AP STATS UNIT ONE
1/51
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
52 Terms
individuals
subjects described by a set of data or part of the set of data
variables
characteristics of individuals
catergorical vs quantitative
categorical variables
places an individual into one of several groups or categories
ex) gender, zip codes, political party, grades
quantitative variables
take numerical values
ex) number of pets, time, height
discrete vs continuous
discrete quantitative variables
countable values
ex) number of siblings
continuous quantitative variables
measurable values
ex) weight
representing categorical data
tables: one way vs two way
bar graphs
one way table
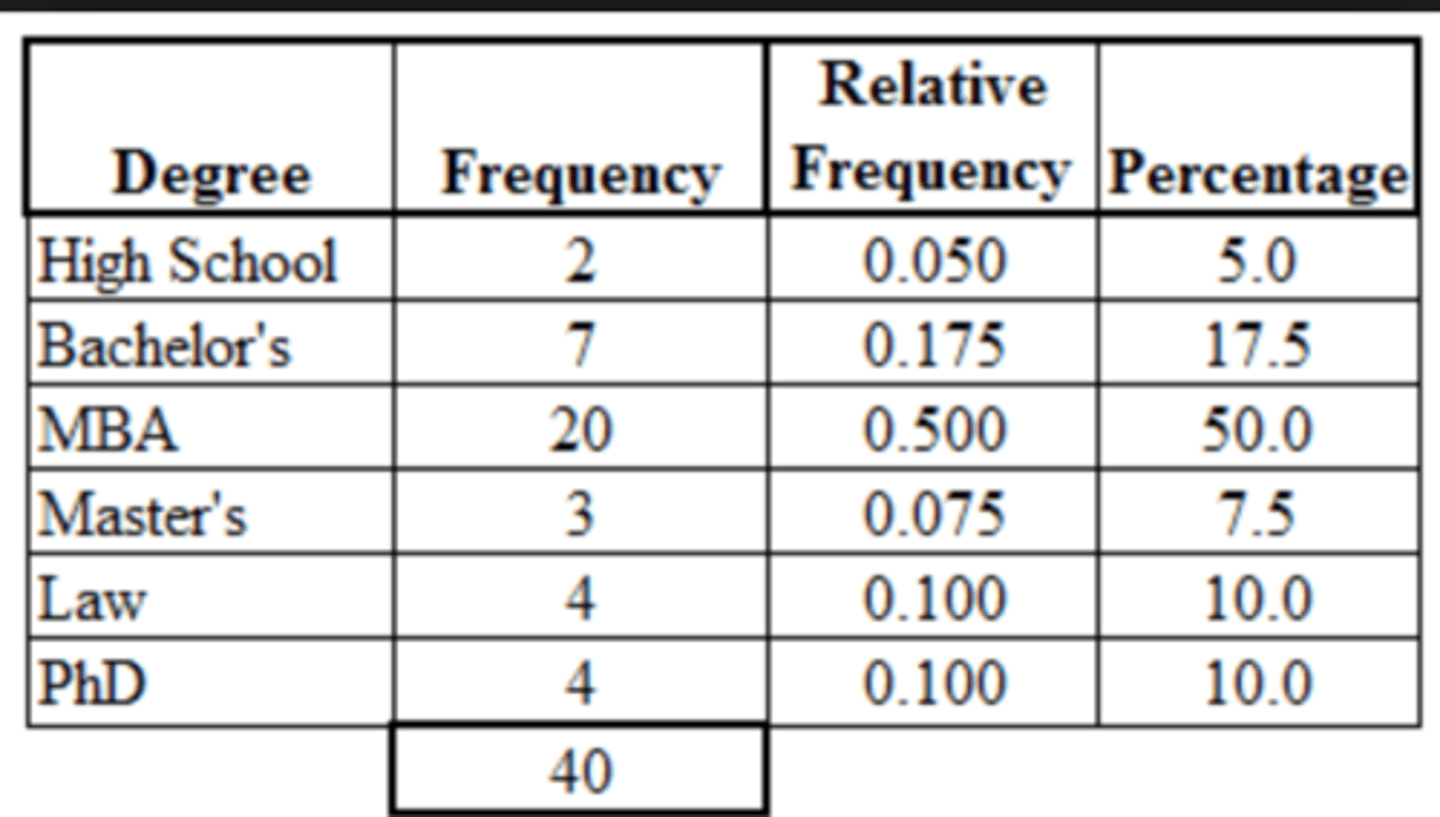
relative count/frequency
count/total = % or decimal
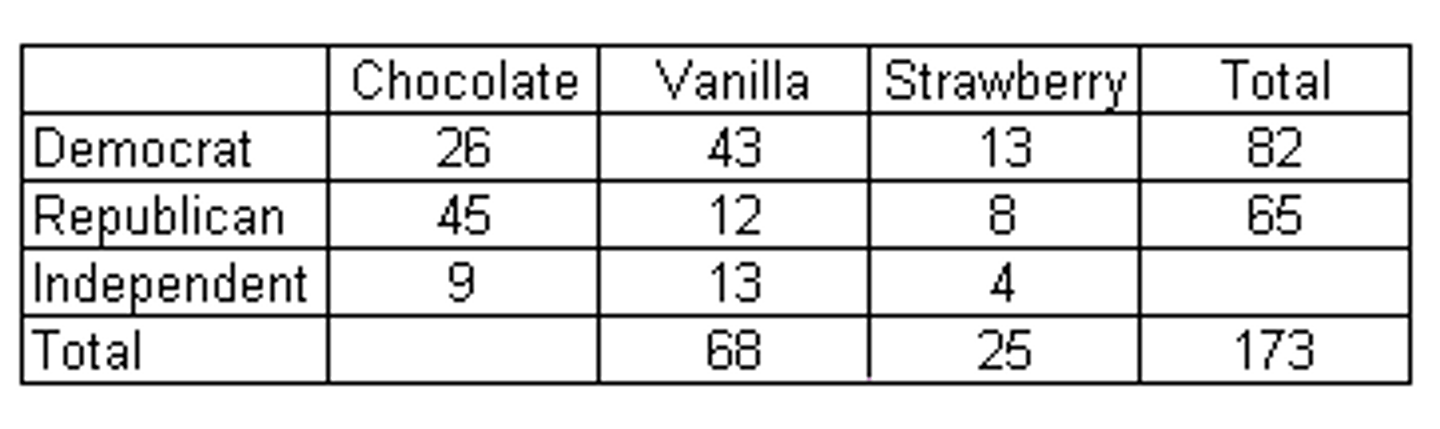
two way table
bar graphs
representing quantitative variables
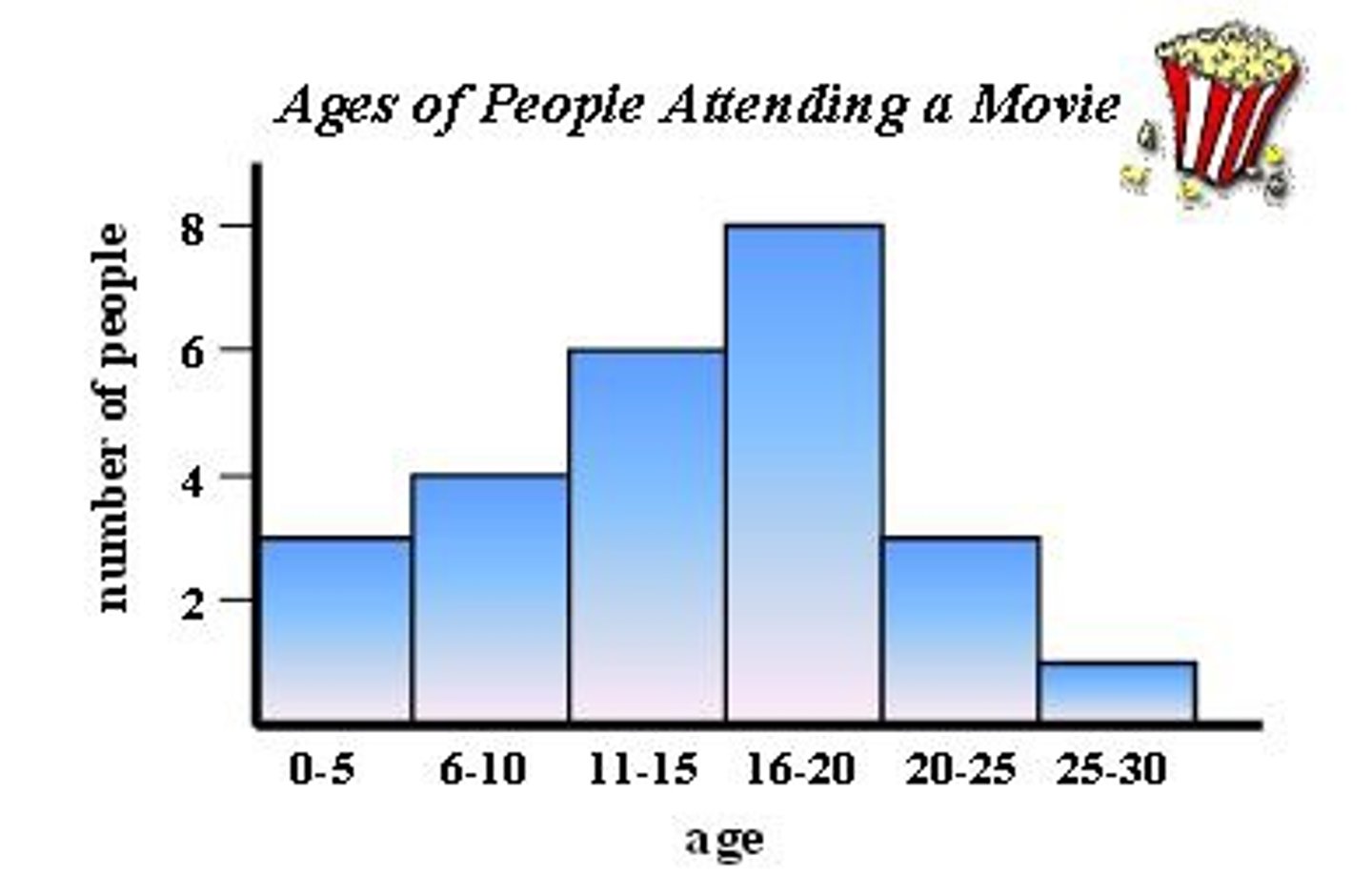
histograms
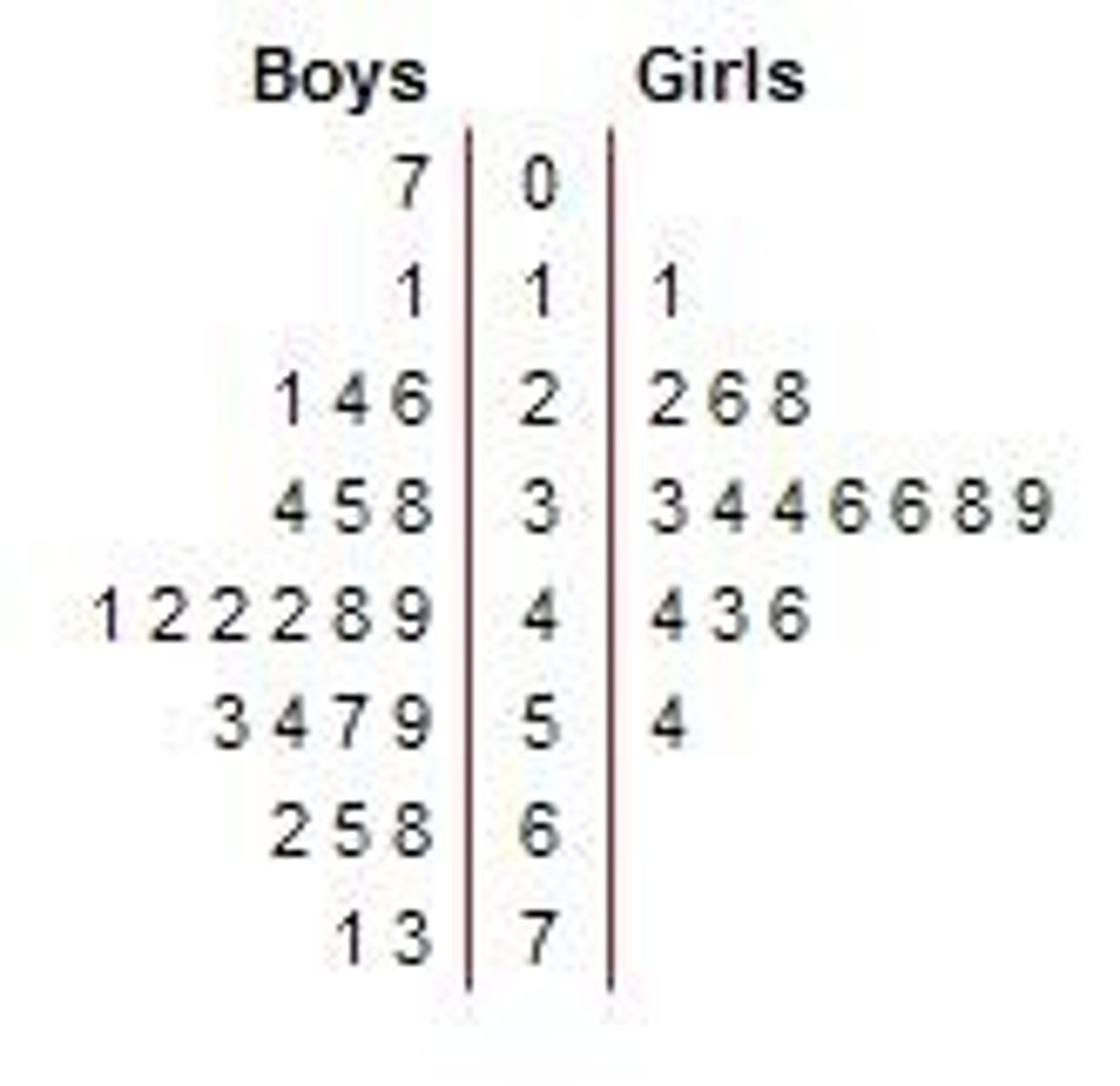
stem and leaf: stemplots, back-to-back stemplots
