MYCOLOGY
1/81
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
82 Terms
Mycology:
a branch of botany dealing with fungi (greek-mykes: fungus).
Mycosis:
a disease caused by fungi; a fungal infection in or on a part of the body.
Fungi:
A kingdom of plantlike spore-forming organisms that grow in masses with out roots, stems, leaves, or photosynthetic pigments.
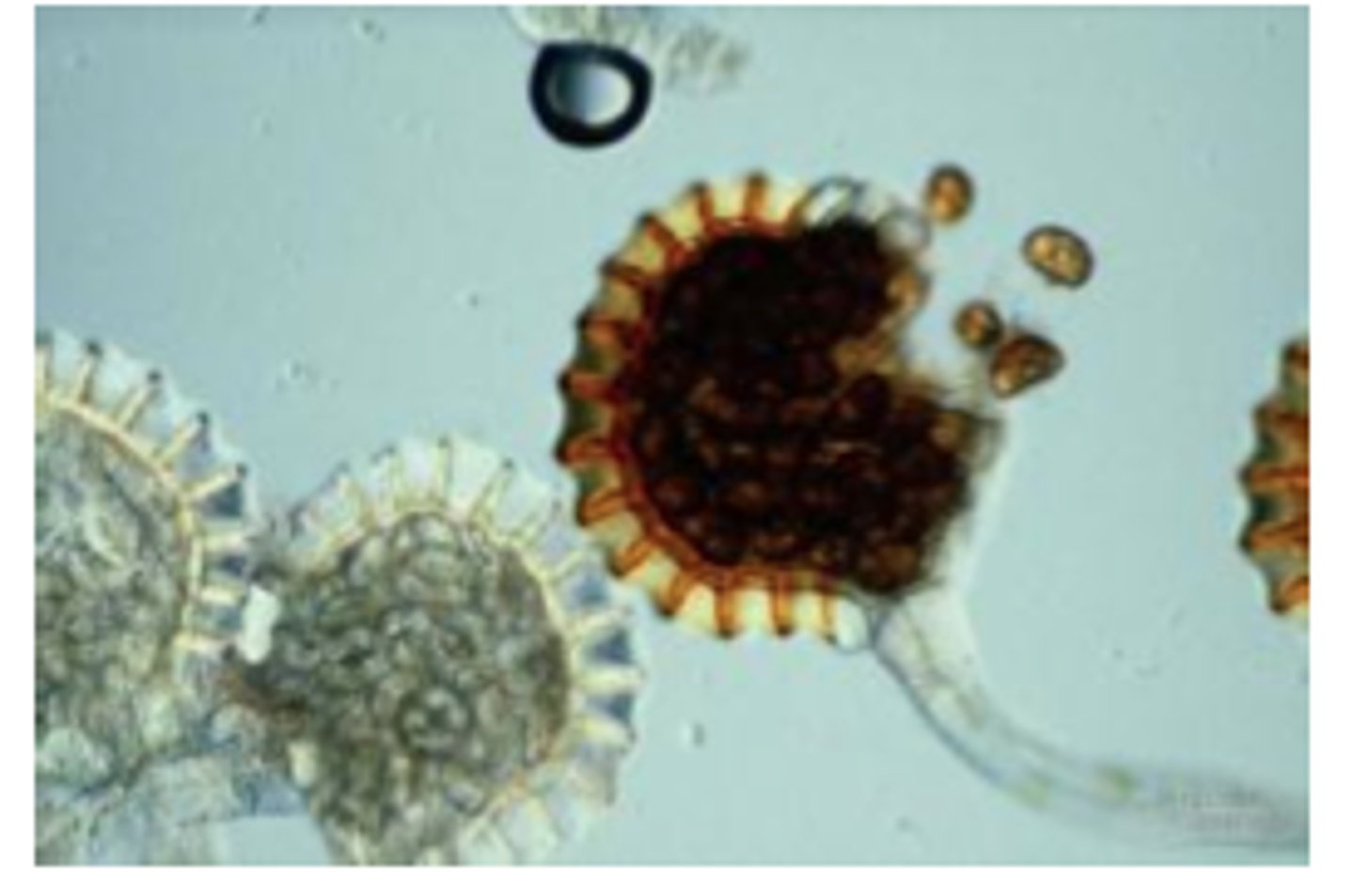
Sporangium:
(large sac-like structure) - a closed sac-like structure where sporangiospores are formed. 725
Eukaryotic:
A single celled or multicellular organism whose cells contain a distinct membrane-bound nucleus.
