CB570 - Module 9 Kidney, Bladder, and Testes Pathology
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
48 Terms
Functions of the Kidney
Regulate fluid and electrolytes in the body, remove waste products, produce hormones.
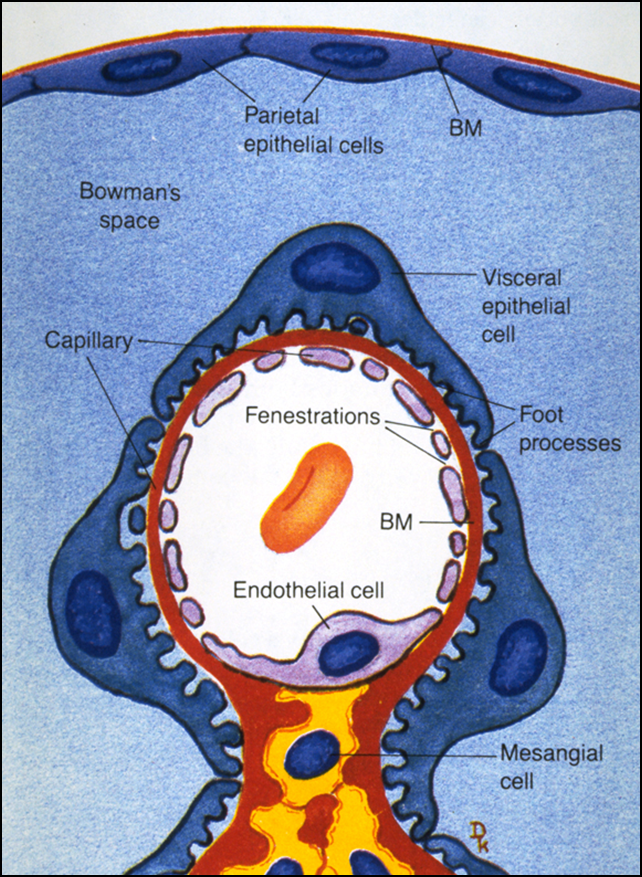
Glomerulus
Capillaries beds and functional units of the kidney, where the filtration happens.
Hormones Produced by the Kidneys (2)
Renin
Erythropoietin
Periodic Acid Shift Stain (PAS Stain)
Stains for the presence of sugar.
Bowman’s Capsule
The cup around the glomerulus, beginning of the urinary space.
Horseshoe Kidney
Associated with Turner’s syndrome. Typically asymptomatic.
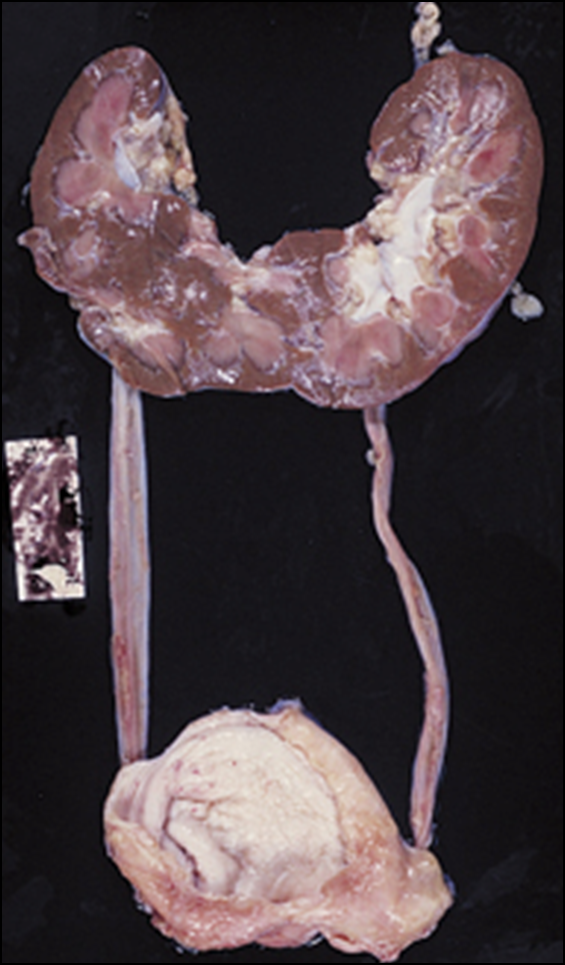
Cystic Renal Dysplasia
Failure of the kidney to develop properly, disorganized and undifferentiated cells. Typically unilateral —> bilateral is not compatible with life.
