Neuroanatomy + Physiology - Unit Exam 1
1/227
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Originally from Olivia_Chandler9 on quizlet
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
228 Terms
Why is studying neuroscience necessary?
to be a well-informed clinician, understand intricacies/etiologies
In order to communicate and swallow effectively, we need:
a well-functioning nervous system
Why study disorders "unrelated" to speech and language?
disorders do not exist in a vacuum - poss. etiology for speech related
What are 3 examples of neurological diseases/conditions that may affect our clients?
Parkinson's, Guillain-Barré, TBI
What is the difference between neuroscience and neurology?
Neuroscience = study of, Neurology = clinical application of
A coronal cut divides the brain into
front and back
A horizontal/transverse cut divides the brain into
top and bottom
A sagittal cut divides the brain into
right and left
From which plane can you NOT view both hemispheres?
sagittal
Directionality of the brain?
DCVR (Don't Cats Vacuum Rarely)
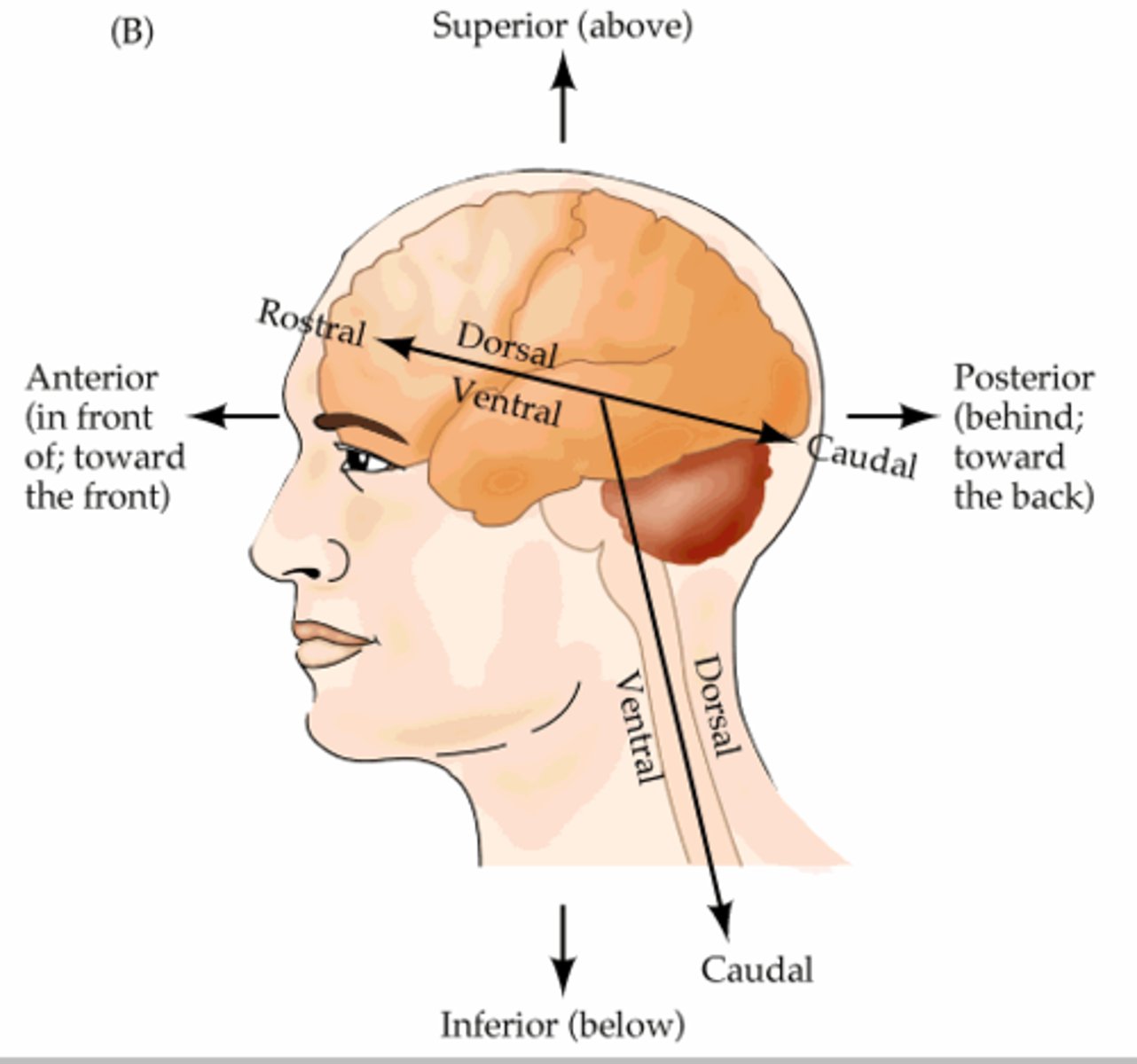
Directionality of the brainstem?