Eukaryotic protists, possess:
Nucleus
Nuclear membrane
Endoplasmic reticulum
Golgi apparatus
Mitochondria
Rigid cell wall
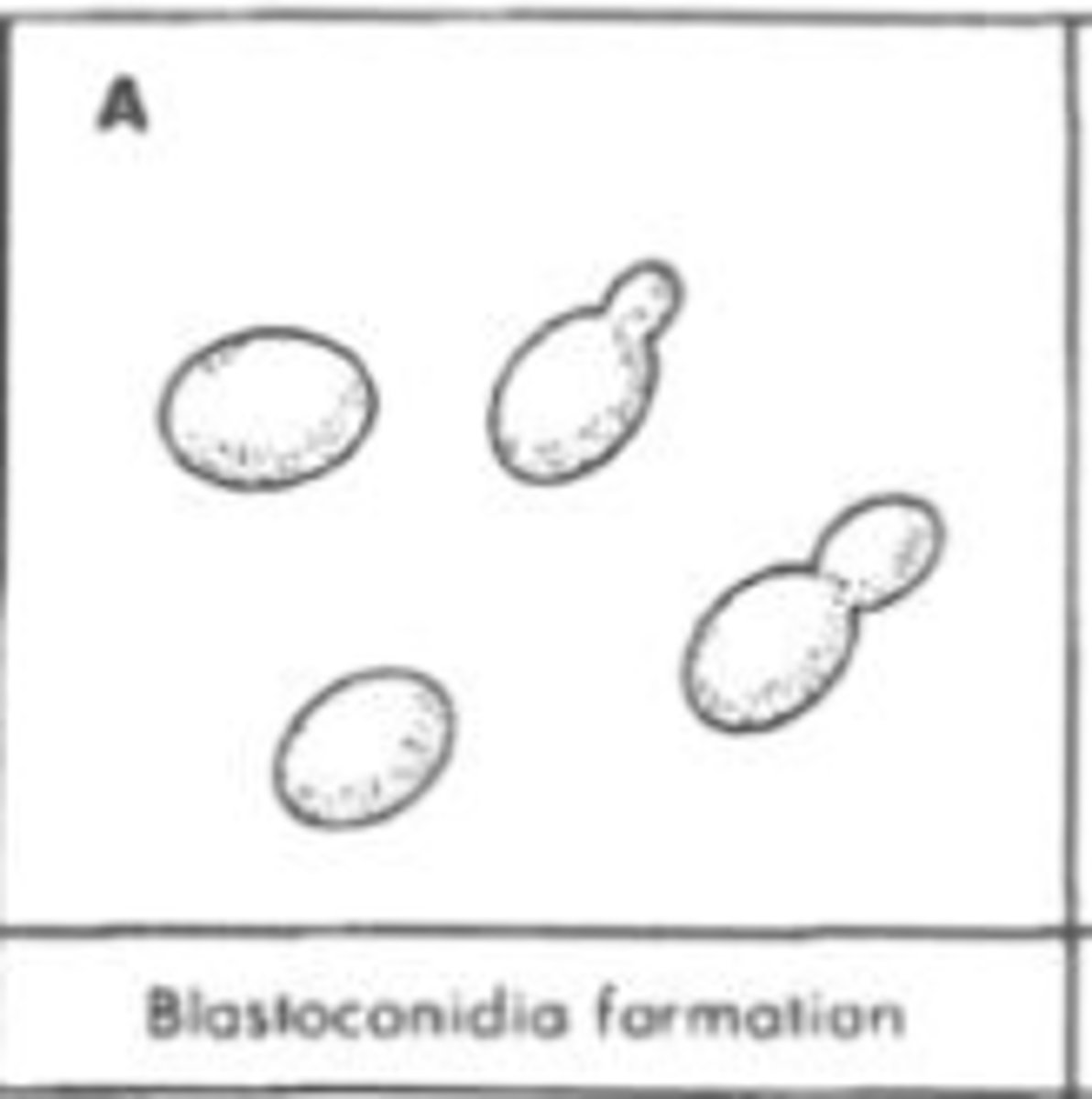
Blastoconidia/Blastospores:
A spore formed by budding, as in yeasts; thin-walled and water-balloon-like. 772
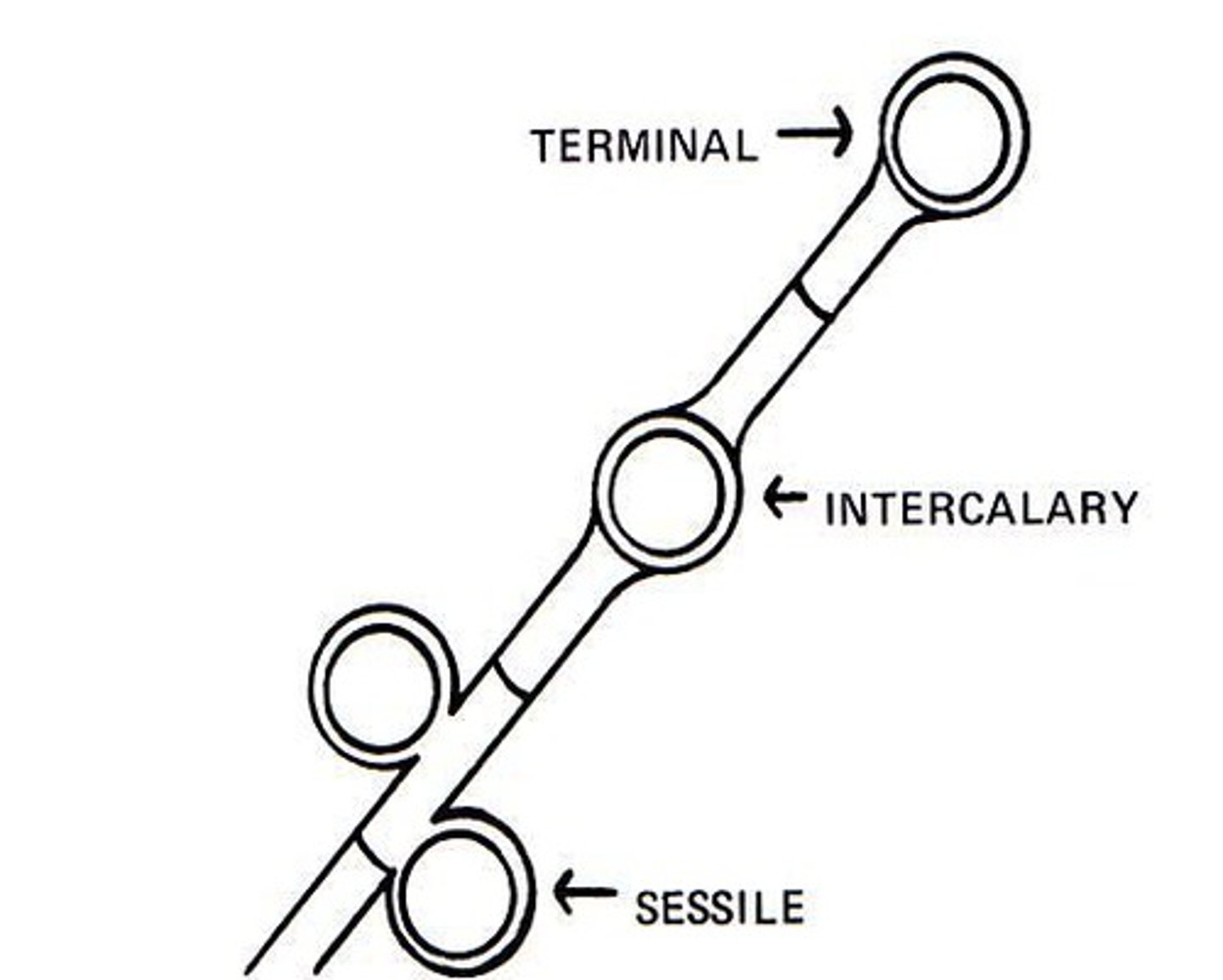
Chlamydoconidia/Chlamydospore:
a spore formed by the rounding-up of a cell; thick-walled; intercalary or terminal position; it is not shed.
Saprophytic:
A plant that derives its nourishment from dead or decaying organic matter.
Septate:
Hyphae that are subdivided into individual cells by transverse walls.