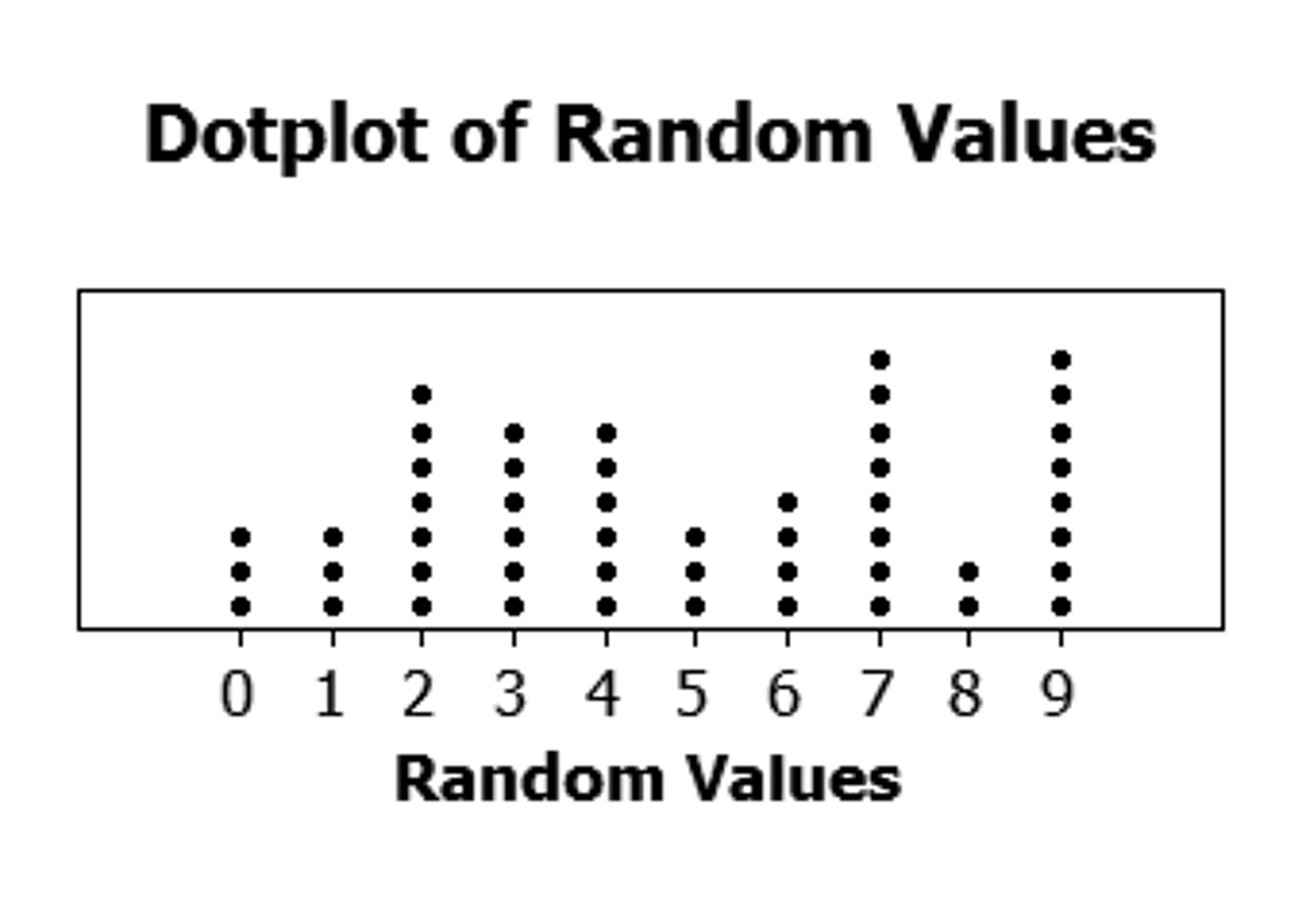
dotplots
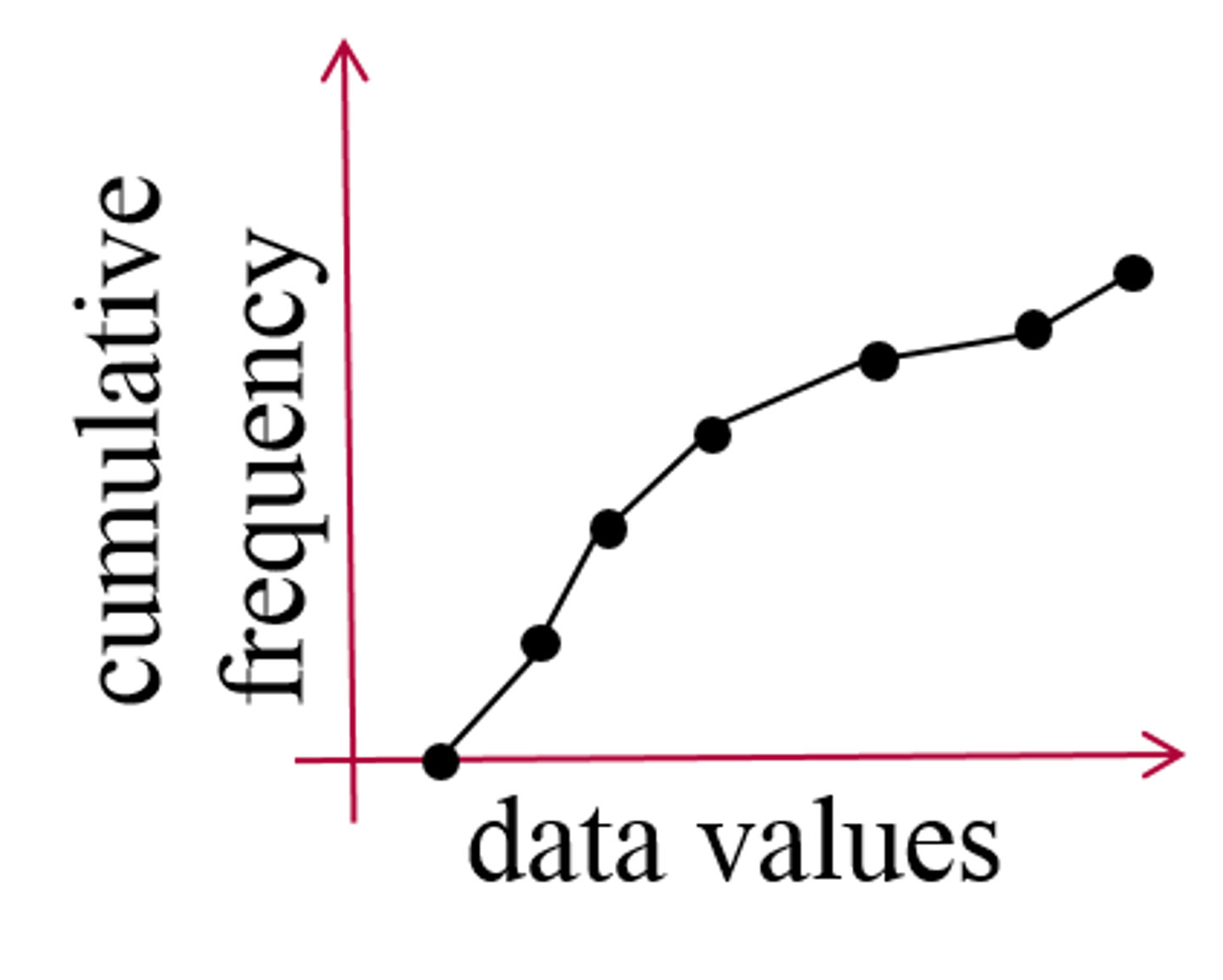
cumulative relative frequency graphs (ogives)
histograms
(max - min)/number of bins
stemplots
DO NOT FORGET KEY
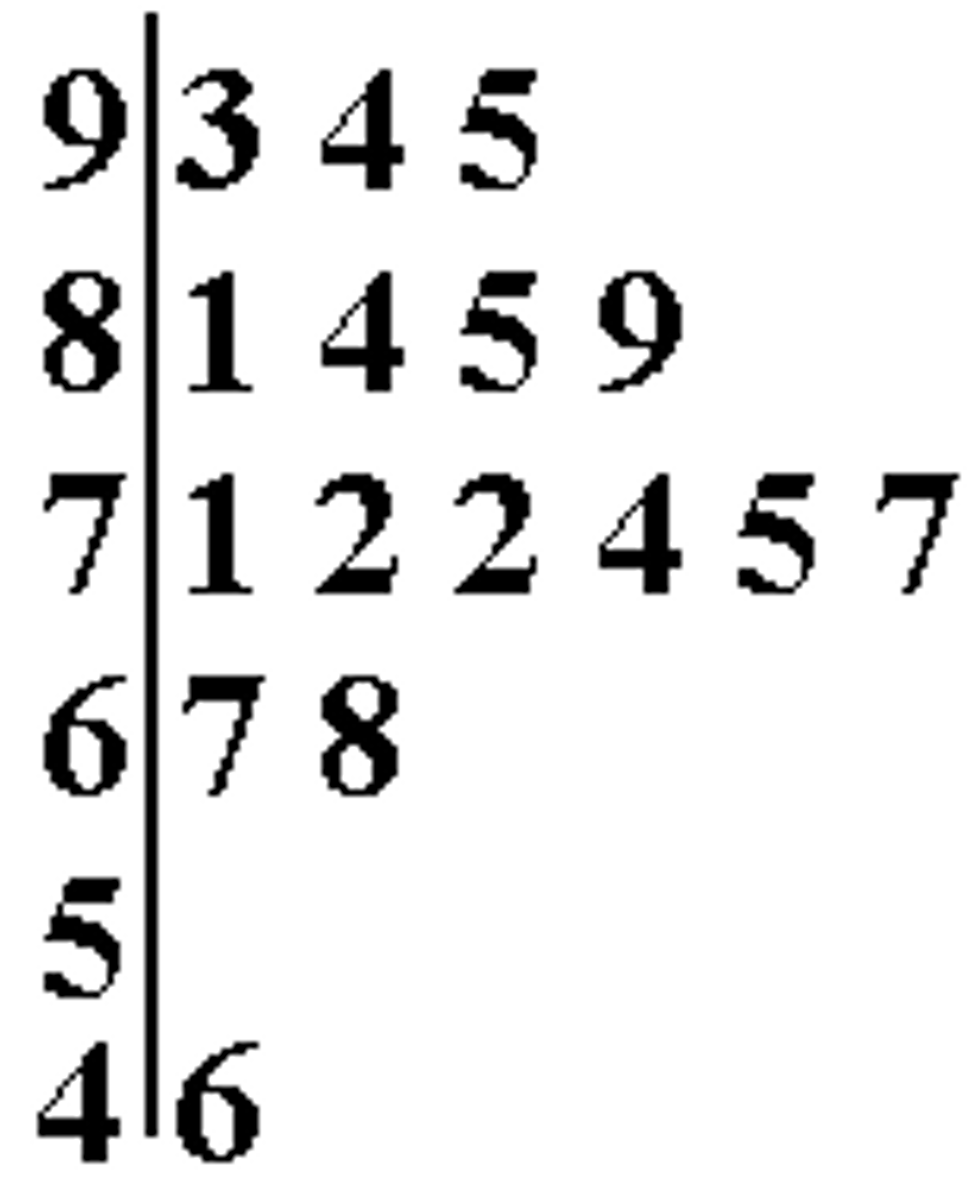
back-to-back stemplot
dotplots
ogives
1. relative frequency
2. add percents together cumulatively
-> start at minimum x value not zero
percentiles
indicate the distance of a score from 0
ex) 99th percentile score = 99% people scored lower
describing distributions
