Health Assesment Exam 2
1/78
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
79 Terms
Describe the ABCDEF mnemonic of melanoma
A: assmetry
B: Border
C: color
D: diameter
E: evolving
F: feeling
define hypopigmentation and provide an example
happens when the melonosytes are destroyed somehow
like in vitiligo
define hyperpigmentation and provide an example
melasma is an example ( mostly in women)
assosiated with hormonal changes
caued by increase in melanin
pigmented nevi
moles; local accumulation of melanin
freckles
flat, melanized patches
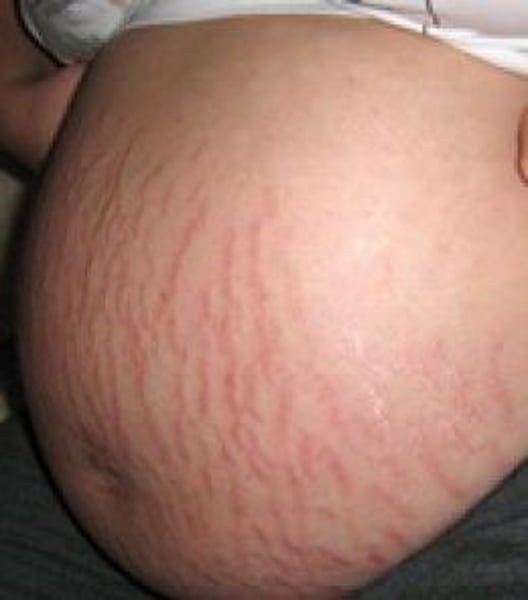
striae
a flat, discolored area on the skin larger than 1 cm
( stretch marks)
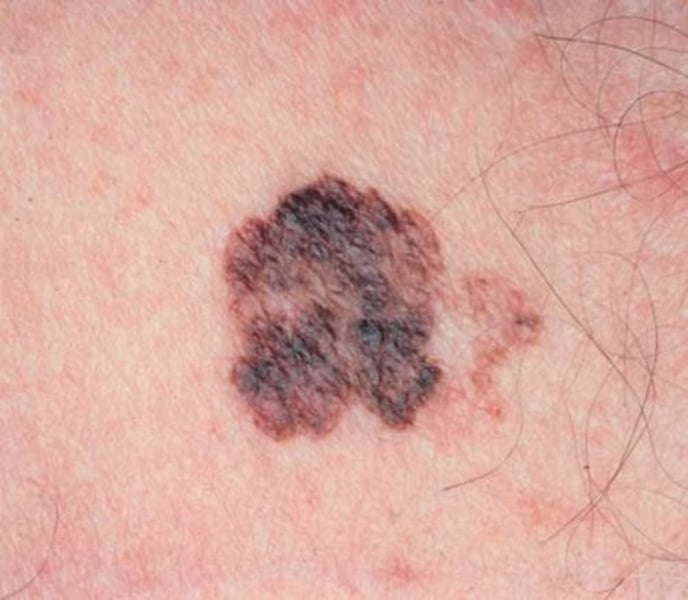
melanoma
most serious
malignant proliferation of melanocytes
irreugulary shaped with color variations
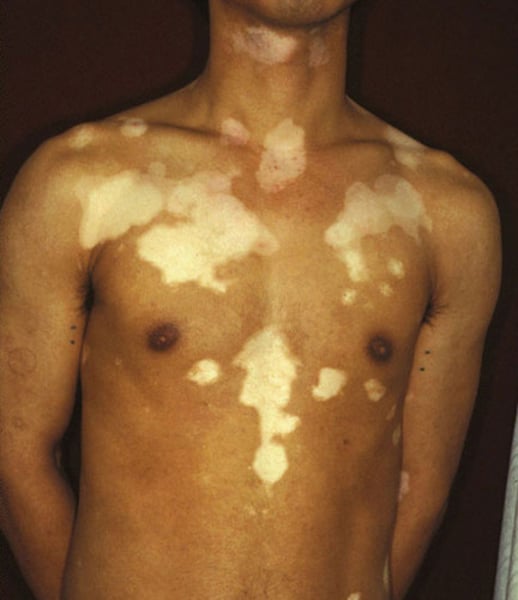
vitiligo
white patches on the skin caused by the destruction of melanocytes associated with autoimmune disorders
explain the clincial significance of cool skin
could be : hypothermia
or they could have clammy, cool skin from shock
localized cold feet and hands could be a sign of peripheral arterial disease
explain the clincial significance of hot skin
increased metabolic rates : fever , hyperthyroidism
heat stroke
possibel signs of inflammation or infection
explain the clinical significance of diaphoresis,
Excess moisture, or diaphoresis, is abnormal in the absence of strenuous activity.
what disease conditons can be assosiated with diaphoresis
Hyperthermia, extreme anxiety, pain, or shock(cool and diaphoretic), hyperthyroidism,hypoglycemia.
describe the process of assesing skin turgor , what locations are most appropriate ?
Technique: Pick up and slightly pinch skin on forearm or under clavicle.
normal and abnormal findings of skin turgor
Skin should be elastic (move easily when lifted).Should return immediately when released="No tenting
what is the cause of 'tenting'?
dehydration or excess weight loss
Reduced mobility- edema, excess scarring, or scleroderma (a rare connective tissue disorder)
what chronic disease can result in skin thickening?
Diabetes mellitus/insulin resistance can cause abnormal collagen resulting from hyperglycemia
Acanthosis nigricans is a condition that causes areas of dark, thick velvety skin in body folds and creases and typically affects the armpits, groin, and neck.
NOT BECAUSE OF POOR HYGIENE
excessively thin skin or shiny skin is the result of what
Decreased thickness of the skin can be seen , arterial insufficiency and aging
The skin may also be shiny and hairless on legs with advanced age and arterial insufficiency
how do thyroid abnormalities impact changes in hair distribution ?
Hypothyroidism can lead to thinning hair, dryness, and brittle hair. Hair may become sparse, particularly on the scalp's outer edges
Hair growth cycles may be disrupted, leading to slower growth and a decrease in overall hair volume.
Hyperthyroidism can also cause changes in hair distribution, though the effects may differ from those of hypothyroidism.
Hair loss or thinning may occur, but it might be more diffuse rather than localized to specific areas.
Although not directly caused by thyroid abnormalities, alopecia areata, an autoimmune condition that leads to hair loss in patches, can sometimes be associated with thyroid disorders.
Thyroid dysfunction can influence the immune system, potentially triggering or exacerbating conditions like alopecia areata..
what is the significance of hair loss on the lower legs
If there is no hair on loweer legs and the person has not shaved the it could mean they have PAD, Alopicia areta, a Vascular Insufficiency, trauma or an injury.
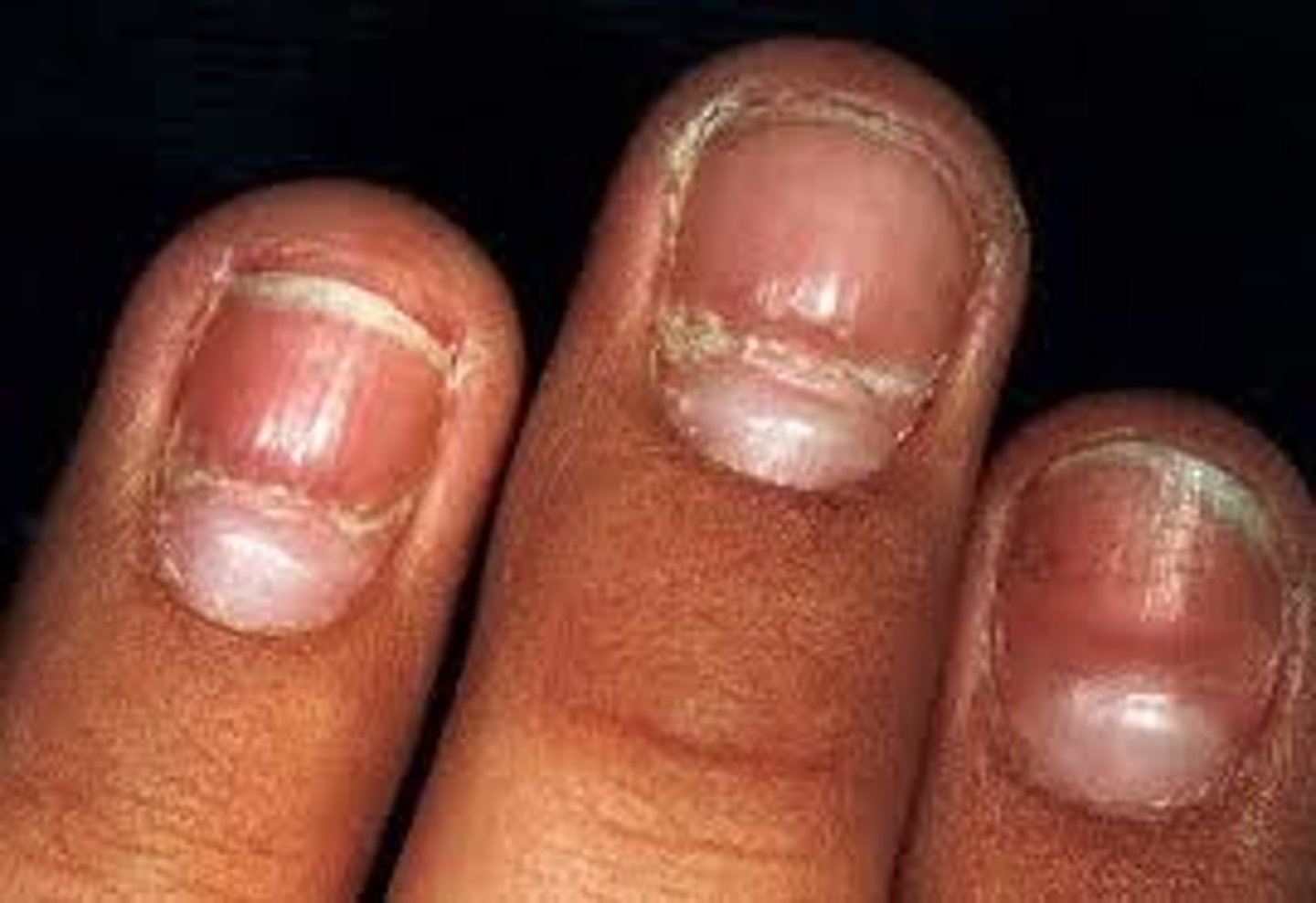
What is kolionychia and what are possible causes?
Koil=hollow.
Onychia = nails.
Also known as "spoon nails".May be congenital.May be caused by anemia or other medical conditions.
