Chapter 13 - Exam 4
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/106
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 3:21 PM on 5/1/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
107 Terms
1
New cards
Culture and Psychology
Two main ways culture intersects with personality psychology
* Individuals may differ from each other to some extent because they belong to different cultures
* Members f groups may differ from each other in distinctive ways
* Cross-cultural psychology
* Cultural psychology
* Individuals may differ from each other to some extent because they belong to different cultures
* Members f groups may differ from each other in distinctive ways
* Cross-cultural psychology
* Cultural psychology
2
New cards
Cross - cultural psychology
generally refers to research that compares cultures with one another
3
New cards
Cultural psychology
a branch of psychology that is focused on how our emotions and behaviors are influenced by or rooted in our individual cultures.
4
New cards
Cross - cultural universals vs specifity
* evidence of both
* culture refers to attributes of groups (mostly psychological attributes)
* Enculturation: Learning your birth culture
* Acculturation: Learning a new culture
* culture refers to attributes of groups (mostly psychological attributes)
* Enculturation: Learning your birth culture
* Acculturation: Learning a new culture
5
New cards
Cross - cultural differences are important
Cross - cultural differences and similarities, and the role of culture in psychology is relatively new … and important!
* *How generalizable are our theories and research findings?*
* *Even if these are accurate, how important are they in another culture?*
* Culture can affect how personality is expressed and emotion is experienced
* What does this mean for our theories and what we (think we) know?
* Cross - cultural understanding
* Varieties of human experience
* *How generalizable are our theories and research findings?*
* *Even if these are accurate, how important are they in another culture?*
* Culture can affect how personality is expressed and emotion is experienced
* What does this mean for our theories and what we (think we) know?
* Cross - cultural understanding
* Varieties of human experience
6
New cards
Characteristics of cultures
* Ethic & emic
* Though & easy
* Achievement & affiliation
* Complexity
* Tightness & looseness
* Head versus heart
* Collectivism & individualism
* Honor, face & dignity
* Though & easy
* Achievement & affiliation
* Complexity
* Tightness & looseness
* Head versus heart
* Collectivism & individualism
* Honor, face & dignity
7
New cards
Etic vs. Emic
Personality and individual differences have
* Aspects that are the same across cultures
* Aspects particular to a specific culture
This is the assumption underlying cultural comparison
\
The universal components of an idea are called etics, and the particular aspects are called emics.
* Aspects that are the same across cultures
* Aspects particular to a specific culture
This is the assumption underlying cultural comparison
\
The universal components of an idea are called etics, and the particular aspects are called emics.
8
New cards
Tough & Easy
Pertains to the variety and number of goals that can be pursued
… And the ease and number of ways of achieving goals
… And the ease and number of ways of achieving goals
9
New cards
Achievement & Affiliation
* Achievement pertains to motivation improve personal performance and accomplish challenging goals
* Affiliation pertains to motivation to improve social interactions and maintain meaningful relationships
The need to achieve could be assessed by looking at children’s stories (the little engine that could )
* Affiliation pertains to motivation to improve social interactions and maintain meaningful relationships
The need to achieve could be assessed by looking at children’s stories (the little engine that could )
10
New cards
Complexity
Based on several variables, such as…
* Interpersonal relationships
* Politics
* Economy
* Architecture
* Industrialization & Technology
Not this simple
* What’s (in)visible to outsiders?
* Interpersonal relationships
* Politics
* Economy
* Architecture
* Industrialization & Technology
Not this simple
* What’s (in)visible to outsiders?
11
New cards
Tightness & looseness
* Based on the amount of deviation from “proper behaviors“ tolerated within the culture
* Tight → Less tolerance for deviation
* Loose → More tolerance for deviation
* Tight → Less tolerance for deviation
* Loose → More tolerance for deviation
12
New cards
Head vs Heart
* Strength of head
* Artistic excellence, creativity, curiosity, critical thinking, and learning
* Strengths of the heart
* Fairness, mercy, gratitude, hope, love, and religiously
* Artistic excellence, creativity, curiosity, critical thinking, and learning
* Strengths of the heart
* Fairness, mercy, gratitude, hope, love, and religiously
13
New cards
Collectivism & Individualism
Importance of needs and rights of the group versus the individual versus the individual
* Self and others
* personality and collectivism
* Need for self-regard
* Sociability, emotion, and motivation
* Behavioral consistency
* vertical & horizontal
* Caution
* Self and others
* personality and collectivism
* Need for self-regard
* Sociability, emotion, and motivation
* Behavioral consistency
* vertical & horizontal
* Caution
14
New cards
Honor, face, & dignity
* Honor
* face
* dignity
The key idea is that individuals are valuable in their own right and this value does not come from what other people think of them.