SOCS (shape, outliers, center, spread)
-> quantitative values only
shape
unimodal, bimodal, uniform, symmetric, left skewed, right skewed
outliers
visual outliers, outlier tests, standard deviation rule
outlier test
Q1-1.5(IQR) lower
Q3+1.5(IQR) upper
standard deviation rule
Mean +- 2*SD
center
mean, median, mode
non-resistant
mean
resistant
median, mode
center for left skewed
mean < median < mode
center for right skewed
mode < median < mean
spread
range, standard deviation, IQR
range
max - min = range
standrad deviation
average deviation of an observation from the mean
variance
(standard deviation)^2
greater standard deviation
greater variation
broader curve
center-spread pairs
standard deviation - mean
IQR - median
IQR
Q3-Q1
boxplots
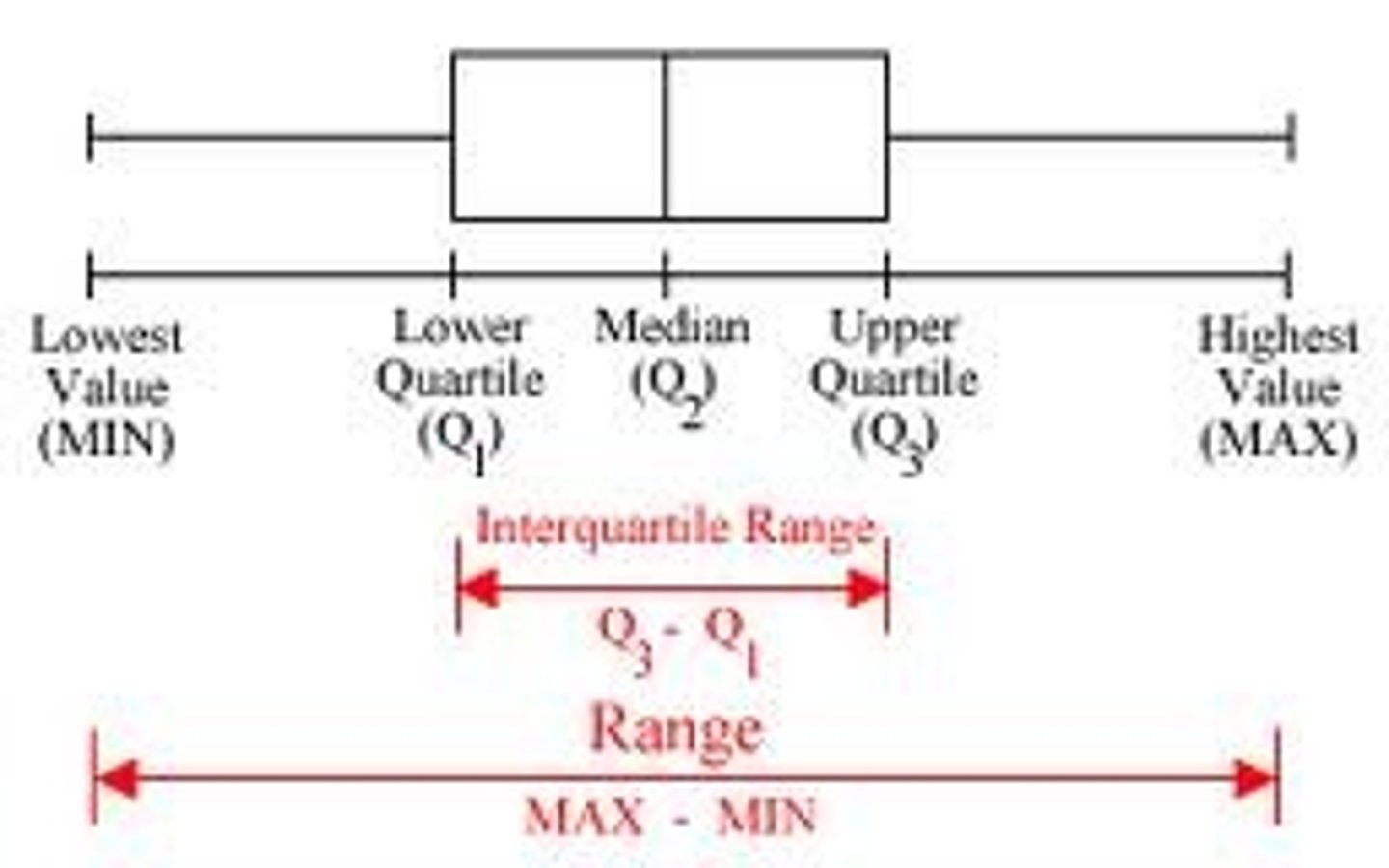
"describe the distribution"
1. create your graph (categorical/quantitative)
2. summarize findings
"compare the distributions"
use comparison words (smaller, greater than, etc)
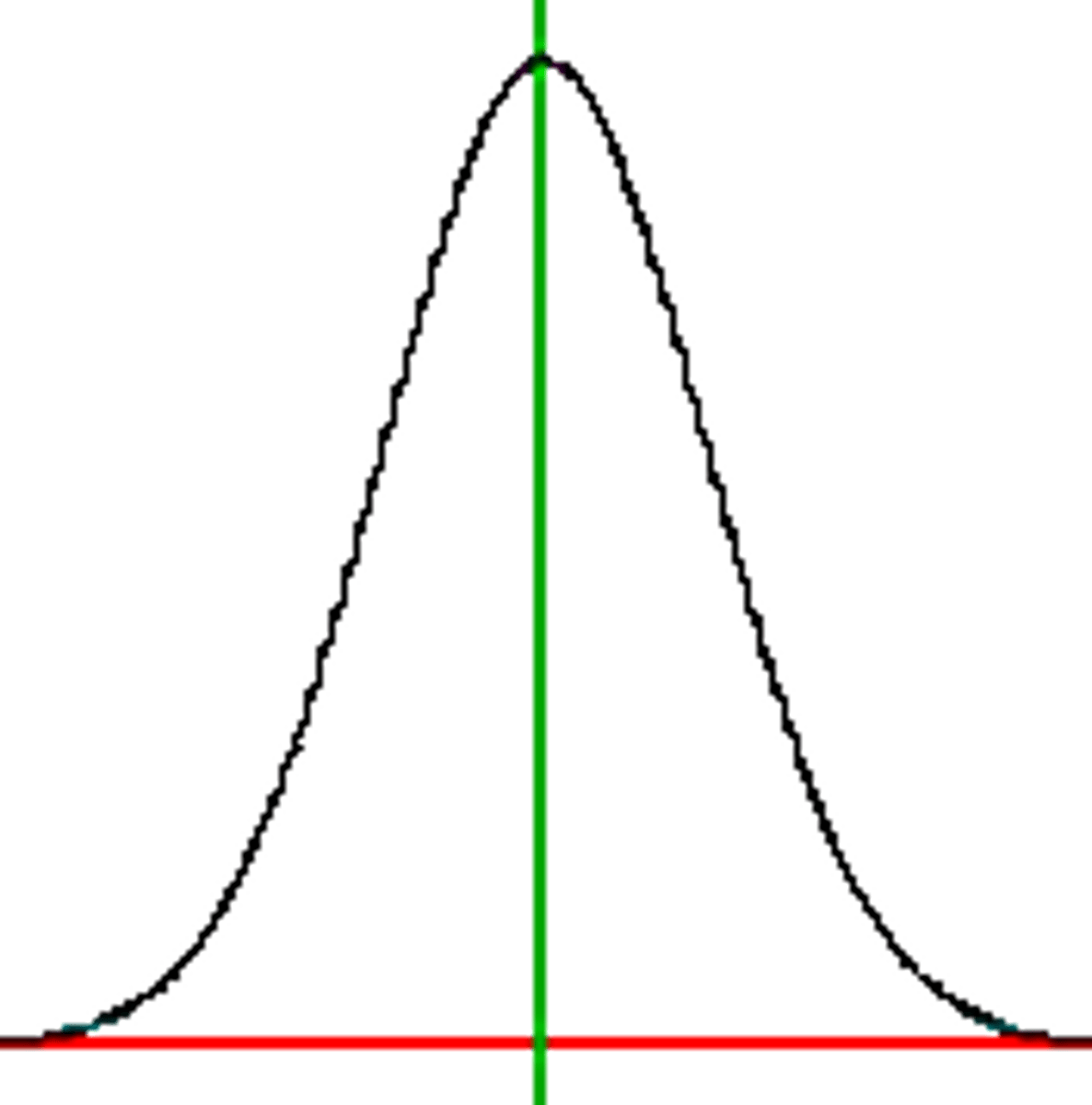
normal curve
