1. Clinical Pharmacy 10 CNS
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
12 Terms
Outline the anatomy of the Brain.
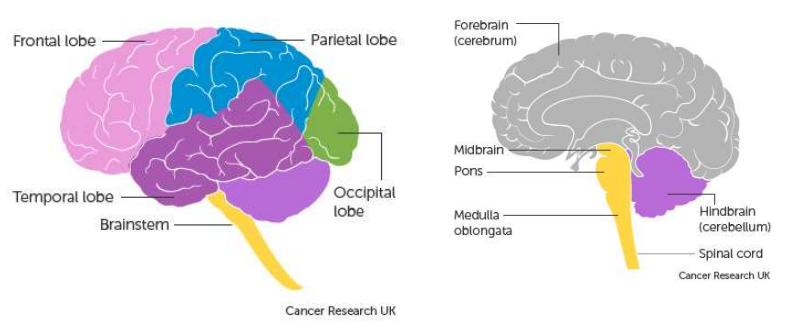
What are the functions of the different parts of the brain?
Frontal lobe:
Speech
Problem solving
Initiating movement
Understanding emotions
Influences character & personality
Parietal lobe:
Recognition
Touch, pressure & pain
Cerebellum:
Balance & posture
Timing & coordination of movement
Temporal lobe:
Sound
Memory storage
Language processing
Occipital lobe:
Vision
Brainstem:
Breathing
Sneezing & coughing
Swallowing
Heartbeat & blood pressure
What are the main principles for antiepileptic drug therapy?
If monotherapy is ineffective or intolerable, try an alternative drug.
Changing between drugs must be done carefully, only withdrawing the first drug once the new regimen is established.
Combination therapy may be necessary but increases the risk of adverse effects and drug interactions.
A single antiepileptic drug should be prescribed wherever possible.
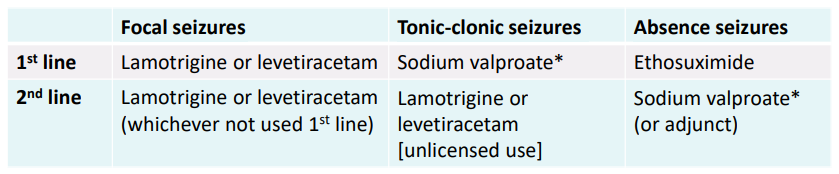
Outline 1st & 2nd line treatment for focal, tonic-clonic & absence seizures.
Outline the emergency management for status epilepticus.
Seizure lasting long or repeated seizures without regaining consciousness
Medical emergency
Position patient to avoid injury, support respiration, maintain blood pressure
Follow emergency management plan (EMP) if available
If no EMP, give buccal midazolam/rectal diazepam (community) or IV lorazepam (hospital)
If no response, call emergency services or seek expert advice
If seizure persists, give second dose of benzodiazepine
Second-line treatment: levetiracetam, phenytoin, or sodium valproate
What is multiple sclerosis (MS) and its key features?
Acquired immune-mediated inflammatory condition of the CNS
Causes demyelination, gliosis, and secondary neuronal damage
Common in young adults
Most common non-traumatic cause of neurological disability in those under 40
Cause unknown, but immune-mediated inflammation triggered by environmental factors
Risk factors: genetic factors, vitamin D deficiency, infections, geographical location (higher prevalence farther from the equator), smoking, obesity during adolescence, and female gender (2-3x more common in females)
What are the most common symptoms of multiple sclerosis (MS)?
Optic neuritis: Swelling of the optic nerve
Transverse myelitis: Swelling of the spinal cord
Cerebellar-related symptoms: Shakiness, coordination issues, slurred speech, trouble with higher-thinking skills
Brainstem syndromes: Double vision, facial sensory issues, unstable gait, vertigo, facial weakness
What are the 3 main patterns of multiple sclerosis (MS)?
Relapsing-remitting MS (RRMS): Most common – relapses with recovery & stability in between; damage builds up over time.
Secondary progressive MS (SPMS): Gradual disability ↑ without relapses; affects 60–70% of RRMS patients.
Primary progressive MS (PPMS): Continuous worsening from onset with no remissions; least common (10–15%).
How is multiple sclerosis (MS) diagnosed?
Urgent referral to consultant neurologist (only they can diagnose MS)
Blood tests to rule out other causes
Diagnosis usually based on:
MRI scan → shows any damage to myelin sheath
Neurological assessment → assesses eye movements, limb strength, balance, coordination, speech & reflexes
Lumbar puncture → white cells in the CSF can indicate immune response to CNS damage
What are some disease modifying therapies (DMTs) for MS & their actions?
Interferon β 1a/1b (SC injection) = balances pro- & anti-inflammatory agents in brain
Glatiramer acetate (SC injection) = binds to MHC molecules & inhibits T cell response to myelin antigens
Alemtuzumab (IV infusion) = depletes circulating T & B lymphocytes
Common side effects = injection-site reactions, lipotrophy, chest tightness, headache, anxiety, nausea
How are specific MS symptoms treated?
Baclofen = 1st line for chronic spasticity; start 5 mg TDS, ↑ gradually (usual 60 mg/day in 3 doses); max 100 mg/day; taper off slowly to avoid withdrawal (e.g. anxiety, seizures)
Gabapentin = 2nd line for spasticity & oscillopsia (off-label); use neuropathic pain dosing
Amitriptyline = for emotional lability (off-label); follow neuropathic pain dosing
How is an MS relapse managed?
Rule out infection (esp. UTI or RTI)
Consider disease fluctuation, progression, or other conditions
Contact MS team promptly
May give methylprednisolone 0.5 g/day PO for 5 days to ↓ relapse length & severity