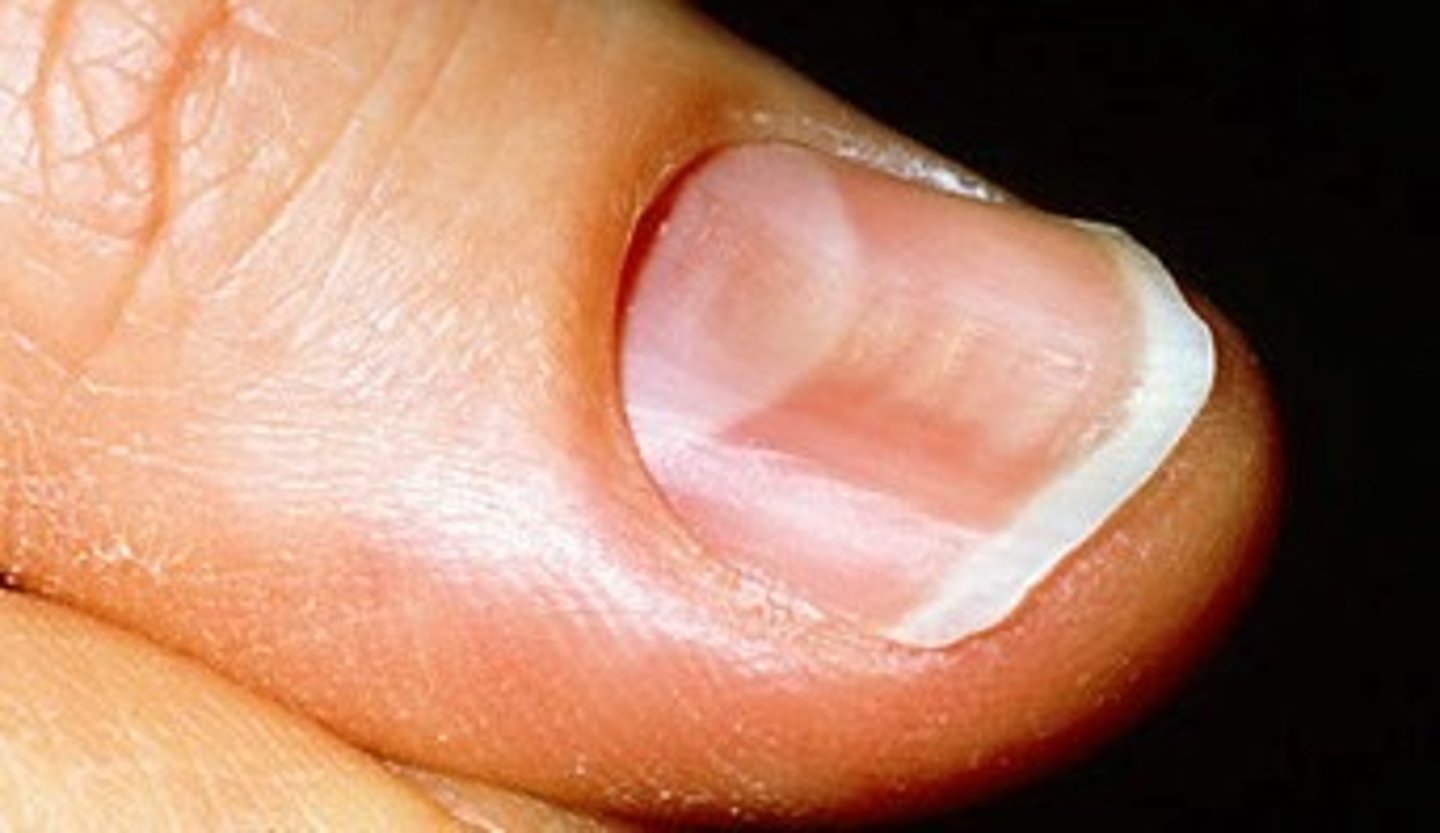
what is leukonchia and what is the possible cause.
Leuk=white
Onychia=nail
Caused by trauma to the nail
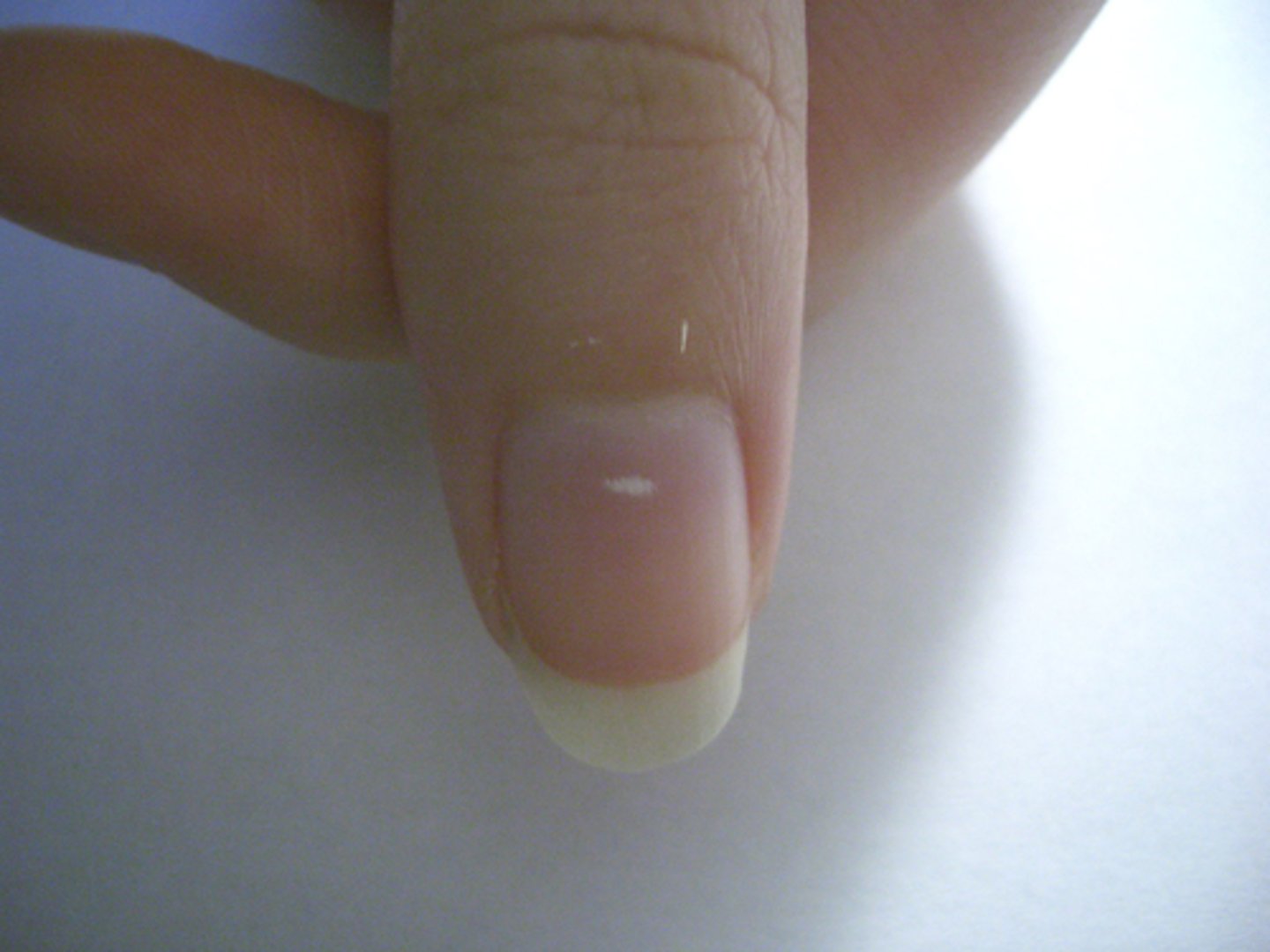
what is clubbing. What does it represent?
Clubbing is associated with chronic hypoxia, e.g.emphysema or congenital heart problems in children.
what are beau's lines?
Transverse groove across the nail. Caused by trauma.Starts at base of nail by cuticle and then grows out
distinguish between stage 1-iv pressure ulcer
stage 1: prolonged redness with unbroken skin
stage 2; partial -thickness skin loss appears as a shallow, opwn ucler with pink wound bed
stage 3: full thickness skin loss with damage to subcutaneous tissue
Stage 4: full thickness skin losswith exposed bone, muscle, or tendon , may have some eschar or slough
what is an unstageable ulcer?