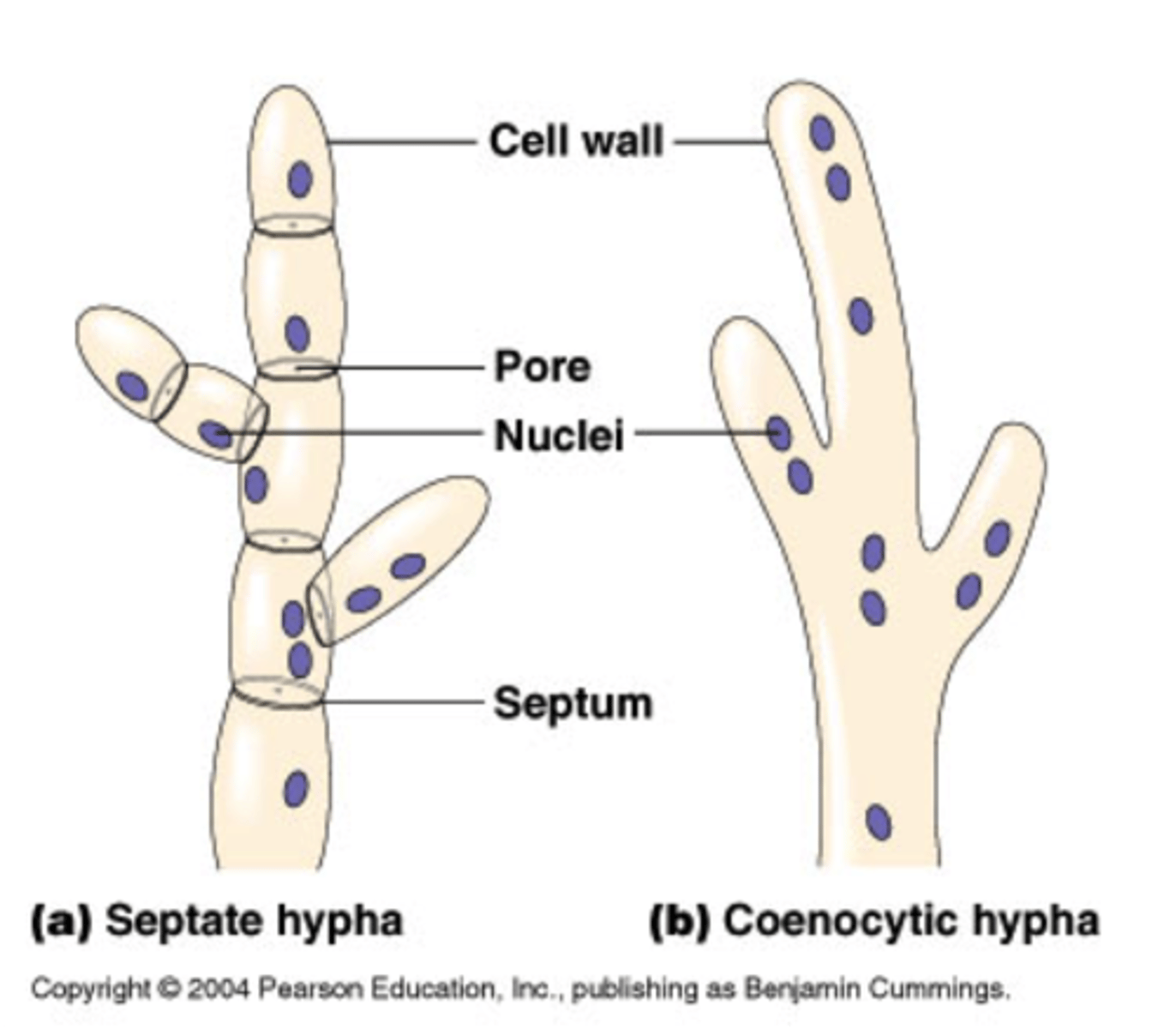
Aseptate:
Those without walls.
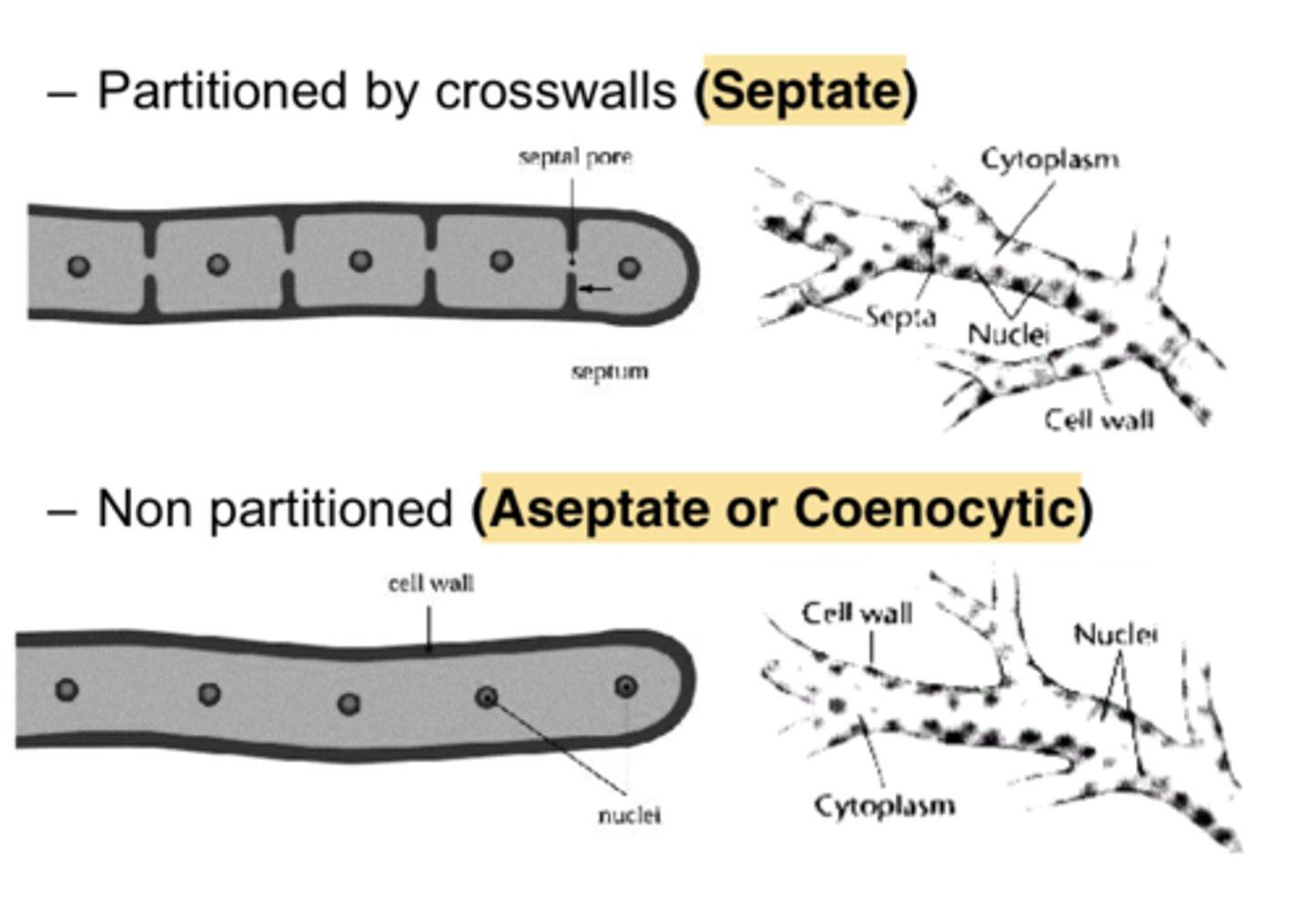
Hyphae:
Basic structural units of mold, tube-like projections.
