Lesson 4, DNA: Transcription and RNA
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
51 Terms
Transcription
First step in gene expression, generating an RNA molecule from a DNA template
Important because:
- if DNA is damaged, that change is permanent, but it is not with RNA (no replication)
- DNA is too large for translational machinery to access it
- DNA contains info that does not need to be translated
- RNA is small and single stranded, and it allows for the translation of a single protein
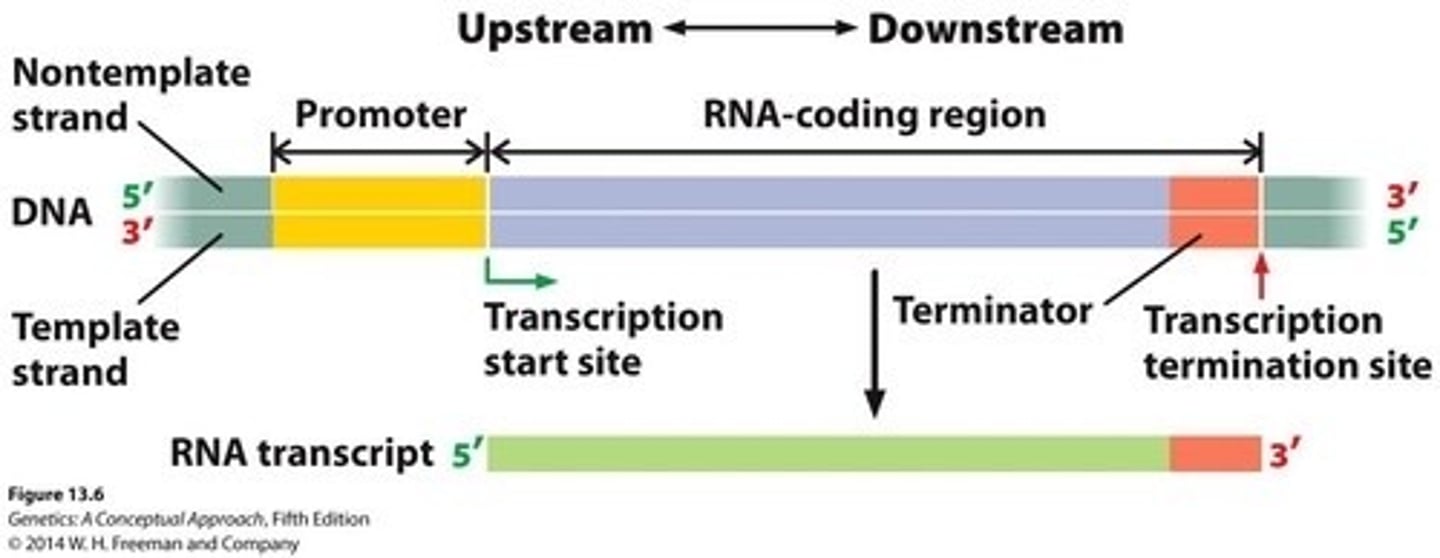
Gene
Transcription unit; a stretch of DNA that encodes an RNA molecule (either mRNA or a functional RNA)
Includes sequences in the DNA that have different roles:
- promotor