eschar or slough may cover the entire wound bed, thus it is unstagable
clavus
small, painful area of thickened skin, usually on the toe; also called a corn
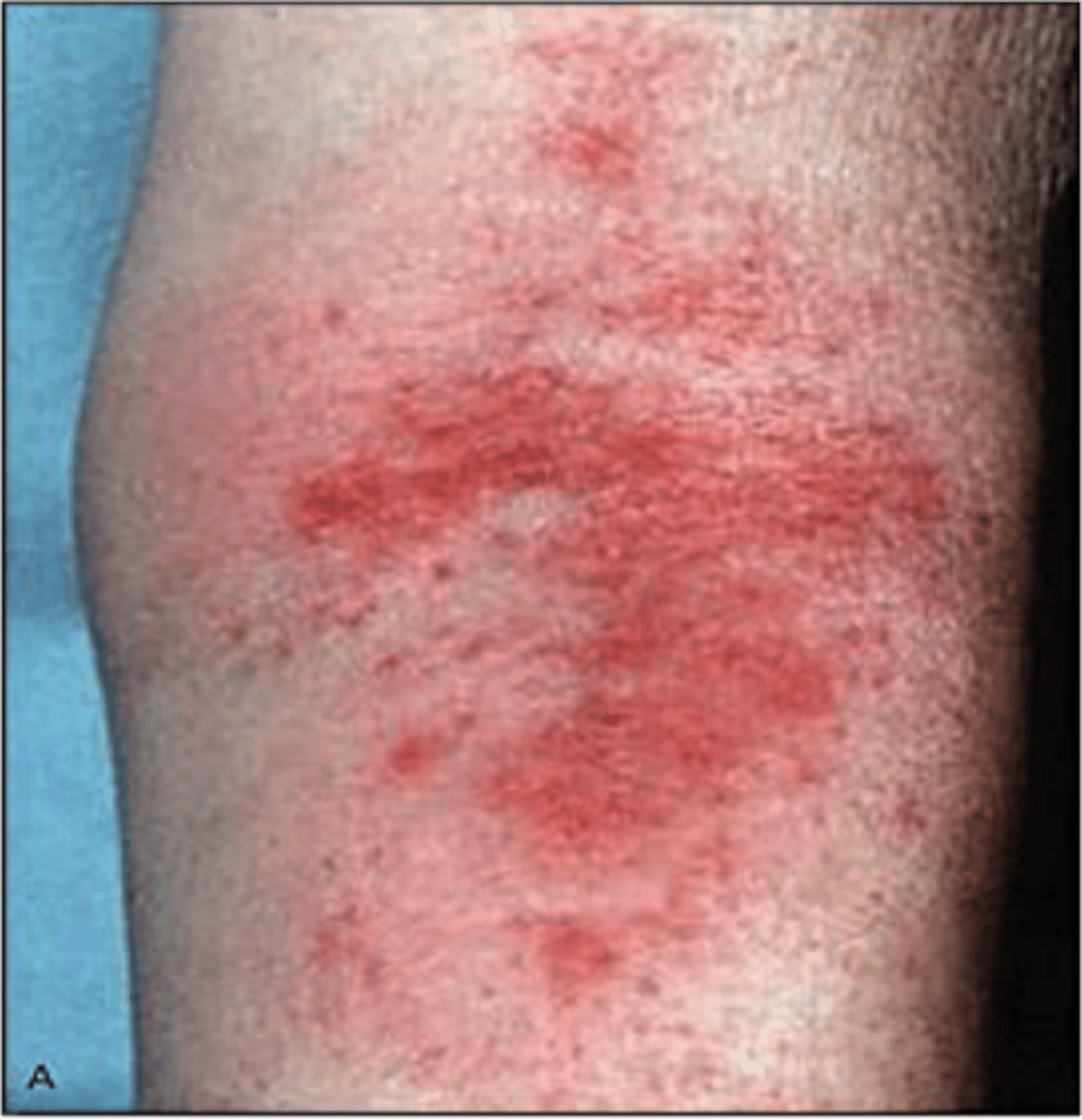
atopic dermatitis
superficial inflammation
seborrheic dermatitis
chronic inflammation
scaly, white, or yellowish skin on scalp, eyebrows, ears, axillae, chest or back
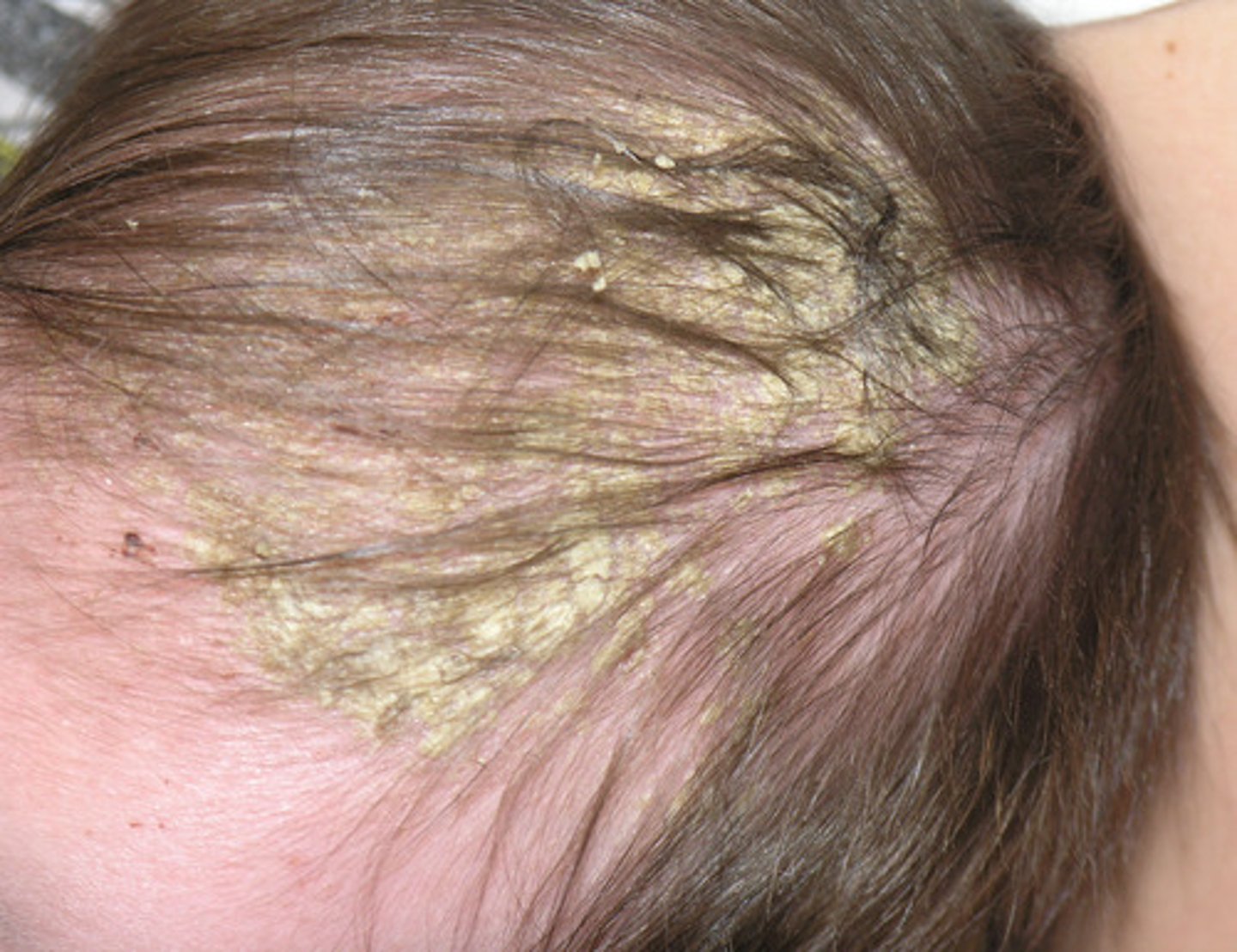
stasis dermatitis
inflammation seen mostly on lower legs of older adults
areas of scaling, petechiae and brown pigmentation
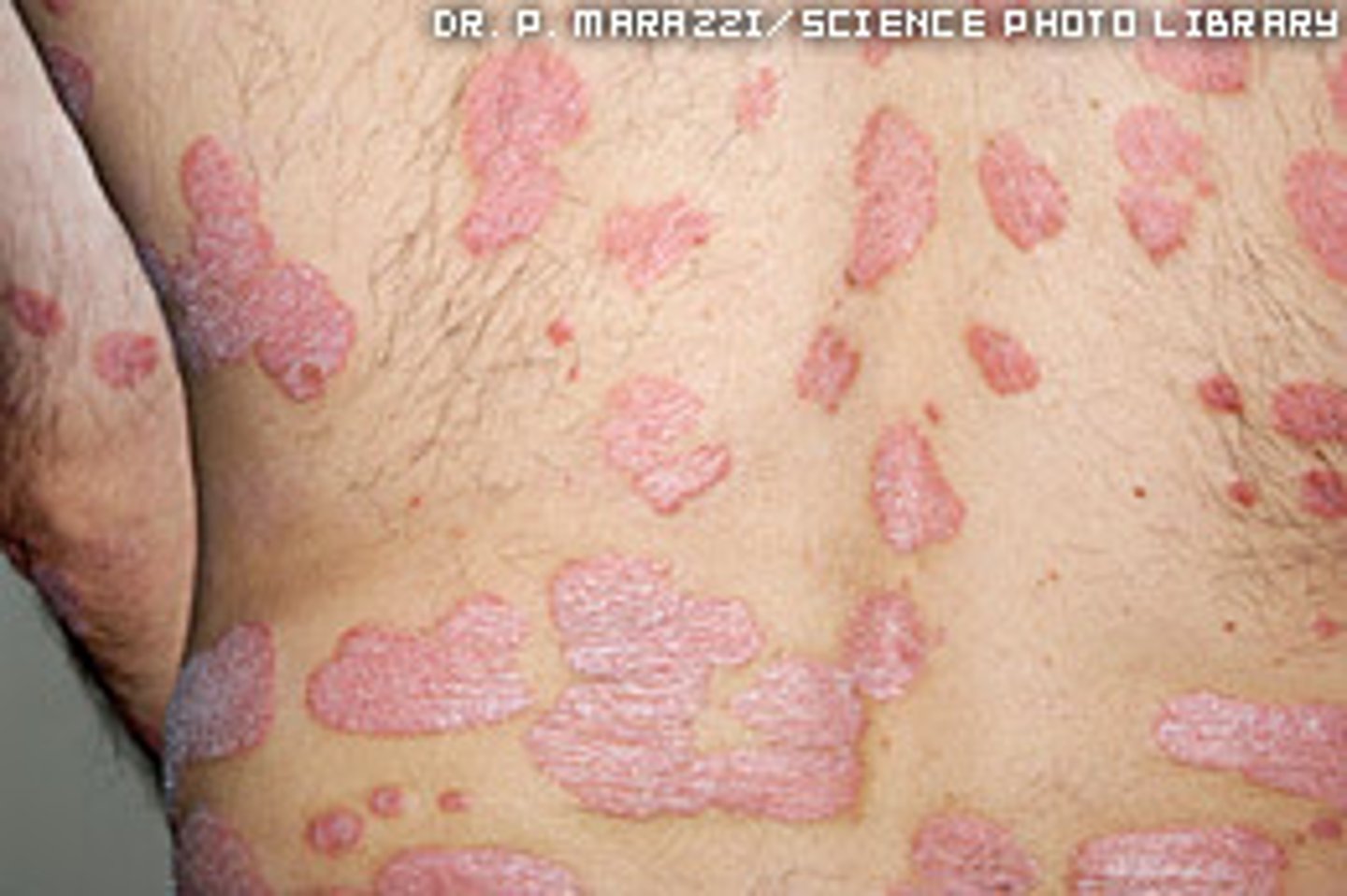
Psoriasis
usually develops by 20
slightly raised erthematous plaques with silvery scales
mostly on elbows, knees, buttocks, lower back, and scalp
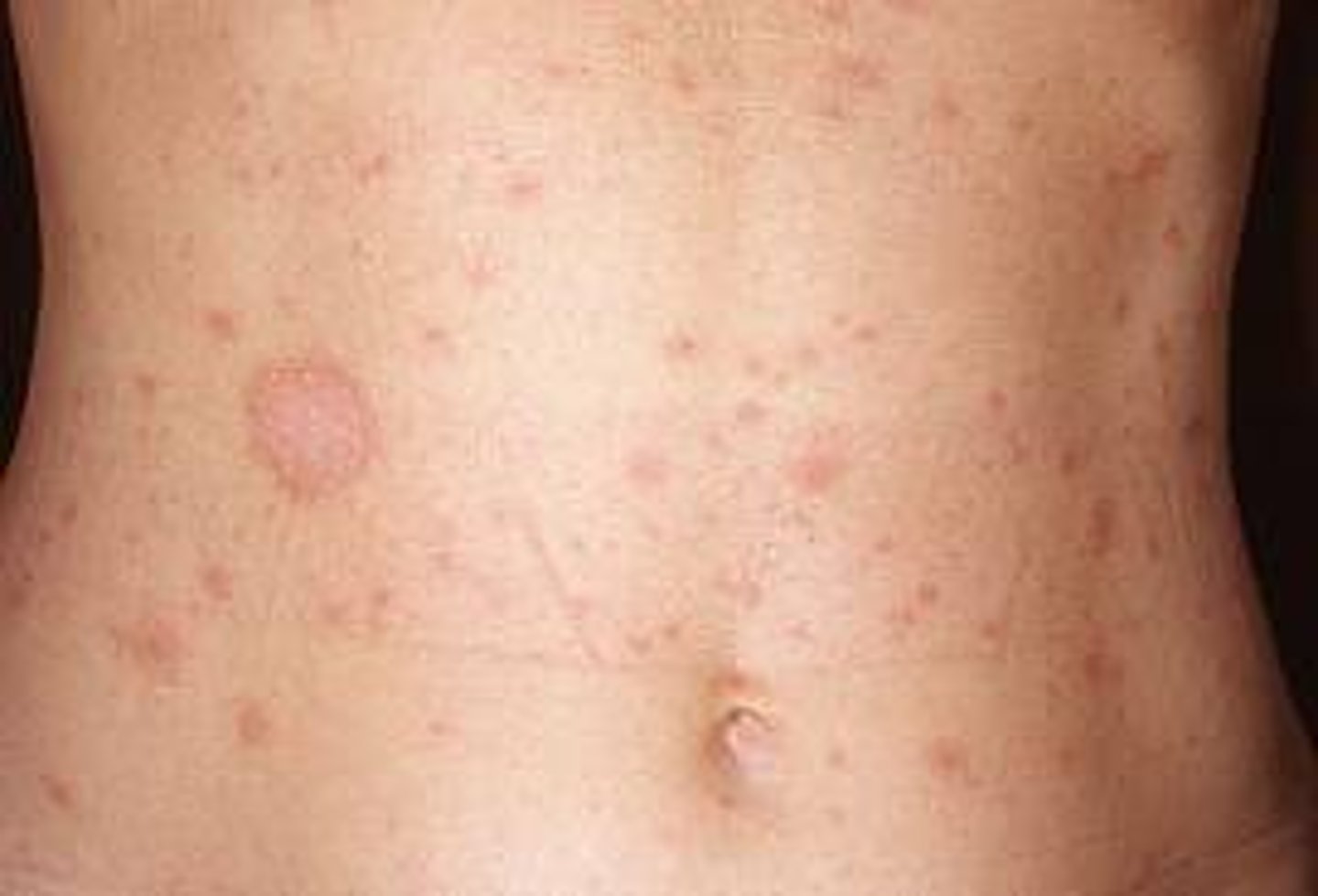
Pityriasis Rosea
acute, self limiting disease of young adults in winter
thought to be viral
