Common measures of variability, skewness, and percentiles
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
17 Terms
What does the spread (variability) tell us and when can it be good or bad
The spread (variability) tells how much sample values depart from expectations and about the diversity of values within our sample.
good : job interview candidates as this maximises the number of possibilities for an employer
bad : manufacturing process where uniform production of goods is essential
Name different measures of variability
range
upper and lower quartiles
interquartile range
standard deviation
variance
What is range
The range is the most simple measure of variability and is simply the largest value in a data set minus the smallest value.
What are the quartiles, their position in the data , and how do you calculate the quartiles
The first quartile is Q1 and it seperates the first 25% of the data from the rest
n + 1 / 4 position in the data
The second quartile is Q2 and is also the median, it seperates the first 50% of the data from the rest
The third quartile is Q3 and it seperates the first 75% of the data from the rest
3(n+1) / 4 position in the data
Q1 or Q3 = lower value + (remainder x (upper value - lower value ))
How do you find the upper and lower quartile?
put the data in ascending order
find the position of the data
use formula : lower value + (remainder x (upper value-lower value))
What is the IQR
IQR= Q3-Q1
What is standard deviation
The sample standard deviation is a measure of variability which uses all the data in its calculation. The sample standard deviation measures the variability about the mean value. The sample standard deviation is denoted by s.
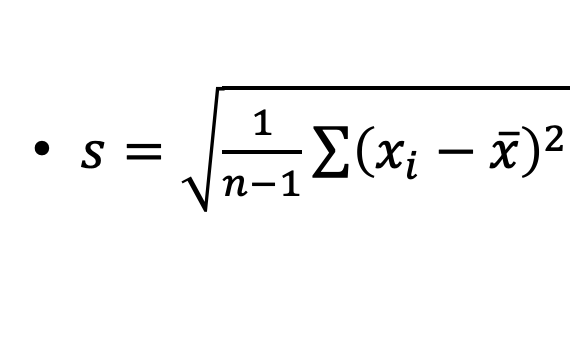
What is variance
The sample variance, s2 is the standard deviation squared i.e.
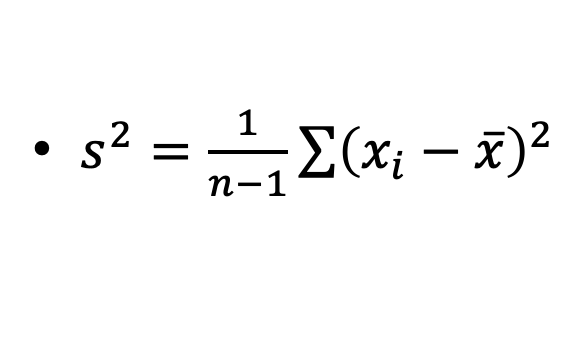
What is skewness used for
In statistical analysis, it is not appropriate to quote all summary statistics, you need to be able to decide which ones. This is determined by the skewness of the data.
What data do we quote if a histogram is symmetrical
the mean and standard deviation
What data do we quote if a histogram is not symmetrical
the median and the IQR
What is skewness statistic
The skewness statistic measures how skewed a data set is. We use R to calculate it.
If -0.5 ≤ skewness statistic ≤ 0.5 , the data is roughly symmetrical
If the skewness statistic > 0.5 , the data is right tail skewed
If the skewness < -0.5, the data is left tail skewed
How does symmetrical data relate to the mean and median
Generally, if the data is symmetrical, then the mean and median will be roughly the same
How does left tail skewed data relate to the mean and median
The mean will often be less than the median
How does right tail skewed data relate to the mean and median
The mean will often be greater than the median
What is a percentile
A percentile is a measure indicating the value below which a given percentage of observations in a group of observations falls. For example, the 20th percentile is the value below which 20 % of the observations may be found.
how to calculate a percentile
to calculate the k th percentile :
order data in ascending numerical data
Pk is located at the k/100 × (n+1) position in the data.
Pk = lower value+(remainder × (upper value-lower value)).