ASA 114: Catamarans
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
49 Terms
A tripod rig refers to the arrangement of a forestry and _________ that support the mast without the need for a __________.
Shrouds, backstay
A forward projection of the bridgedeck designed to soften the impact of the seas is called a __________.
Nacelle
On catamarans without fixed keels, a _________ slides vertically through a trunk in each hull to provide lateral resistance and improved performance when sailing to _________.
Daggerboard, windward
A catamaran’s _________ is derived from the buoyancy in its two widely separated hulls. Even so, care must be taken to avoid overloading, and to distribute weight __________.
Stability, evenly
Located on the forwards crossbeam, the _________ _________ provides reinforcement to counter the effect of forestay tension.
Seagull Stiker
The downward force of the catamaran’s mast is supported by the center _________ integrated into the bridgedeck structure. The main sheet traveler is often mounted over the _________ crossbeam.
Crossbeam, aft
A typical cruising catamaran sail plan consists of a large _______-________ mainsail and a roller-furling jib.
Fully-battened
When a catamaran’s steering wheel is turned, the ________ operate together because they are connected by a tie rod. They are smaller than those on a monohull, but their efficiency is increased due to the lack of ________.
Rudders, heeling
Name four systems or components that must be duplicated on a catamaran:
Engines, running gear, cooling, exhaust, electrical, fuel, bilge pumps
An engine’s _______ battery is generally collocated with that engine and charged by an _______ on the same engine.
Start, alternator
Take care to ensure that levels in the _______ and ________ tanks are balanced, especially if they are located away from the boat’s centerline.
Freshwater, fuel
Less heeling makes preparing meals easier on a catamaran than a monohull, but it’s still advisable to take _______ to avoid burns and _________.
Precautions, scalds
The catamaran’s fully-battened mainsail is very heavy; hoisting is made easier by using a halyard with a ________ ________.
2:1 purchase
When sailing to windward, the high profile of a catamaran creates ________ that slows the boat speed. Combined with its increased _________ due to shoal-draft keels, this requires a catamaran to sail at ________ angles and ________ boat speeds than a monohull to achieve good windward VMG.
Windage, leeway, wider, faster
When trimming the mainsail for best close-hauled performance, it is best to center the boom with the ________ and then use the _________ to trim the sail for optimum twist.
Traveler, mainsheet
Due to its large mainsail, the catamaran is susceptible to weather-vaning if boat speeds is too low when ________. If the boat stalls, the jib may be ________ to assist the turn.
Tacking, backed
The key to effective tacking is to have the best possible boast speed, be close hauled, turn the wheel _______, ease the traveler a little and quickly trim the _______ on the new side. Building _______ is important before trimming the ________ onto the new close hauled course.
Steadily, jib, speed, mainsail
The catamaran’s faster ________ ________ exaggerates the ________ wind speed and angle, which affect how a catamaran’s sailor should steer and trim.
Boat speed, apparent
When sailing to windward, daggerboards should be _______ to reduce leeway. When sailing downwind, daggerboards should be _______ to reduce drag and turbulence.
Lowered, retracted (raised)
When sailing downwind, find your course for best downward VMG by sailing a _______ course and noting boat speeds than and apparent wind speed on different headings.
Shalom
When jibing a catamaran, it’s important to jibe _______ and use the traveler and main sheet to control the large _________.
Slowly, mainsail
A lack of heeling and reduced weather helm reduce the sensory cues that indicate when to reef. Consult the manufacturer’s charts that recommend the _____ ______ at which to reef. ________ state and approaching squalls should also be factored into the skipper’s decision.
Wind speeds, sea
To maintain better control when sailing in gusty conditions, ________ ________ in gusts when sailing windward, and _______ _______ when sailing downwind.
Head up, bear away
The large size of the catamaran, which can cause difficulties when docking or maneuvering under power, is greatly overcome by the use of its ________ screws.
Twin
Slow-speed maneuvering is enhanced by using ______ power and direction of thrust, which moves the pivot point toward the ________ with the least thrust.
Differential, hull
Care must be taken when slow-speed maneuvering under power in windy conditions due to the shoal ________ and the _________ of the high freeboard and large deckhouse.
Keels, windage
Motor sailing with one engine saves _______ but affects the balance of the boat.
Fuel
Rudders become ineffective at low speeds. Therefore, when docking a catamaran, center the ________ and maneuver the boat with the two _________.
Wheel, engines
Name four of the steps involved to safety hoist and secure a dinghy in davits:
Close the fuel tank vent, remove loose gear, position dinghy under davits, lower hoisting lines, attach shackles to lifting points, remove drain plug, exit dinghy, raise bow and stern simultaneously, cleat off the tackle, secure with bow and stern lines, check for chafe points
Dinghy boarding is conveniently done at the ________, which offers a low step to embark. Remember to maintain three ________ ________ ________ at all time.
Transom, points of contact
When picking up a mooring buoy, prepare the ________ lines in advance and approach directly ________ or into the current, aiming to pick up the mooring buoy just inside the bow.
Bridle, upwind
Anchoring or picking up a mooring buoy goes far more smoothly if the person at the bow uses a set of agreed _______ _______ to communicate with the helm.
Hand signals
The purpose of the _________ is to keep an anchor or mooring ball centered between the two hulls.
Bridle
Name four features of a catamaran structure and performance that affect Man Overboard recovery.
Higher speeds, lack of windward performance, pronounced leeway, helm visibility, high freeboard, propellers close to surface
The key to avoiding a Man Overboard situation is to keep the crew safely on board by rigging _______ and using ________.
Jacklines, tethers
One of the primary causes of catamaran capsize is being _______ because of having too much sail set.
Overpowered
List five post-capsize response procedures.