* face
* dignity
The key idea is that individuals are valuable in their own right and this value does not come from what other people think of them.
15
New cards
Similarities when describing cultures and individuals
* Culture complexity
* Cultural tightness
* Collectivist/individuals
* Cultural tightness
* Collectivist/individuals
16
New cards
Cultural Complexity
* Cultural complexity is comparable to the characteristic of cognitive complexity
* Cognitive complexity: an individual’s capacity to perceive minor aspects and subtle differences
* Cognitive complexity: an individual’s capacity to perceive minor aspects and subtle differences
17
New cards
Cultural Tightness
* Cultural tightness is comparable to the personality trait of conscientiousness
* And the trait of intolerance for ambiguity
* And the trait of intolerance for ambiguity
18
New cards
Collectivist/Individualist
* The collectivism versus individualism spectrum parallels the allo -centrism versus ideo- centrism spectrum
* Both dimensions pertain to values focused on the importance of the individual versus the group
* Allo - cetrism: the individual is more important than the group
* Ideo - cetrism: The group is more important than the individual
* Both dimensions pertain to values focused on the importance of the individual versus the group
* Allo - cetrism: the individual is more important than the group
* Ideo - cetrism: The group is more important than the individual
19
New cards
Comparing the same trait across cultures
\*\*Most common approach
* Environmental and sociocultural factors are believed to contribute to variations in development, expression, and maintenance of personality
* Most cross-cultural studies have focused on the Big Five
* Environmental and sociocultural factors are believed to contribute to variations in development, expression, and maintenance of personality
* Most cross-cultural studies have focused on the Big Five
20
New cards
Different traits for different countries
Different traits for different cultures
* Do traits have the same meaning across cultures?
* The big five are found in more than 50 cultures
* CEA might be only universal traits
\
* Create endogenous scales
* Some of the big five traits have emerged
* Factors other than the Big Five that have merged: unselfishness, gentle temper, dependency/fragility, positive valence, negative valence, pleasantness, engagement, interpersonal relatedness
* Do traits have the same meaning across cultures?
* The big five are found in more than 50 cultures
* CEA might be only universal traits
\
* Create endogenous scales
* Some of the big five traits have emerged
* Factors other than the Big Five that have merged: unselfishness, gentle temper, dependency/fragility, positive valence, negative valence, pleasantness, engagement, interpersonal relatedness
21
New cards
Thinking & Values
Thinking
* To what degree do people from different cultures differently?
* Holistic perception and the self
* May be related to collectivism - individualism
Values
* How can seemingly obvious and basic values vary across cultures?
* The search for universal values
* Seek values that are universal to all cultures
* Implications
* Possible list of 10 universal values
* To what degree do people from different cultures differently?
* Holistic perception and the self
* May be related to collectivism - individualism
Values
* How can seemingly obvious and basic values vary across cultures?
* The search for universal values
* Seek values that are universal to all cultures
* Implications
* Possible list of 10 universal values
22
New cards
WHY are cultures different? \n \n What determines the specific, distinctive psychology that a particular culture develops?
23
New cards
The Ecological approach
* Older model
Ecology → culture → socialization → personality → behavior
* New model
Ecology → culture → socialization → personality → behavior
* New model
24
New cards
Challenges for cross cultural personality research
* Ethnocentrism
* Assumptions
* Cultural Relativism
* Subcultures & Multiculturalism
* Assumptions
* Cultural Relativism
* Subcultures & Multiculturalism
25
New cards
The universal of human condition
* Newer emphasis on how people are psychologically similar
