16. Integrative Cardiovascular Pathophysiology
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
42 Terms
What are the ABCD of drugs for cardiovascular issues?
A= ACE inhibitors; B= Beta blockers; C= CCBs; D= Diuretics
What organs/tissues are targeted for immediate changes to BP?
Heart: cardiac output can be adjusted to change hydrostatic pressure
Arteries/arterioles: responsible for total peripheral resistance (TPR)
What organs/tissues are targeted for long-term change to BP?
Kidneys: responsible for blood volume
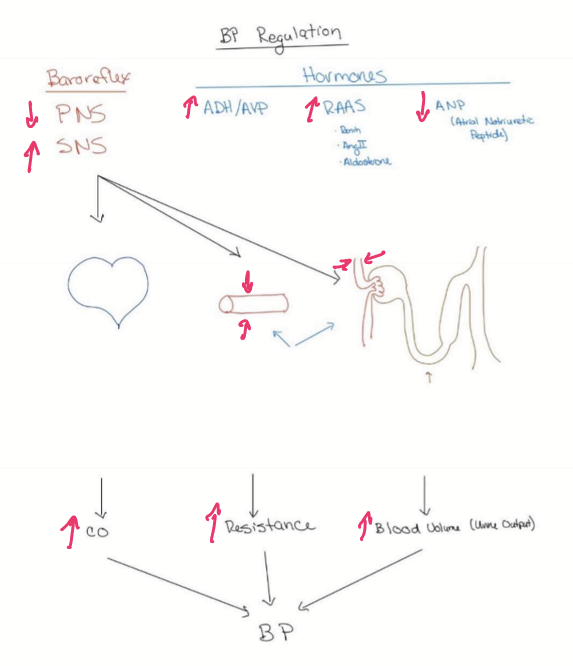
What is baroreflex?
Reflexive mechanism to maintain constant BP. Uses PNS and SNS with negative feedback loops.
Where are baroreceptors located?
In the Aortic arch and carotid sinus
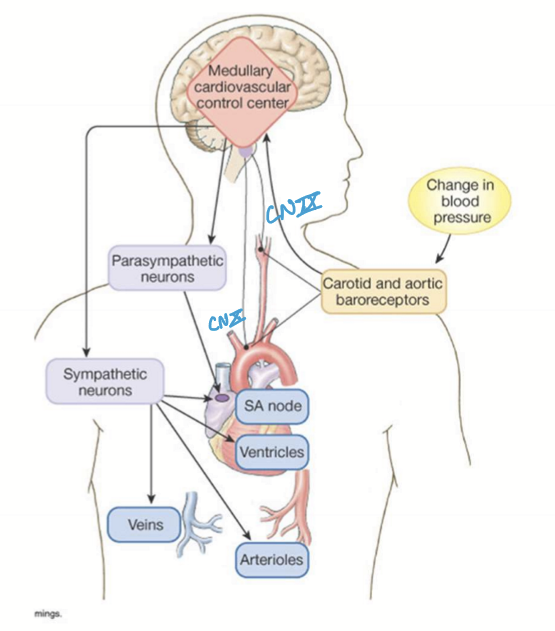
What CN are the afferent portions of the baroreflex?
CN IX and X
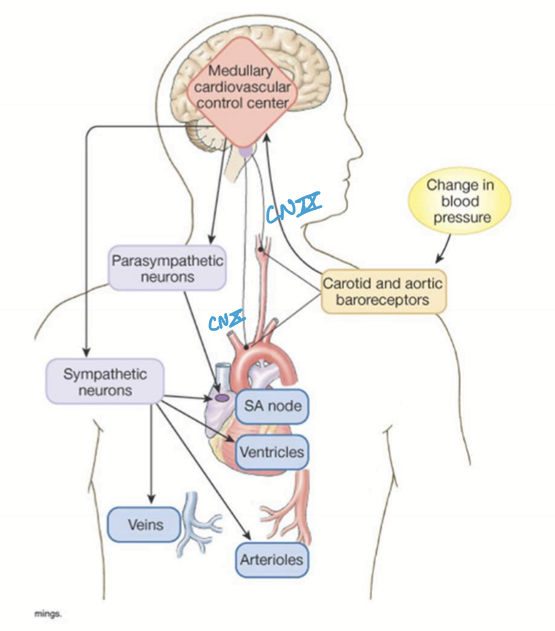
What parts of the brain are responsible for the baroreflex?
