4.1.3 Alkenes
1/93
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
94 Terms
Are alkanes saturated or unsaturated?
unsaturated
What is the functional group in alkenes?
C=c
What is the general formula of alkenes?
CnH2n
What bonding exists between alkene molecules?
induced dipole-dipole
Where do we source alkenes from?
crude oil
cracking
elimination reaction
What are alkenes used for?
plastics
laquers
detergents
fuels
in a prop-1-ene what is the bond angle of C1?
120*
in a prop-1-ene what is the bond angle of C3?
109.5*
What is a hydrocarbon?
a compound that only consist of hydrogen and carbon
What are C=C bonds made of?
one sigma bond
one pi bond
Describe the rotation of a C=C bond
restricted rotation
In a C=C bond, how is the sigma bond formed?
direct overlap of orbitals directly beyween bonding atoms
How is a pi bond formed?
fouble, sideways overlap of adjacent p orbitals above and below the bonding C atoms
Draw a diagram to show a C=C double bond

Draw a diagram to show the formation of a pi bond
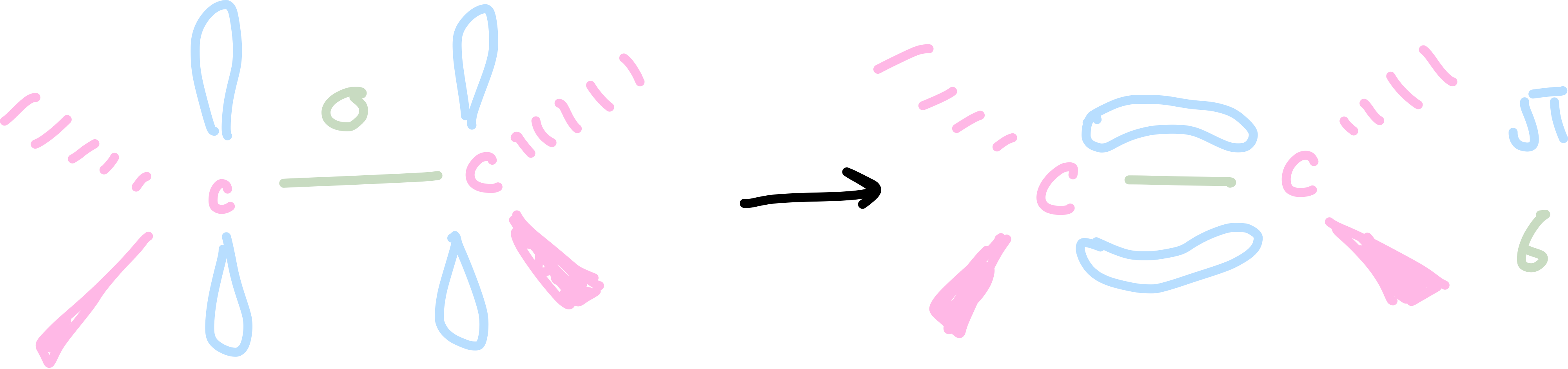

Explain the shape around each C atom in a C=C double bond
120* / trigonal planar
three bonding regions and no lone pairs of electrons
bonding regions repel each other equally
all of the atoms are in the same place
Define stereoisomers
compounds with the same structural formula but with a different arrangement of atoms in space
Where does E/Z isomerism occur?
molecules containing a C=C bond
Why does E/Z steroeisomerism require a C=C bond?
it can’t rotate so the atoms attatched to the C=C are fixed in space
What is the criteria for a compound to show E/Z steroisomerism?
most have a C=C bond
each C of the C=C bond must have two different groups attached to it
What is the criteria for a compound to be a Z isomer?
the groups with the highest prioority are on the same side of the double bond
What is the criteria for a molecule to be a E steroisomer?
the groups with higher priority are on diagonally opposite sides of the double bond
Who set out the rules to classify stereoisomers?
Sidney Cahn
Kelt Ingold
Vladimir Prelog
When were the rules to classify steroisomers set out?