- coding region
- terminator
Functional RNA
A RNA molecule that functions without being translated. Carries out a job in the cell as RNA.
- rRNA
- tRNA
- ncRNA
Template strand
The DNA strand that provides the template for ordering the sequence of nucleotides in RNA
- Read in the 3' to 5' direction so that new DNA is generated in the 5' to 3' direction
- COMPLEMENTARY to the RNA molecule being synthesized
Can encode different genes than its complementary DNA strand
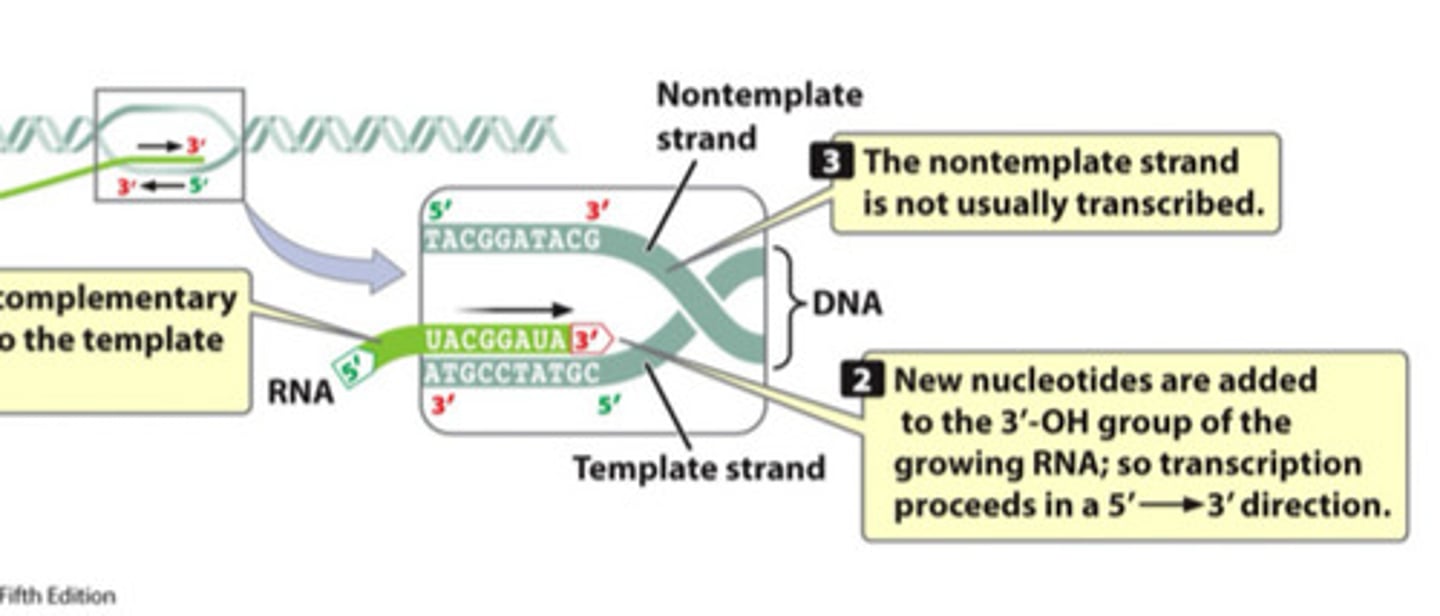
Coding strand
the strand of DNA that is not used for transcription
- IDENTICAL in sequence to mRNA, except it contains uracil instead of thymine
Can encode different genes than its complementary DNA strand