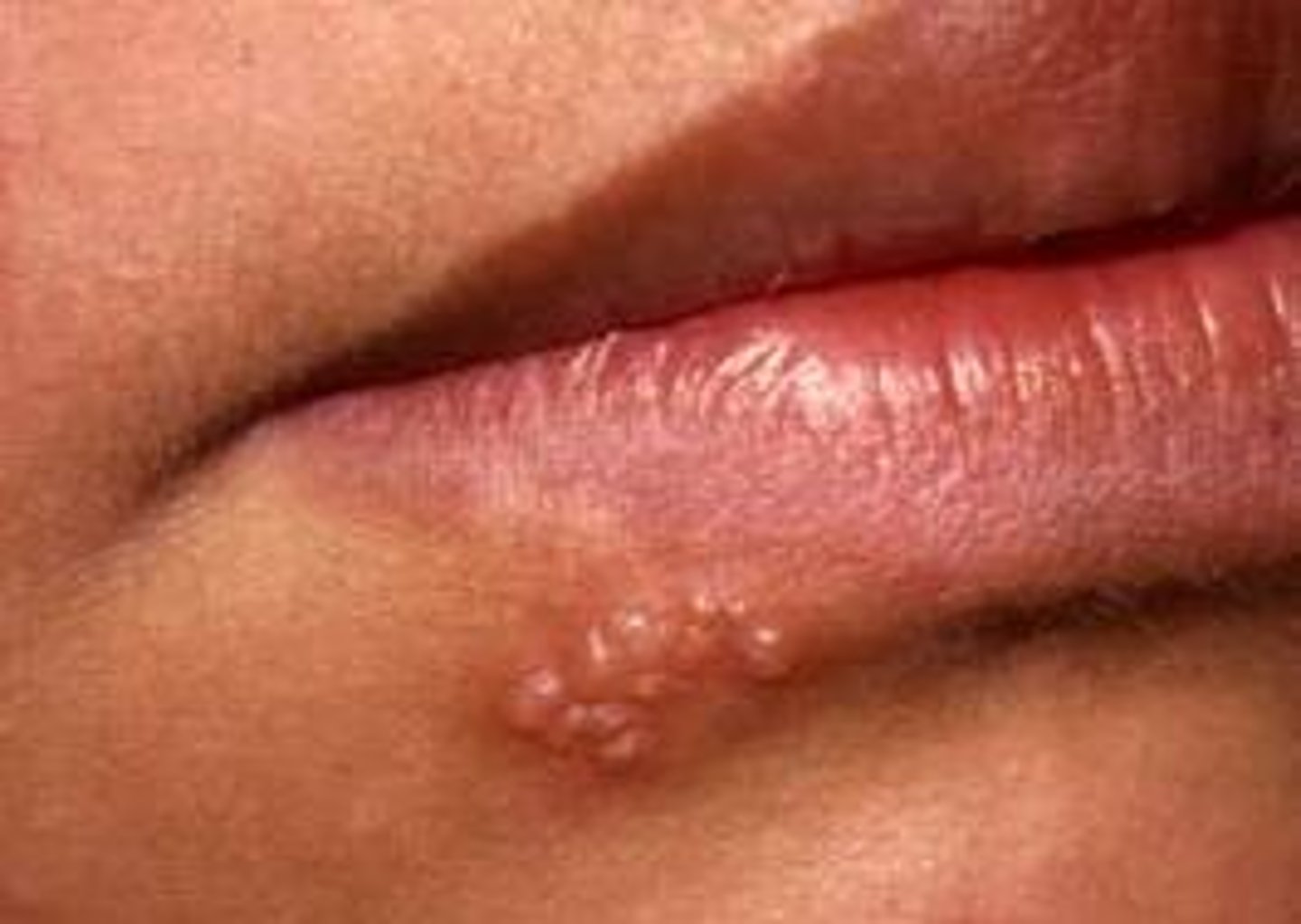
herpes simplex viral
outbreaks triggered by sun exposure, stress, fever
griuped vesicles with an erthematous base
very painful and highly contagious
eruption lasts about two weeks
herpes varciella ( chicken pox) viral
lesions erupt in crops
painful and highly contagious
infectivity lesions along sensory nerve line
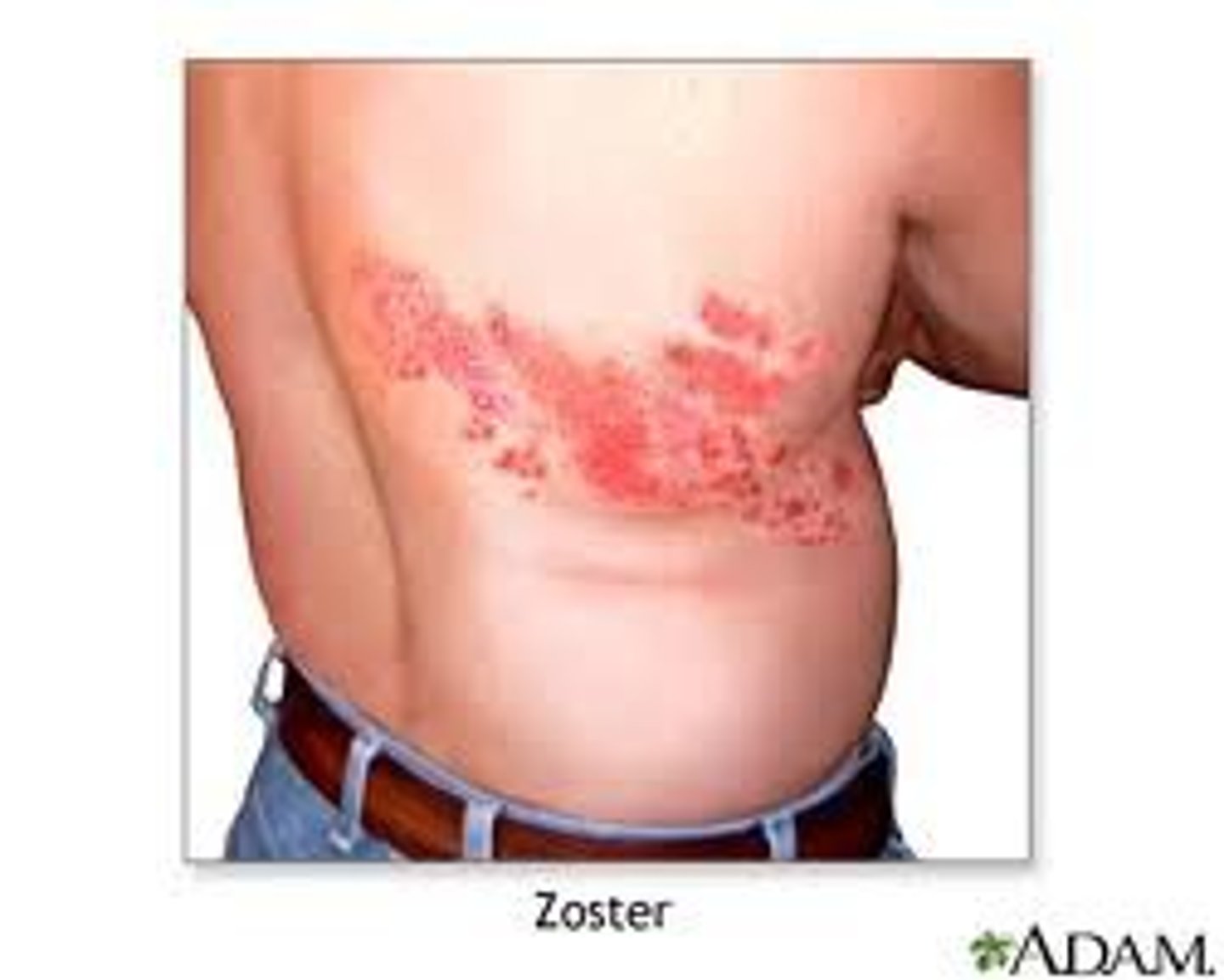
herpes zoster ( shingles) viral
grouped lesions along sensory nerve line
tinea infections ( lesions from fungal infection)
a fungal infection of the skin or feet
like ringworm (tinea corporis)
jock itch ( tinea cruris )
scaling and balding ( tinea capitis)
athlesets foot ( tinea pedis)
candidiasis ( fungal infection )
affect superfical layers of skin and mucous memebranes
celluitis ( Lesions caused by baterial infection)