1951
How are groups on the C=C bond assigned priority?
higher atomic number = higher priority
If the 2 atoms attatched to a carbon atom in a double bond are the aame what must you find?
the first point of difference
For molecules where the atoms attatched to the carbon atom in a double bond is the same how do you assign priority?
the higher atomic number a the first point of difference is given higher priority
Out of CH2CH2OH and CH2CH2Cl which has highest priority?
CH2CH2Cl
What are cis/trans isomers?
special type of E/Z isomerism
What is the criteria for a compound to show cis/trans isomerism?
must have a C=C bond
each carbon of the C=C bond must be attached to 2 different groups
two groupd on the C=C bond must be identical
If there are 2 hydrogen atoms in the steroisomer then will the cis isomer be Z or E?
Z
If there are 2 hydrogen atoms in the steroisomer then will the trans isomer be Z or E?
E
Which nomenlature should be used for steroisomerism by preference?
E/Z
Compare the reactivity of alkanes and alkenes
alkenes are more reactive than alkanes
WHy are alkenes more recative than alkanes?
C=C bond
What types of reactions do alkenes undergo?
addittion
What happens in an addition reaction?
a group is added across the C=C double bond
Which bond breaks in an addition reaction an why?
pi bond
How many products are formed in addition reaction?
1
What is the atom economy of an addition reaction and why?
100% - there are no waste products
What is the chemical test for a C=C group?
add bromine (or bromine water)
What is a positive result for C=C group?
bromine is decolourised
Write an equation for the testing/ positive result of C=C test
CH2=CH2 + Br2 → CH2BrCH2Br
What is the reagents needed to form alkane from alkene?
Hydrogen gas (H2)
What are the conditions needed to react hydrogen and alkene?
Nickel catalyst (Ni(s))
150*C
What reagents are needed to form hydrogen halide (and BR2) from alkane?
HX or X2
What conditions are required to react hydrogenhalide (and BR2) and alkane?
no catalyst
room temperature
What are the reagents to form an alcohol from an alkene?
steam
What are the conditions to react steam and alkene?
high temp (>100*)
high pressure
concentrated phosphoric acid
What mechanism d alkenes undertake when reacting?
electrophilic addition
What is an electrophile?
an electron pair acceptor
Why do alkenes attract electrophiles?
the C=C bond is a region of high electron density
How is the electrophilic addition mechanism shown?
curly arrow model
What does a curly arrow show in a model?