* Differences in rules for appropriate behavior might mask similar motivations and desired behaviors
* Culture may influence how people want to feel more than how they actually feel
* Same desires that manifest differently (ex. to please parents)
* Degree of similarity of persons and situations and seems higher than originally expected
* Differences in rules for appropriate behavior might mask similar motivations and desired behaviors
* Culture may influence how people want to feel more than how they actually feel
* Same desires that manifest differently (ex. to please parents)
* Degree of similarity of persons and situations and seems higher than originally expected
26
New cards
Learning
* Learning based approaches explain personality in terms of the learning process
* Implies everyone should behave the same in the same environment or situation
* Implies everyone should behave the same in the same environment or situation
27
New cards
Behaviorism
Behavior is the direct result of a person’s environment
28
New cards
Direct Observation
The causes of behavior can be directly observed
29
New cards
Functional Analysis
Determining how behavior is a function of one’s environment
30
New cards
Habituation
* Simplest form of behavior change as a result of experience
* **A decrease in responsiveness withe each repeated exposure to something**
* **A decrease in responsiveness withe each repeated exposure to something**
31
New cards
Classical Conditioning
A unconditioned response (Feeling itchy) that is naturally elicited by one stimulus (lice) becomes elicited also by a new, conditioned stimulus (the word lice)
US + NS = > CR
Stimulus - response (S-R) conception of personality
US + NS = > CR
Stimulus - response (S-R) conception of personality
32
New cards
Operant Conditioning
Behaviors are learned by the effect of the behavior on the environment
Two main consequences
* Reinforcement
* Punishment
Two main consequences
* Reinforcement
* Punishment
33
New cards
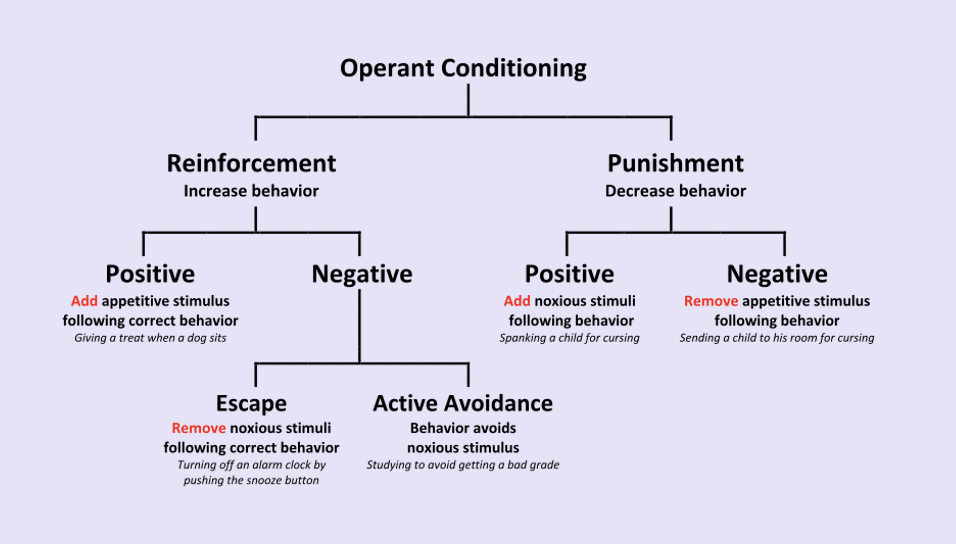
Operant Conditioning
34
New cards
Limitations
* Ignores thinking, motivation, and emotion
* Ignores the social of dimension of learning
* Organism are treated as essentially passive
* Ignores the social of dimension of learning
* Organism are treated as essentially passive
35
New cards
Social Learning Theory
* Dollard & Miller’s Theory
* Rotter’s Theory
* Bandura’s Theory
* Rotter’s Theory
* Bandura’s Theory
36
New cards
Dollard & Miller’s Theory
Aimed to integrate psychoanalytic theory and behaviorism and proposed that a drive is a need that stimulates a behavioral response
37
New cards
Rotter’s Theory
Emphasizes the role of expectancies in determining behavior
* Locus of control - the more motivated you will be to try to make a difference.
* Locus of control - the more motivated you will be to try to make a difference.
38
New cards
Bandura’s Theory
Monkey see, monkey do.
39
New cards
Bandura’s Social Learning Theory
* Self - efficacy
* Learning occurs due to observation and modeling
* Humans learn nearly everything by observation
* Learning occurs due to observation and modeling
* Humans learn nearly everything by observation
40
New cards
Motivation
What do you want?
How will you try to get it?
^^**Goals**^^ and ^^**strategies**^^
* Goals drive behavior
* Strategies get you there
People do not always behave consistently with their stated goals
How will you try to get it?
^^**Goals**^^ and ^^**strategies**^^
* Goals drive behavior
* Strategies get you there
People do not always behave consistently with their stated goals
41
New cards
Short - Term & Long - Term Goals
Long - term goals helo organize short - term goals
Short - term goals help achieve long - term goals
Short - term goals help achieve long - term goals
42
New cards
Idiographic Goals
Current concerns : Motivations that persist until goal met / dropped
* Personal projects : Efforts put into goals
* Personal Strivings : Long - term goals that organize life
* Personal projects : Efforts put into goals
* Personal Strivings : Long - term goals that organize life
43
New cards
Nomothetic Goals
* Essential motivations that almost everyone pursues
* Broad goals almost all people pursue
* Broad goals almost all people pursue
44
New cards
Strategies
How do you get what you really, really want?