Medullary nucleus tractus solitarius
Cardiovascular center of medulla and pons coordinate PNS and SNS regulation via sympathetic vasomotor center and cardiac control center
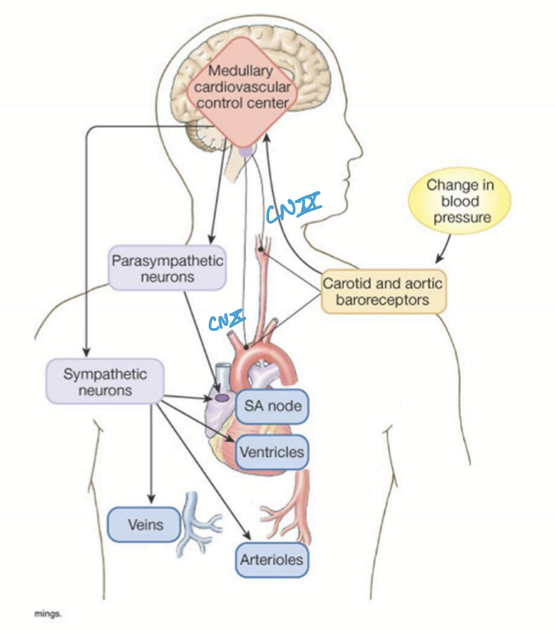
What is the efferent nerves of the baroreflex?
Sympathetic stimulation (NorE then Epi)
PNS inhibition
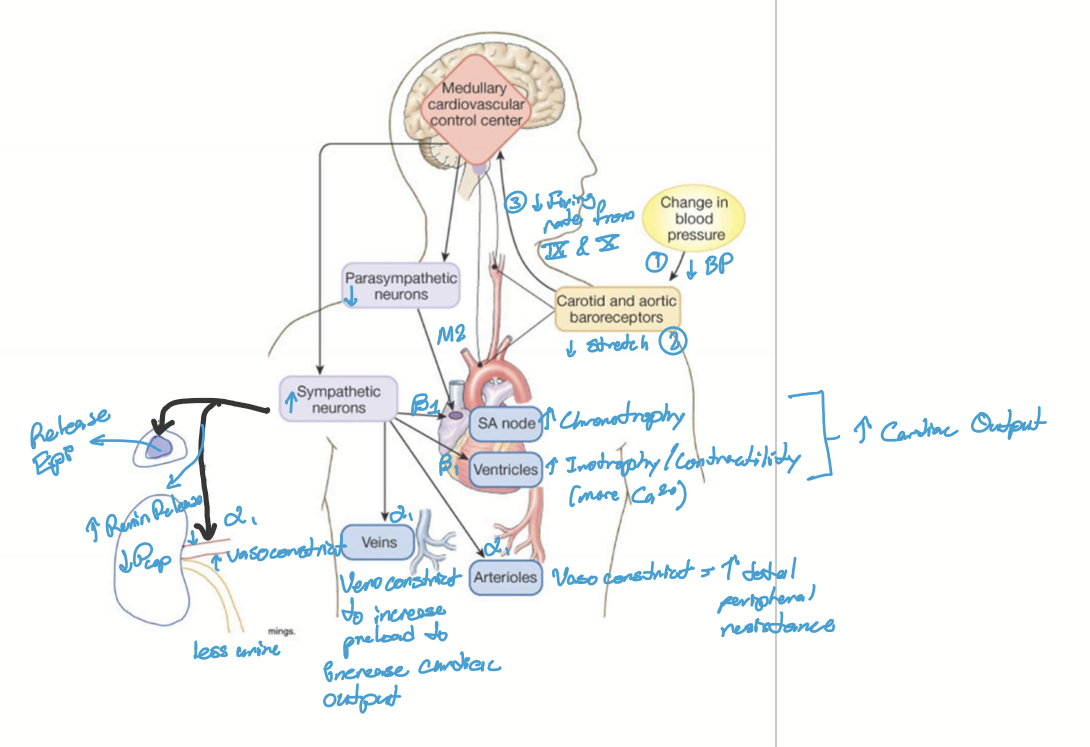
What is the mechanism for baroreflex?
Decrease in BP (MAP <100mmHg)
Decreased stretch of baroreceptors in carotid and aortic arch
Less stretch causes the firing of CN IX and X to medullary nucleus tractus solitarius
SNS and PNS cause various effects: increase in chronotropy, increase inotropy, increase preload; increase total peripheral resistance; Volume expansion via renal artery constriction and renin secretion
Stimulates Endocrine system for redundancy: Epinephrine release and renin release
BP increased
What are Antidiuretic hormone (ADH) and arginine vasopressin (AVP)
Peptide hormone from the posterior pituitary that regulates blood pressure (vasopressin) and osmolarity (antidiuretic)
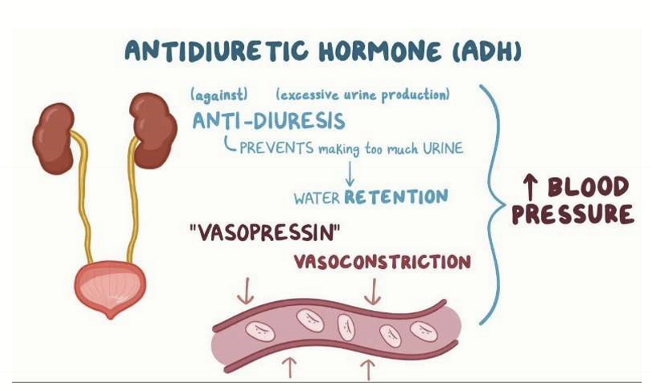
What does vasopressin do?