Make a head count, check for injuries, secure crew to inverted boat, secure ditch bag and life raft, salvage what you can, send distress signals
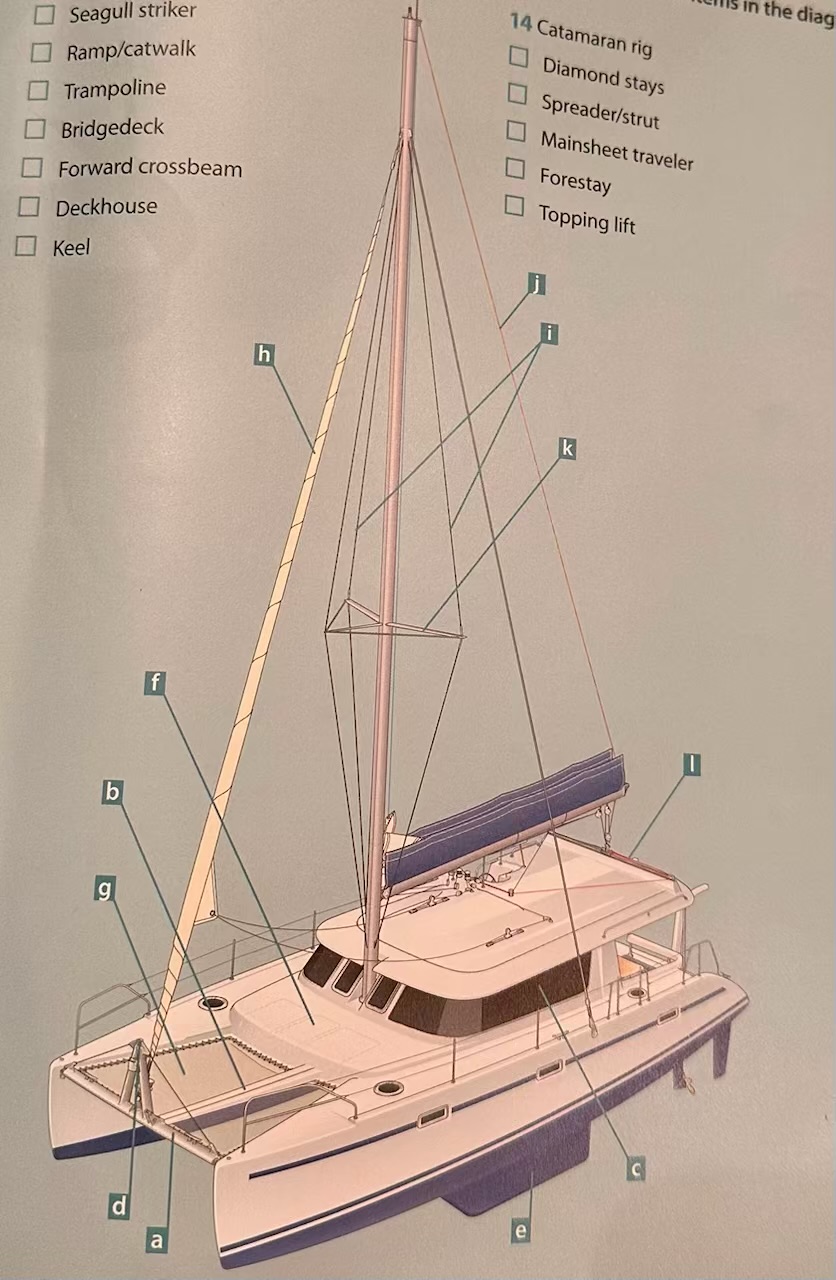
Where is the seagull striker?
D.
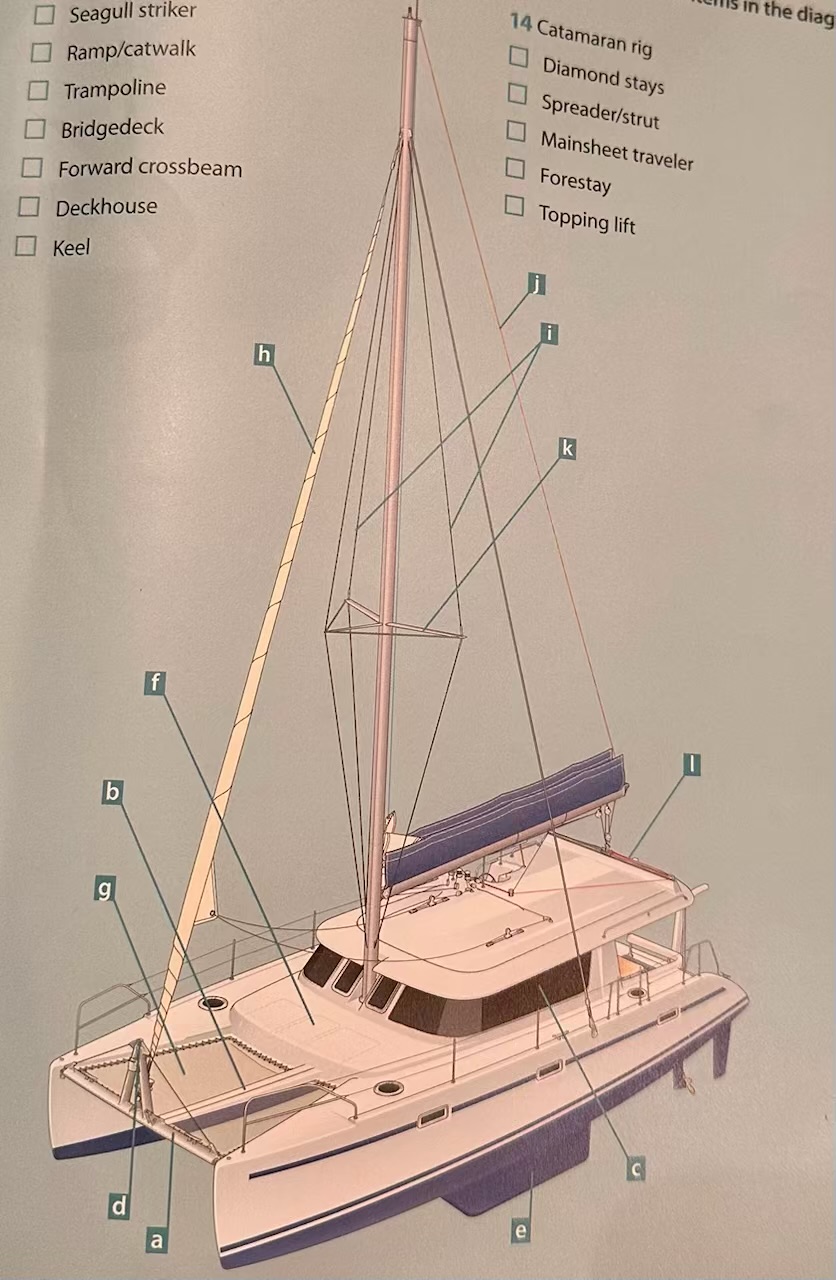
Where is the ramp/catwalk?