A symmetrical, bell-shape that describes the distribution of many types of data
-> almost all data lie within 3 standard deviations
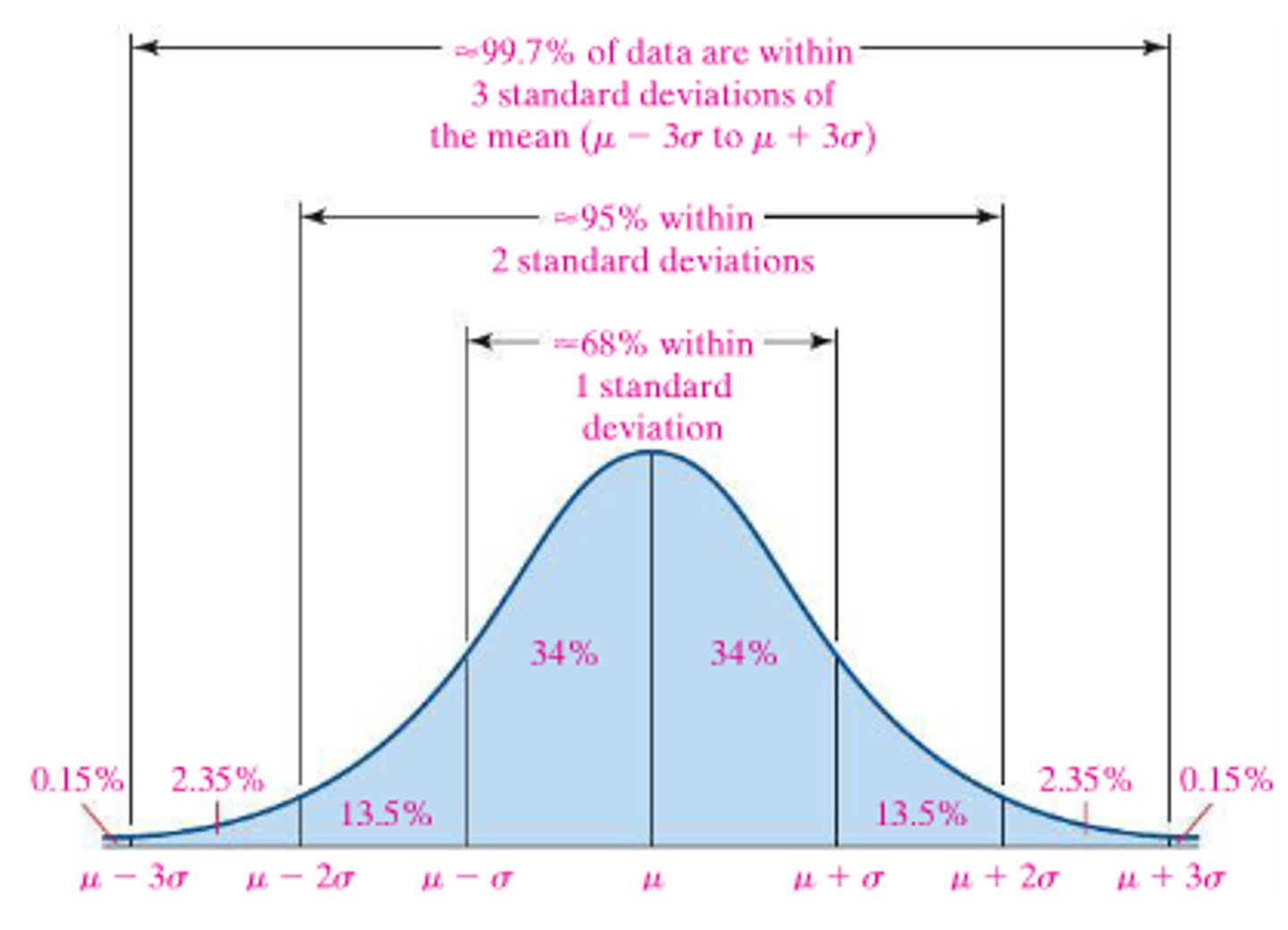
emperical rule
68-95-99.7
standardizing
making the mean 0 and standard deviation of 1 through z-scores, calculation of how far away an observation is from its mean
-> not just for normal distributions
z-score
(x-mean)/standard deviation
z-score interpertation
how many standard deviations you are away from the mean
ex) z-score of .67 means that score X is .67 SD away from the mean
