HUMANBIOLOGY_CHAPTERTWENTYSIX
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
muscular system
organ system consisting of skeletal muscles whose contractions form the basis of movement and posture
skeletal system
organ system consisting of bones, cartilage, ligaments, and tendons; functions include support, movement, and protection
muscle
organ that powers movements in animals by contracting; consists of muscle tissue and other tissue types
bone
organ consisting of bone tissue, cartilage, and other tissues
marrow cavity
space in a bone shaft that contains marrow
red bone marrow
marrow that gives rise to blood cells and platelets
yellow bone marrow
fatty marrow that does not produce blood cells or platelets
bone tissue
connective tissue consisting of cells embedded in a mineralized matrix
tendon
band of fibrous connective tissue that attaches a muscle to a bone
skeletal muscle
organ that generates voluntary movements between pairs of bones; composed of bundles of skeletal muscle tissue and other tissue types
skeletal muscle tissue
voluntary muscle tissue consisting of long, unbranched, striated cells with multiple nuclei
muscle fiber
muscle cell
myofibril
cylindrical subunit of a muscle fiber, consisting of parallel protein filaments
sarcomere
one of many repeated units in a myofibril of a muscle cell
motor neuron
neuron that transmits a message from the central nervous system toward a muscle or gland
creatine phosphate
molecule stored in muscle fibers; donates its high-energy phosphate to ADP, regenerating ATP
Mobility in vertebrates is made possible by what systems?
skeletal and muscular
In vertebrates, bones of the skeleton not only provide movement and support, but also function to supply ______ to the rest of the body and produce ______ within the bone marrow.
minerals; blood cells
Under the direction of the nervous system, components of the ______ system contracting and pulling against components of the _____ system give vertebrates the ability to move under their own volition.
muscular; skeletal
What organs compose the vertebrate skeleton?
bones
The vertebrate skeleton is composed mostly of what two types of connective tissue?
cartilage; bone
Ligaments are bands of connective tissue that attach _____.
bone to bone
Structures called ______ contain a marrow cavity, blood vessels, nerves, and cells that secrete a hard extracellular matrix consisting of collagen and minerals.
bones
What describes bone tissue?
cells in a hard extracellular matrix
How do hormones from the parathyroid and thyroid glands influence bones?
They control the absorption and release of calcium from bones.
Mobility in vertebrates is made possible by what systems?
skeletal and muscular
The biceps, trapezius, quadriceps, and sartorius are all examples of ______.
skeletal muscles
Bone and cartilage compose the majority of the vertebrate _____.
skeleton
What are muscle fibers?
individual muscle cells
Connective tissue that attaches one bone to another bone is called a ______.
ligament
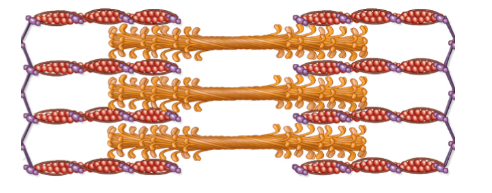
The muscle structure shown in the entire diagram is a single ______.
sarcomere
The bones are a reservoir for the mineral ______ , which is vital for muscle contraction, blood clotting, and other essential functions.
calcium
To stimulate muscles to contract, a ______ delivers a signal at a specialized synapse between the neuron and a muscle cell.
motor neuron
What type of muscles generate voluntary movements?
skeletal
Muscle cells generate ______ through aerobic respiration as long as the demand for oxygen doesn't exceed the supply of oxygen.
ATP
A muscle is an organ composed of parallel bundles of ______, which are individual muscle cells.
muscle fibers
A sprain is an injury to a ______.
ligament
What is a sarcomere?
the functional units if myofibrils
When the central nervous system sends signals for muscles to contract, the signals are conveyed to muscles by ______.
motor neurons