B.
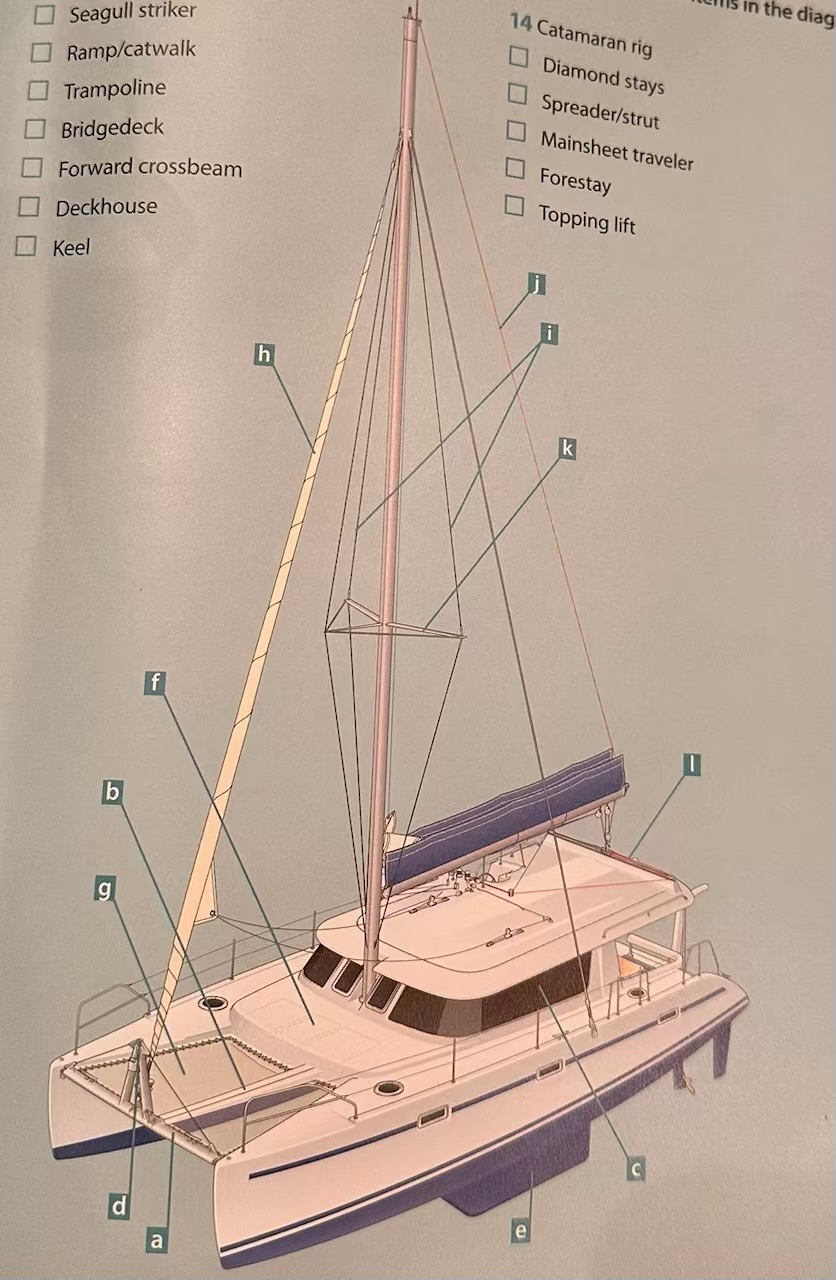
Where is the Trampoline?
G.