the movement of an electron pair to either break or make an electron pair
Draw the electrophilic addition mechanism for ethene an hydrogen bromide
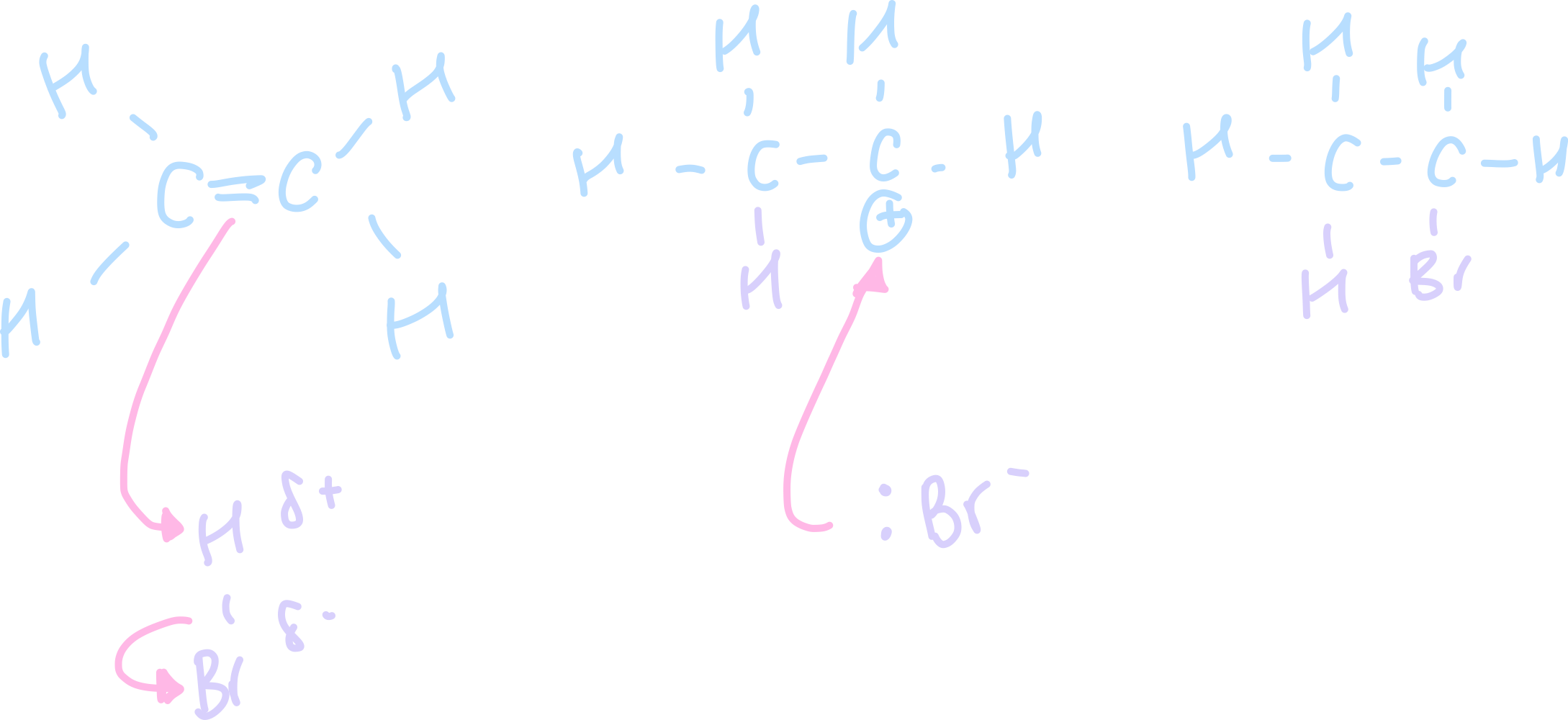
Explain/ describe the electrophilic addition of ethene and hydrogen bromide?
HBr is a polar molecule bcause Br is more electronegative than H and there is a permanent dipole
H acts as an electrophile (of HBr)
H of HBr is attracted to electron dense pi bond
H accepts a pair of electrons from pi bond
pi bond breaks by heteolytic fission
CH bond forms, HBR bond breaks
carbocation and Br-
combine to form the organic product
Why is HBr a polar molecule?
Br is more electronegative than H
Which bit of the HBr acts as an electrophile?
H
Where does H of HBR accept an electron from?
pi bond
When H accepts electron pair from pi bond what bonds are formed and broken
CH bond formed
HBr bond broken
What are the intermediate products of electrophilic addition of ethene and HBr?
Br-
carbocation
What is the final product of electrophilic addition of HBr and ethene?
Bromoethane
What happens when an unsymmetrical molecule undergoes an addition reaction with an alkene?
2 products are formed
What 2 products are formed when propene and hydrogen bromide react?
2 bromopropane
1 bromopropane
What can we label the 2 products as when 2 products are made from electrophilic substitution of alkene?
major and minor
How do we determine which is the major or minor product?
based on carbocation
What is Markownikoff’s rule?
when a hydrogen halide reacts with an unsymmetrical alkene, the hydrogen of the hydrogen halide attatches itself to the carbon atom wth the larger number of hydrogen atoms
Are carbocations wit more alkyl groups more or less stable?
more
Why are carbocations with more alkyl groups attatched more stable?
the alkyl groups donate electrons toward the positive charge which allows the charge to spread
How are carbocations classified?
primary (1 alkyl)
secondary (2 alkyl)
tertiary (3 alkyl)
Which is the major product?
the product in which the O or halide attatches to the C with the largest number of alky groups attatched
Why is the product where the more electronegative atom of unsymetrical molecule is attatched to carbocation with more alkyl groups major?
it is more stable
When alkenes join together what do they form?
addition polymers
What type of reaction is the joingin of many alkene monomers?
addition polymerisation
What are the reagents for addition polymerisation?
alkene monomer
What are the conditions for addittion polymerisation?