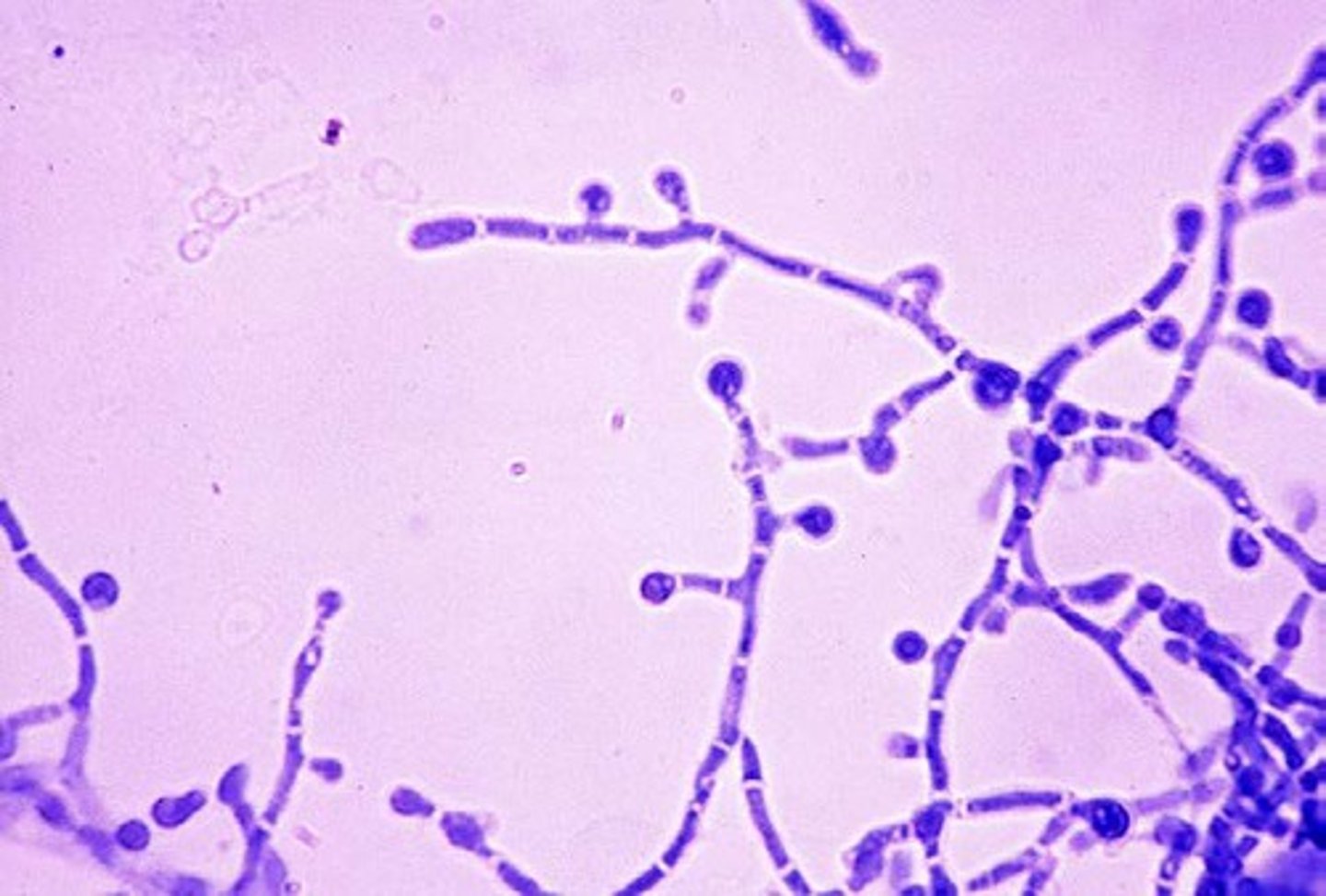
Pseudohyphae :
Elongated buds that have failed to separate and are connected together to form a link-of-sausage appearance. 772
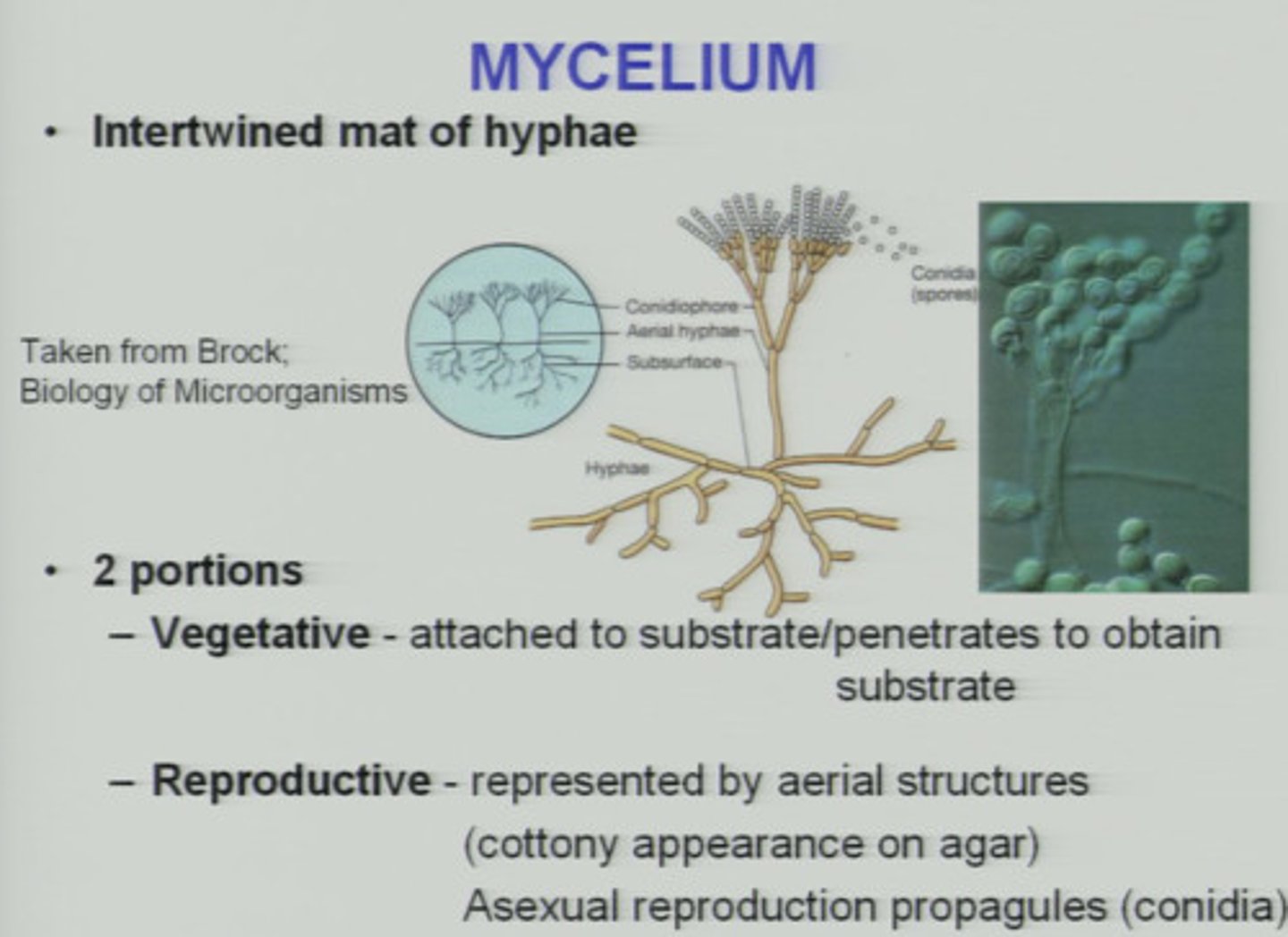
Mycelium:
Loose network of hyphae.