mRNA
Messenger RNA, carries genetic information for proteins.
rRNA
Ribosomal RNA, RNA component of ribosomes.
- Encoded by large genes; cleaved after transcription and assembled/processed in the nucleolus by snoRNAs
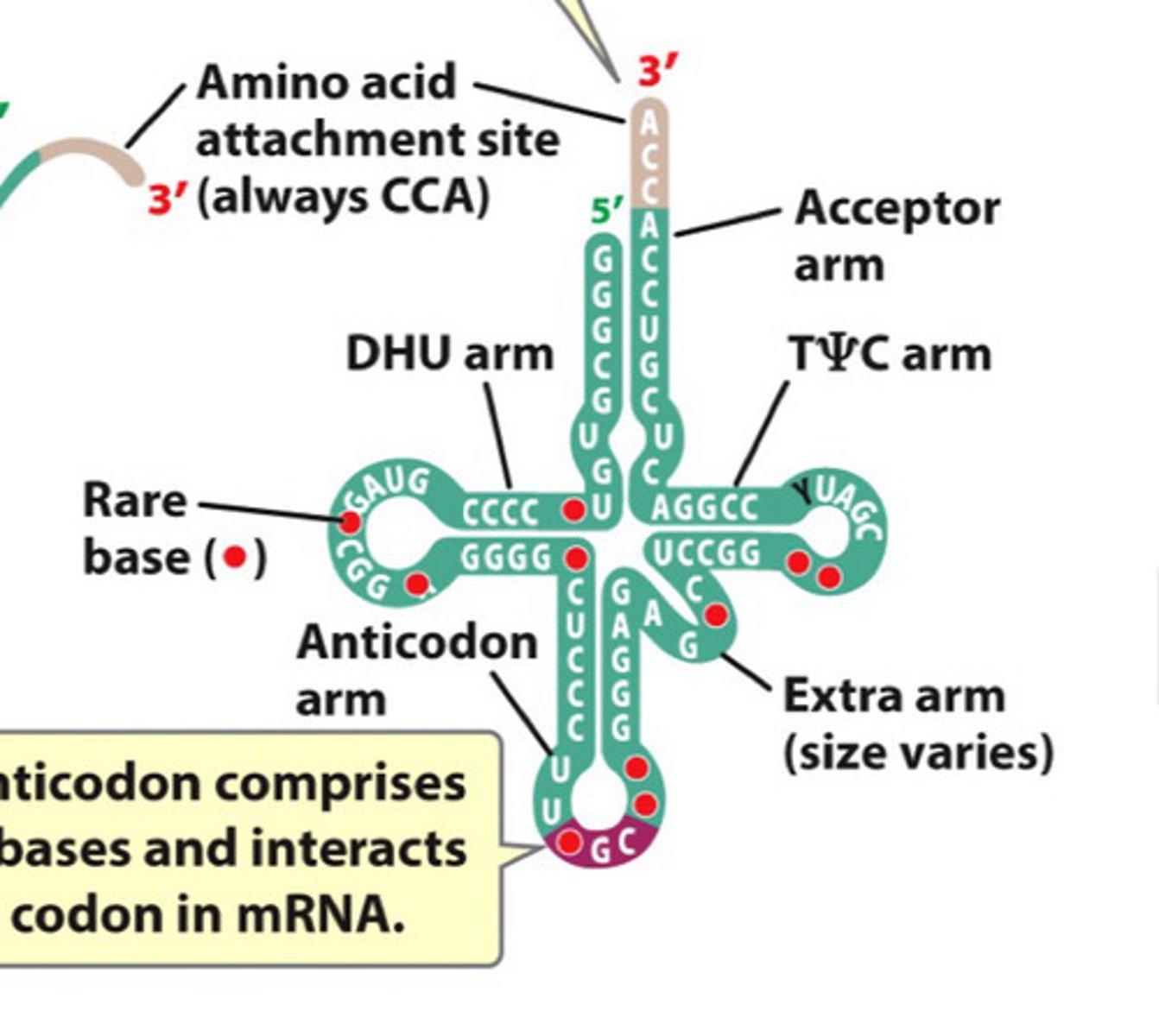
tRNA
Transfer RNA, links amino acids during translation
- characteristic secondary structure -
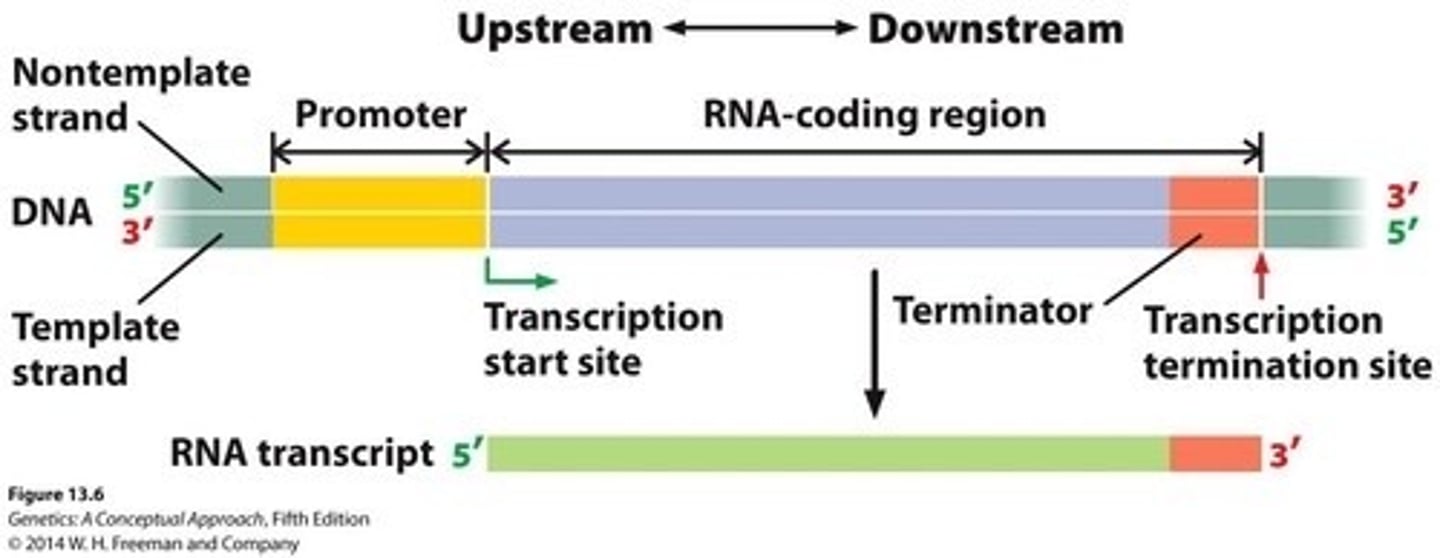
Promotor
DNA sequence initiating transcription process.
Shifting this region, will shift the transcription start site, because consensus sequences must always be at the -10 and -35 positions (bacteria)
Terminator
DNA sequence signaling end of transcription.
Sigma Factor
Protein aiding bacterial RNA polymerase initiation.