high temperature
high pressure
Draw the general equation for the formation of a polymer from alkene monomers
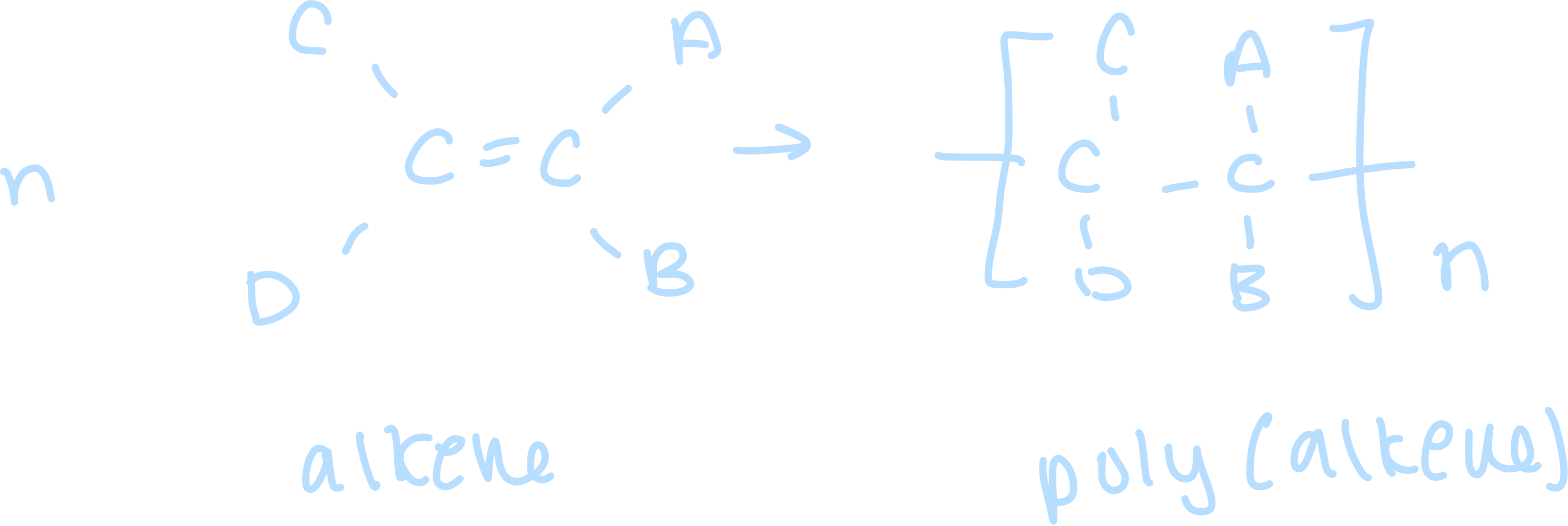
What does n represent in polymerisation?
thousands of monomer units
What is ethene polymerised to form?
poly(ethene)
What is polyethene used for?
packaging and bags
Give 2 problems with the disposal of addition polymers
they are not biodegradeable
burning produces toxic gases
Why are addition polymers non-biodegradable?
the C chain is non polar and can not be broken down by hydrolysis
they are very table and do not break down naturally or by microorhamisms at landfil sites
What can addition polymers produce when burned?
toxic gases
What gases are produced when pVC or other chlorine containing polymes is burnt?
HCl and Cl2
How can waste addition polymers be processed?
combustion for energy production
removal of toxic wste products
used as organic feedstock
sorted into types and recycled
What are the benefits of combusting addition polymers?
burned as fuel to produce energy
Give an example of removing toxic waste products from addition polymers?
removal of HCl formed during combustion of PVC
How are waste addition polymers used as organic feedstock for plastics?
they are cracked into smaler chain alkanes and alkenes as an organic feedstock to produce new plastics
What are the benefits of using waste addition polymers as organic feedstock for plastics?
feedstock recycling
What are the roles of chemists in minimising damage of addition polymers?
develop biodegradeable poymers
develop photodegradeable polym ers
use an alkaline scrubbers to neutralise toxic HCl gas produced in burning
How are biodegradeable polymers broken down?
by microorganisms in water
Give an example of a biodegradeable polymer
PLA (polylacticacid)
What are photodegradeable polymers
polymers that are oil based that contain bonds weakened by absorbing light (C=O bonds)
How can we neutralise toxic HCl gas produced when chloropolymers are burned>
use an akaline scrubber