microeconomics graphs
1/25
Earn XP
Description and Tags
all the graphs i need to know
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
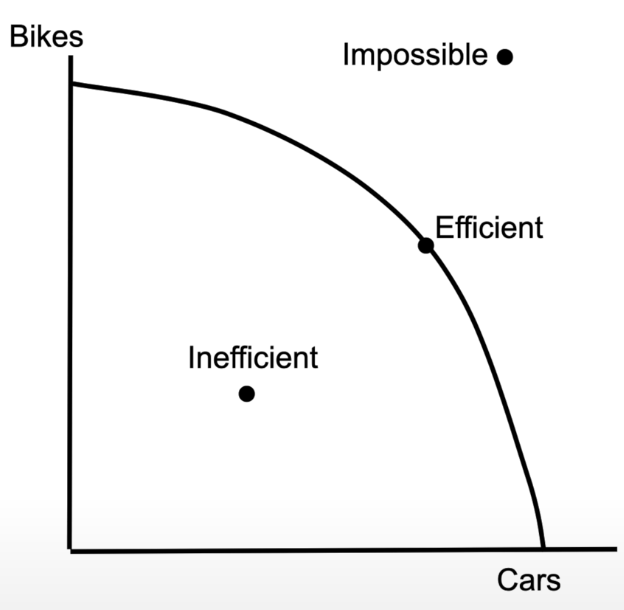
production possibilities curve
shows you can produce two different goods
any point outside the curve is impossible
any point inside the curve is inefficient
any point on the curve is efficient, as you are using all resources to the fullest
find the point on the curve that is most efficient for the socially optimal quantity (the quantity that society actually wants)
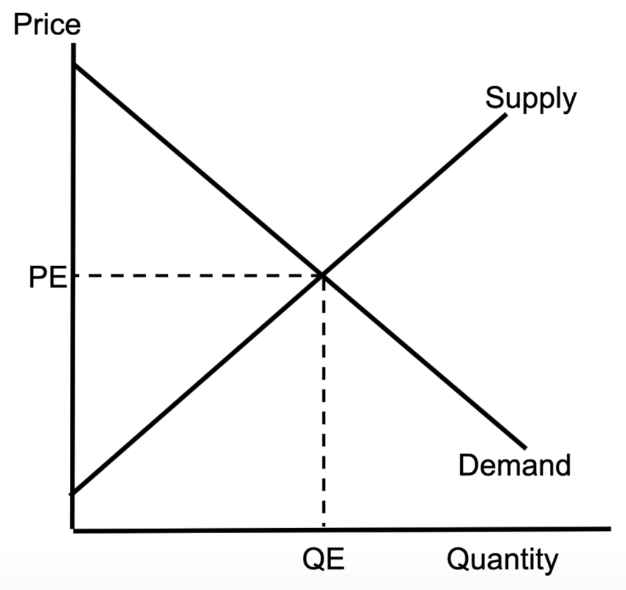
supply and demand
supply and demand showing a competitive market
shows equilibrium
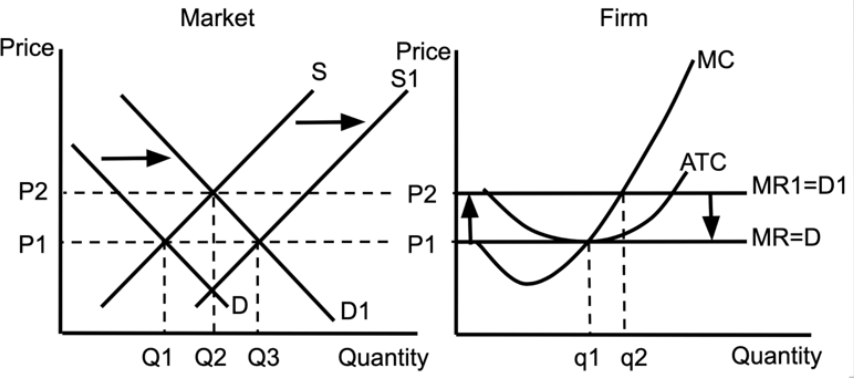
curve shifting
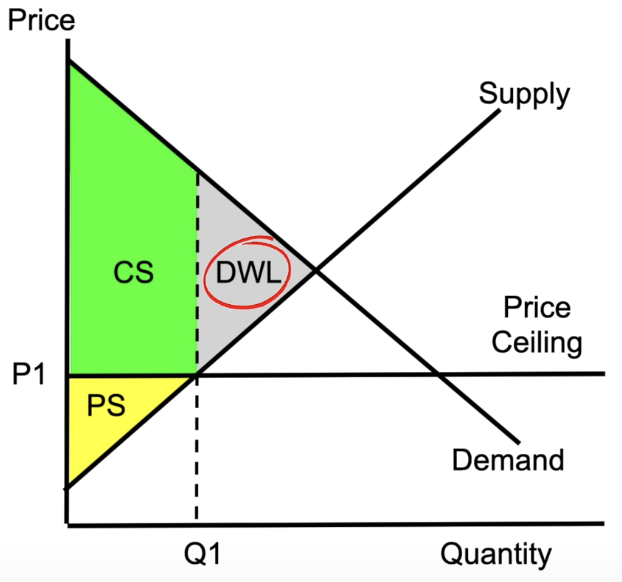