1. Vegetative - nutrient absorbing and water exchanging portion
2. Aerial - extends above the substrate
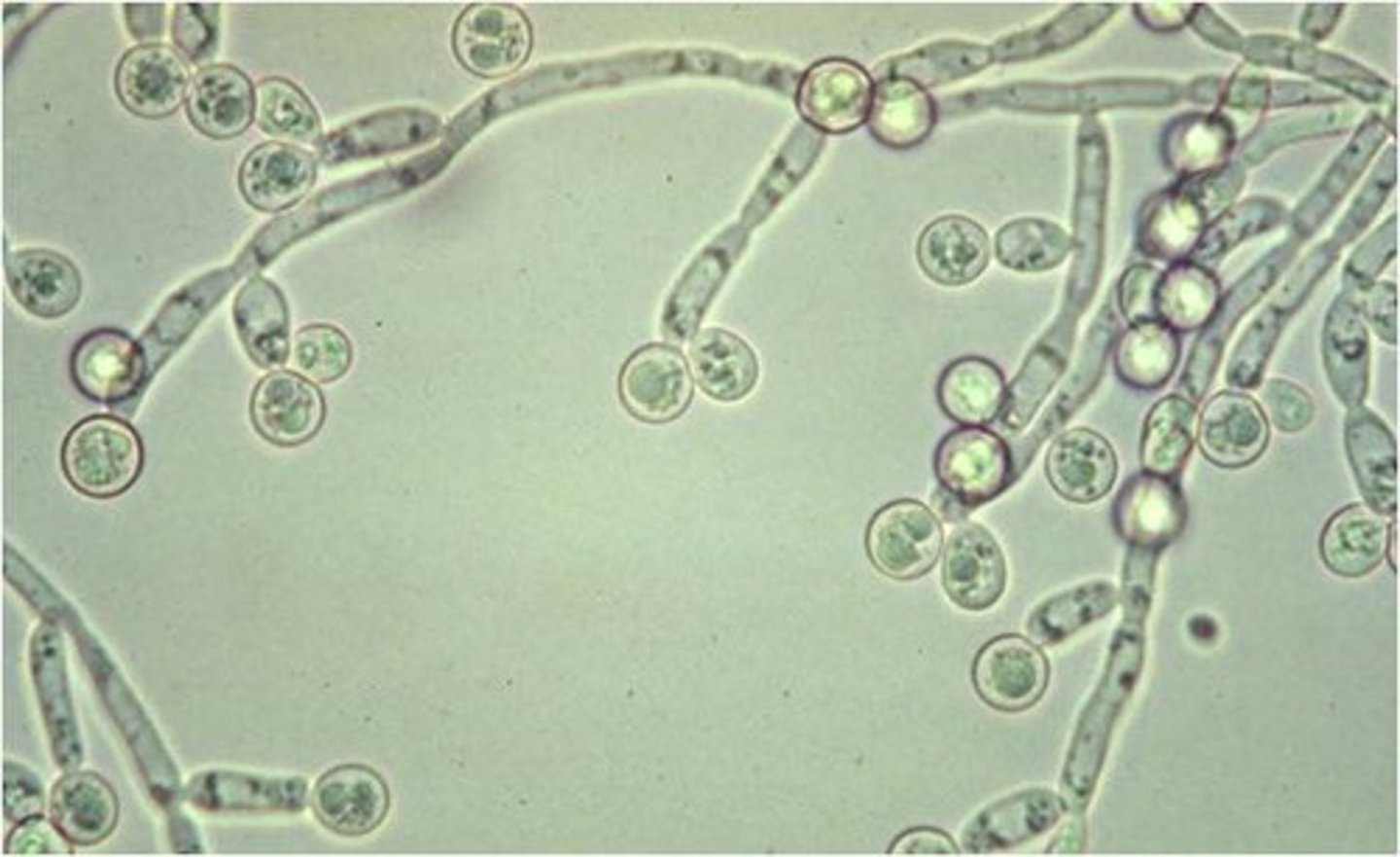
Yeast
unicellular fungus that reproduce by budding (2.5 to 6 microns )
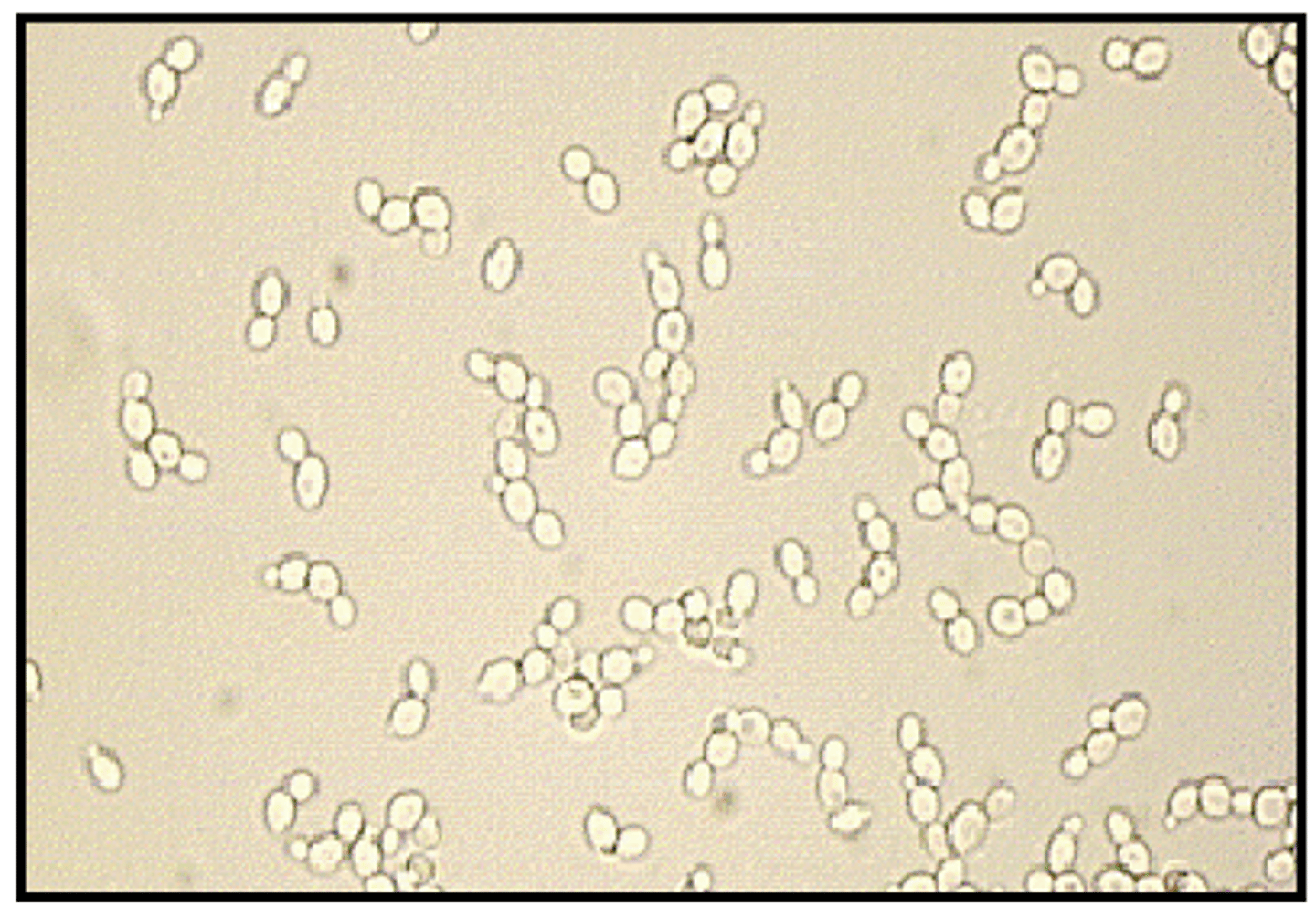
GENERAL CHARACTERISTICS OF FUNGI
Yeast - single cell forms
Multiple cells that form filaments - molds
Unicellular / multi-cellular
Lack chlorophyll
Heterotrophic
Saprophytic and/or parasitic
Many are ubiquitous
Reproduce by spores, either sexually asexually stage
- May be derived directly from mycelium or fruiting bodies
CELLULAR MORPHOLOGY Vegetative Structures
Hypha / hyphae
Tubular filament or threads branched or
unbranched
Septate: possessing crosswalls
Aseptate (coenocytic): lacking crosswalls
Vegetative Structures: Mycelium:
Mass of hyphae
Vegetative mycelium
Growth in or on a substrate
Aerial or reproductive mycelium
Projects above the substrate and may be comprised of or support elaborate spore bearing, fruiting bodies
Vegetative Structures Characteristics:True hyphae:
Filamentous, flat-ended cells form transitional cells
Do not show points of constriction
Vegetative Structures Characteristics:pseudohyphae:
Regular points of constriction (link sausages)
Produced in nutritionally poor environment
May bud to form blastospores (yeast cells) with lesser diameter than true hyphae
3 types of clinically significant hyphae:
Coenocytic - sparsely septate
Pigmented/dark - septate of the dematiaceous fungi
Septate - non pigmented hyphae of the hyaline molds
Colonial Morphology (Gross): Molds
Cottony, wooly, powdery, or fluffy
Optimum temperature: 25-30C
Colonial Morphology (Gross): Yeasts
Smooth, pasty, mucoid, butyraceous
Optimum temperature: 35-37C
Colonial Morphology (gross):Dimorphic Fungi:
Possess both mold and yeast phases
Can be temp dependent (thermal)
Medically important dimorphic fungi
H. capsulatum
B. dermatidis
P. marneffei
C. immitis - non-thermally dimorphic
P. brasiliensis
S. schenkii
Colonial Morphology (gross):Dimorphic Fungi:
-Mold/mycelial/saprophytic phase
Produce delicate hyphae, <1-2 mm, mold form of colonies have cobweb or hair like appearance
-Yeast/tissue/parasitic phase
Can grow on media with cyclohexamide or anti fungal
-Pigmentation - Noteworthy characteristic
Dematiaceous: dark
Hyaline: absence of color
Growth rate is significant
CULTURE MEDIA
- Normal tubes / plates optional (BAP, Choc, etc.)
- Battery recommendations
With or without blood
With or without cycloheximide
With Antibacterial Agents
-Large culture tubes recommended (150 x 25mm)
Poured in thick slants
Do not screw down cap
CULTURE MEDIA: Large Culture Tubes
ADVANTAGES:
Easily stored, less space
Easily handled, less hazardous
Lower dehydration
DISADVANTAGES:
Poor isolation
Reduced surface for growth
CULTURE MEDIA: Petri-dishes
ADVANTAGES:
Provide larger surface of growth
Mixed culture easier to separate
Provide maximum aeration
DISADVANTAGES:
Tendency to dehydrate during incubation
Hazardous for cultivation of certain systemic mycoses