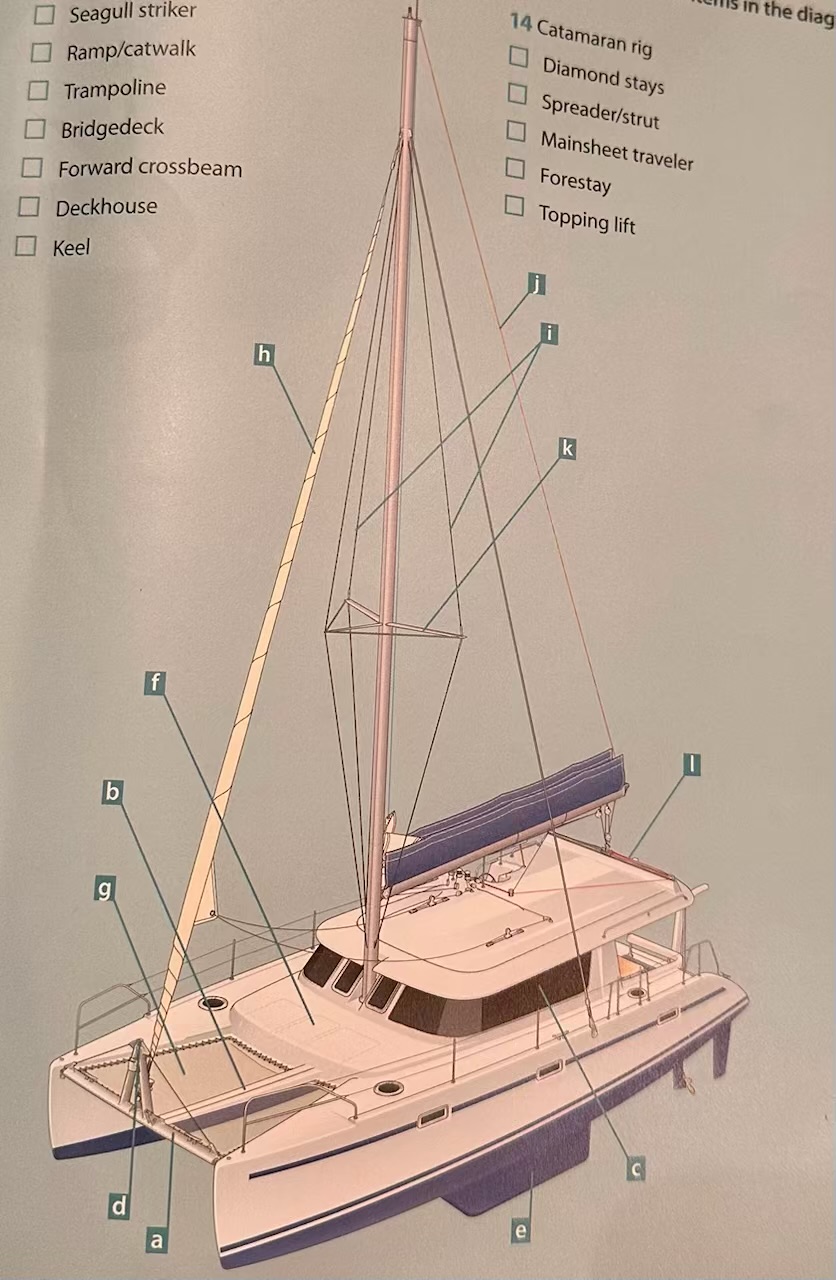
Where is the Bridgedeck?
F.
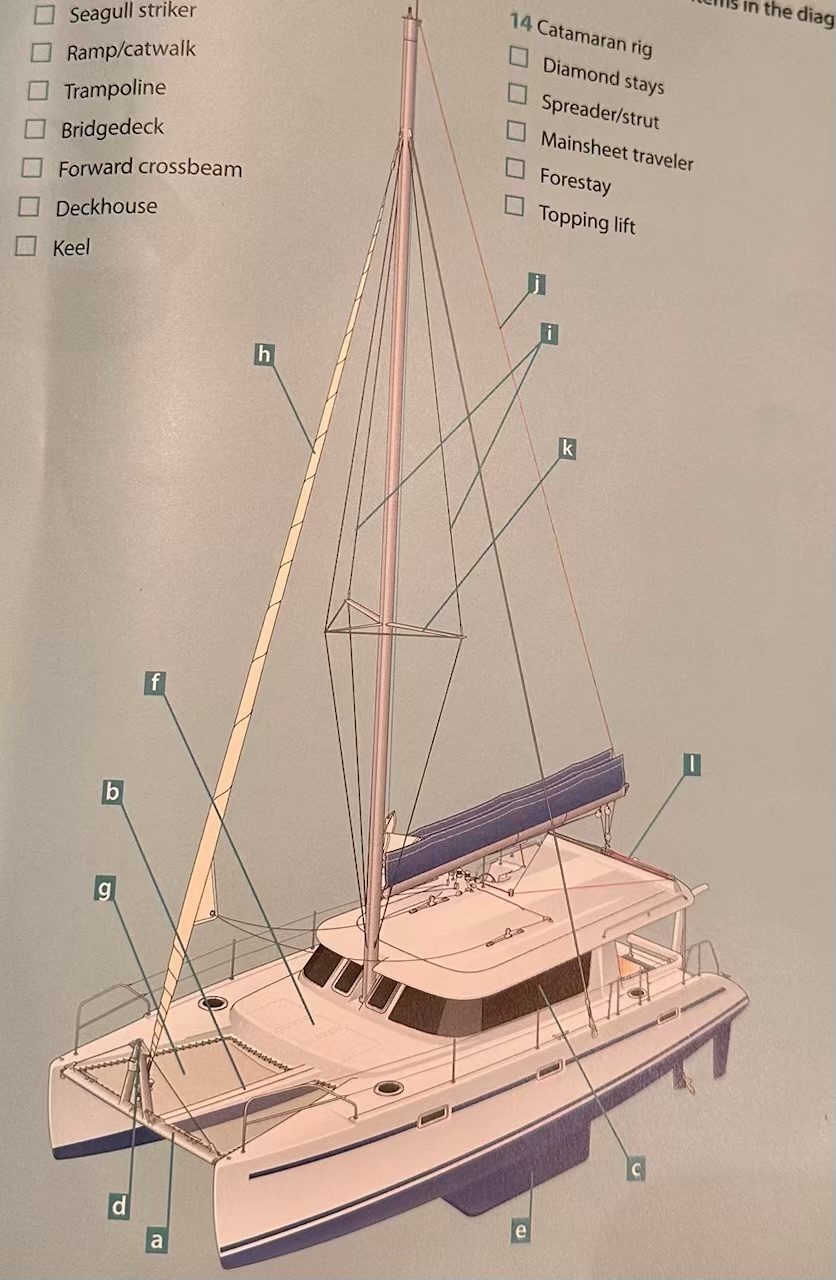
Where is the Forward crossbeam?
A.