* Scripts: Basic strategies based on an abstraction of typical patterns
* Broad strategies: Help you organize and pursue important goals
* Scripts: Basic strategies based on an abstraction of typical patterns
* Broad strategies: Help you organize and pursue important goals
45
New cards
Defensive Pessimism (vs Optimism)
Defensive Pessimism: Assumes the worst, which is motivating
Optimism: Assumes the best will happen, which is motivating
* Some consistency across situations
* Advantages and disadvantages to both strategies
* Optimists tend to be happier, but pessimists might not be happier as optimists
Optimism: Assumes the best will happen, which is motivating
* Some consistency across situations
* Advantages and disadvantages to both strategies
* Optimists tend to be happier, but pessimists might not be happier as optimists
46
New cards
Emotion
A type of procedural knowledge
A set of mental and physical procedures
A set of mental and physical procedures
47
New cards
Core emotions
Happiness , sadness, anger, fear, surprise, disgust
48
New cards
Circumplex model
* of emotion contrasts the degrees to which emotions are aroused versus unaroused and negative versus positive; another widely used rotation of this model contrasts emotions on the dimensions of excited versus bored and alarmed versus serene.
49
New cards
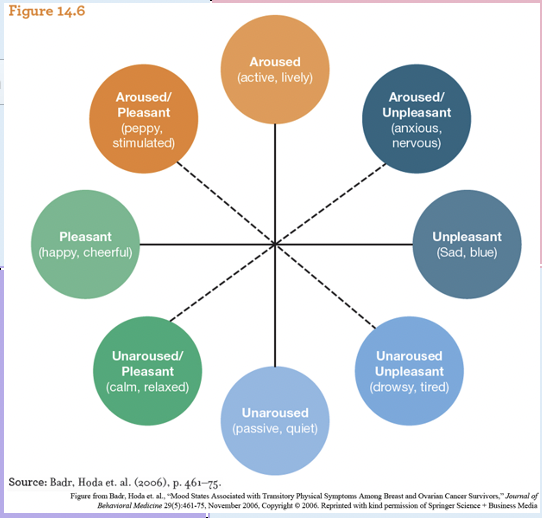
Emotions Circumplex
50
New cards
Stimuli, Responses & Functions of Emotions
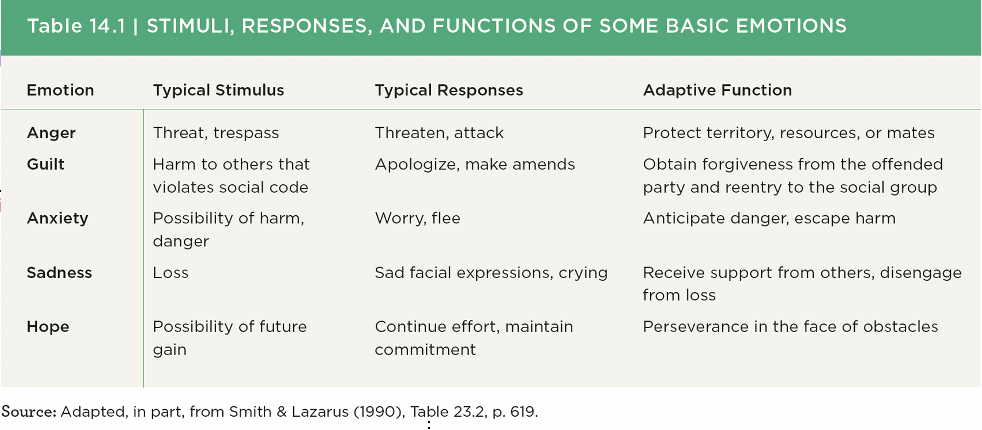
51
New cards
Individual Differences in Emotional Life
* Differences are core aspects of personality
* Emotional experience
* Preference for emotions
* Affect intensity
* Rate of change
* Emotional Intelligence
* Alexithymic - At the low end of the emotional intelligence scale are peo-
ple sometimes characterized as
* Related to emotional expressiveness, quality of personal relationships, levels of optimism and cognitive control
* Emotional experience
* Preference for emotions
* Affect intensity
* Rate of change
* Emotional Intelligence
* Alexithymic - At the low end of the emotional intelligence scale are peo-
ple sometimes characterized as
* Related to emotional expressiveness, quality of personal relationships, levels of optimism and cognitive control
52
New cards
Cognitive - Affective Personality System (CAPS)
The most important aspect of many systems of personality and cognition is their interaction
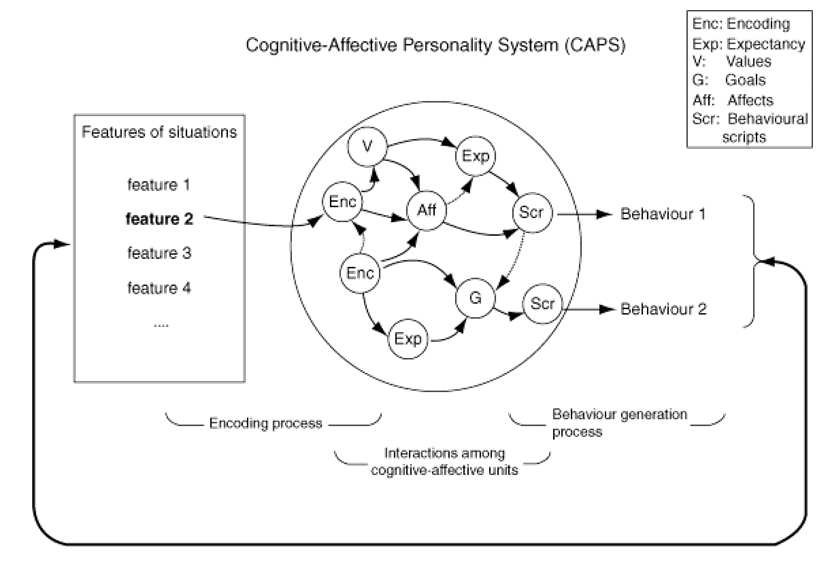
53
New cards
Belief. emotions, and action tendencies (BEATS)
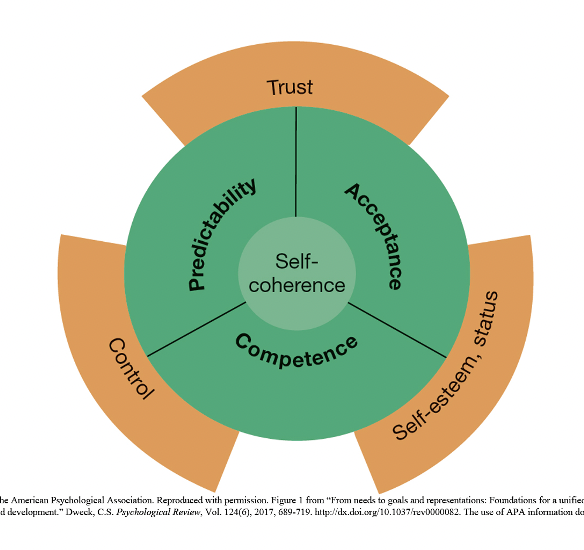
* Personality emerges form mental representations of BEATS that are relevant to important goals
* People have basic needs that combine to produce emergent needs, from which the final need for self - coherent or meaning in life emerges