It cause vasoconstrction and volume expansion by increasing water reabsorption
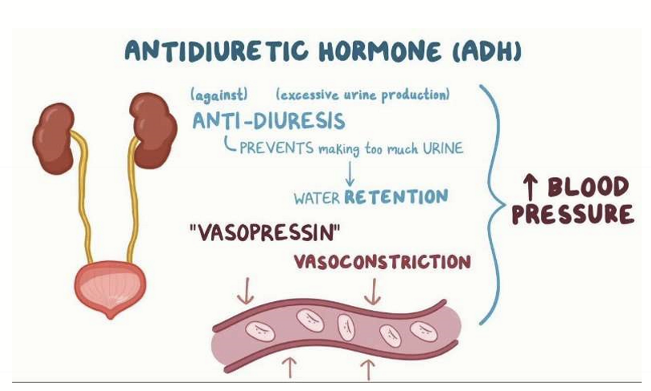
What does antidiuretic hormone do?
Decreases osmolarity by increasing water reabsorption in kidneys
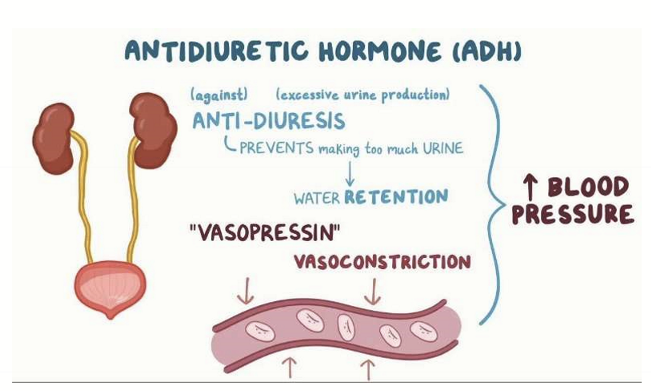
When is ADH and AVP secreted and from where?
ADH and AVP is secreted when there is low BP or high osmolarity sensed by neurons of the hypothalamus. The posterior pituitary gland is then stimulated to secrete ADH/AVP, causing an increase in BP.
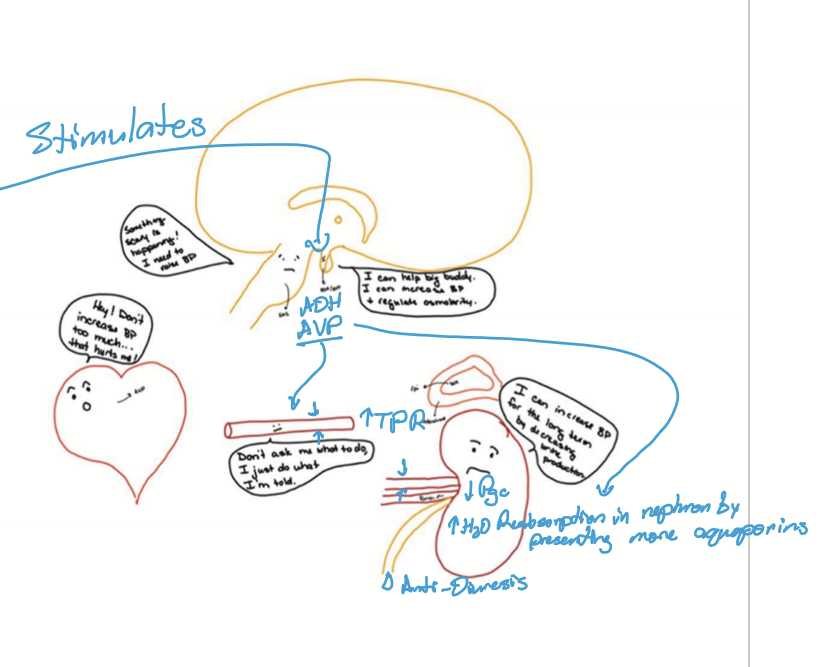
What stimulates the neurons of the hypothalamus to let it know the BP is low/high osmolarity?
High SNS
High Angiotensin II
Hyperosmotic plasma
What is the Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone system (RAAS) do?