Eukaryotic Initiation
More complex than bacterial transcription initiation
- 3 types of multisubunit (12 subunits) RNA polymerase recognizes TATA box (-25 ish) in promotor
- General transcription factors assemble on the core promotor and recruit RNA polymerase II to the transcription start site (no sigma factor)
- Utilizes a core promotor AND regulatory promotor
Upstream
Region of DNA that is closer to the 5' transcription start site or past it
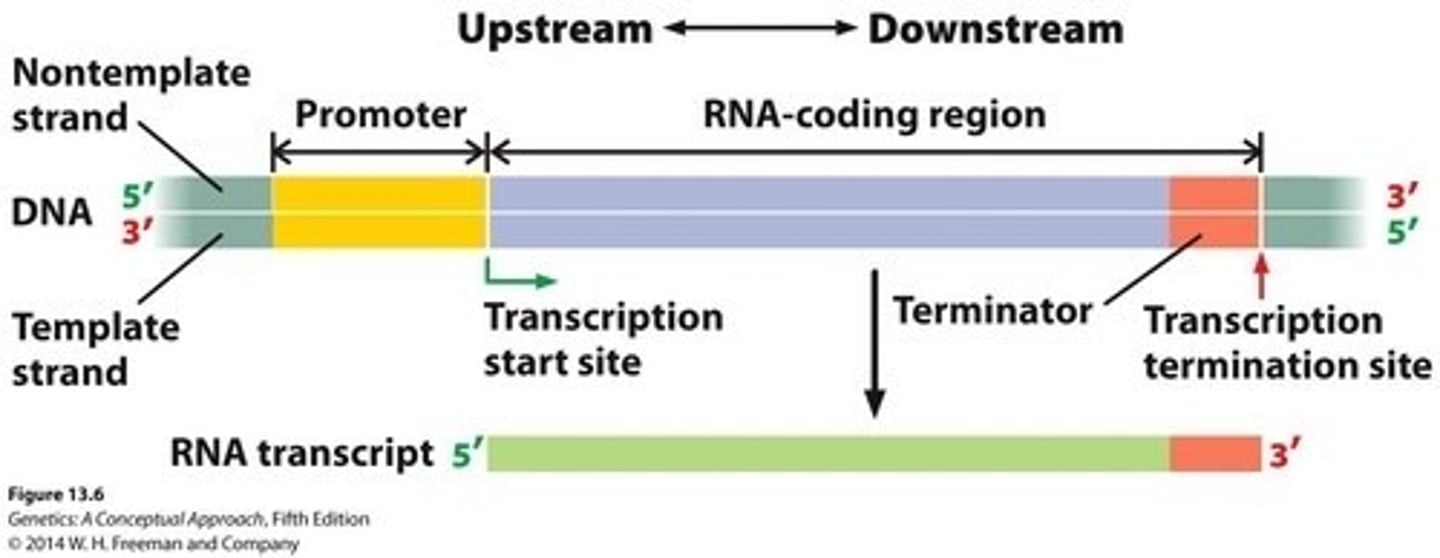
Downstream
Region of DNA that is closer to the 3' transcription termination site
RNA polymerase
Enzyme that synthesizes RNA from DNA template.
- Large
- Always adds to 3' OH (built 5' - 3')
- Unwinds and rewinds DNA in the absence of helicase
- Initiates new strand synthesis (no need for primers)
- Weak proofreading ability
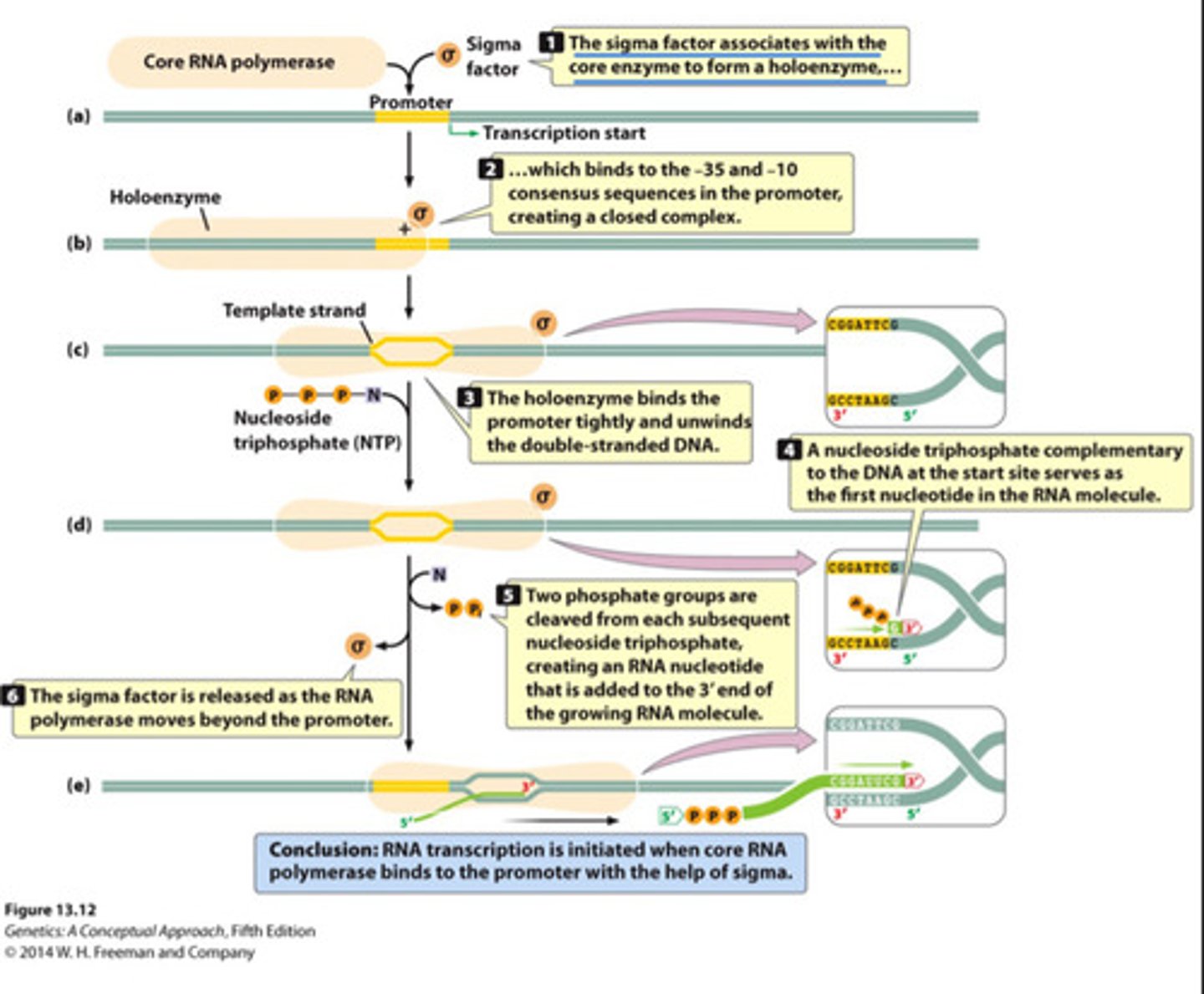
Bacterial transcription initiation