Polycystic Kidney Disease
Autosomal dominant genetic disorder which causes cysts on the kidneys, liver, and ovaries. Presented with blood in the urine and increased nitrogen in the blood. Transplant and dialysis are necessary by midlife.
Nephrotic Syndrome
Protein lost to the blood due to glomerulus damage. Results in lack of protein, high blood lipid (liver compensation), and edema.
Nephritic Syndrome
Inflammatory response to the kidney, causing reducing glomerular filtration and urine. Symptoms include blood in the urine, lack of urine, and hypertension.
Factors Which Prevent Proteins from Crossing the Glomerulus (2)
Epithelial cell foot processes
Negative charge of the basement membrane
Minimal Change Nephrotic Syndrome
Most common cause of nephrotic syndrome in children.
Epithelial cells lose foot processes.
Types of Inflammatory Glomerulonephritis (3)
Anti-GBM antibody (basement membrane rxn)
Immune complex (post-infection)
Anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibody (binding PNM)
Membranous Glomerulopathy (Immune Complex Disease)
Most common cause of nephrotic syndrome in adults, immune complexes “gum up” the glomerulus.
HIV-Associated Nephropathy
Damage to the kidney associated with HIV, can be shown with a silver stain to show matrix proteins leaking into improper spaces.
Diabetic Glomerulopathy
Most common cause of end stage renal failure, related to hyperglycemia. Basement membrane thickens and foot processes are lost.
Results in protein loss.
Revealed with PAS stain for sugar.
Amyloid Nephropathy
Abnormal proteins in the blood gum up the kidney, such as excess antibody chains in lymphoma patients.
Negative for PAS stain.
Crescentic (Rapidly Progressive) Glomerulonephritis
Massive proliferation of parietal epithelial cells, Bm disrupted, foot processes lost, fibrin formation.
Benign Nephrosclerosis
Scars on the kidney formed during hypertension. Kidney atrophies due to reduced blood flow.
Most common cause of end stage kidney disease in the black adult demographic.
Renal Infarct
Caused by an embolism typically, areas of necrosis on the kidney.
Renal Cortical Necrosis
Can be caused by shock, lack of blood flow to the outer regions of the kidney.
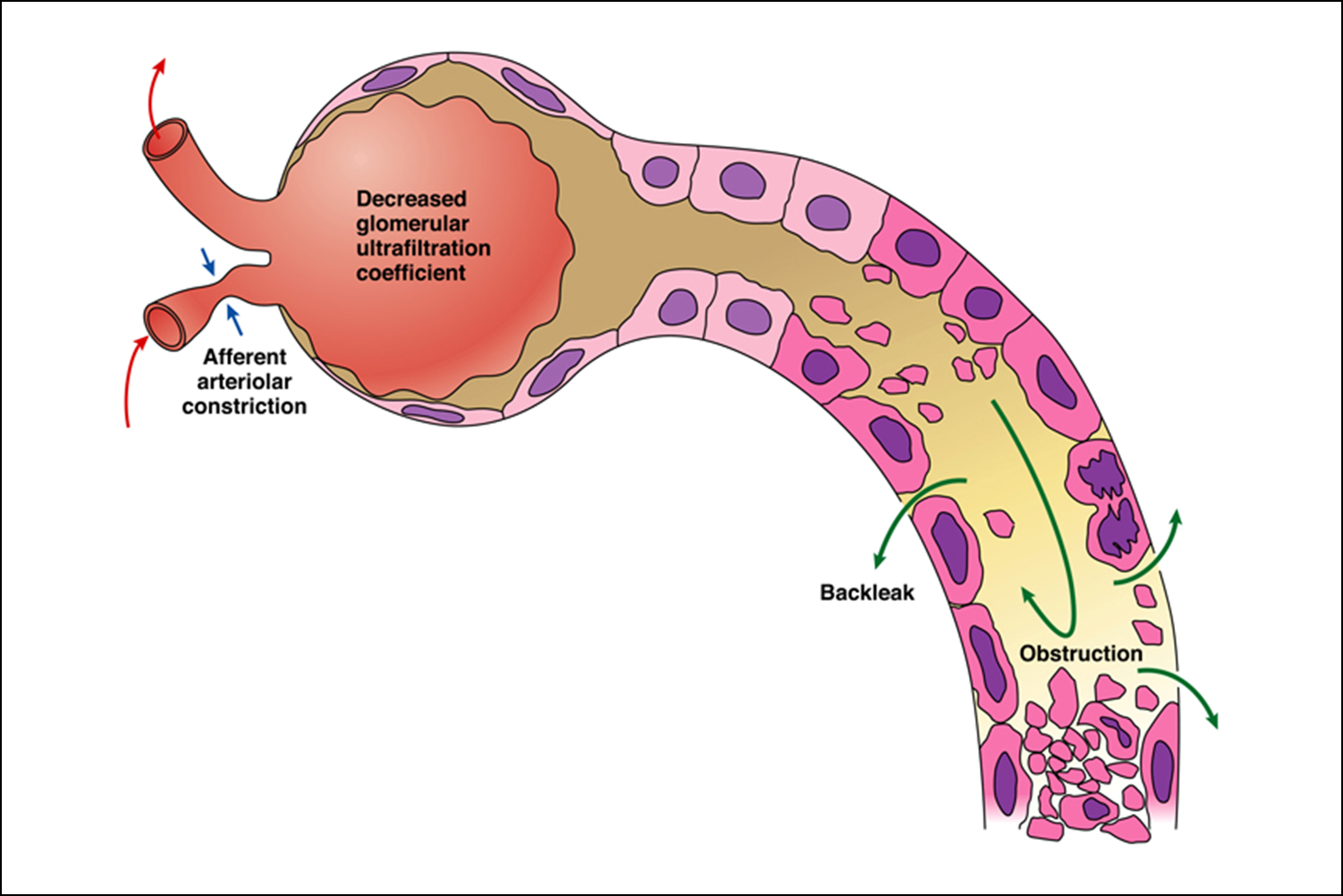
Acute Tubular Necrosis (ATN)
Urine concentrating tubules are damaged or poisoned, can cause backleak and renal failure.
Pyelonephritis
Angle of urine expulsion must be acute, if it is flattened then UTIs can travel up the ureter via urine reflux and infect the kidney.