Histoplasma
Blastomyces
Coccidioides
Media used for primary Recovery
BHI Agar w/out & with antibiotics
Chromogenic agar
Dermatophyte test medium
Inhibitory mold agar
Mycophil agar
Potato flake agar
Mycosel agar
SABHI agar
Yeast extract phosphate
Selective Media
-Antibiotics added
Chlorampenicol
Broad spectrum
Bacteriostatic
- Cycloheximide
Inhibits most saprophytic fungi
- Gent and Cipro
Selective Media: BHI Agar
Available with antibiotics or blood
For dimorphic
Mold / fungi @ 20C
Yeast @ 35C
- For recovery of saprobic and pathogenic fungi
Selective Media: SABHI Agar
For isolation of significant fungi from mixed flora specimen (i.e. sputum)
Saprobic and pathogenic fungi
Selective Media: Mycosel Agar
Inhibits bacteria and saprophytic fungi
Cycloheximide, chlorampenicol, dextrose
- For dermatophytes
Selective Media: Dermatophyte Test medium (DTM)
Selective for dermatophytes
Infects skin, hair, or nails
For screening purposes only:
Subculture to a medium w/out antibiotics for maintenance
Selective Media: Corn Meal Agar
Morphological studies of Candida
Nutritionally deficient, C. albicans produces chlamydospores
Selective Media: Czapek's Agar
Differential ID of Aspergillus species
Laboratory Safety in Mycology
All mold cultures and clinical specimens must be handled in a class II BSC
Keep pathogenic isolates sealed
Direct Microscopic Examination:Gram Stain:
Spore and hyphae stain Gram positive
Candida albicans appears black
Large blastospores / pseudohyphae
Direct Microscopic Examination: Potassium Hydroxide (KOH)
10-40% KOH
For demonstrating fungal hyphae and spores in clinical material
Skin, hair, nails, other tissue
Clears opaque material and hydrolyzes the keratin in epithelium
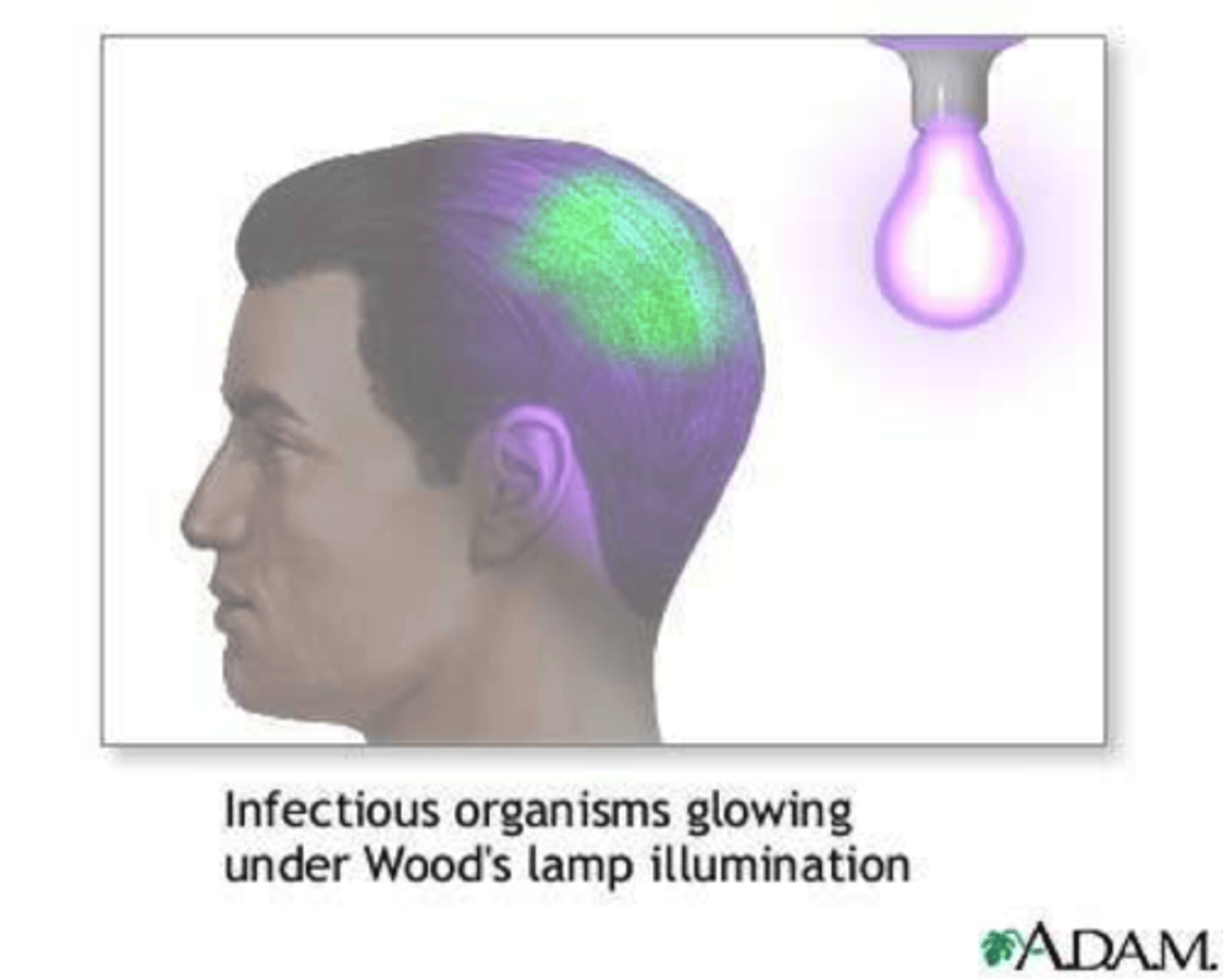
Diagnosis of Cutaneous Mycoses
Wood's black light
Detecting infected hairs by fluorescing a bright, yellow-green
Wash affected skin sites with 70% isopropanol
- Obtain small fragments / scales
Skin or nail
Scrape with scalpel or slide
Mince as needed
- Add KOH and coverslip
- Heat may accelerate clearing process (may be overdone!)
Nails may require 30 minutes.
Press coverslip gently, express bubbles
- Clearing apparent as change in preparation to turbid
Thick, opaque samples
Unsatisfactory for examination
Obscured hyphae and spores
Interpretation
Hyphae demonstrate uniformity in size and symmetry
Reporting:
Depends on Lab SOP
(+) Dermatophyte
Branching hyphae, occasional arthrospores
(+) Tinea versicolor
Short, stubby hyphal elements and grape-like clusters of spores
(+) Candida:
Pseudohyphae & chlamydospores/blastospores
Avoid Reporting False Positives
Mosaics and other artifacts such as cholesterol deposits
Cell wall skeletons
Hyphae do not grow geometrically (e.g. sharp acute or right angles)
Lactophenol Cotton Blue (LCB) Stain
- Temporary wet mounts for staining inocula from culture
- Fungal morphology in LCB mounts
Basis of textbook descriptions
- Fungicidal and sporicidal
LCB Procedure
- Work under a biological safety hood
- Special care in obtaining inoculum with needle