One multisubunit RNA polymerase recognizes -10 and -35 consensus sequences in promotor to orient the polymerase and begin transcription.
- Sigma factor protein guides RNA polymerase to the promotor and binds it to the template strand
Prokaryotic transcription termination
Transcription ending:
1. Rho independent- GC rich loop by palindrome, then UUU rich sequence. mRNA pulling itself out.
2. Rho dependent- rho protein run behind RNA pol. When there is a termination signal- a small loop forms and rho pushes the mRNA out.
Rho-dependent termination
in prokaryotes (50%), termination of transcription by an interaction between RNA polymerase and the rho protein.
- Binds at Rut site on new RNA strand and moves along the strand until it reaches the transcription bubble, where it separates RNA from the DNA template.
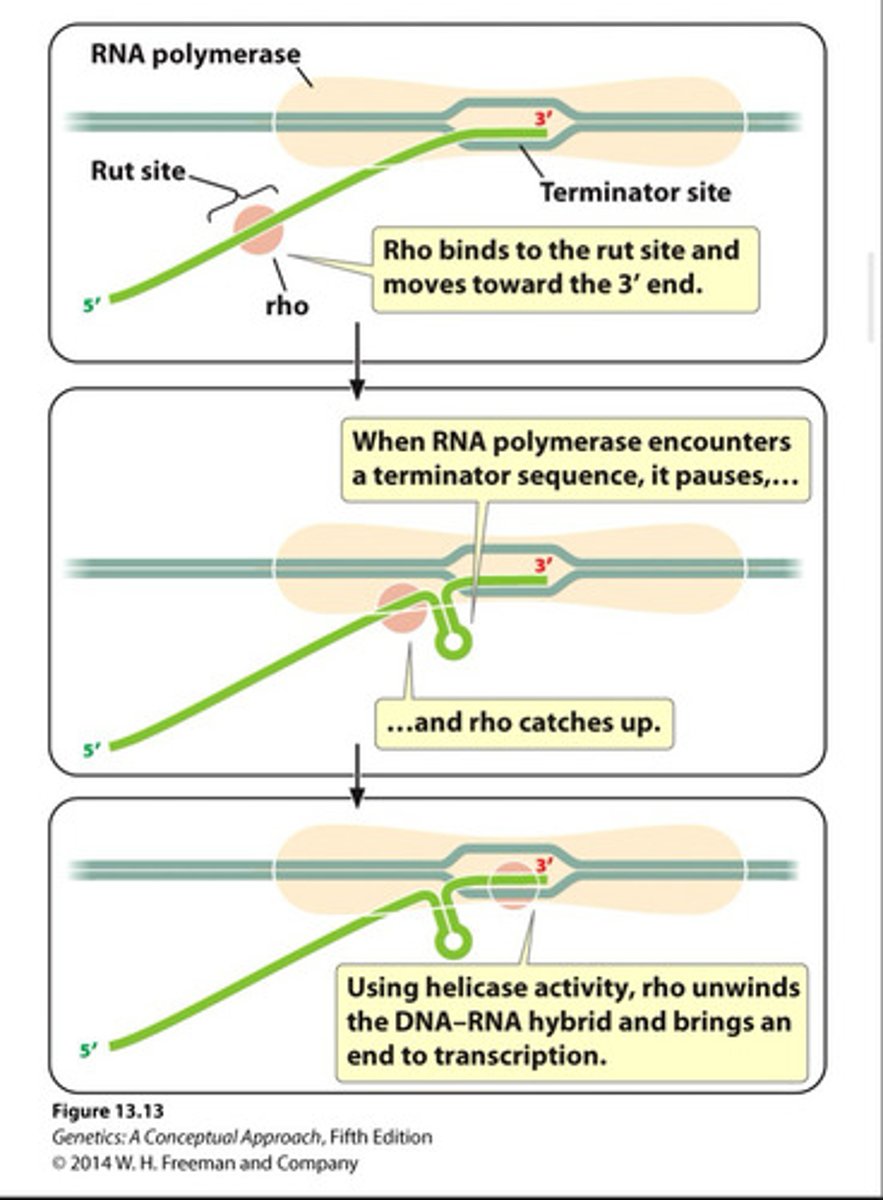
Rho-independent termination
In prokaryotes (50%), GC rich loop by palindrome, then UUU rich sequence. mRNA pulling itself away.