acute streptococcal or staphlocccal infection of skin and subcutaneous skin and tissue
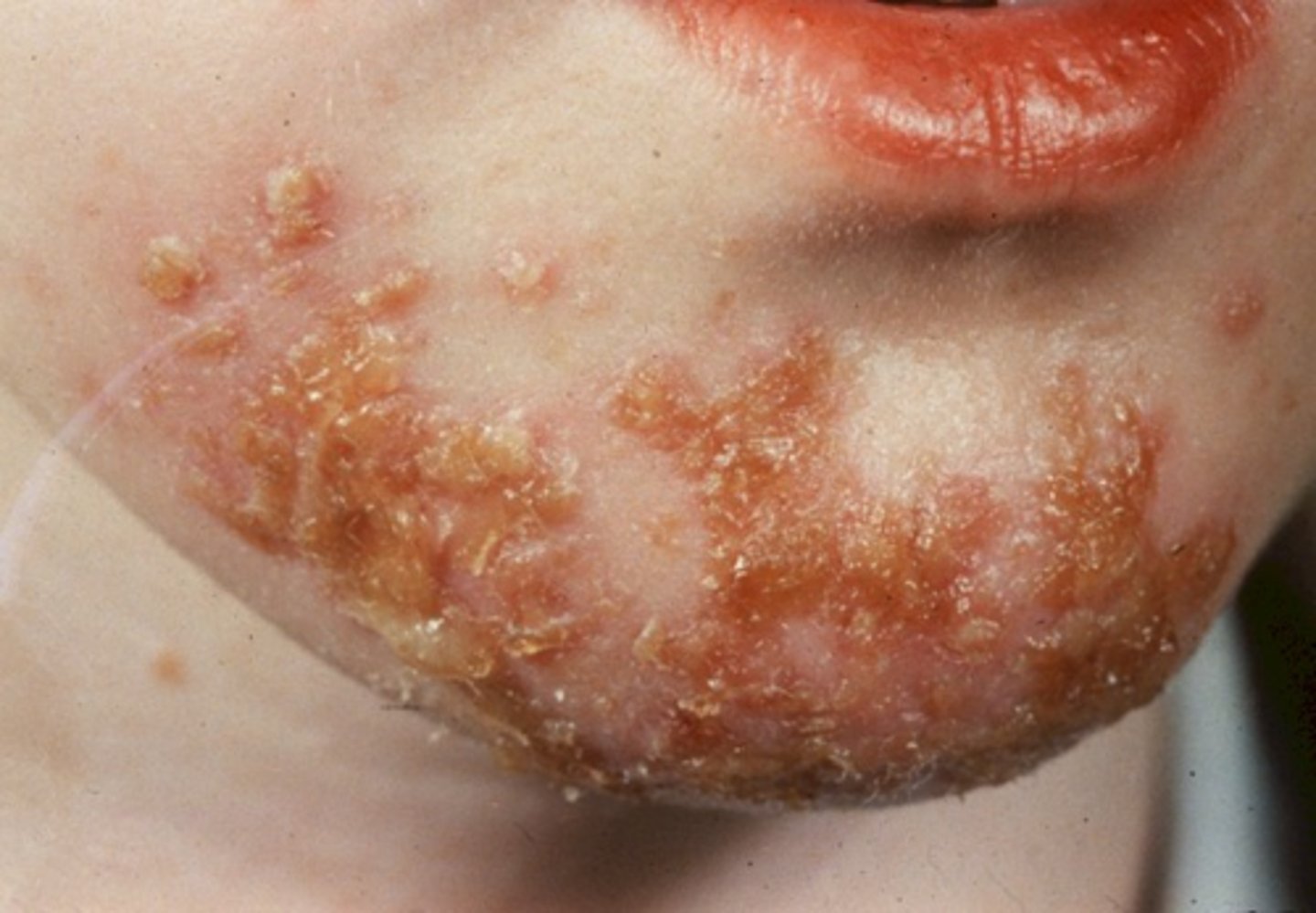
impetigo ( bacterial)
highly contagious group a streptococcal infection
generally occurs on face, around mouth and nose
follicultis ( bacterial infection )
inflammation of hair follicles
furuncle/abscess ( bacterial)
staphylococcal infection
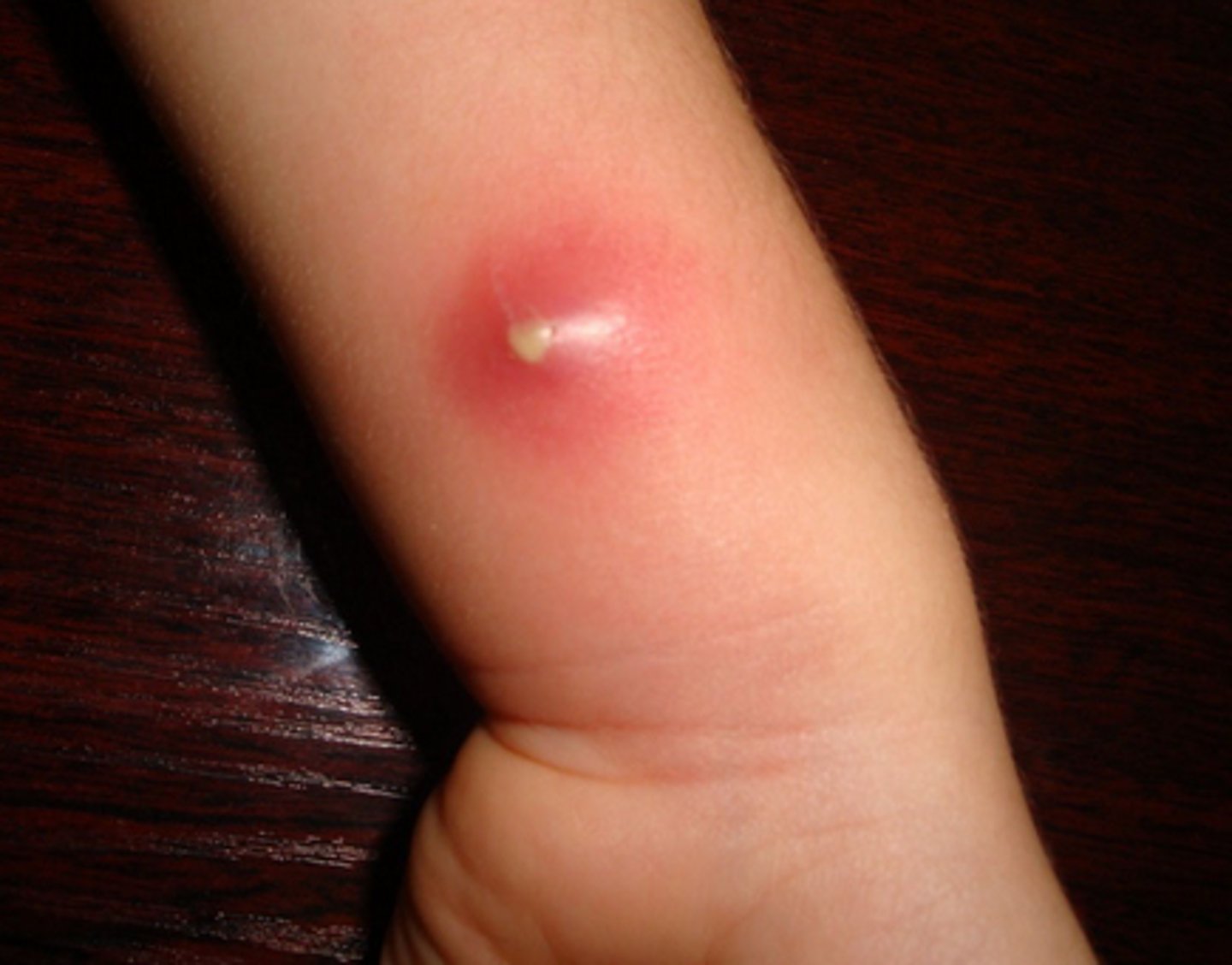
scabies ( caused by anthropods)
highly contagious mite sarcoptes scabei
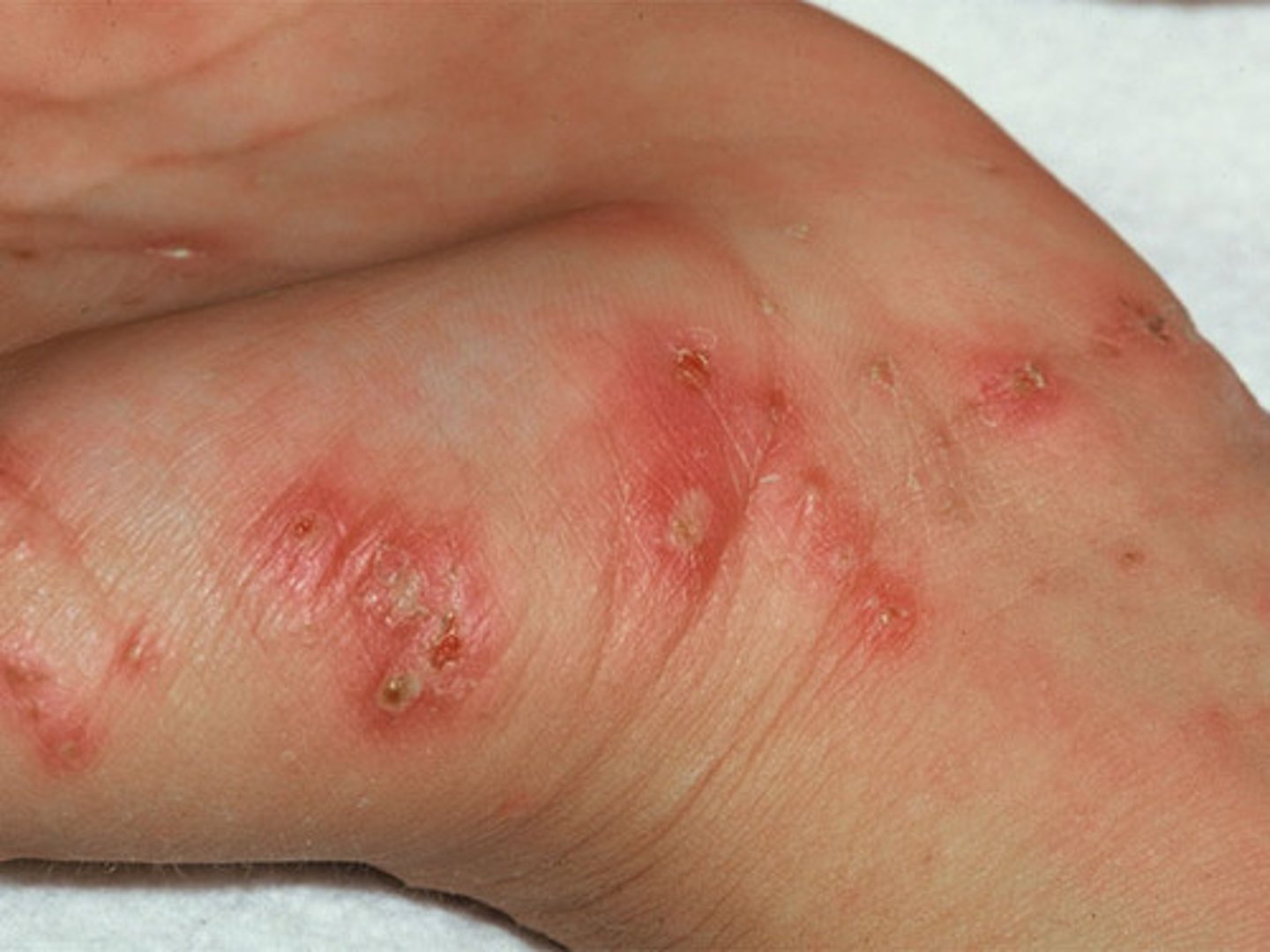
lyme disease ( anthropods)
tick infected with borrelia burgdorferi
spider bites ( anthropods)
majority from black widow or brown recluse spiders
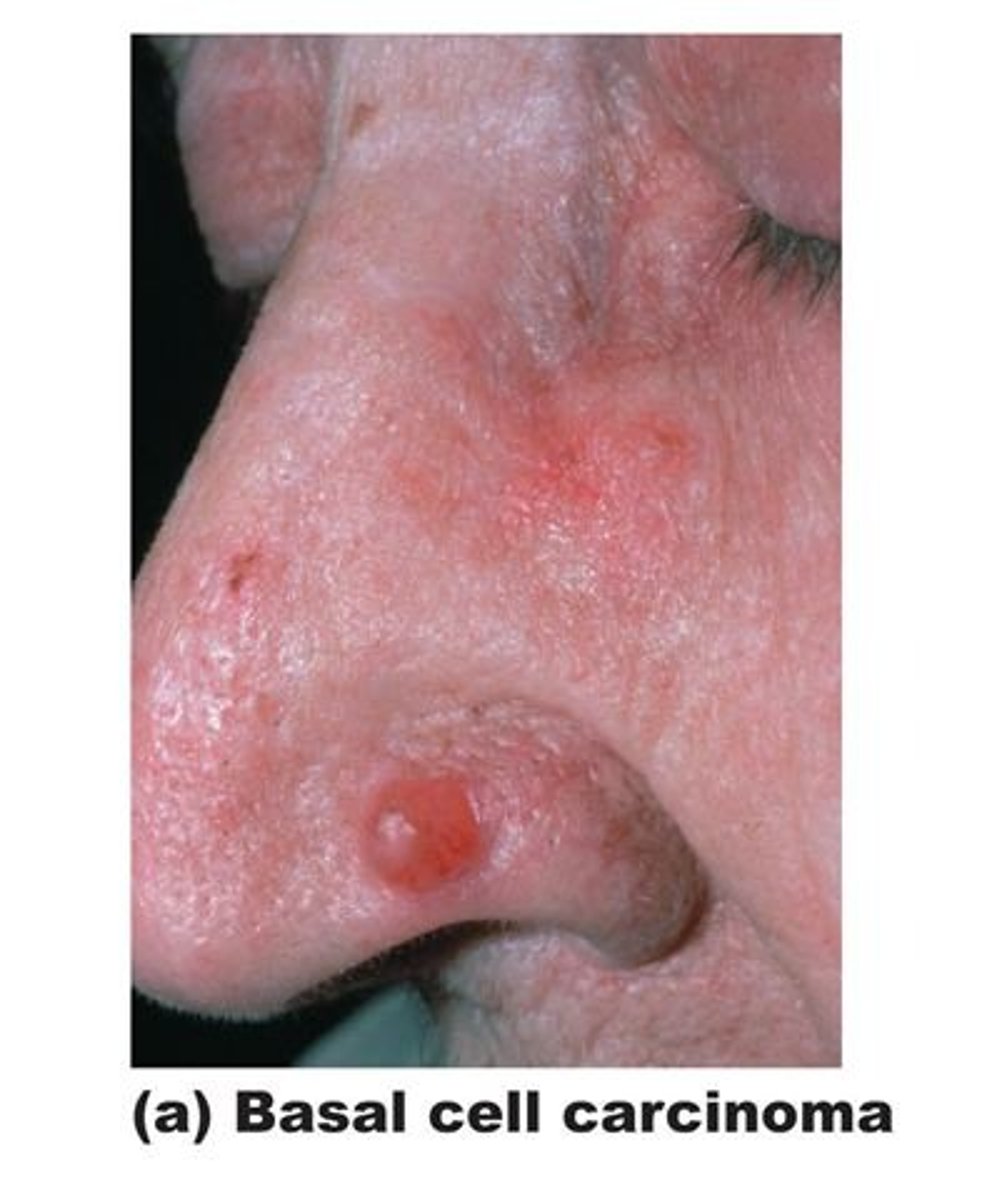
basal cell carcinoma
most common
locally invasisive; rarely metastasizes
nodular pigmented lesions with depressed center and rolled borders
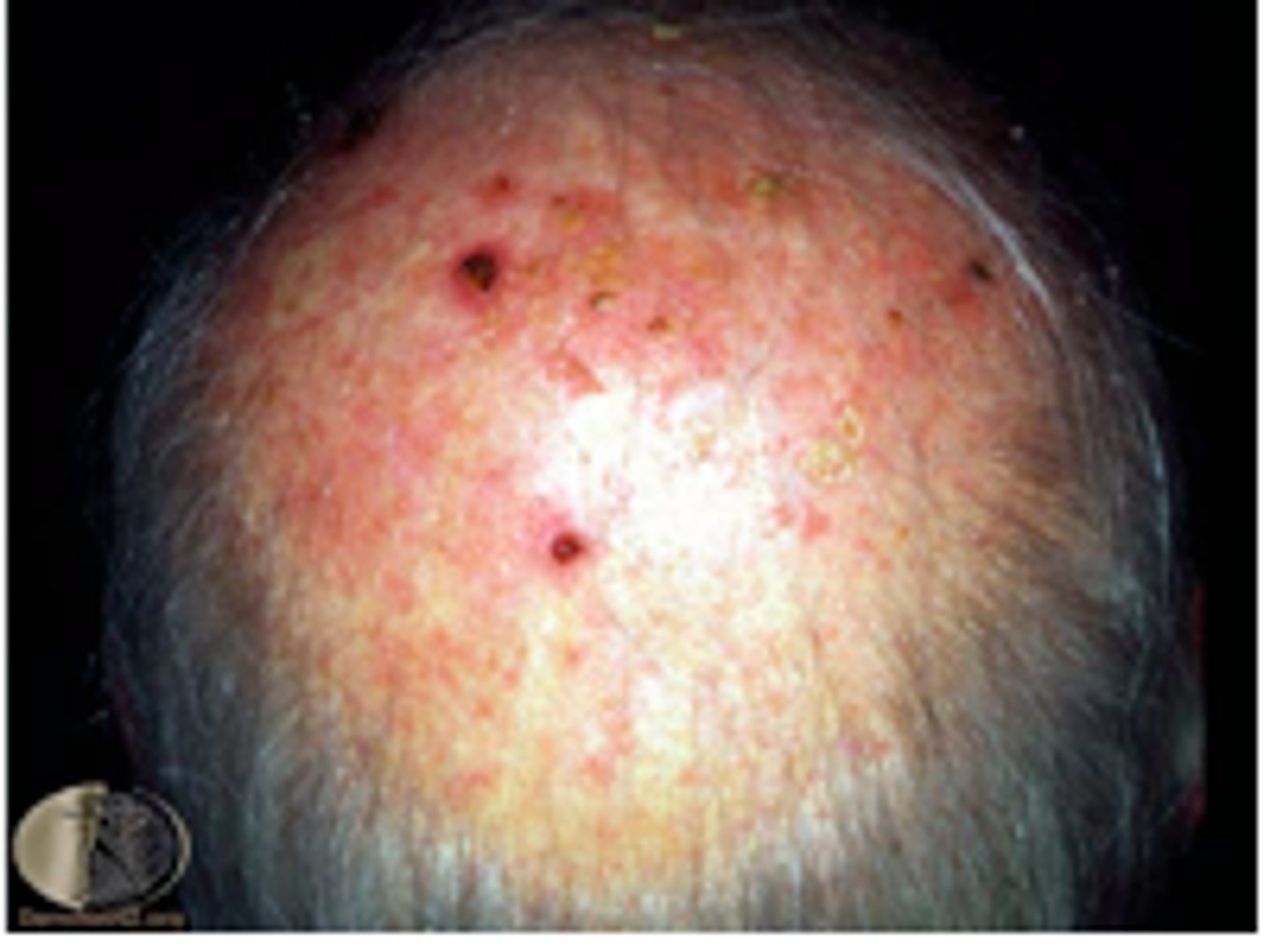