- Care taken to acquire small portion of medium which contains mycelium
- Transfer to slide, apply coverslip
-Apply few drops of stain
Gently heat
Examine:
Fungal mycelium and fruiting structures take on delicate light blue color
Negative Staining
Reagent:
India ink or nigrosin stain
-Routinely utilized for staining CSF
Demonstrate large capsules enveloping blastospores of Cryptococcus neoformans
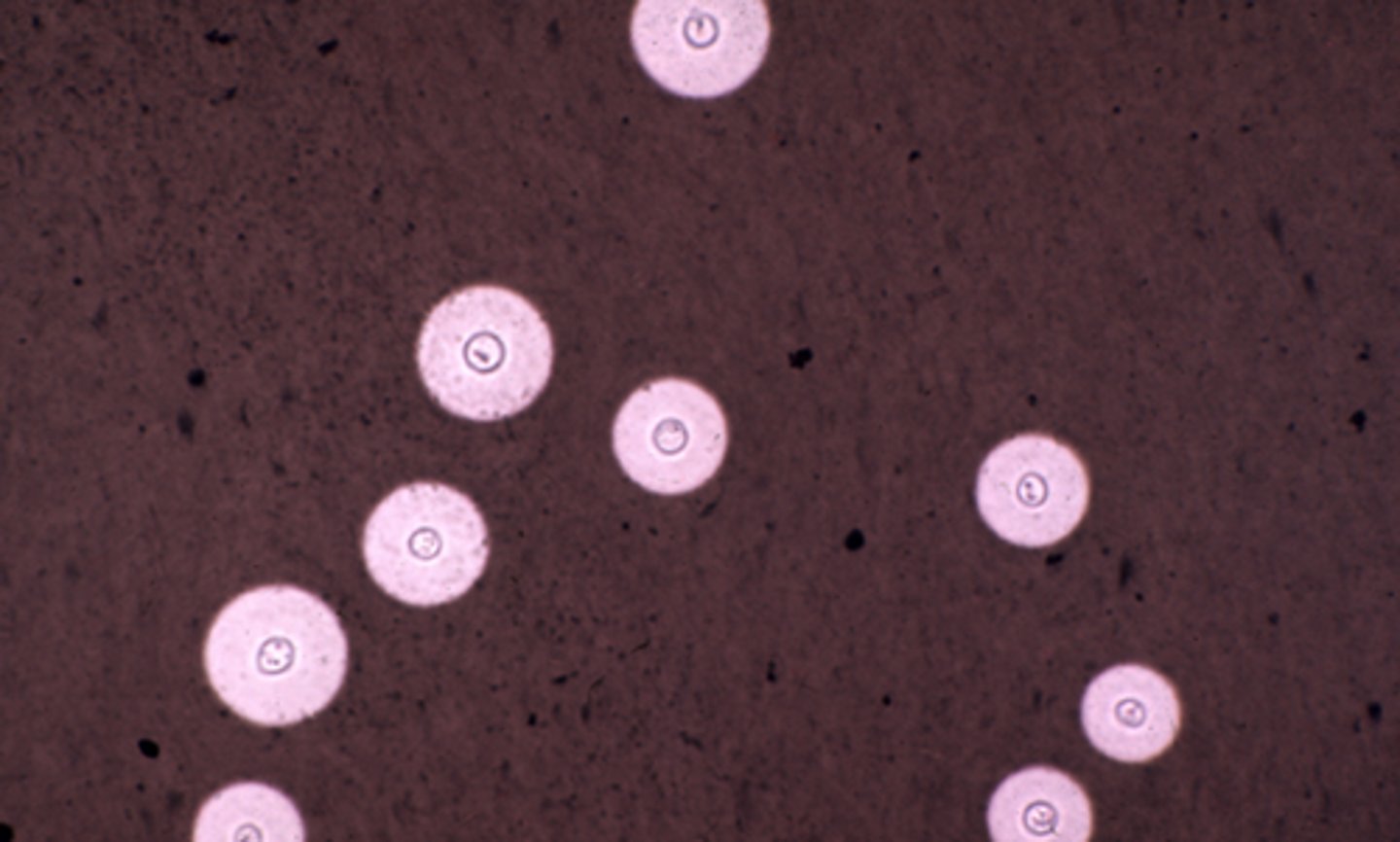
Germ Tube Test
ID Candida albicans
Germ tube:
Long, narrow tubes projecting outward from blastospores
Not pseudohyphae, not constricted at their point of origin
Germ Tube Test: Procedure
Reagent: 0.5 ml serum (human, rabbit, or bovine)
Inoculate serum
Incubate 2 hrs, 35C
Place a drop to slide / cover
- Examine:
Germ tube appear as short hyphal like extensions
Half the width, 3-4 times the length of yeast cell
-Test not valid if examined after 2 hours
Yeast Assimilation Test: Principle
-Yeast species are differentiated based on Carbon and Nitrogen usage (assimilate)
- If (+) will show growth or turbidity
- Considered along with morphology and reproductive structures
- Commercial kits:
API 20C
Vitek Yeast card
YT microplate
Yeast Fermentation Test: Principle
- Consists of an organism suspension + carbohydrate
- If (+) will show gas bubbles
- Rarely used (long incubation), replaced with assimilation test
- Used as back-up test
Special Culture Techniques: Slide Techniques
- Designed for microscopic examination
Fungi in natural state
Used on dermatophytes only
- Materials:
SAB-DEX medium
Long coverslip (sterile)
- Cut 1 cm square block of SabDex agar out of plated medium
Place on sterile slide
Inoculate each corner block
Place heated coverslip glass directly on surface agar block
- Incubate in Petri-dish
30 C until obvious growth occurs
Examine:
Gently lift coverslip from surface of agar block
Portions of mycelium adhere to underside of coverslip
-Place on slide containing drop of LCB stain
- Examine microscopically
Tease mount
- Equipment:
Dissecting needles or pointed applicator sticks (spuds)
- Procedure:
Dig out small portion of colony to be examined
- Include some subsurface media
Place on slide in drop of LCB stain
Tease colony apart
Overlay w/ cover slip
- Examine:
10X
40X
Oil immersion
Teasing colony disrupts delicate fruiting structures of filamentous molds
Scotch Tape Preparation
- Better suited to preserve spore arrangements
- Especially delicate filamentous molds
Scotch Tape Preparation Procedure: Culture
- Press sticky side of tape to surface of colony
Picking up portion of aerial mycelium
- Place drop LCB stain on slide
- Place sticky side down on slide
Stretch tape over stain
Lower gently
- Examine
Scotch Tape Preparation Procedure: Skin
- For diagnosis of Tinea versicolor
- Tape is applied directly to skin
- Scales adhere to the tape
- Place drop LCB stain (or KOH) on slide
- Place sticky side down on slide
- Stretch tape over stain
Lower gently
- Examine
Periodic Acid Schiff (PAS)
Stain used to detect fungi
