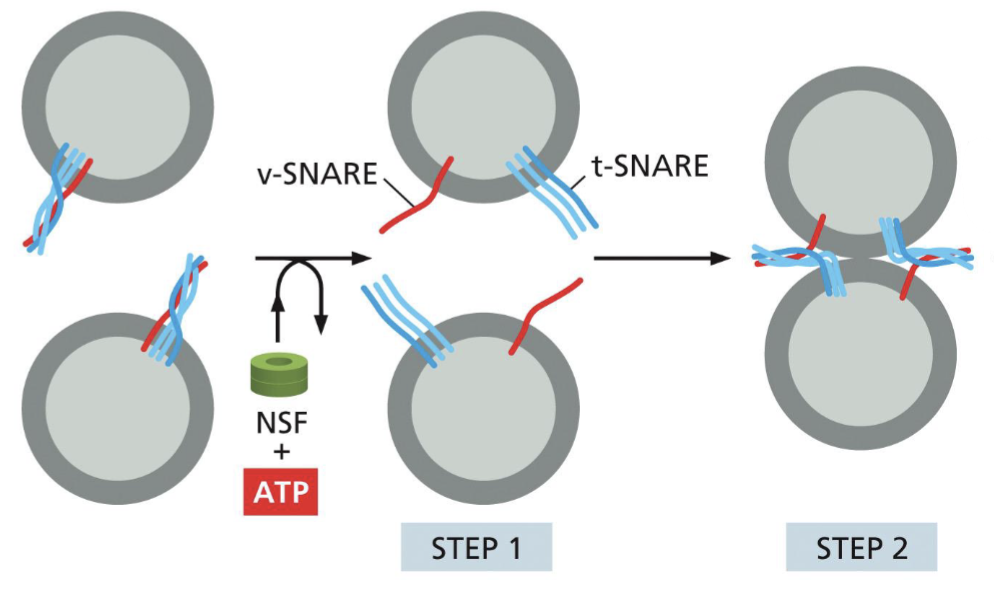
Vesicles that bud from exit site…
has COP II coat, form a vesicular tubular cluster by fusing with each other (this moves to golgi apparatus). NSF, using ATP, untangles v-SNARE and t-SNARE on its vesicles → tangle v-SNARE and t-SNARE on opposite vesicles → fuse together
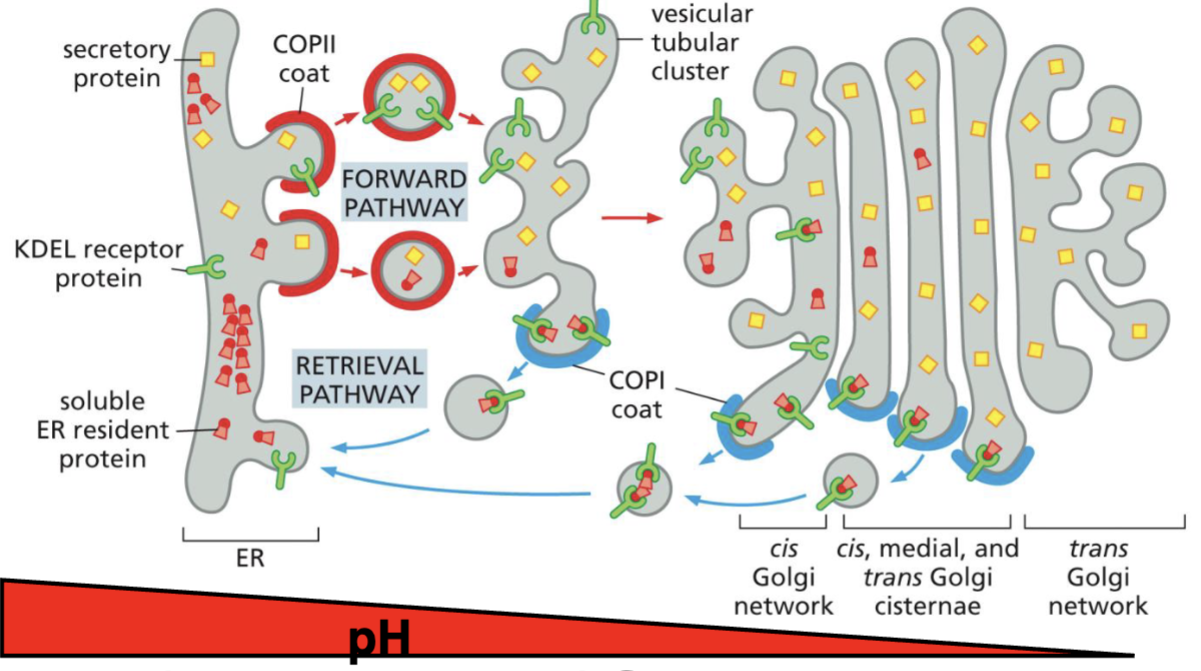
What coated vesicles does Retrieval (Retrograde) transport use?