- Inverted repeats allows for hairpin formation which destabilizes RNA:DNA hybrid
- Poly A stretch in template follows repeats (poly U stretch generated in RNA)- there are only two hydrogen bonds between U:A and T:A, so this region is weak
- leads to dissociation between the DNA and RNA
Ribonucleotides
Building blocks of RNA, containing ribose.
Sigma factor
Protein that controls the binding of RNA polymerase to the promoter in bacteria
- Guides RNA polymerase to the promotor and binds it to the template strand.
- After a short stretch of RNA is synthesized, this protein drops off and RNA pol continues (abortive initiation)
- Allows tight binding of RNA polymerase to template
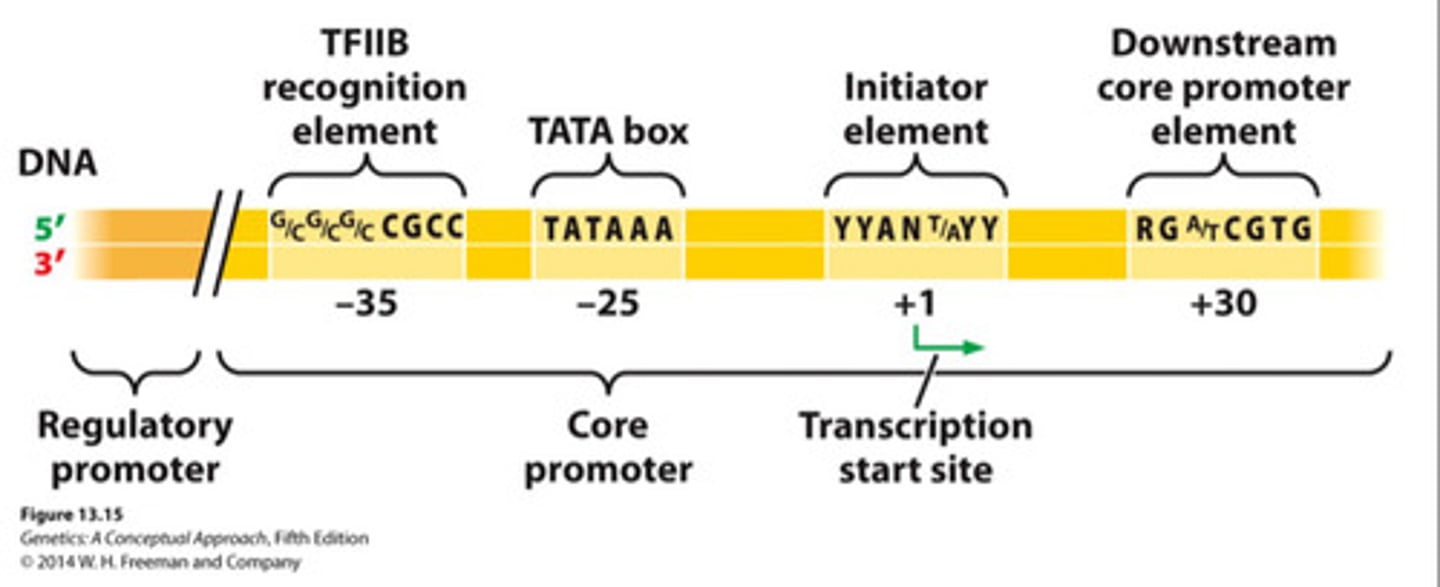
-10 and -35 boxes
Consensus sequences in prokaryotic promoters.
Abortive initiation
Short RNA synthesized with sigma factor before RNA polymerase moves on without it.
Core promoter
Essential DNA sequence for initiating eukaryotic transcription - not sufficient alone
Contains the TATA box, around -25
Regulatory promotor
DNA sequence located immediately upstream of the eukaryotic core promotor; contains consensus sequences to which transcriptional regulator proteins bind.