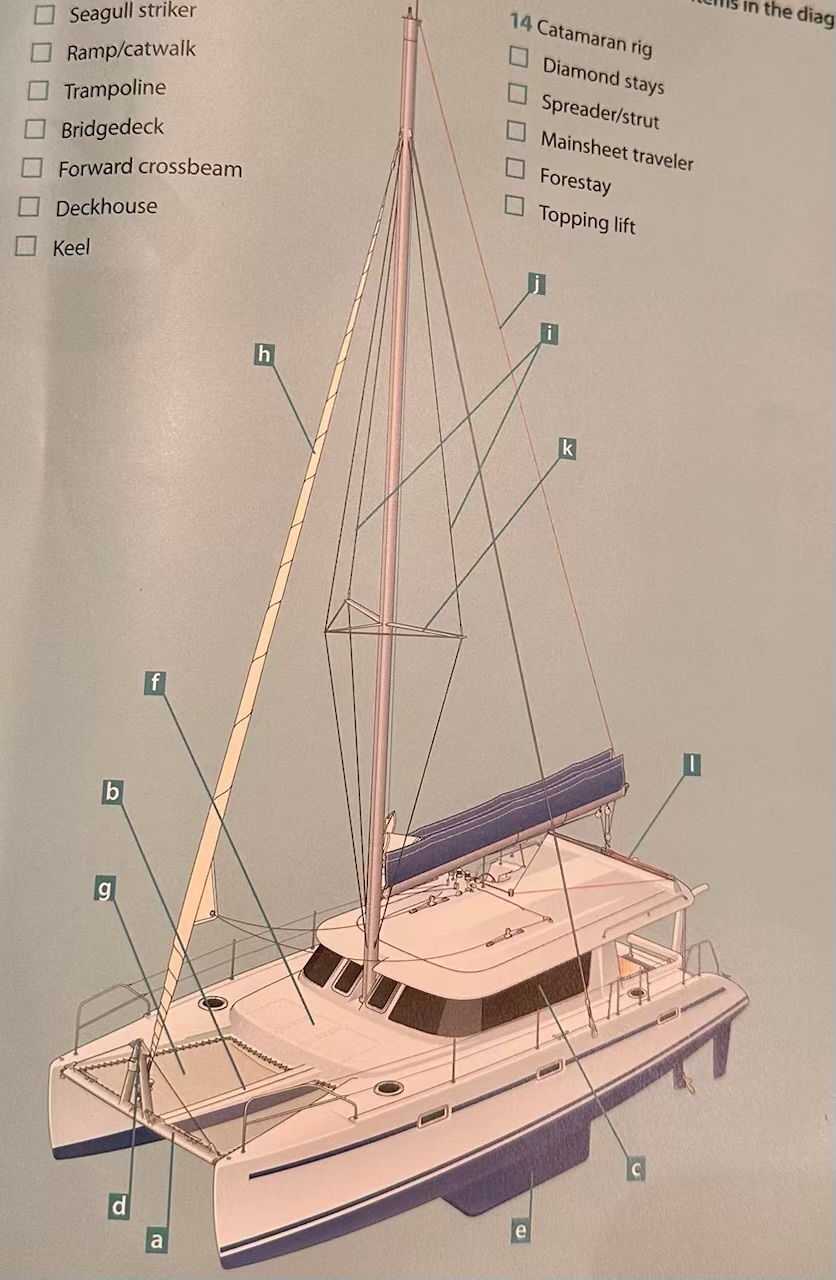
Where is the Deckhouse?
C.
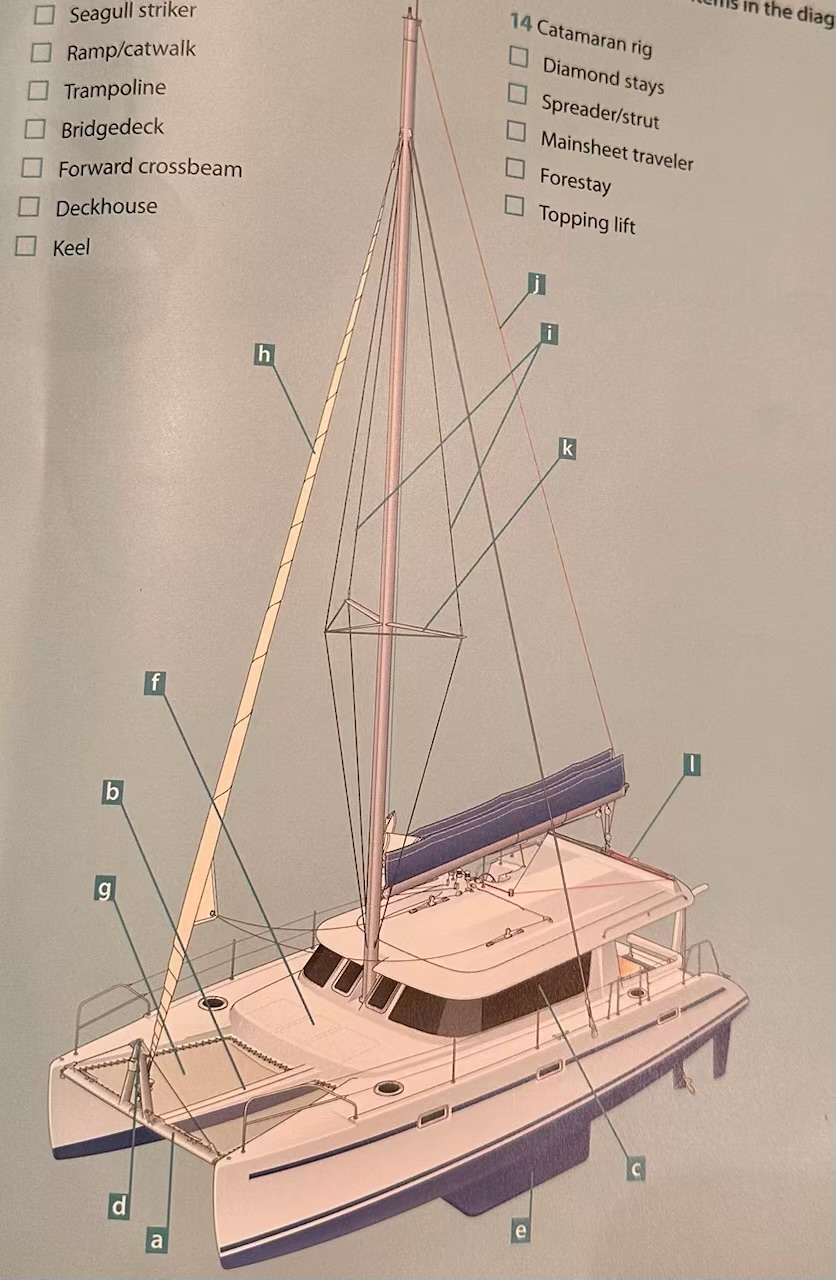
Where is the Keel?