A powerful hormon system that is responsible for long-term control of blood volume and BP
What is initially secreted in the RAAS?
Renin is secreted first to start RAAS
What does RAAS target?
SNS, ADH/AVP, Vessels, and salt to increase BP and osmolarity
What is the mechanism of RAAS?
Low BP sensed by juxtaglomerular cells in the kidneys
Renin is secreted into blood and converts angiotensinogen to angiotensin I
Ang I is converted to Ang II by Angiotensin Converting Enzyme (ACE) in pulmonary capillaries
Ang II stimulates secretion of aldosterone from zona glomerulosa of the adrenal cortex
Functions of all 3 hormones increase BP
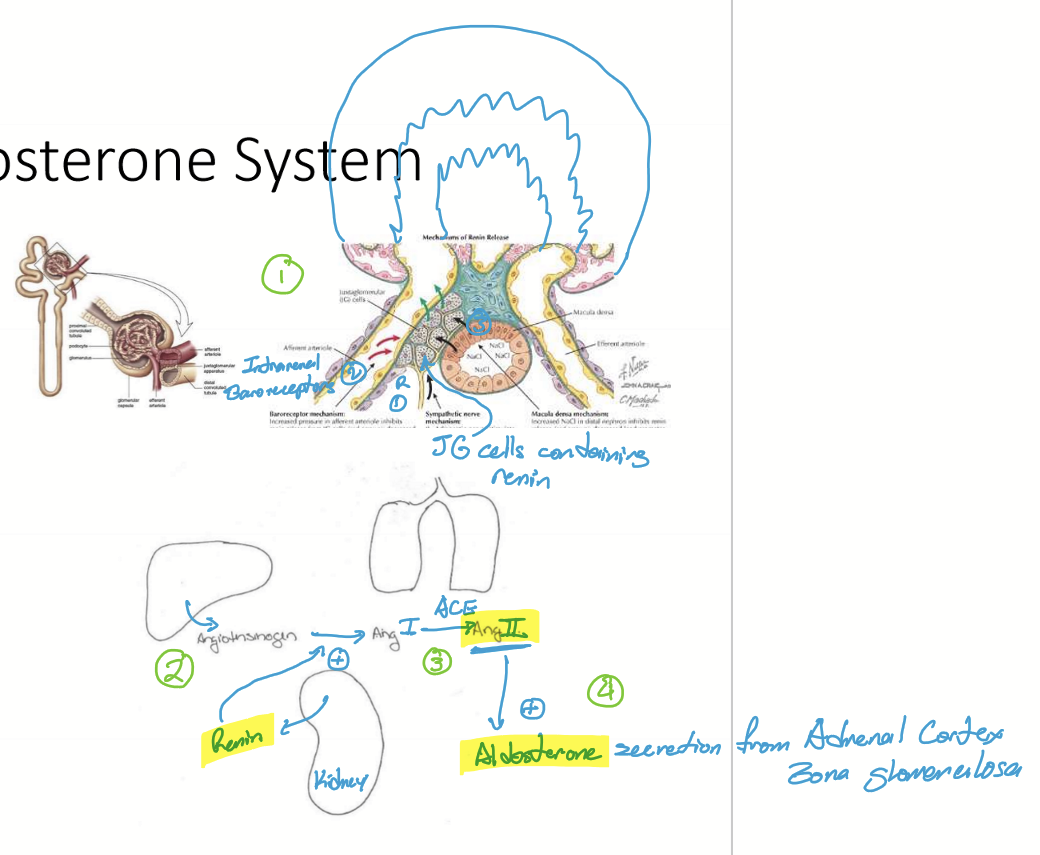
How do juxtaglomerular cells sense low BP?