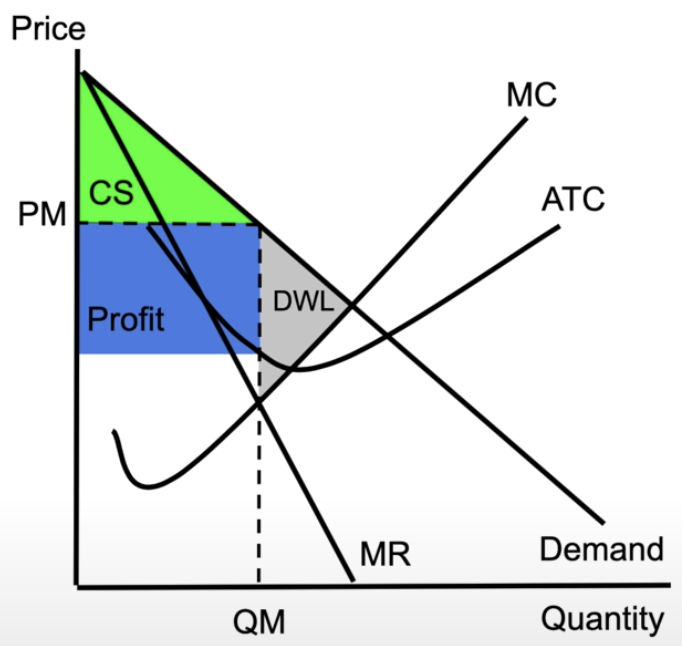
consumer vs producer surplus
consumer surplus: what people are willing to pay for a good - what they actually pay
producer surplus: what people actually pay vs what suppliers wanted to sell it for
total surplus = sum of both

supply and demand with a price ceiling
eg. government limits the maximum price
causes a smaller producer surplus and larger consumer surplus
creates dead weightloss: the idea that we aren’t producing the socially optimal quantity (producing less than they want)
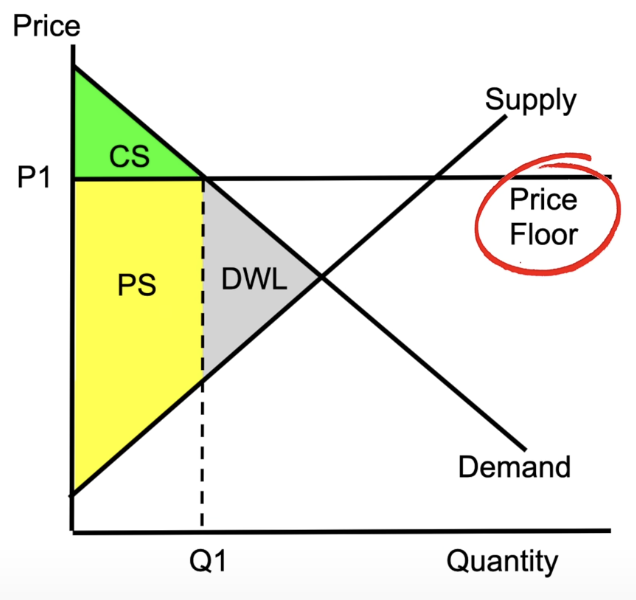
supply and demand with a price floor
eg. the price can’t fall below a certain point
causes smaller consumer surplus and larger producer surplus
creates dead weight loss: producing more than they want