* Basic motivations lead to goals: goal create BEATS
* People have basic needs that combine to produce emergent needs, from which the final need for self - coherent or meaning in life emerges
* Basic motivations lead to goals: goal create BEATS
54
New cards
Williams James
Me (Epistemological self)
I (Ontological self)
* Theoretically distinct but often confused in practice
* Recent research focuses on the me
I (Ontological self)
* Theoretically distinct but often confused in practice
* Recent research focuses on the me
55
New cards
Psychological Self (Contents and purposes of the self)
* Influences behavior
* Organizes
* Memories
* Impressions and judgements of others
* knowledge
* Jobs
* Self - regulation
* Information - processing filter
* Help us relate to others
* Identity
* Organizes
* Memories
* Impressions and judgements of others
* knowledge
* Jobs
* Self - regulation
* Information - processing filter
* Help us relate to others
* Identity
56
New cards
Self Knowledge
* Knowledge you have about yourself
* Declarative Knowledge
* Facts you know
* Procedural Knowledge
* Relational self - said to be based on past experiences that direct how we
relate with each of the important people in our live
* Implicit self - self-relevant behavioral patterns are not readily accessible to
consciousness
* Declarative Knowledge
* Facts you know
* Procedural Knowledge
* Relational self - said to be based on past experiences that direct how we
relate with each of the important people in our live
* Implicit self - self-relevant behavioral patterns are not readily accessible to
consciousness
57
New cards
Declarative Self
* Who you think you are
* Self esteem
* High and low self esteem
* Attempts to increase self-esteem may backfire
* Self - esteem can be too high
* How to legitimately increase self - esteem
* Self esteem
* High and low self esteem
* Attempts to increase self-esteem may backfire
* Self - esteem can be too high
* How to legitimately increase self - esteem
58
New cards
Self - Schema
* Who you think you are --- but --- Organized
* Consequences for how you process information
* Not based only on memories of specific events
* Consequences for how you process information
* Not based only on memories of specific events
59
New cards
Self - Reference & Memory
* Long term memory
* Self - reference effect
* Increases accessibility
* Explains why your most meaningful memories stay with you the longest
* Depends on culture
* Self - reference effect
* Increases accessibility
* Explains why your most meaningful memories stay with you the longest
* Depends on culture
60
New cards
Self - Efficacy
* Self - schema helps you set limits for what you attempt to do
“YOU CAN DO IT“
“YOU CAN DO IT“
61
New cards
That person that you are…
…Is that the only person that you are or could be?