SNS (Beta 1) stimulation
Respond to low Cl conc in tubule
Baroreceptors
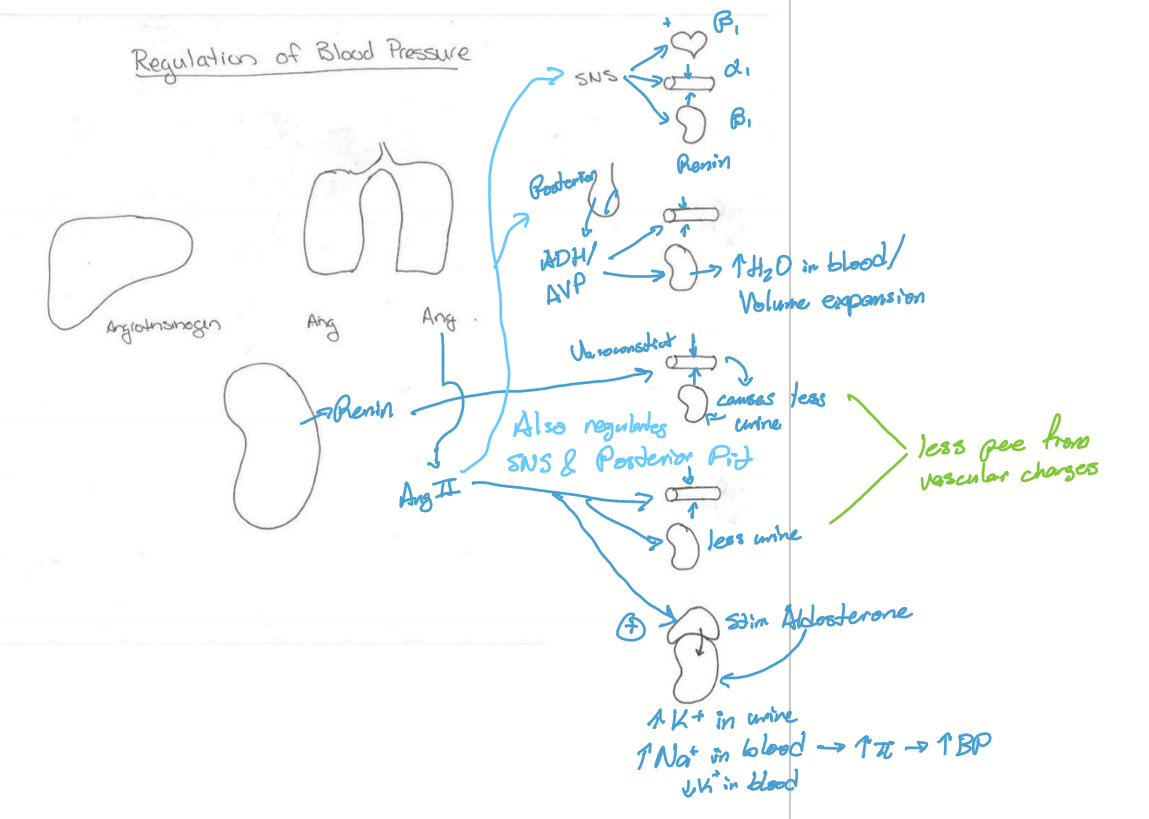
What effects does Renin have?
Increase TPR
Causes volume expansion
Stimulates Ang II production
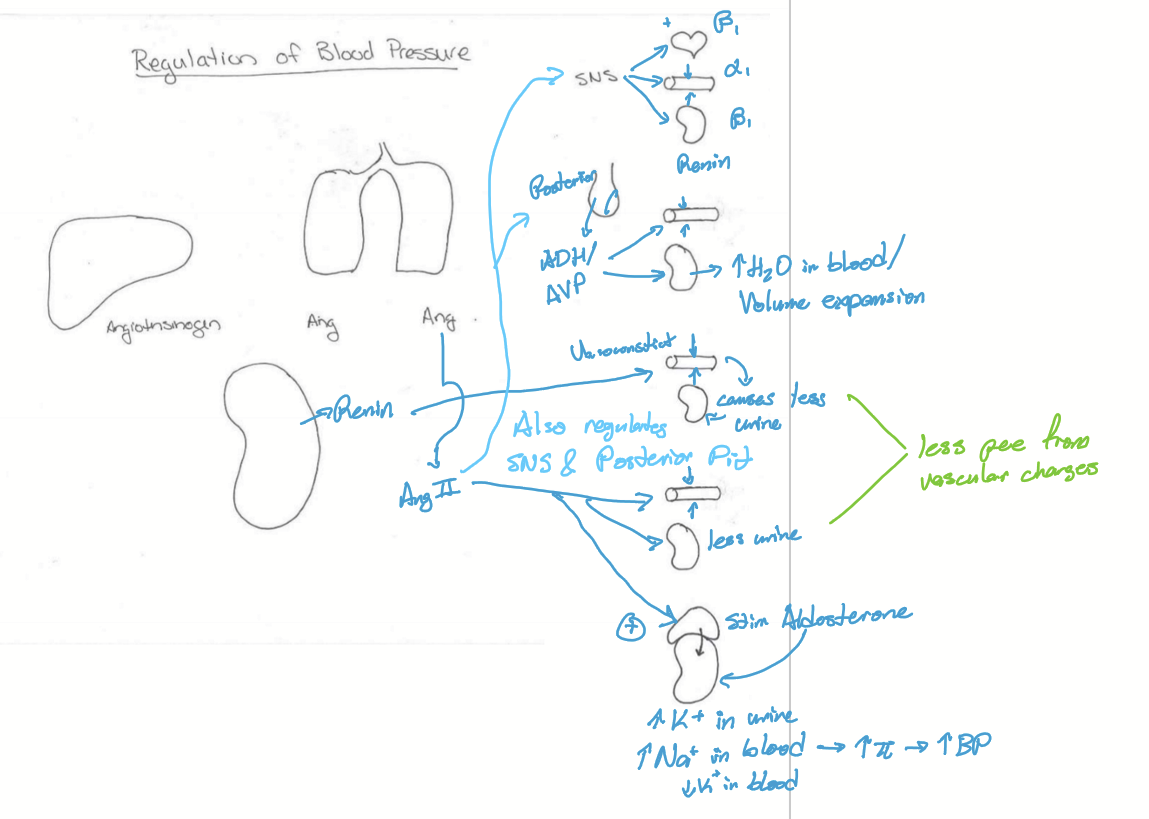
What effects does Ang II have?