- Regulates level of transcription - can increase or decrease the rate at which a gene is transcribed
TATA box
Common core promoter element in eukaryotes.
General transcription factors
Proteins assembling on core promoter to recruit RNA pol II.
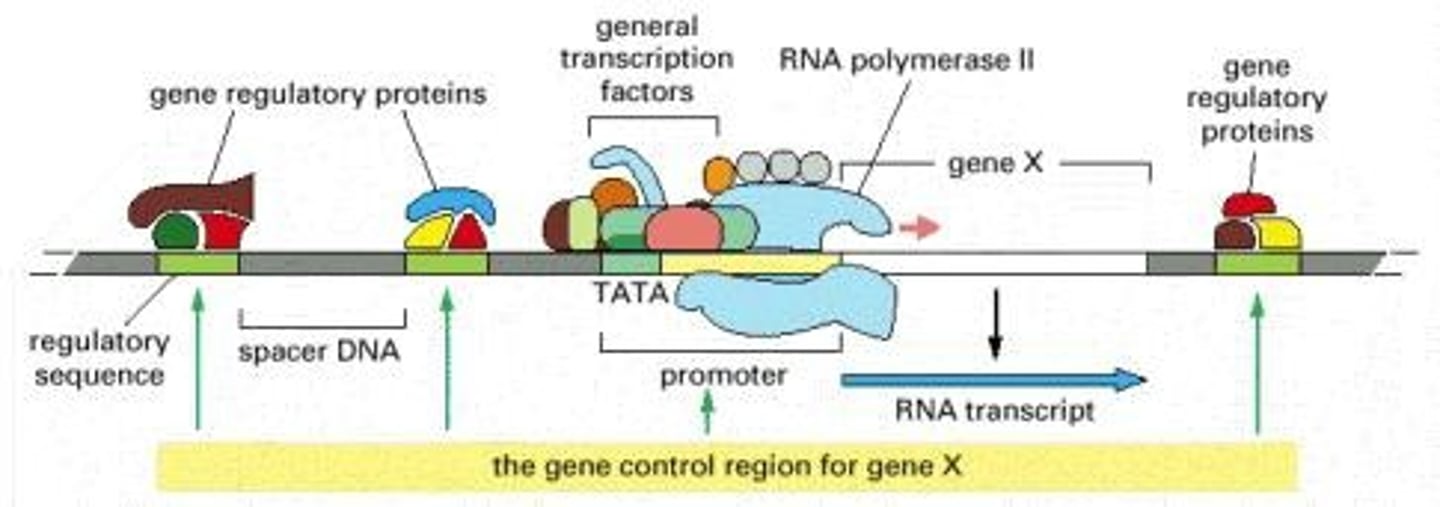
TFIID
9 different polypeptides (transcription factors) that must fully assemble before transcription can begin
- Includes TBP (TATA-box binding protein)
Open complex
Strain on DNA by TBP of TFIID causes DNA to open, allowing for RNA pol to being adding nucleotides to synthesize RNA transscript
Transcriptional factors
Proteins that bind to regulatory promoters of DNA to regulate transcription.
Eukaryotic Termination
Process where transcription continues beyond the end of the gene - sequence in RNA causes nuclease to break pre-mRNA from the transcription machinery
- Transcription continues, with degradation of non-coding RNA being generated.
RNA pol I
Eukaryotic polymerase responsible for transcribing rRNA genes
- rRNA genes contain a promotor and have Rho-like termination
RNA pol II
Main polymerase of eukaryotic transcription - transcribes protein encoding genes as well as regulatory RNAs
Co-linearity
The number of nucleotides in the gene should be proportional to the number of amino acids in the protein
- except that mRNA contains sequences that are not part of the protein - in eukaryotes, genes in the DNA were larger than the RNAs
Discovery of introns
Exons
Coding regions of DNA that express proteins.
These are found in mature mRNA
Primary mRNA transcript
Initial mRNA containing both introns and exons.
Mature mRNA
Processed mRNA containing only exons. In eukaryotes, only this mRNA can be exported from the nucleus.
Splicing
Removal of introns from pre-mRNA.
- depends on consensus sequences in the intron to know where to cut.