62
New cards
Possible Selves
* Images and ideas we have or can create of the other selves we could be
* Possible future selves may affect goals
* Evidence that it affects mate preferences
* Want future selves that fulfill the needs for self-esteem, competence, and meaning
* People want to fulfill needs for similar future selves.
* Possible future selves may affect goals
* Evidence that it affects mate preferences
* Want future selves that fulfill the needs for self-esteem, competence, and meaning
* People want to fulfill needs for similar future selves.
63
New cards
Self - Discrepancy Theory
* Interactions between our possible selves and the actual selves and the actual determine your feelings about life
* Ideal self
* Discrepancy leads to depression
* Ought self
* Discrepancy leads to anxiety
* Ideal self
* Discrepancy leads to depression
* Ought self
* Discrepancy leads to anxiety
64
New cards
Procedural Self
* Not conscious and not possible to explain to others
* Learned by doing and watching others
* Relational selves
* Relational self-schema
* Deeply ingrained and difficult to change
“Your actions define you. Not your words“
* Learned by doing and watching others
* Relational selves
* Relational self-schema
* Deeply ingrained and difficult to change
“Your actions define you. Not your words“
65
New cards
Implicit Selves
* Includes the relational self
* Has been measure with the Implicit Association Test (IAT)
* Implicit self - esteem
* High implicit self - esteem: respond more quickly when “me“ and “good” are paired than when “me“ and “bad“ are paired
* Predicts responses to success and failure
* Only weakly related to declarative self-esteem
* Implications for narcissism
* Implicit shyness
* Implication
* Has been measure with the Implicit Association Test (IAT)
* Implicit self - esteem
* High implicit self - esteem: respond more quickly when “me“ and “good” are paired than when “me“ and “bad“ are paired
* Predicts responses to success and failure
* Only weakly related to declarative self-esteem
* Implications for narcissism
* Implicit shyness
* Implication
66
New cards
Changing the self
* Practice and feedback
* psychotherapy
* Life events
* time
* fake it
* psychotherapy
* Life events
* time
* fake it
67
New cards
Relationships Deal - Makers
* Deal - makers: traits that promote good relationships
* Extraversion and agreeableness
* Being liked is associated with being high on communal traits
* Number of friends and degree of agreement or conflict
* Success in relationships and at speed dating
* Extraversion and agreeableness
* Being liked is associated with being high on communal traits
* Number of friends and degree of agreement or conflict
* Success in relationships and at speed dating
68
New cards
Relationships Deal-Breakers
* Deal-breakers: Traits that prevent or undermine relationships
* Inverse of traits for deal-makers
* Untrustworthy and anger issues
* Dispositional contempt
* Rejection sensitivity
* Inverse of traits for deal-makers
* Untrustworthy and anger issues
* Dispositional contempt
* Rejection sensitivity
69
New cards
Sexual Relationships
* Mating behavior
* Mate selection & attraction
* Mating startegies
* Jealousy
* Mate selection & attraction
* Mating startegies
* Jealousy
70
New cards
Attraction
All - Want the highest likelihood of healthy offsprings who will survive and reproduce
Women - Place higher value on economic security and prefer older mates
Men - Place higher value on physical attractiveness and prefer younger mates
\*\* Attraction is influenced by more than physical characteristics
\*\* Culture matters
Women - Place higher value on economic security and prefer older mates
Men - Place higher value on physical attractiveness and prefer younger mates
\*\* Attraction is influenced by more than physical characteristics
\*\* Culture matters
71
New cards
Matting Strategies
* Differences between men and women explained in terms of reproductive success
* Some similarities
* Some similarities
72
New cards
Jealousy
* Gender difference in the experience of jealousy
* Sexy son hypothesis - This hypothesis proposes that a few women
consistently—and many women occasionally—follow an atypical reproductive strategy
* Sexy son hypothesis - This hypothesis proposes that a few women
consistently—and many women occasionally—follow an atypical reproductive strategy
73
New cards
Sociasexuality
* Men are generally higher than women
* Implications of high versus low levels
* Implications of high versus low levels
74
New cards
Sexual Orientation
* 1950s survey
* Homosexuality was listed as a mental disorder until the 1970s
* Problems
* An explanation of the origin of homosexuality is not empirically well established or widely accepted
* Homosexuality was listed as a mental disorder until the 1970s
* Problems
* An explanation of the origin of homosexuality is not empirically well established or widely accepted
75
New cards
Romantic Orientation
* Much less studied than sexual orientation
* Often conflated with sexual orientation (split attraction model)
* Implications of distinction between the two largely unknown
* Often conflated with sexual orientation (split attraction model)
* Implications of distinction between the two largely unknown