Stimulates SNS
Stimulates ADH/AVP from posterior pituitary
Increases TPR
Volume Expansion
Stimulates aldosterone
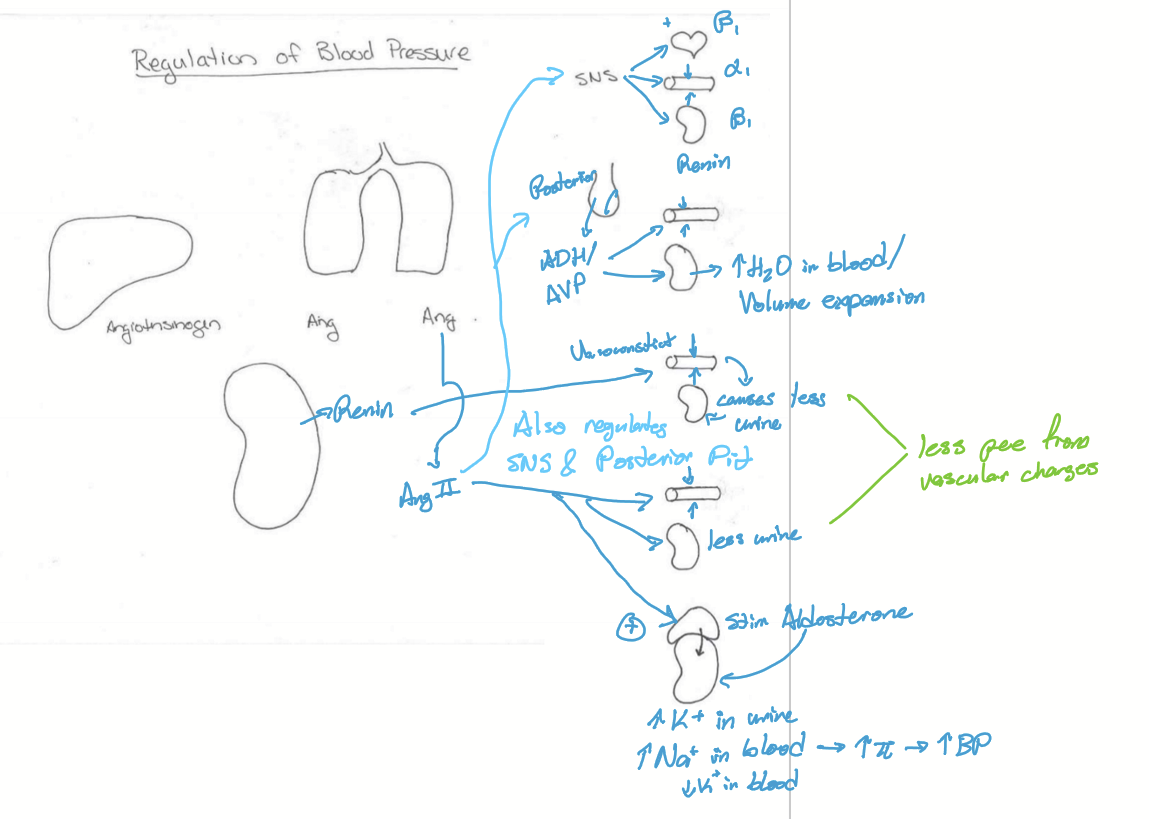
What effects does Aldosterone have?
Volume expansion
Regulates osmolarity via sodium and potassium exchange
Regulates electrolytes via sodium and potassium exchange
What is the function of Atrial Natriuretic Peptide?