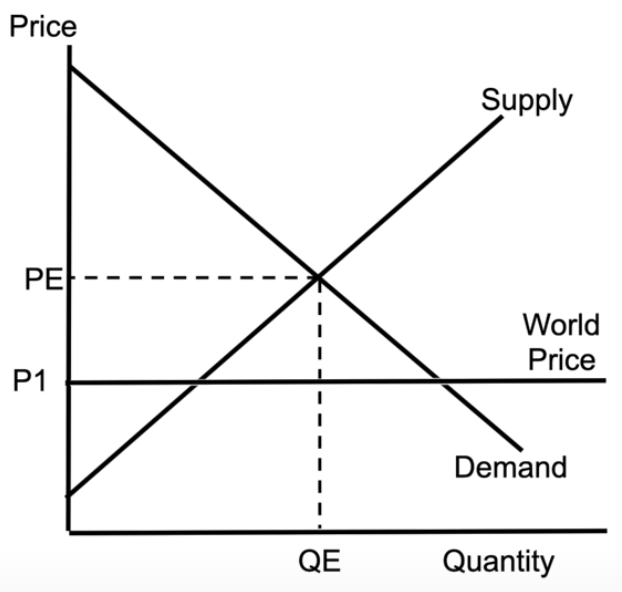
supply and demand showing result of trade
shows result of international trade
PE = domestic price of the product
P1 = the price we can get it for, if we buy it from other countries
no dead weight loss, which explains why economists like international trade
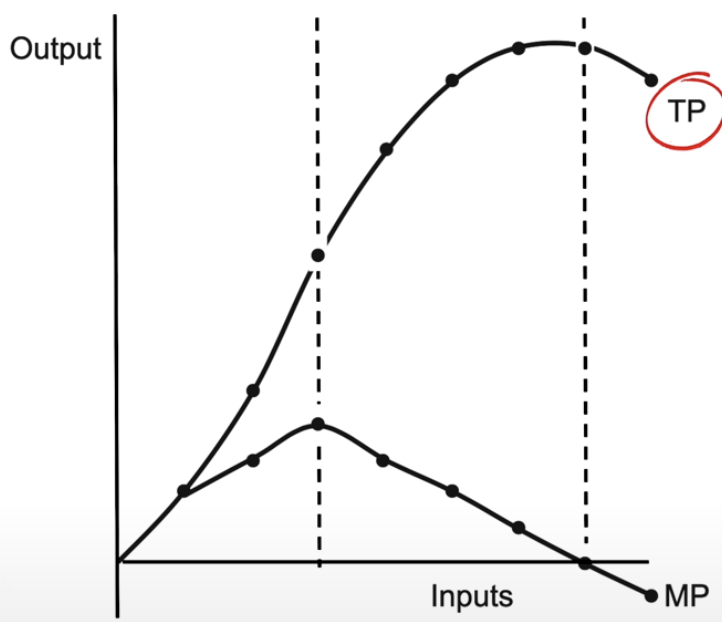
short-run production function
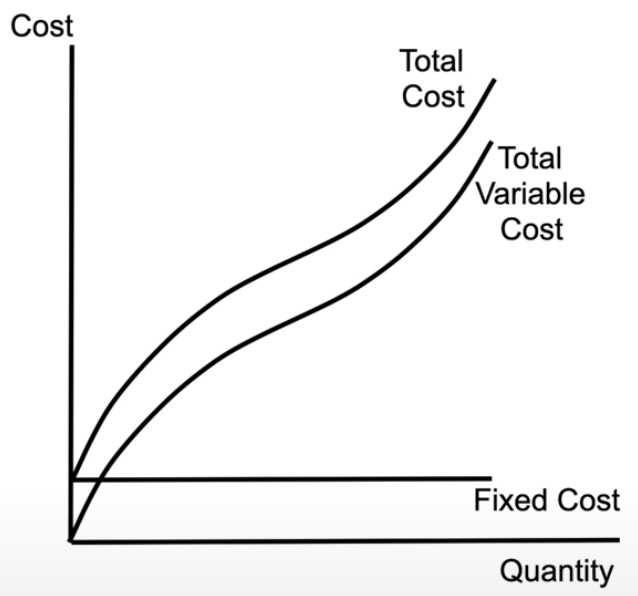
TP = total product = total amount produced
as you hire more workers TP increases at an increasing rate, then increases at a decreasing rate, then eventually starts decreasing
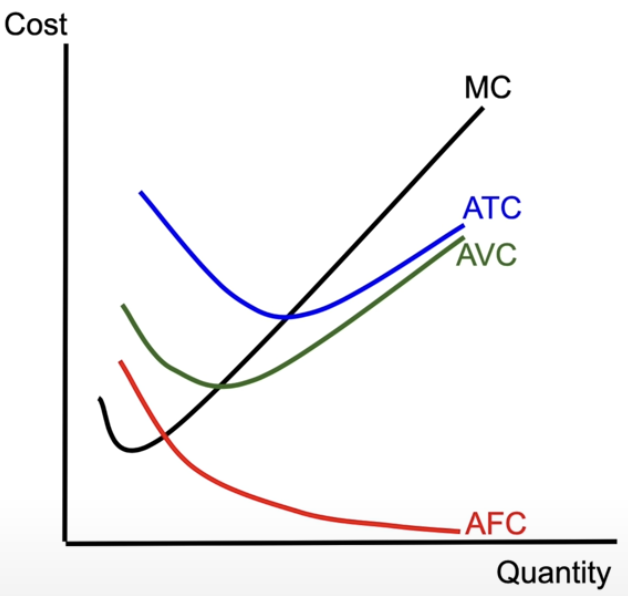
short-run per unit cost curves
MC = marginal cost → decreases then increases
tells you how much to produce