76
New cards
Attachment Theory
Patterns of relationships with others are consistently repeated with different partners throughout life
77
New cards
Love & Attachment - **John Bowlby**
* Saw attachment as the basis of love
* Based on evolutionary theory
* Desire for protection leads to attachments
* Working models of others and working models of the self are based on childhood experiences
* Children learn lessons from early experiences with adult caregivers
* Based on evolutionary theory
* Desire for protection leads to attachments
* Working models of others and working models of the self are based on childhood experiences
* Children learn lessons from early experiences with adult caregivers
78
New cards
Love & Attachment - **Mary Ainsworth**
* Developed the strange situation task
* Three types of attachment
* Anxious - ambivalent: caregivers are inconsistent or chaotic
* Avoidant: Caregivers rebuff attempts for contact and reassurance
* Insecure
* Secure attachment: Have a confident faith in self and caregivers
* Self-fulfilling nature
* Three types of attachment
* Anxious - ambivalent: caregivers are inconsistent or chaotic
* Avoidant: Caregivers rebuff attempts for contact and reassurance
* Insecure
* Secure attachment: Have a confident faith in self and caregivers
* Self-fulfilling nature
79
New cards
Love & Attachment
* Attachment patterns are self - fulfilling
* Change is difficult but not impossible
* Even people with secure attachments can have relationship problems
* Moving to two dimensions: anxiety and avoidance
* Evidence of unconscious priming of attachment figures
* Change is difficult but not impossible
* Even people with secure attachments can have relationship problems
* Moving to two dimensions: anxiety and avoidance
* Evidence of unconscious priming of attachment figures
80
New cards
Conscientiousness & Job Performance
* Predictive validity of supervisor ratings = .41 or .70 percent accuracy
* Predictive validity of absenteeism = .33 or 67 percent accuracy
* **Predicts all criteria for all occupations**
* Related to citizenship performance
* Related to success of ones spouse
* use to alleviate bias in testing
* Predictive validity of absenteeism = .33 or 67 percent accuracy
* **Predicts all criteria for all occupations**
* Related to citizenship performance
* Related to success of ones spouse
* use to alleviate bias in testing
81
New cards
Leadership & Management
* Get people to do things with persuasion, counseling, and suggestion
* Predictors of management performance: emotional stability, consciousness, extraversion, openness
* Dark triad - leadership styles are selfish, impulsive, exploitative, and toxic
* Predictors of management performance: emotional stability, consciousness, extraversion, openness
* Dark triad - leadership styles are selfish, impulsive, exploitative, and toxic
82
New cards
Occupational Choice
* Hierarchy of needs: Employee motivation
* Personality - job fit: Find the best niche for your personality
* Holland’s six types realistic, investigative, artistic, social, enterprising, conventional
* Personality - job fit: Find the best niche for your personality
* Holland’s six types realistic, investigative, artistic, social, enterprising, conventional
83
New cards
Behaviors and success in relationships and careers are affected by personality
and are critically important for how life turns out
84
New cards
Personality Disorders
Configurations of personality traits, characteristics, and styles that are
* socially undesirable
* extreme
* and cause dysfunction
There is not an exact point that differentiates between normals and disorder personality
Prevalence: about 15% of American adults
* socially undesirable
* extreme
* and cause dysfunction
There is not an exact point that differentiates between normals and disorder personality
Prevalence: about 15% of American adults
85
New cards
Personality Disorders in the DSM
* First edition: 1952
* Mistake: DSM-III
* Controversy
* Current edition: DSM-5-tr IN 2022
* Two systems for personality disorders
* Purposes
* Make diagnosis more objective
* Insurance billing
* Mistake: DSM-III
* Controversy
* Current edition: DSM-5-tr IN 2022
* Two systems for personality disorders
* Purposes
* Make diagnosis more objective
* Insurance billing
86
New cards
Defining Personality Disorders
* Usually (more) extreme personality attributes
* In terms of context (ex. cultural)
* Distortions of reality
* Problematic
* Cause of functional impairment for the individual
* Can cause issues for others
* Interpersonal in nature
* Relatively stable over time
* Just like personality
* Often ego-syntonic (Not all PD’s)
* Symptoms can be seen as normal and valued aspects of personality by the individual
* Can think others are the ones with the problem
* In terms of context (ex. cultural)
* Distortions of reality
* Problematic
* Cause of functional impairment for the individual
* Can cause issues for others
* Interpersonal in nature
* Relatively stable over time
* Just like personality
* Often ego-syntonic (Not all PD’s)
* Symptoms can be seen as normal and valued aspects of personality by the individual
* Can think others are the ones with the problem
87
New cards