Hormone protects heart from high afterload to decrease hypertrophy
Decreases BP
Counter-regulatory system to RAAS
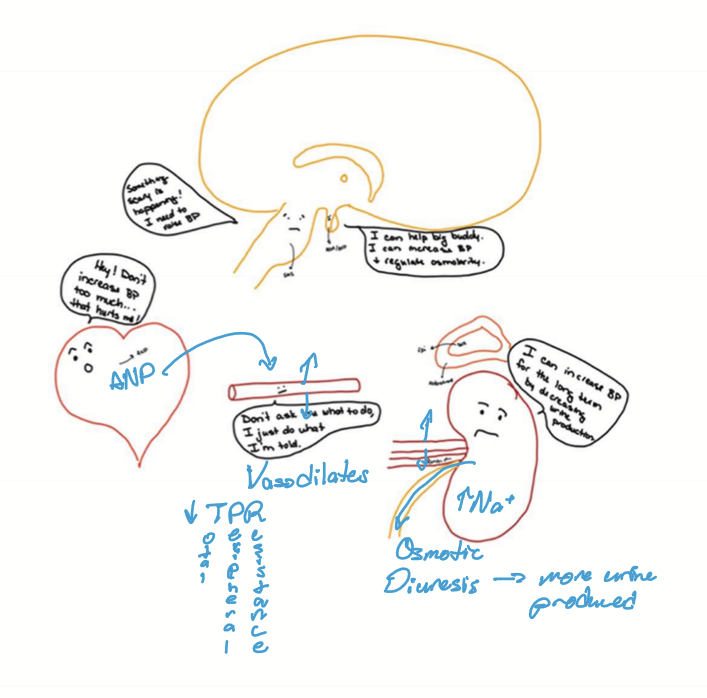
What is the mechanism for Atrial natriuretic peptide?
High BP causes sheer stress in right atrium, stimulating ANP secretion
ANP then causes vasodilation and diuresis
Vasodilation increases urine output and decreases blood volume
Natiuresis: salt and water wasting
BP decreases
What are some etiologies for hypotension?
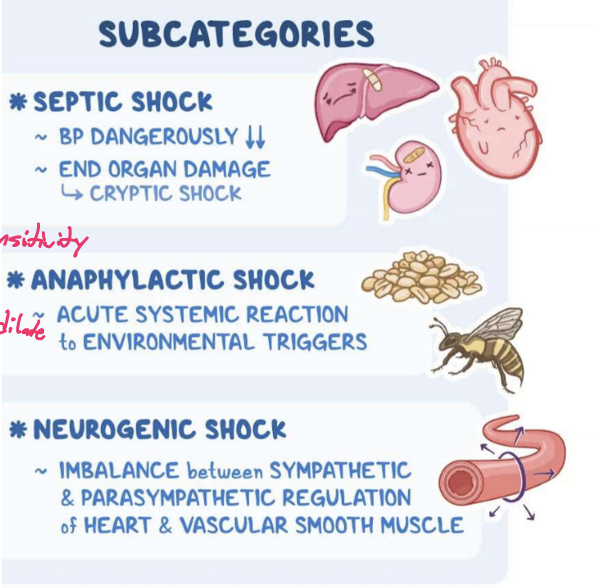
Shock:
Septic shock d/t LPS release
Anaphylactic shock d/t severe allergic reaction
Neurogenic shock d/t trauma to the brain or spinal cord
Cardiogenic shock d/t heart failure or arrest
Hypovolemic shock d/t hemorrhage
Diurnal effects (Nadir)
Therapeutics for HTN (at night before bed)
How is low BP compensated?
Increasing cardiac output
increase heart rate
increase inotropy
increase preload
Increasing TPR
vasoconstriction
Volume expansion
Decrease filtration (GFR)
Tubule
increase sodium and water reabsorption
What is the goal of BP?
To ensure proper nutrient delivery
What does HTN cause?
End-organ damage with increased risk for CVA and CHF
What are the types of hypertension?
Essential or primary HTN
Secondary HTN
What are some factors that increases risk for primary HTN?
Non-modifiable:
age 65+
rage: african americans
FHx
Modifiable:
Overweight
smoking
high sodium
stress
alcohol intake
What are some factors that increase the risk of secondary HTN?
Pheochromocytoma
Conn’s Syndrome
Cushing’s syndrome
Hyperthyroidism
Acromegaly/gigantism
sympathetic dysregulation
renal disease
obstructive sleep apnea
medications: Estrogens; Decongestants; NSAIDs; Recreational drugs (Cocaine)
What are the stages of blood pressure?