squamos cell carcinoma
intially appears as a red, scaly patch
Kaposi's sarcoma
devlops in conective tissue of immunosupressed
dark bluepurple macules, papules, nodules, and plaques
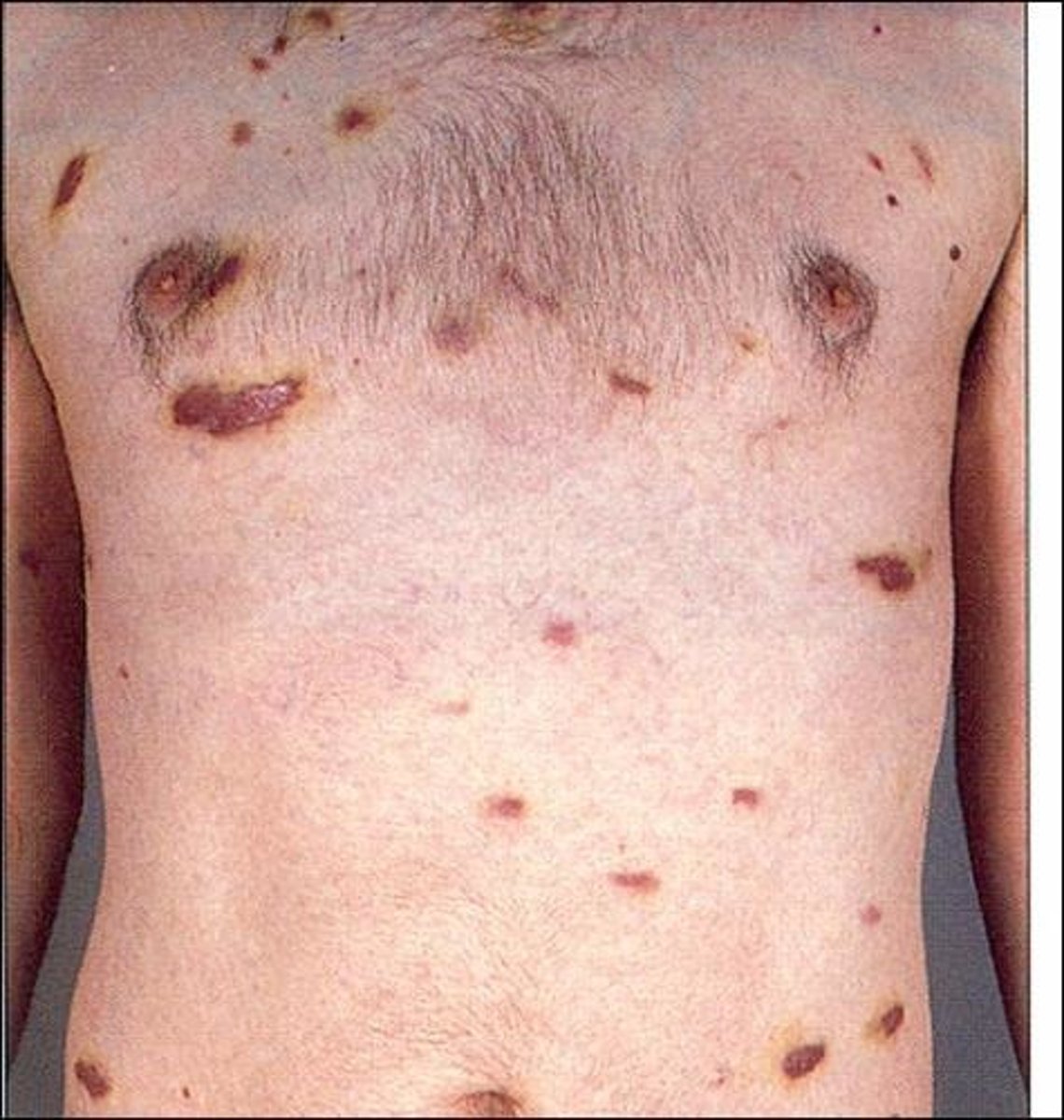
Ecchymosis
bruise
dark red, purple, yellow
pediculosis ( hair)
lice on the body are called pediculosis corporis
pubic lice are called pediculosis pubis
Spread through person-to-person contact and shared clothing.
Alopecia areata ( hair)
chronic inflammatory disease of hair follicles resulting in hair loss on scalp
Unknown cause- believed to be autoimmune disorder, metabolic disease and stressful events.
Multiple round patches of hair loss
hirsutism ( hair)
increase in growth of facial, body, or pubic hair in women( PCOS)
Unwanted hair growth in women with an increase in hair on the face, body and pubic area.
