IB HL Biology (Theme B)
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
54 Terms
What structure of proteins refers to the sequence of amino acids?
Primary
How are proteins differentiated?
Through their R-Groups
what is the role of carbohydrates
providing energy through glucose
hexose monosaccharides contain
six carbon atoms; are soluble, stable, create respiration for ATP, and vital for photosynthesis. Glucose, fructose, and galactose
what monosaccharides are hexose shaped
glucose, fructose, galactose
how many carbon atoms are in pentose?
five carbon atoms
what monosaccharides are pentose-shaped
deoxyribose and ribose
why is glucose so important for cells?
glucose is vital for cellular solubility, transportability, oxidation, and stability
what are the two anomers of glucose?
alpha and beta glucose
a-glucose contains
one downward carbon in hydroxyl group
b-glucose contains
one upward carbon in hydroxyl group
what do different hydroxyl groups do?
create polymers with different structures
when are disaccharides formed?
formed when two monosaccharides are joined together via condensation reaction
Glucose + Glucose =
Maltose
Glucose + Galactose =
Lactose
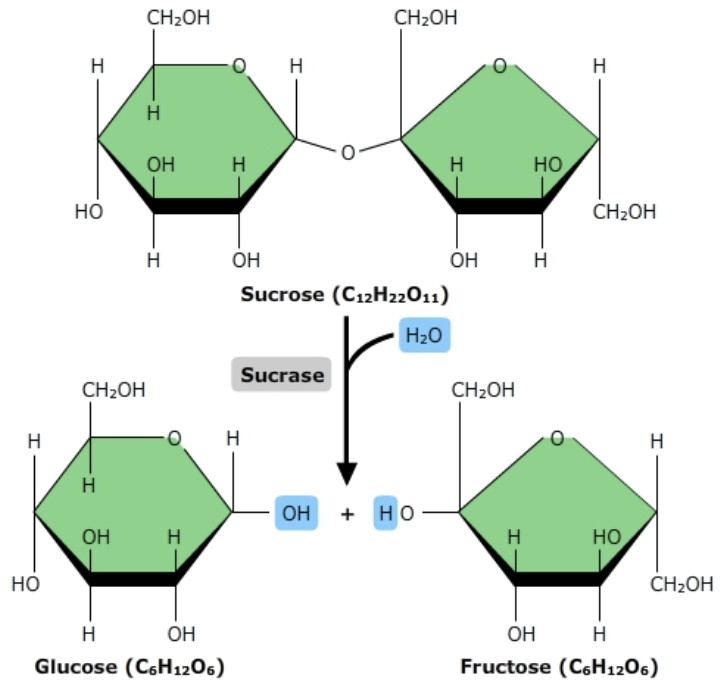
Glucose + Fructose =
Sucrose
condensatiion reactions
linkage of two molecules w/covalent bonds release water molecule
hydrolysis reactions
when molecules are broken down into two smaller molecules by adding water molecule and breaking covalent bonds
what are the functions of hydrolysis reactions?
breaking down polymers into monomers
what are anabolic reactions?
reactions which require energy in order to synthesize larger molecules
what are catabolic reactions?
break down larger molecules, such as carbohydrates, lipids, and proteins from ingested food, into their constituent smaller parts
what are polysaccharides?
polymers with many monosaccharide monomers covalently bonded; formed by condensation reactions
what is starch made up of?
starch is made up of amylase and amylopectin
what is amylase
a linear polysaccharide made up of a-glucose molecules
what is amylopectin
a branched polysaccharide that is part of a starch molecule, made up of a-glucose molecules
what differentiates a-glucose from b-glucode
the orientation of the hydroxyl group. a-glucose are building block of starch, b-glucose is building block of cellulose.