COPI coated vesicles (vesicles from vesicular tubular clusters and Golgi go to ER)
What do the retrieval proteins have?
has ER retrieval signals
Soluble ER proteins have KDEL (retrieval signal) → which needs to be bound by KDEL receptor for the protein to be brought back
What signal does KDEL receptor have?
some ER membrane proteins have a retrieval signal.
for KDEL, it has KKXX at C terminus → binds to the COPI coats, which is packaged into vesicles
KDEL Receptor and Mechanism of Retrieval of ER-Resident Proteins
KDEL cycles between ER and Golgi
ER: higher pH, lower affinity for KDEL (releases KDEL)
Golgi: lower pH, higher affinity for KDEL (grabs onto KDEL to bring back to ER)
Different mechanism for Retrograde Transport
Different transport rates: some cycle but transport to ER at a slower rate (so will accumulate in Golgi)
Chunks of proteins retained in resident compartment: no space to come in
Transport of protein from CGN to TGN basic info
vesicles are kept close to Golgi cisternae by tethering proteins
Processing of N-linked oligosaccharides occurs int eh Golgi
Transport of protein from CGN to TGN - 2 models
both uses COPI coated vesicles
Vesicular Transport Model: COPI coated vesicles move forward on one Golgi cisterna to the next (faster)
Cisternal Maturation Model: “everyone gets promoted” returning uses COPI vesicles (slower)
What is the cargo when transporting TGN to late endosome?
lysosomal hydrolases → needed for lysosome function and for degradation of macromolecules, synthesized in the ER, processed in Golgi, active at acidic pH
TGN vesicles going to late endosome what happens?
The cargo is coated in clathrin → transported to late endosome → mature into lysosomes
What happens when extracellular material gets into the cell via vesicles? (lysosome)
Joins early endosome (which has digestive enzymes) → gobble more things up = late endosome → eventually gets degraded, and we call this organelle lysosome
What happens to late endosome, after it becomes lysosome?
It will still have hydrolase left → fuse it to endosome and go through process again
Detailed Mechanism for Lysosome being made
N-linked oligosaccharide added to ER
mannose is phosphorylated by…
Phoso-N acetyl glucosamine is added
N-acetyl glucosamine is removed → phospho left
= M6P
M6P receptor in TGN package lysosomal hydrolase
Lysosomal hydrolases relased into late endosome
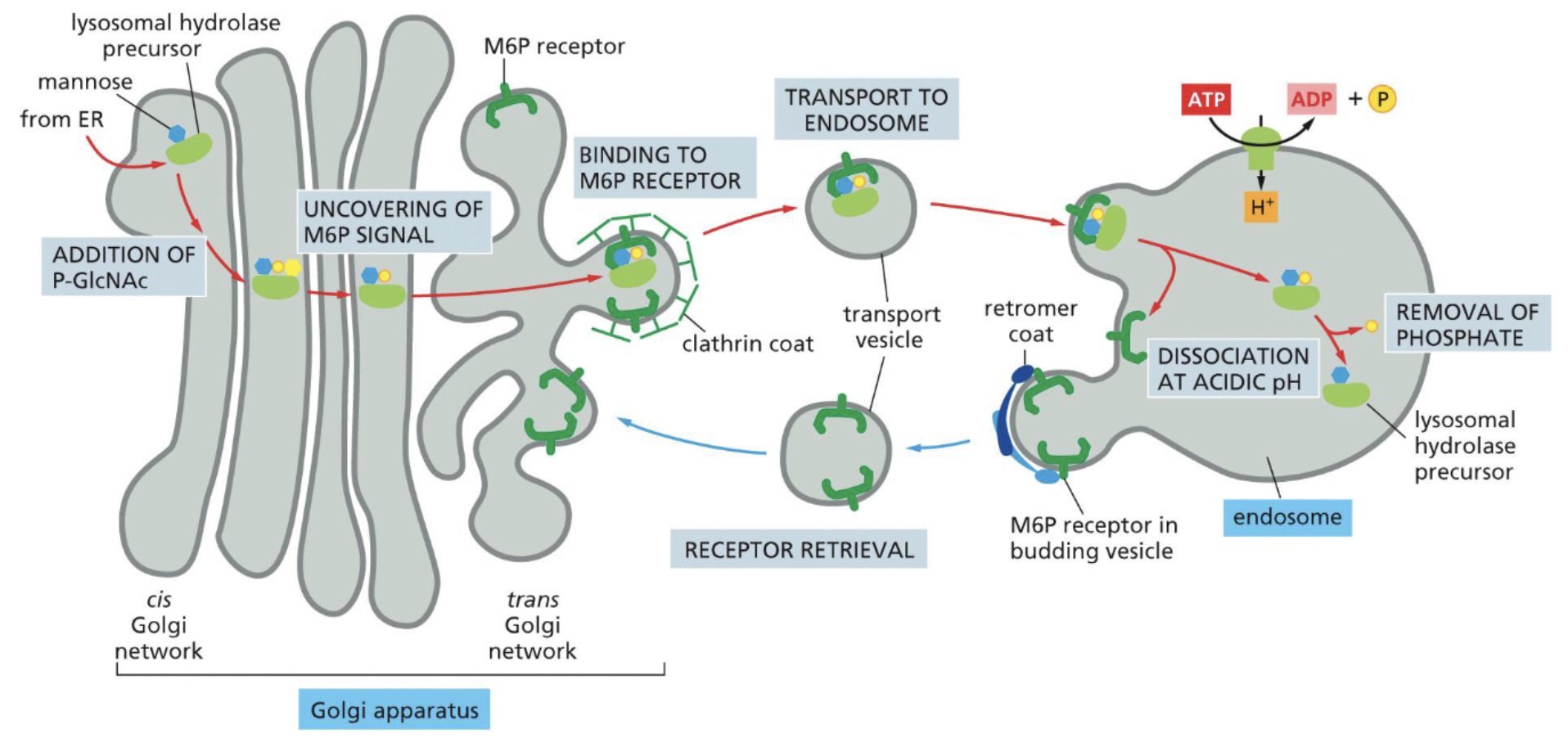
Affinity of M6P receptor
Lysosome: at low pH = decreased M6P receptor affinity = release cargo
Golgi: at high pH = increased M6P receptor affinity = grab on to send it to lysosome