E.
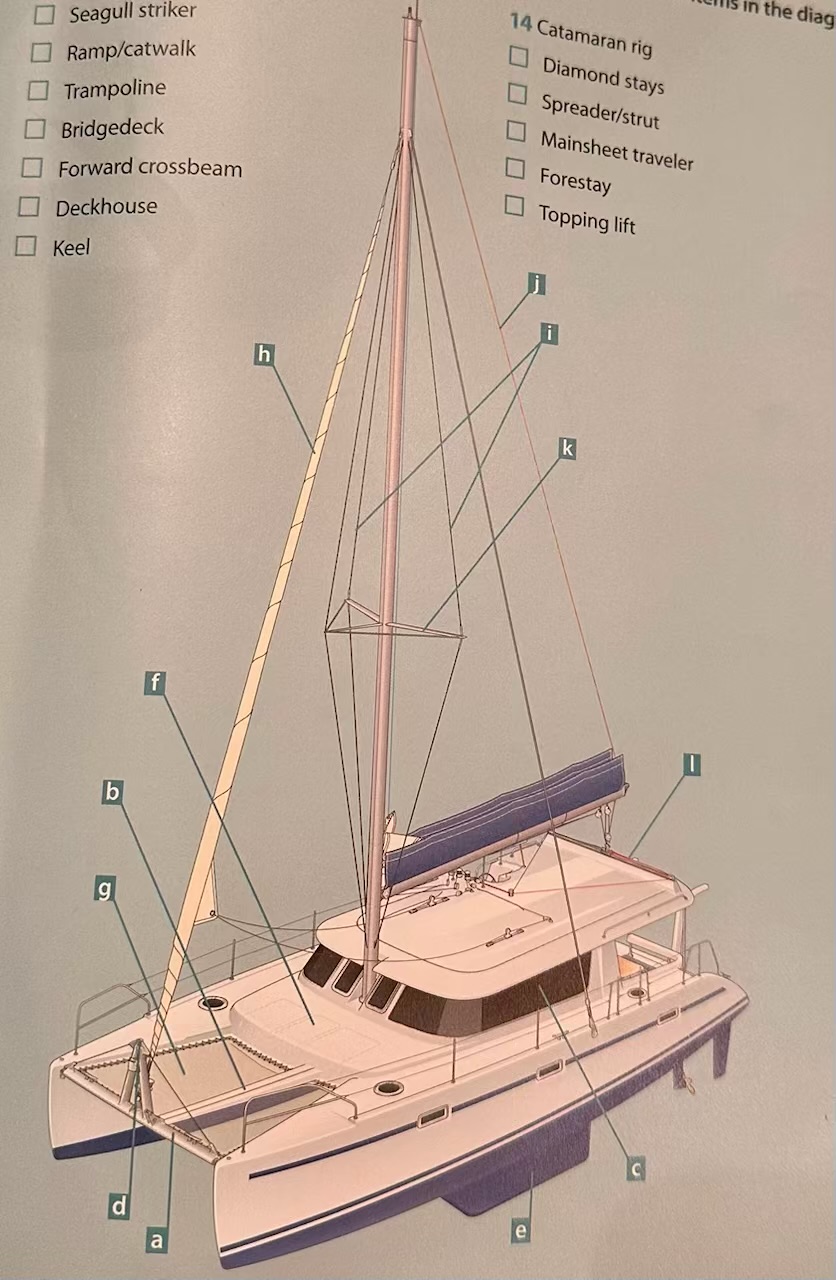
Where are the Diamond stays?
I.
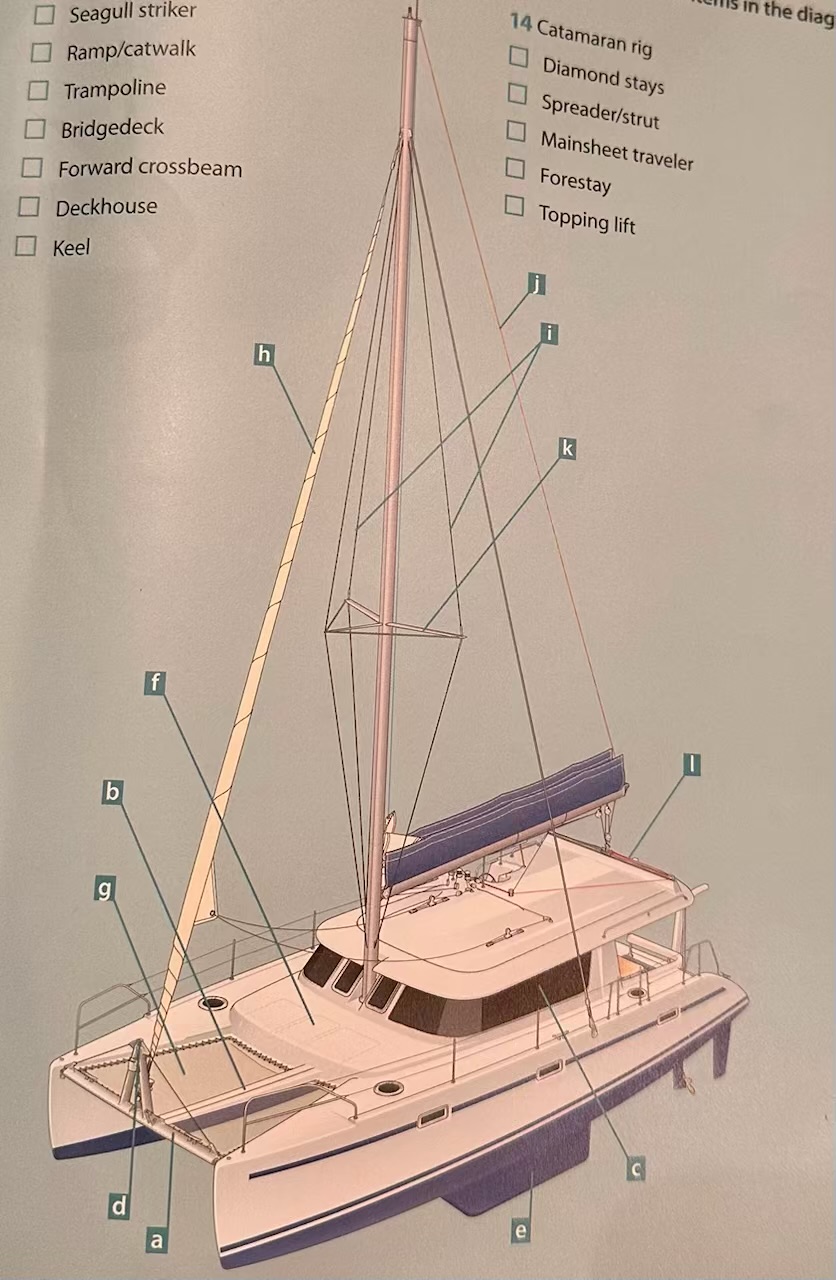
Where is the Spreader/strut?