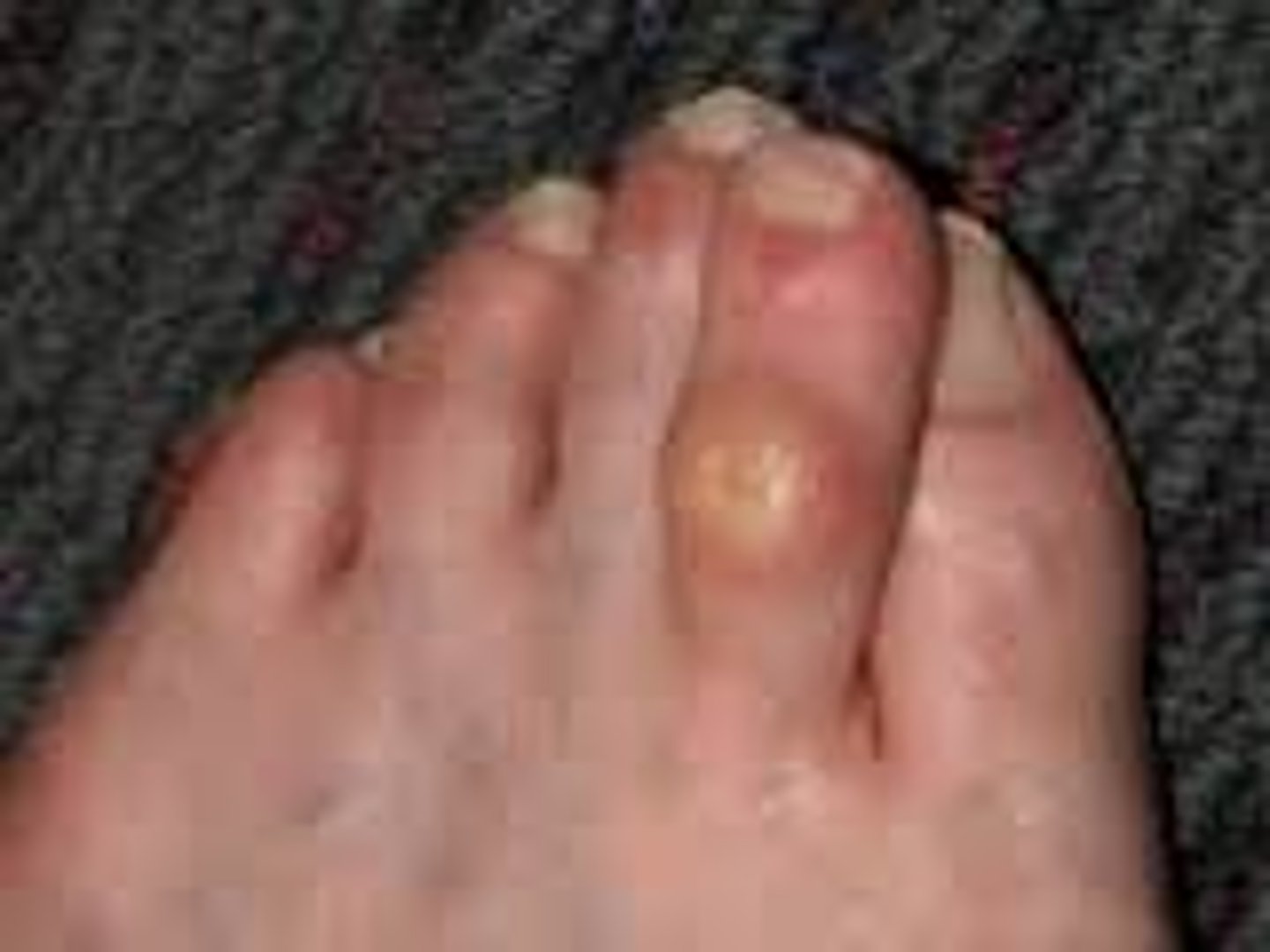
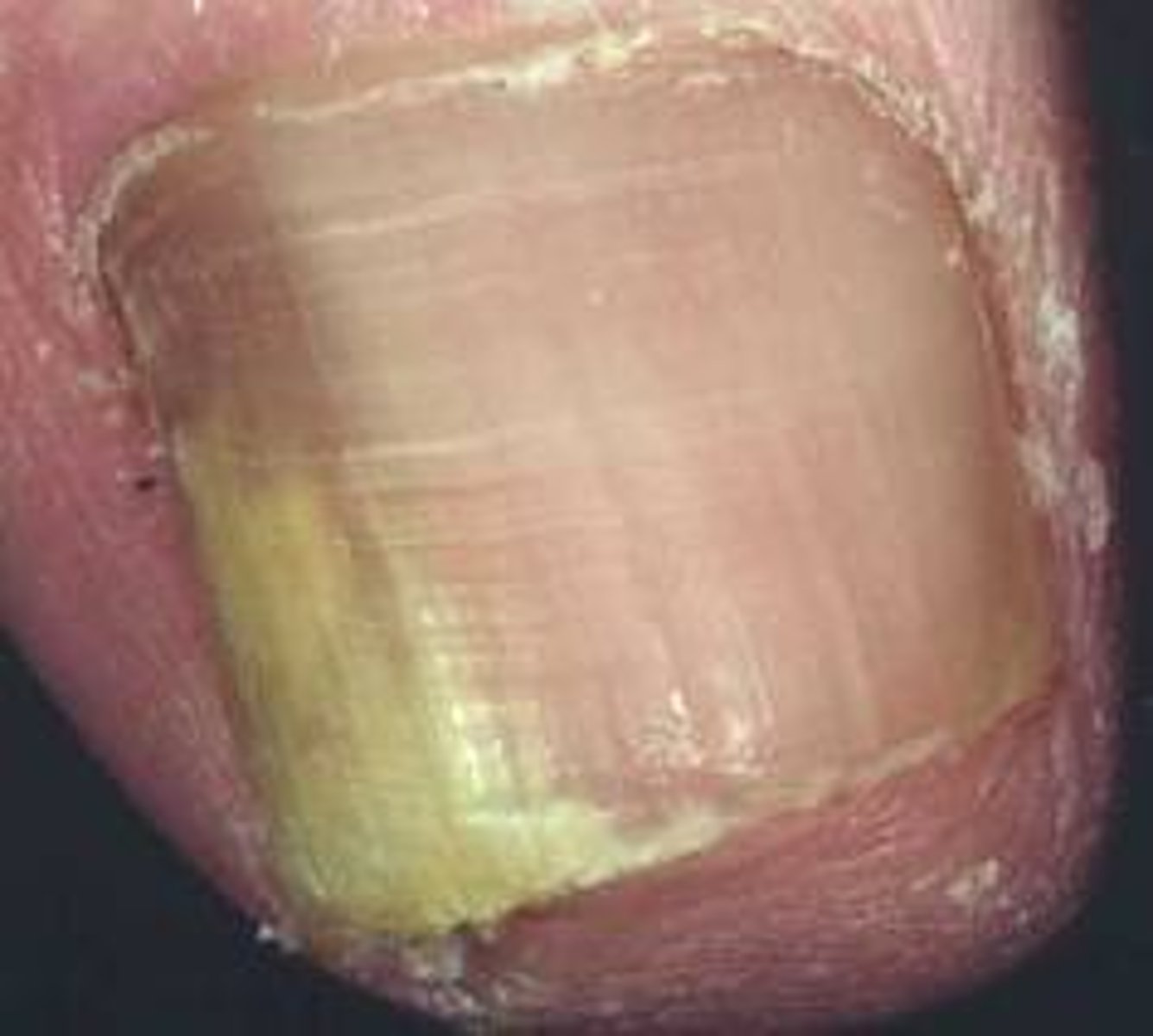
onychomycosis ( nails)
Fungal infection of nail plate caused by Tinea unguium
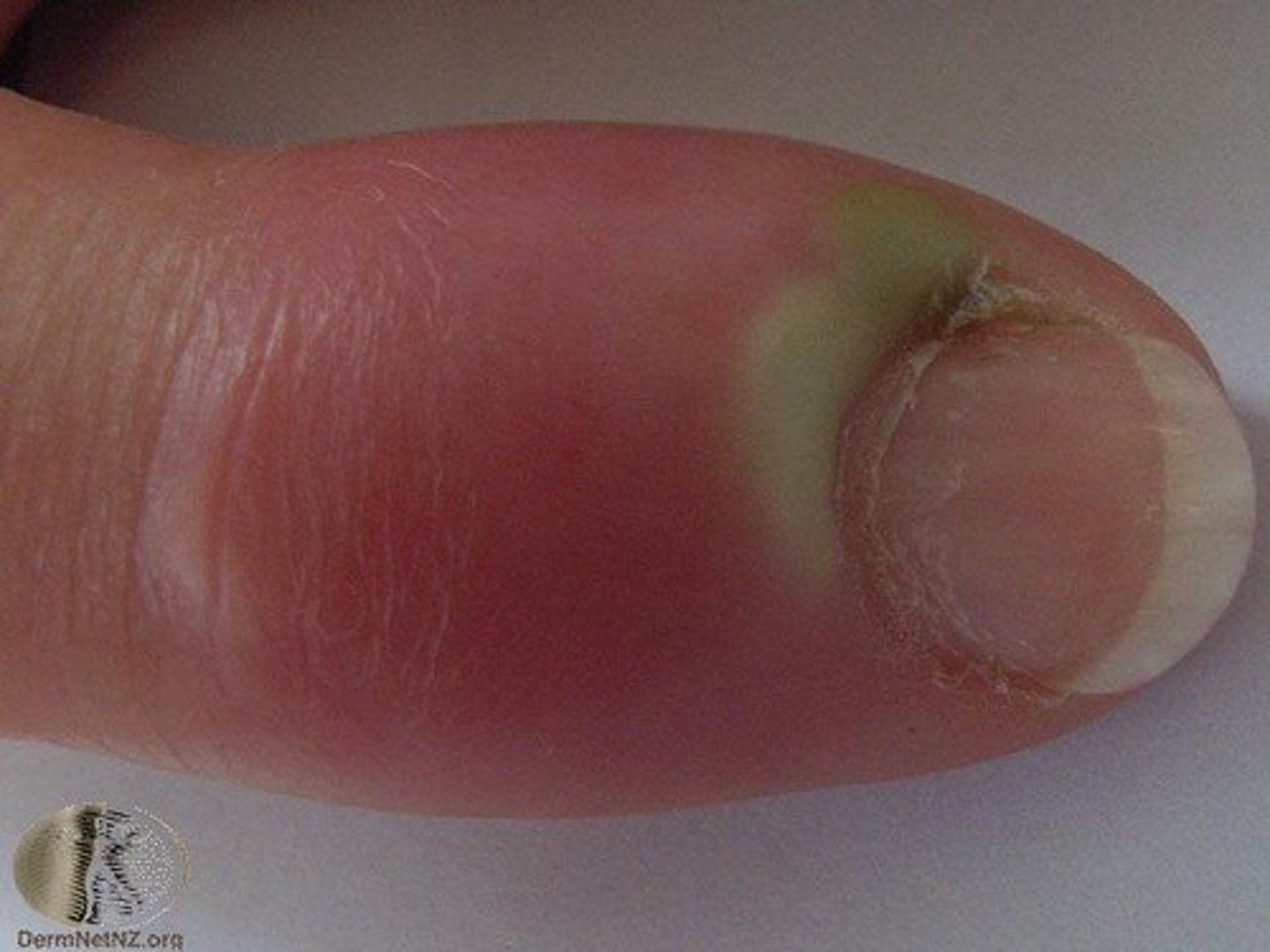
paronychia ( nails)
Acute or chronic infection of cuticle.
Lay term: "infected hangnail".
Rapid onset of very painful inflammation at base of nail,abscess may form.
Inflammation develops slowly usually starting at nail base and works along side of nails.
Frequent exposure to moisture,nail biting are risk factors.
process for assesment of the jugular vein for pulsations
1.elevate patient 30-45 degrees ( can be as high as 90 degrees if venous pressure is elevated
elevate chin slightly and tilt head away from side being examined
use pen light to create tangential light
observe for pulsations ( should NOT be able to visualize vein itself)
THIS GIVES YOU INFO ON PRESSURE IN RIGHT ATRIA ( so unexpected findings would be right sided heart failure
expected findings for rate, rythm, amplitude, and countour
rate- 68bpm ( pace)
rhythm- irregular or regular
amplitude - 2+
contour- bounding
assesment for orthostatic hypotension , and when should it be completed
a decrease in SBP of at least 20mm hg and or/ DBP of at least 10mm hg within 3 min of standing
Generally assosiated with fluid volume deficit, antihypertensive medications or prolonged bed rest
this happens during blood pressure assesment
s1
( lub)
closing of mitral and tricuspid valves
indicates beginning of systole
s2
( dub)
closing of aortic and pulmonic valves
indicating beginning of diastole
s3 ( what disease can it indicate and when are these normal/ abnormal)
often heard at apex
kentucky
rapid filling against the ventricle the ventricle wall
occurs during diastole
can be normal in children and pregnaant women
when heard in adult over age 30 it can be ( CHF) congestive heart failure
s4(what disease can it indicate and when are these normal/ abnormal)
tenessee
rush of blood heard with atrial contraction against the ventricles after atrial contraction
can be normal in athlletes and adults younger than 30
although usually its an abnormal sound
noncompliant or stiff ventricle , hypertrophy of ventricle, CAD, HTN, MI, aortic and pulmonic stenosis
occurs before s1
what is a heart murmur
abnormal heart sound is typically due to a leaky valve
difference between a systolic and diastolic heart murmur
systolic heart murmur is heard for symptoms of right and left heart failure as well as heart muscle contraction
Diastolic murmur - occurs during heart muscle relaxation between beats.
significance of unilateral assemetry vs bilateral edema
bilateral - heart failure, renal failure, or liver disease
unilateral-
valvular heart disease
disorders involving valves of the heart that impact the heart's ability to pump blood effectively to the lungs or tissues of the body and cause the heart to work harder
angina pectoris
chest pain that results when the heart does not get enough oxygen
unstable angina
chest pain that occurs while a person is at rest and not exerting himself
myocardinal infarction
heart attack
left ventricular failure
fatigue
SOB
orthopnea
dyspnea of exertion
displaced apical pulse and palpable thrill
S3 heart sound
systolic murmur
crackles in lungs
right ventricular failure
dependent peipheral edema
S3 heart sound
systolic murmumr
weight gain
ditended jugular vein
infective endocarditis
inflammation of endothelium that lines heart and cardiac valves. most commonly damages mitral valve, then aortic and tricuspid valves. commonly caused by bacteria that are normally present in the body. can also occur after an invasive medical or dental procedure. symptoms: valvular dysfunction, may affect organ systems, chest pain, CHF, clubbing, meningitis, low back pain, arthralgia, arthritis
pericarditis
inflammation of the sac surrounding the heart ( perricardium )
venous thrombosis (thrombophlebitis)
Thrombus develops within a vein (inflammation of vein); caused by venous stasis, damage to inner layer of veins, and hypercoagulability; dilated superficial veins, edema, redness of extremity, warmth, tenderness, increased circumference of affected extremity
symptoms: low grade fever
fatigue
extremity may feel tense, full and heavy
nodules or lumps
pain ( 50% asymptomatic)
warm to hot or cool to cyanotic with severe edema
aneurysm
an excessive localized enlargement of an artery caused by a weakening of the artery wall.