Major personality disorders (OLD)
Old (but still used) system
* 10 major disorders in three clusters
* Cluster A: odd and eccentric patterns of thinking
* Cluster B: impulsive and erratic pattens of behavior
* Cluster C: anxious and avoidant emotional styles
* 10 major disorders in three clusters
* Cluster A: odd and eccentric patterns of thinking
* Cluster B: impulsive and erratic pattens of behavior
* Cluster C: anxious and avoidant emotional styles
88
New cards
Major personality disorders (NEW)
New (better but not perfect) system
* Alternative DSM - 5 Model for personality disorders (AMPD)
* Criterion A: Personality Functioning Impairment
* Criterion B: Maladaptive Traits
* Six specific personality disorders
* Four were deleted
* Politics and money involved
* Meh
* Alternative DSM - 5 Model for personality disorders (AMPD)
* Criterion A: Personality Functioning Impairment
* Criterion B: Maladaptive Traits
* Six specific personality disorders
* Four were deleted
* Politics and money involved
* Meh
89
New cards
Other Systems & Frameworks
* ICD - 11’s chapter on personality disorders and related traits
* Like the DSM’s AMPD but traits are optional
* Model from Psychodynamic Diagnostic Manual - 2 (PDM-2)
* Big Five / Trait Model
* Personality disorders are extreme, maladaptive variants of normal personality traits
* Like the DSM’s AMPD but traits are optional
* Model from Psychodynamic Diagnostic Manual - 2 (PDM-2)
* Big Five / Trait Model
* Personality disorders are extreme, maladaptive variants of normal personality traits
90
New cards
Personality Disorders
* Paranoid PD
* Schizoid PD
* Schizotypal PD
* Antisocial PD
* Borderline PD
* Histrionic PD
* Narcissistic PD
* Schizoid PD
* Schizotypal PD
* Antisocial PD
* Borderline PD
* Histrionic PD
* Narcissistic PD
91
New cards
Paranoid PD
\
* Distrust and suspiciousness that involves interpreting the motives of others are malevolent
* Distrust and suspiciousness that involves interpreting the motives of others are malevolent
92
New cards
Schizoid PD
\
* Detachment from social relationships and restricted range of emotional expression in interpersonal settings
* Core belief that dependency and love are dangerous, and the social world is impinging and engulfing
* Detachment from social relationships and restricted range of emotional expression in interpersonal settings
* Core belief that dependency and love are dangerous, and the social world is impinging and engulfing
93
New cards
Schizotypal PD
* Social and interpersonal deficits involving acute discomfort with and reduced capacity for close relationships, distortions in cognition and perception, and eccentricities in behavior
94
New cards
Antisocial PD
* Disregard for and violation of the rights of others since age 15
* Core belief that they can do whatever they want because everyone is selfish, manipulative, dishonorable, or weak
* Core belief that they can do whatever they want because everyone is selfish, manipulative, dishonorable, or weak
95
New cards
Borderline PD
\
* Instability in interpersonal relationships, self - image, and effects
* Core belief of not knowing who they are and that others are one-dimensional and defined by their effects on the individual
* Instability in interpersonal relationships, self - image, and effects
* Core belief of not knowing who they are and that others are one-dimensional and defined by their effects on the individual
96
New cards
Histrionic PD
* Excessive emotionality and attention seeking
* Core belief that the world is best understood in terms of gender (power) and gender conflicts, and there is something problematic with their gender (weak) and its meaning
* Core belief that the world is best understood in terms of gender (power) and gender conflicts, and there is something problematic with their gender (weak) and its meaning
97
New cards
Narcissistic PD
* Grandiosity, a need for admiration, and lack of empathy
* Core belief that they need to be perfect to feel OK, and the more they have the better they’ll feel (about themselves)
* Core belief that they need to be perfect to feel OK, and the more they have the better they’ll feel (about themselves)
98
New cards
Avoidant PD
* Social inhibition, feelings of inadequacy, and hypersensitivity to negative evaluation
* Core belief that they’re in constant danger they must elude and others are sources of extreme danger or protection
* Core belief that they’re in constant danger they must elude and others are sources of extreme danger or protection
99
New cards
Dependent PD
* Excessive need to be taken care of that leads to submissive and clinging behavior and fear of separation
* Core belief that they’re inadequate and others are powerful, and they need their care
* Core belief that they’re inadequate and others are powerful, and they need their care
100
New cards
Obsessive - compulsive PD
* Preoccupation with orderliness, perfectionism, and mental and interpersonal control that severely limits flexibility, openness, and efficiency
* Core belief that most feelings are dangerous and must be controlled, and others are less precise or not in control
* Core belief that most feelings are dangerous and must be controlled, and others are less precise or not in control