K.
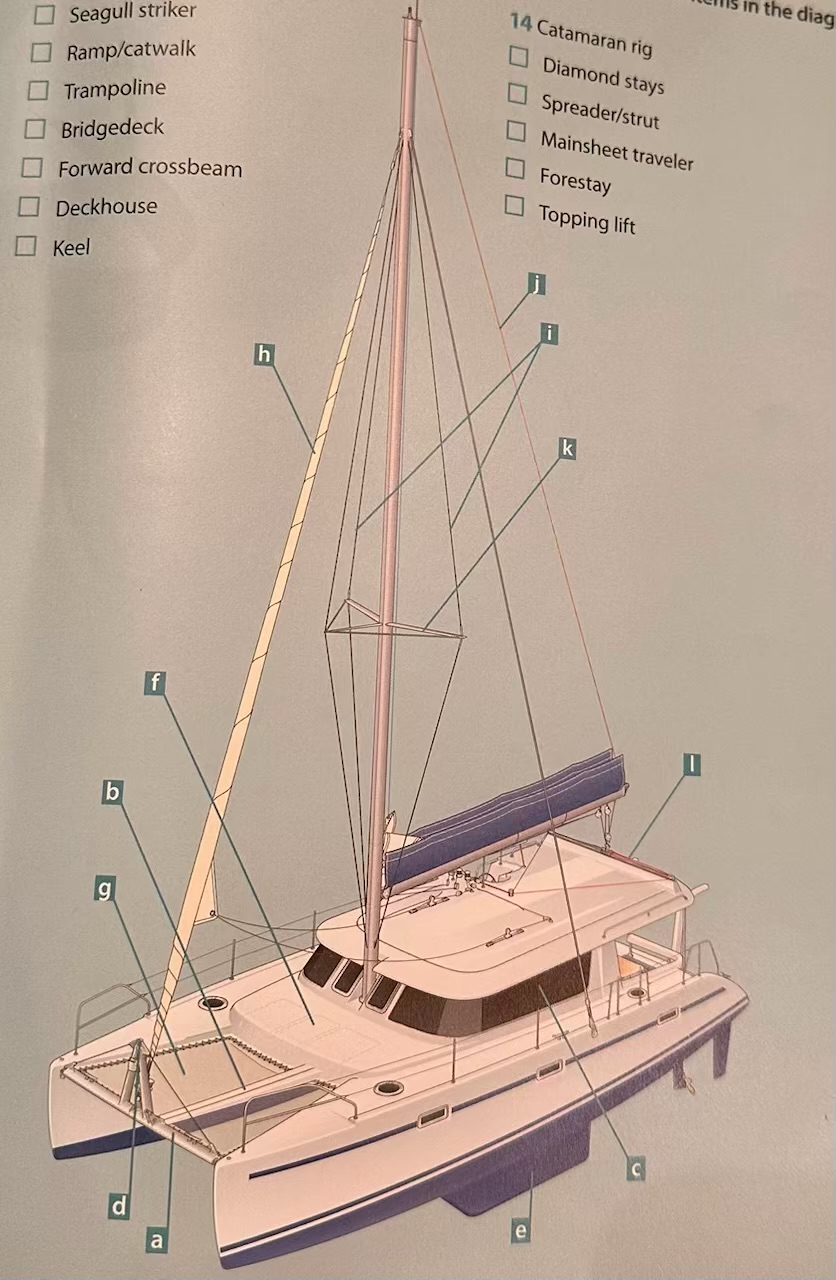
Where is the Mainsheet traveler?