Can be acute of chronic.
Causes of Chronic Pyelonephritis (2)
Ureteral reflux
Obstruction
Nephrolithiasis
Kidney stones, can be made of calcium, infection material, or uric acid.
Hydronephrosis/Hydroureter
Dilation of the renal collecting ducts and ureter respectively, due to obstruction typically by kidney stones.
Wilms Tumor
Most common abdominal solid tumor in children, forms on the kidney.
Renal Cell Carcinoma
Accounts for 90% of kidney cancers.
Oliguria
Lack of urine
Transitional Cell Carcinoma of Ureter
Transitional cells are stretchy cells (for filling with urine), only appear in the bladder and ureter, so this cancer is specific to this tissue.
Congenital Exstrophy of Bladder
Lumen of the bladder is external due to lack of abdominal formation. Gene mutation is unknown.
Acute Hemorrhagic Cystitis
Bladder is damaged via inflammation. Risk factors include being female, pregnancy, or infection.
Causes painful urination.
Transitional Cell Carcinoma of Bladder
Tumor in the bladder. Standard of care is to induce inflammatory reaction via BCG infection (TB family member)
Bladder Carcinoma Staging
A (non-invasive)
C (invasive)
Cryptorchidism
Testes do not drop from the abdomen. Causes infertility and high risk of germ cell neoplasms in teens and 20s.
Leydig Cell Tumor
May present in a teen with cryptorchidism. Tumor of the cells surrounding the germ cells in the testicle.
Embryonal Carcinoma
Type of testicular cancer where embryonic layers begin to form.
Intratubular Germ Cell Neoplasia (Carcinoma In Situ)
Early stage cancer of the testicles.
Seminoma
Malignant germ cell tumor in the testicle. Lance Armstrong had this.
Choriocarcinoma
Testicular tumor that secretes hCG, would cause a positive pregnancy test on a male.
Types of Scrotal Masses (Benign, 3)
Hydrocele (collection of fluid, hematocele is blood collection)
Varicocele (varicose veins, cause infertility)
Spermatocele (ductule collection of fluid)
Prostatitis
Prostate inflammation, typically from E. coli.
Nodular Prostatic Hyperplasia
Enlarged prostate typically seen in older males. May cause trouble with urination, frequent urination, or frequent pyelonephritis.
Prostatic Adenocarcinoma
Most common cancer in males.
Markers for Prostate Damage (2)
PSA
PAP
Not perfect because things like ejaculation can cause level spikes.
Prostatic Adenocarcinoma Staging
A or B (Localized to prostate, non-invasive)
C or D (metastasis and lymph node invasion)