Stains fungal elements well
Nocardia spp. do not stain well
Calcocluor white
Stain used to detect fungi
Used with KOH; KOH clears specimen while calcofluor shows fluorescence
Use fluorescence microscope
Fungal elements show apple-green or blue white fluorescence
Cutaneous Mycoses (superficial)
Superficial scaling
Rarely invades deeper tissues
Forms demonstrate hyphae and arthrospores only
Culture: forms hyphae and arthrospores only
Cutaneous Mycoses (superficial): Clinical characterization:
Habitat from geophilic to zoophilic to anthrophilic
Clinical types
Designated by Latin binomial
Tinea capitis
Tinea pedis
Microsporum audouii
most important cause of Tinea capitis in school children
Tinea capitis
Spread by direct contact with infected hairs on caps, hats, combs, clippers
Causes hair to fluoresce
M. canis
causes an inflammatory Tinea capitis
Zoophilic
Usually acquired from puppys or kittens
Trichophyton mentagrophytes
Most common species isolated
Causes T. barbae, T. capitis, T. corporis, T. pedis, and onychomycosis
T. rubrum
2nd most common spp
T. pedis, T. corporis, T. cruris, onychomycosis
T. tonsurans
T. capitis, T. pedis, T. corporis and onychomycosis
Malassezia furfur
Tinea versicolor
Microsporum gypseum
T. corporis and T. capitis
Recovered from hair and skin
Epidermophyton flocossum
Tinea cruris, onychomycosis
Tinea pedis
Candida albicans
Cutaneous candidiasis/moniliasis
Systemic dx in immune compromised
Thrush
Subcutaneous Mycoses: Clinical significance:
-Caused by fungi inhabiting soil/decaying vegetation
- Usually induced by trauma
- Disseminated forms
- Some individuals predisposed to systemic infections
Sporothrix schenckii
Causes sporotrichosis
Hazard to gardeners, florists
Causes "rose gardener's dx"
Also pulmonary, osteomyelitis
Systemic (deep) Mycoses: Clinical significance:
Soil fungi usually involved
Infections due to inhalation of spores
Disseminated forms invade organs
Each spp has a favorite organ
Certain individuals predisposed
Coccidioides immitis
Causes coccidiomycosis "Valley fever"
Skin infection
Osteomyelitis
Meningitis
Arthritis
Histoplasma capsulatum
Causes histoplasmosis
Confused with Leishmania (similar morphology and found in RE system)
Causes "Spelunker's dx"
Found in bat and pigeon droppings
Blastomyces dermatitidis
Causes blastomycosis pp. 745
Paracoccidoides brasiliensis
Causes paracoccidiomycosis pp. 746
Opportunistic Mycoses: Clinical significance:
Nonpathogenic fungus that cause subcutaneous and disseminated infection
In immunosuppressed or debilitated patients
HIV and Diabetes mellitus
Treatment with corticosteroids, cytotoxic drugs and antimicrobials
Zygomycetes
Produces large, ribbon-like hyphae
ID by presence/absence of rhizoids, structure and position
3 commonly encountered:
Rhizopus, Mucor, Absidia
Cryptococcus neoformans
Causes Cryptococcosis
Aspergillus
Causes Aspergillosis
Most frequently encountered fungus in lab
A. fumigatus - most common spp.
Penicillium marneffei
From mucocutaneous infection to disseminated infection