L
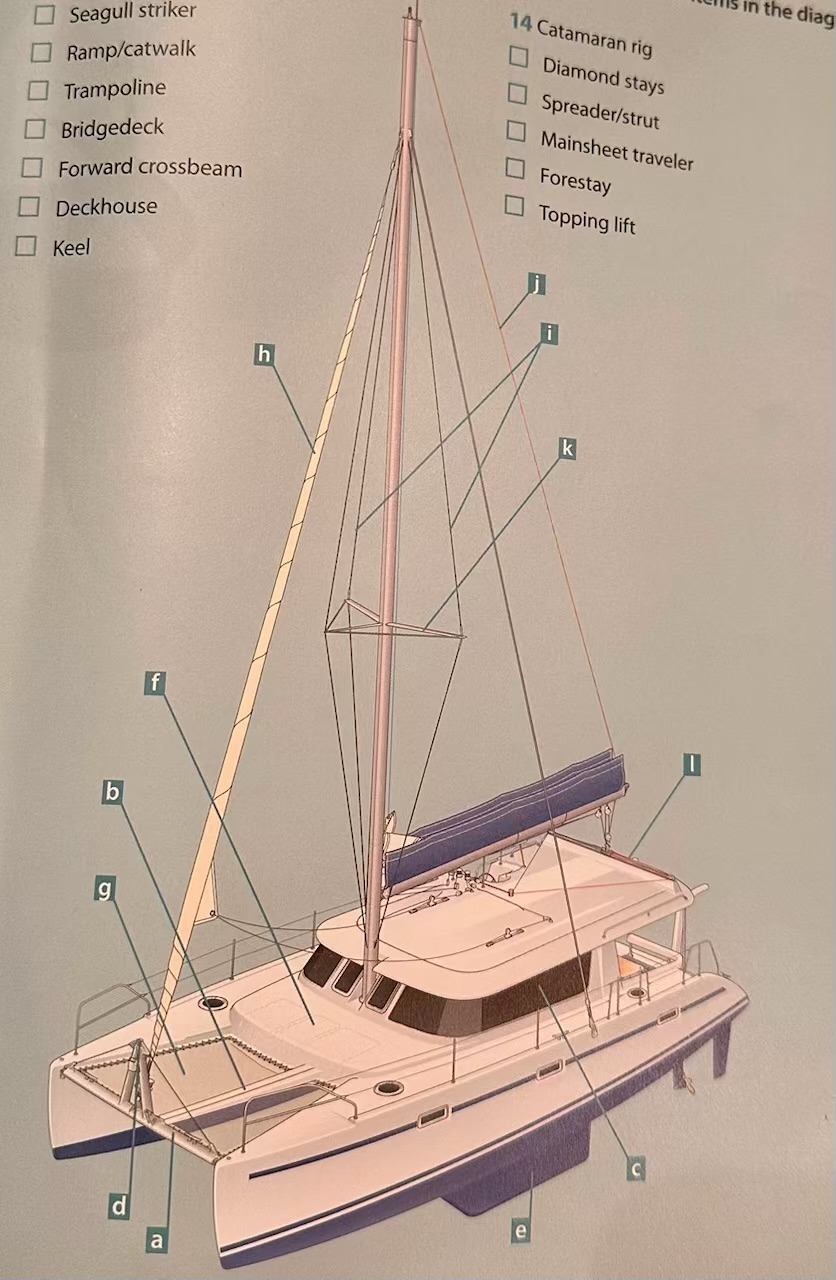
Where is the Forestay?
H.
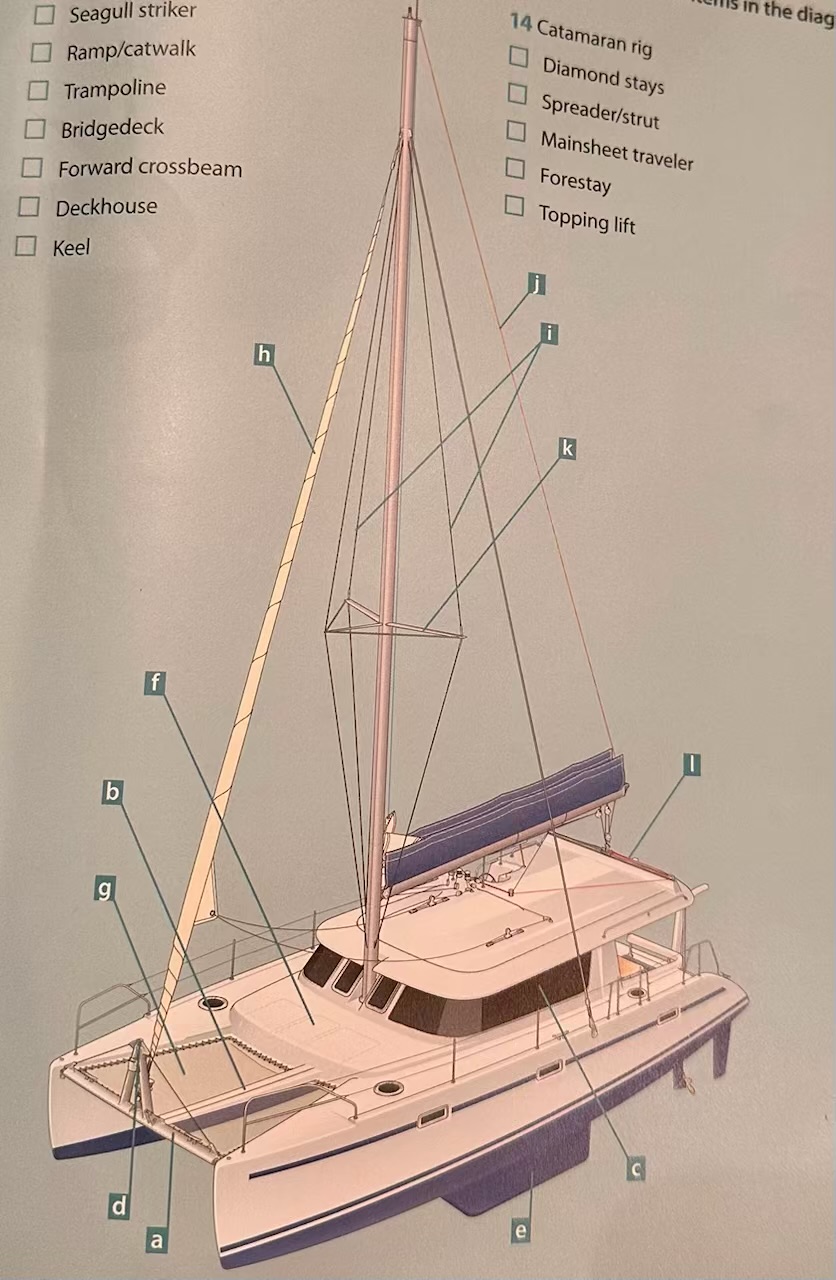
Where is the Topping lift?
J.