- 5' AG cute site followed by GU in the intron
- 3' CAG in intron followed by G after cut site
- involves small nuclear RNAs (snRNAs)
Mechanisms: snRNPs (snurps), 'lariat' structure
ONLY OCCURS IN EUKARYOTES
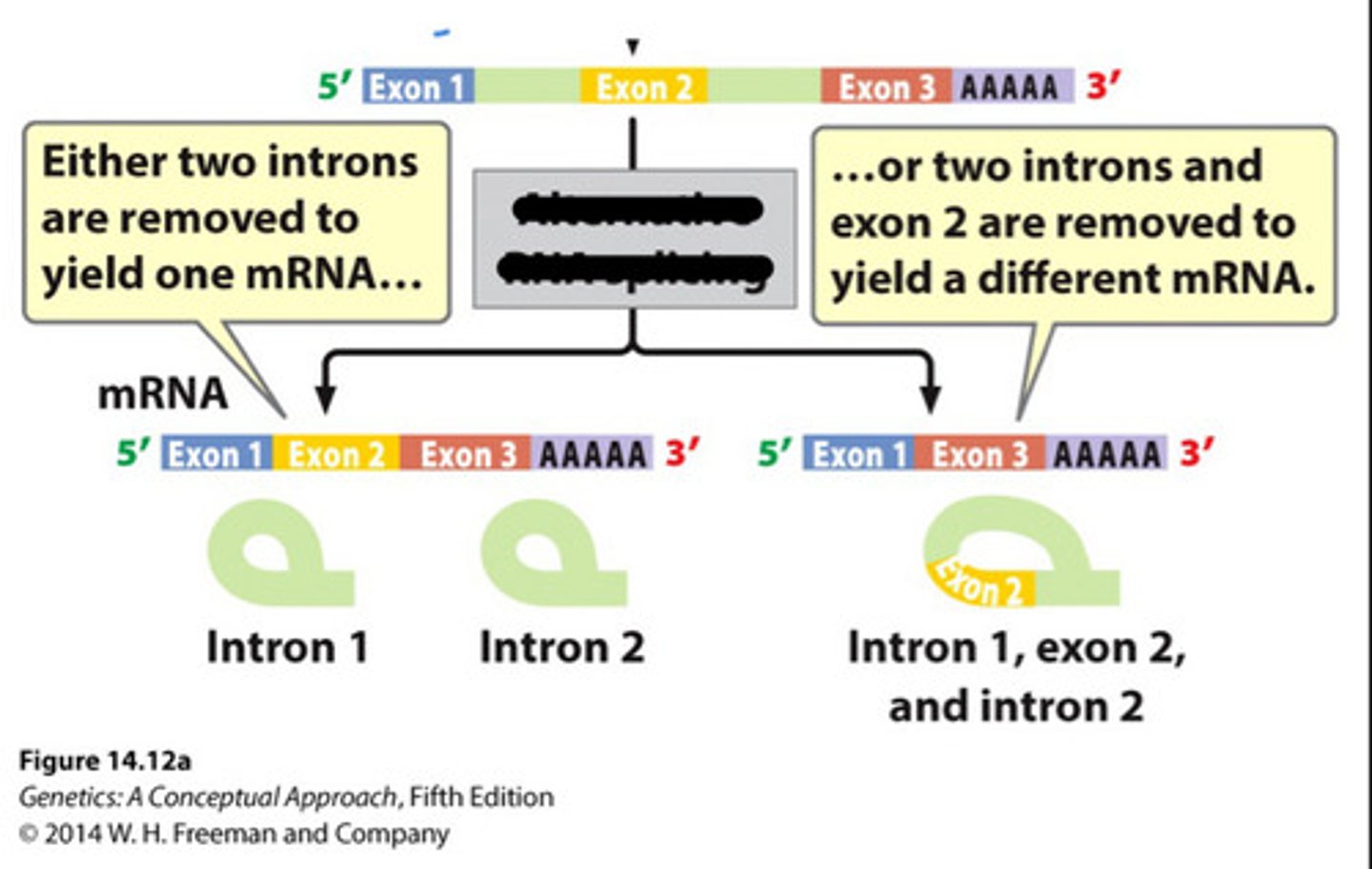
Alternative splicing
Genes with many introns can have differential splicing, which results in different patterns of exons - the order of the exons remains the same, but some can be skipped.
One gene can code for several proteins*
RNA pol III
Eukaryotes only, transcribes tRNA and other small RNAs.
- promotor for this polymerase is downstream of the start site and it has Rho-independent-like termination
5' Cap
Modified guanine added to mRNA's 5' end.
Functions:
- protects the mRNA from degradation
- regulates export
- aids in ribosomal binding; translation
Poly A tail
String of adenine nucleotides added to mRNA - makes it more stable and protects it from degradation
Open Reading Frame (ORF)
Coding region in mRNA that translates to protein.
5' UTR
Untranslated region aiding mRNA export and translation.
3' UTR
Untranslated region involved in stability (miRNA interaction) and translation.
snoRNA
Small nucleolar RNA involved in rRNA processing.
siRNA
Small interfering RNA regulating gene expression.
- can inhibit translation by causing cleavage and degradation of complementary mRNA
miRNA
Micro RNA involved in post-transcriptional regulation.
- can inhibit translation by causing cleavage and degradation of complementary mRNA
piRNA
Piwi-interacting RNA targeting transposons.
CRISPR
Bacterial micro RNA that is important for defense
- now used as a bio-tool
LncRNA
Long non coding RNA, gene silencing (Xist in x-chromosome inactivation)