standard normal curve
for any normally distributed curve
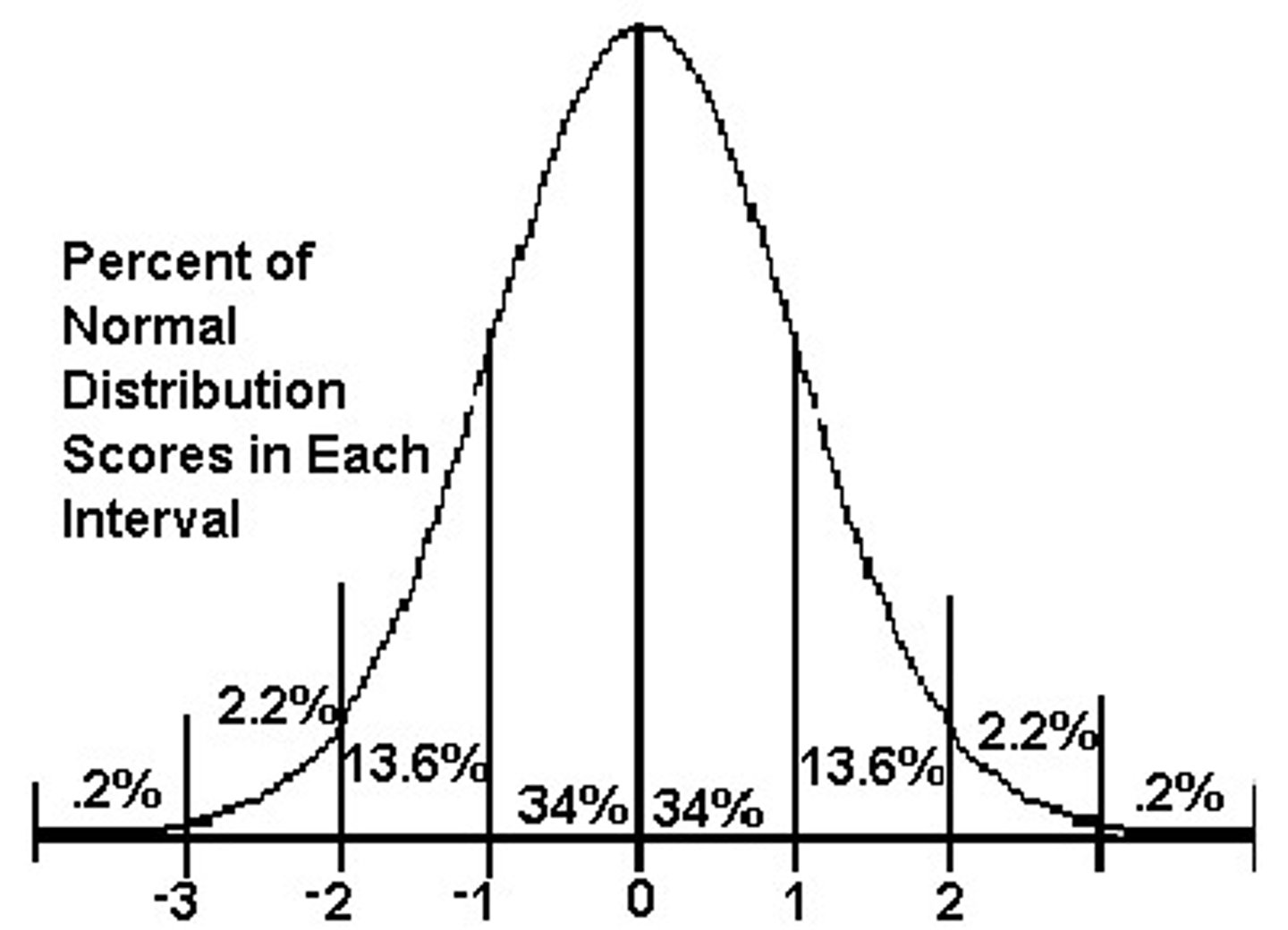
standard normal probability table
calculator-directions:
2nd -> vars
2: normalcdf(
percent of data below/between/above z-score of X
P(z < z score number)
calculator directions
SHOW probability, test name, numbers plugged into calculator
percent of subject below/between/above number X
P(x < number)
calculator directions
SHOW probability, test name, numbers plugged into calculator
comparison of below/between/above number X and z-score of X
give out same exact results
using z scores in word problems (for FRQs only)
P(x < number) = P (z < z score number)
percentages to z-score
(opposite of cards 46-49)
calculator directions:
2nd -> vars
3: invNorm(
percentages to raw data
1. percentile -> percentage below
2. calculator directions
3. plug in z score, mean, and standard deviation
4. solve for x
percentage lies BETWEEN distribution when
percentage to raw data
(1 - middle/symetrically orientated percentage)/2 = area