peripheral vascular disease
diseases of blood vessels outside of the heart and brain
venous insiffucentcy
deep vein thrombosis
arterial insiffucenxy
most common causes is atherosclerosis or hardening of the arteries
blood flow may be comppletley stopped if a blood clot lodges in a narrowed area
leg cramping when you walk
chest pain or heart attack
pain after eating
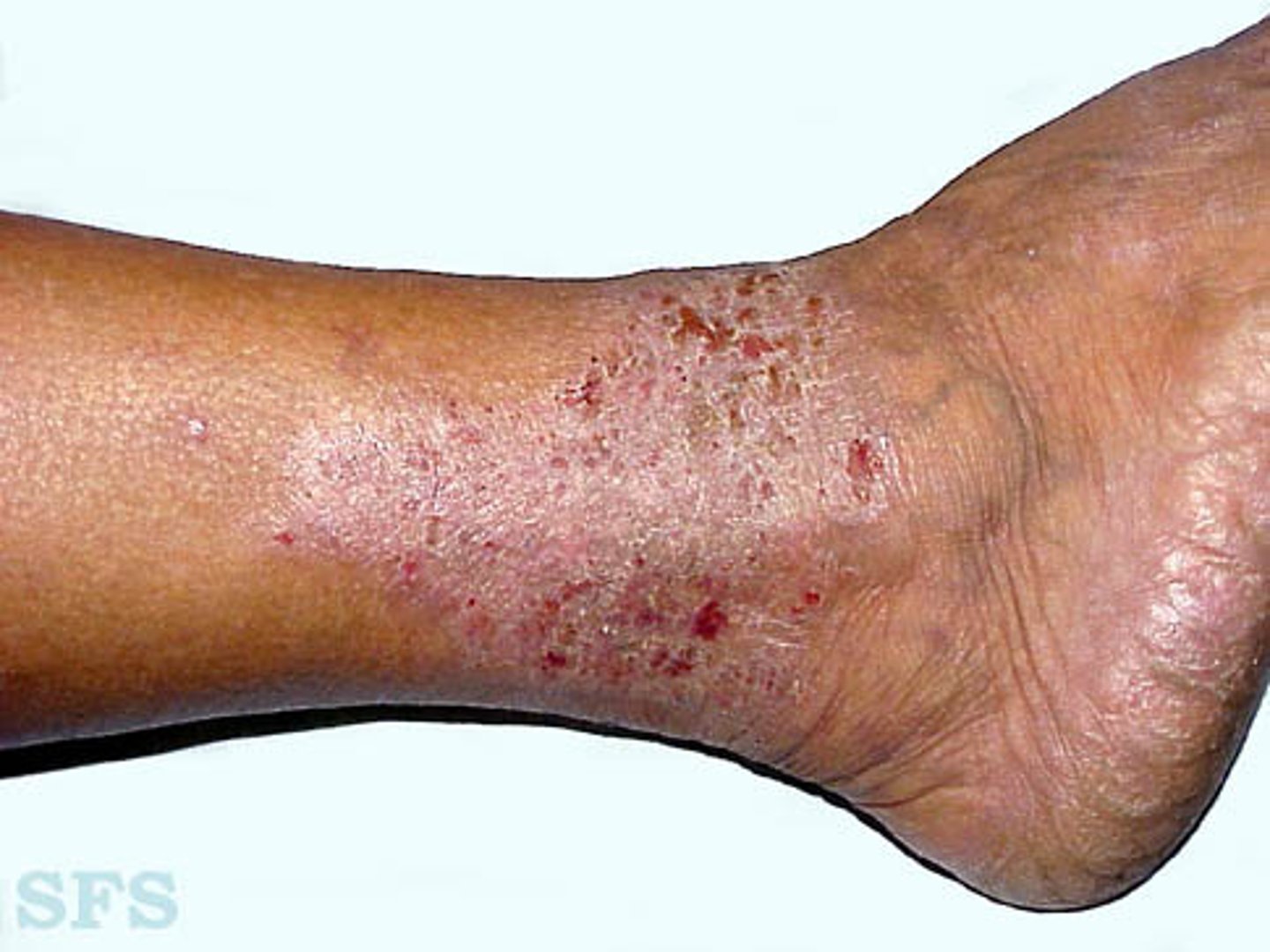
arterial insufficency symtoms
absence of hair
shiny, thin, taut, pale
cooler skin temp
ulceration on tips of toes, foot or laterl malleous
diminshed or absent pulses
thickened nails
range of motion for the elbow joint
Hinge joint:
Flexion- bend elbow so lower arm moves toward should and hand is level with shoulder
Extension- straighten elbow
Hyperextension- bend arm back as far as possible (not everyone can hyperextend)
Internal rotation of the shoulders
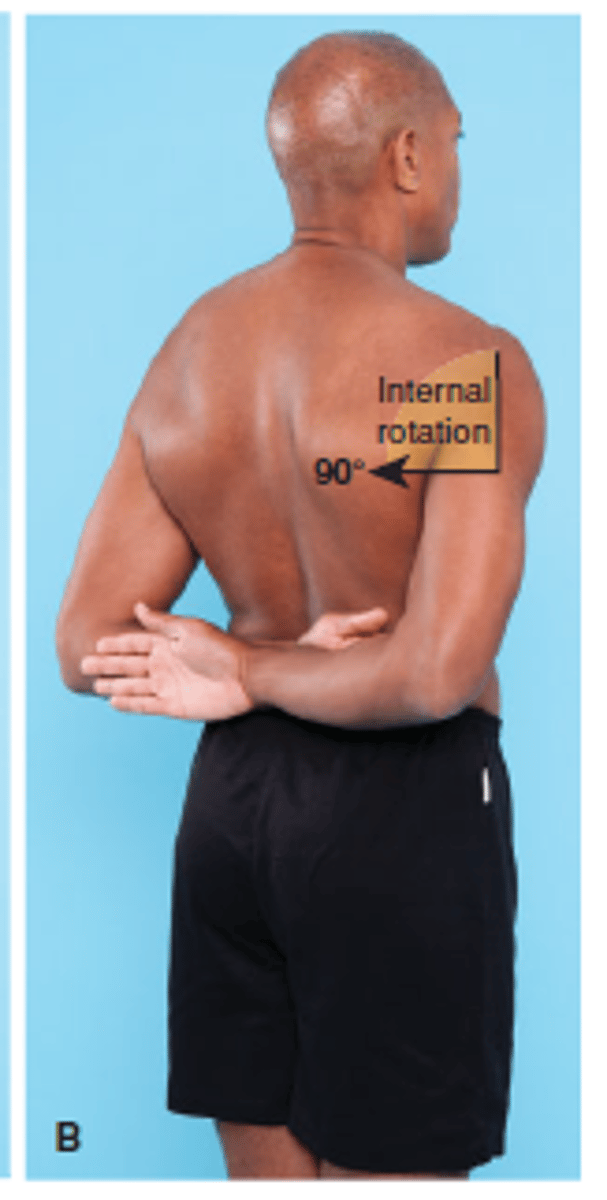
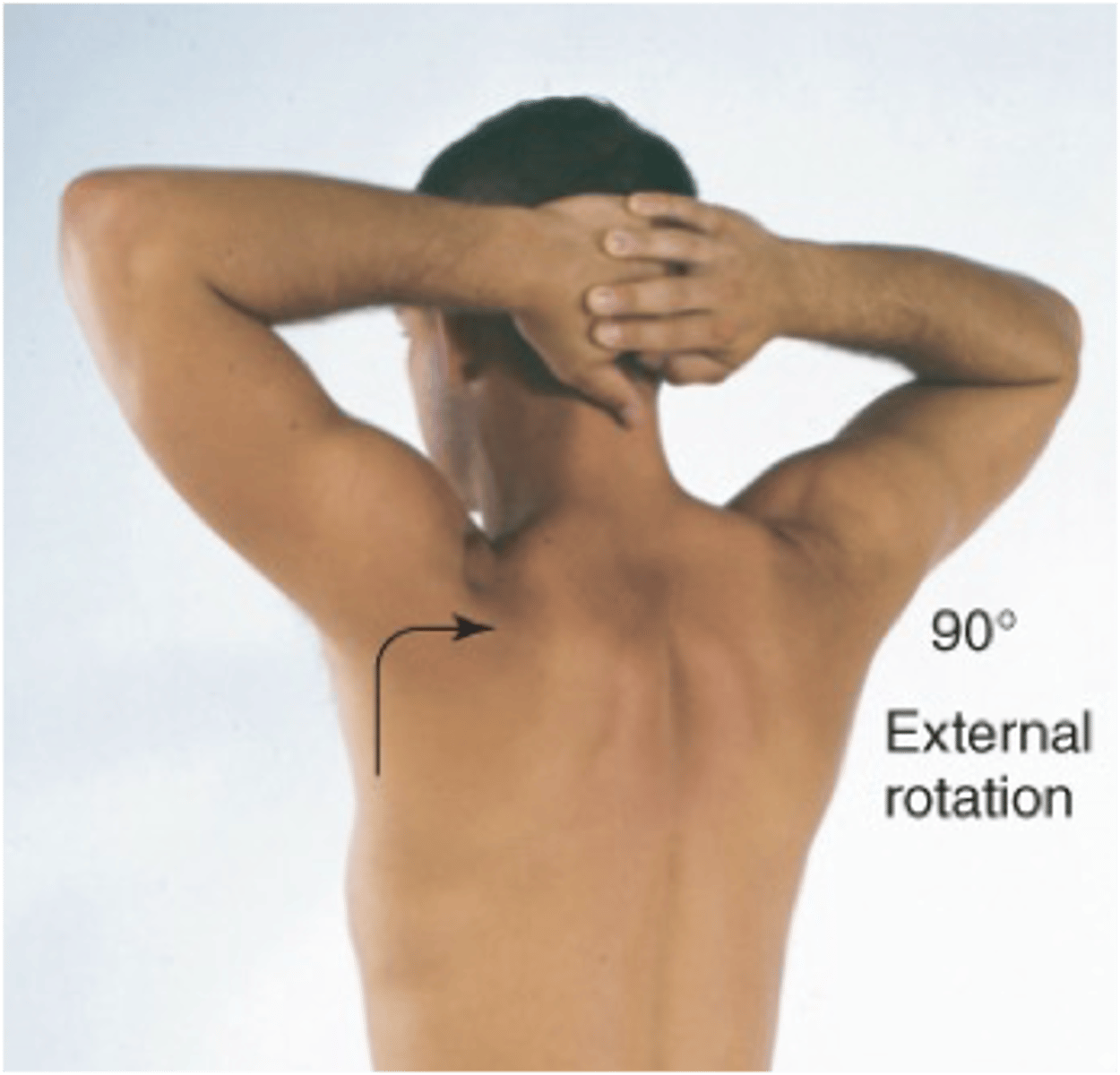
External rotation of the shoulders
Describe the seven Fs of abdominal distension.
obesity ( fat)
Air or gas ( flatulence)
ascites ( intersitual fluid)
cyst or abcesses
pregnancy ( fetus)
feces ( constipation/fecal impaction)
tumor
hernia ( bowel pushing through abdominal wall musculature)