RDCV (Raging Dogs Cry Vivaciously)
What is the cephalic flexure?
point at which directionality changes between brain and brainstem
What is a decussation?
crossing over
Afferent fibers are?
sensory
Efferent fibers are?
motor
In efferent fibers, signal travels from brain to?
neuromuscular junction
Gray matter consists of?
neuronal cell bodies and dendrites
White matter consists of?
myelinated fibers (neuronal axons)
Tracts are named from?
start to end
What is gray matter in the CNS?
nuclei
What is gray matter in the PNS?
ganglia
What is white matter in the CNS?
tracts
What is white matter in the PNS?
nerves
How many layers of cells comprise the neocortex?
six
How many Brodmann's areas are there?
50
Brodmann's areas are divided by?
cytoarchitecture
What are Brodmann's areas used for?
identifying different parts of brain that correspond to different functions
What does it mean that the CNS mediates all bodily communication?
no body part can communicate with another without going through the CNS
CNS is protected by what 3 things?
bony shell, meninges, CSF
What is meant by lower vs. higher segmental levels?
hierarchy of function (and relative location)
What is the lowest segmental level?
spinal cord
The highest segmental level is the?
cerebral cortex
What is the nonthinking brain responsible for?
autonomic functions
Evolutionarily, what is the most recent segmental level?
cerebral cortex
What are "higher-order" functions?
consciousness, learning, intelligence
All areas of the brain are interconnected via?
white matter tracts
Name 3 major structures of the brain
cerebrum, brainstem, cerebellum
The PNS includes?
cranial and spinal nerves
The PNS divides into the?
somatic and autonomic nervous systems
The somatic NS mediates?
skeletal muscle reflexes and volitional movement
the autonomic NS mediates?
involuntary activity
The autonomic NS divides into?
sympathetic and parasympathetic NS
Name 3 functions of the sympathetic NS.
dec. saliva production, inc. heart rate, widen pupils
Name 3 functions of the parasympathetic NS.
inc. saliva production, dec. heart rate, dec. pupil size
What structure connects the brain's hemispheres?
corpus callosum
What is an example of left-brain function?
language
What is an example of right-brain function?
spatial awareness
The WADA tests for?
cerebral dominance
What does it mean that the brain has contralateral sensorimotor control?
left brain initiates right side of body, vice versa
What is neuroplasticity?
the ability of neural connections to form rapidly in response to stimuli
When is the brain most plastic?
early in life
Why is the critical period important?
many important brain connections being formed
What are the 3 primary embryonic vesicles?
rhombencephalon, mesencephalon, prosencephalon
The prosencephalon divides into?
diencephalon and telencephalon
The telencephalon contains?
cerebral cortex, basal ganglia, limbic system, lateral ventricles
The diencephalon contains?
hypothalamus, thalamus, 3rd ventricle
The mesencephalon contains?
midbrain, cerebral aqueduct
The rhombencephalon divides into?
metencephalon and myelencephalon
The metencephalon contains?
pons, cerebellum, 4th ventricle
The myelencephalon contains?
medulla
The cerebral hemispheres are part of which vesicle?
telencephalon
Ridges of brain are called
gyri
Valleys of brain are called
sulci
Convoluted surface of cortex allows for?
more space for brain = higher levels of functioning
Hemispheres are separated by?
longitudinal fissure
Longitudinal fissure is also called?
interhemispheric fissure
What are the 4 primary lobes?
frontal, parietal, temporal, occipital
The central sulcus is also called?
fissure of Rolando
The central sulcus marks the boundary between
frontal and parietal lobes
What 2 "primary" cortexes are separated by the central sulcus?
primary motor and primary somatosensory
The primary motor cortex AKA
precentral gyrus
The primary somatosensory cortex AKA
postcentral gyrus
The lateral fissure AKA
Sylvian fissure
Anteriorly, lateral fissure separates?
frontal and temporal lobe
Posteriorly, lateral fissure separates?
parietal and temporal lobe
The parieto-occipital sulcus separates?
parietal and occipital lobes
What is the preoccipital notch?
small indentation demarcating parietal and occipital lobes
What is the largest lobe?
frontal
The precentral gyrus is BA #?
BA 4
The functional representation of body is called?
homunculus
The premotor cortex is BA #?
BA 6
The prefrontal cortex is BAs #s?
BA 8-11
What part of the frontal lobe performs only cognitive functions?
prefrontal cortex
What are the names of the frontal lobe's 3 horizontal gyri?
superior, middle, and inferior frontal gyrus
What BAs is the inferior frontal gyrus?
BA 44/45
In dominant hemisphere, inf. frontal gyrus is?
Broca's area
What does Broca's area control?
motor control for speech and processing of language structure
The postcentral gyrus is located in what lobe?
parietal lobe
The angular and supramarginal gyri are located in what lobe?
parietal
The postcentral gyrus is BAs #s?
BA 1-3
How do we recognize sensations?
parietal sensory association areas
The occipital lobe contains the?
primary visual cortex
The primary visual cortex is BA #?
BA 17
The association visual cortex is BA #s?
BA 18/19
What is the function of the association visual cortex?
recognize what we see
The temporal lobe contains the primary ______ cortex?
auditory
Heschl's gyrus contains the
primary auditory cortex
The primary auditory cortex is BAs #s?
BA 41/42
What is the function of the auditory association cortex?
Recognize what we hear
The superior temporal gyrus contains
Wernicke's area