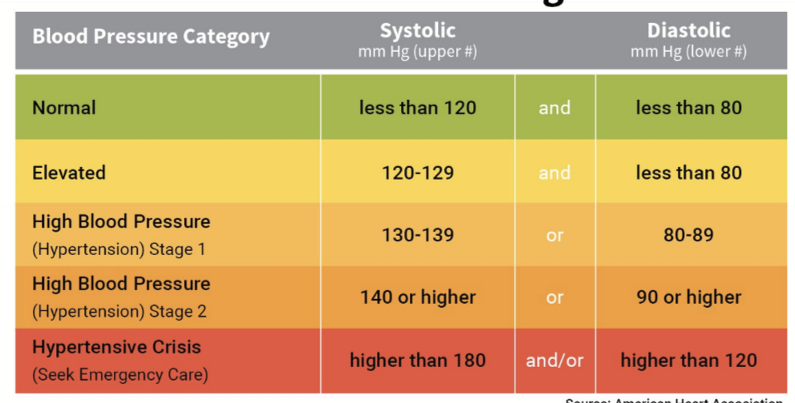
What needs to be present for stage 1 HTN patient to receive further treatment?
Hx: Heart attack/stroke
Diabetes mellitus
Renal disease
Hyperlipidemia
What is done for stage 2 HTN?
2 or more medications, often combined for compliance
What is hypertensive crisis:
When >180/120. Risks of organ damage and complications. Crisis retests after 5 minutes. Call 911 or have family take to emergency room.
When does malignant HTN occur?
During hypertensive crisis, where extremely high BP causes organ damage.
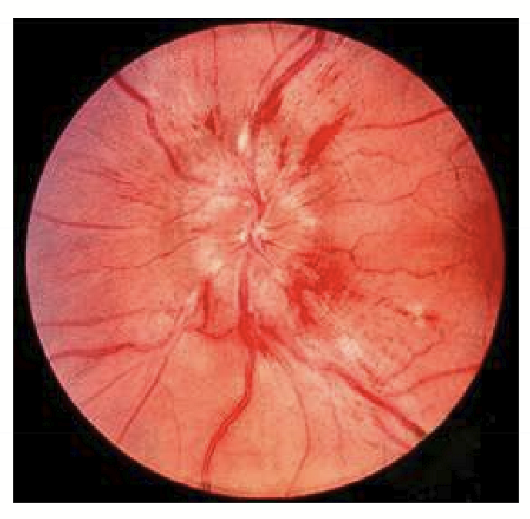
What is malignant hypertensive retinopathy?
When there is bilateral swelling of the optic nerve head (not papilledema) causing: Reduced vision, eye pain, flame-shaped hemorrhages, and headaches.
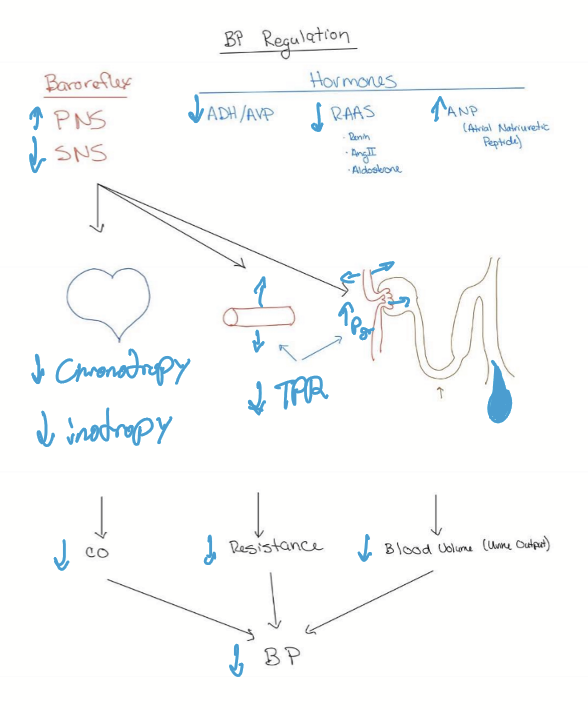
What is the body’s response to HTN?
Heart decrease CO: Decrease HR, Inotropy, and preload
Vasodilation
Kidney decreases blood volume
Increase filtration
Decrease sodium and water reabsorption to increase excretion
What are some lifestyle changes to decrease BP?
smoking cessation
alcohol rehabilitation
diabetes in control
low salt diet
eat better
exercise
What are some cardioinhibitory drugs for HTN?
Negative iontropic and chronotropic:
Beta blockers: metoprolol
CCB: Verapamil (phenylalkylamine) and Diltiazem (benzothiazepine)
Other:
Cardiac Glycosides (digoxin, oubain)
Nitroglycerin (NO)
What are some vasodilators to treat HTN?
CCB: amlodipine - dihydropyridine; diltazem - benzothiazepine
Alpha1 blockers: terazosin (hytrin)
Renin receptor blockers
Angiotensin II receptor blockers: losartan
ACE inhibitors: Lotensin (benazepril)
Vasopression Receptor Blockers (vaptan)
Endothelin receptor blockers
ANP agonists
What are some diuretics to treat HTN?
Furosemide
Thiazide
Spironolactone
Amiloride
Vaptan
Acetazolamide
Flosin: SGLT-2 blockers