ATC = average total cost - decreases, hits a minimum, then increases
tells you how much profit or loss you’re making per unit
AVC = average variable cost → nears ATC
AFC = average fixed cost → asymptote heading toward y = 0
short-run total cost curves
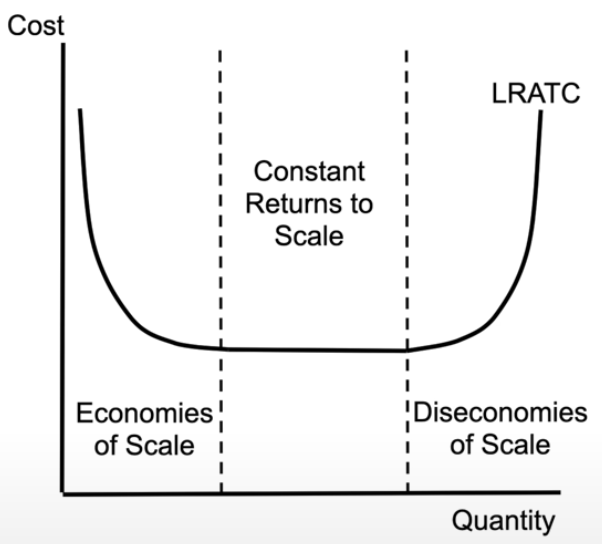
long-run average total cost curves
in the long run, if all of our resources are variable, we end up with this
shows all the sum of all short run curves
economies of scale = as a company produces more goods or services, the average cost per unit decreases
constant returns to scale: when you increase inputs to a production process by a certain proportion, the output will increase by the same proportion
diseconomies of scale = average cost per unit of production increases as its output increases
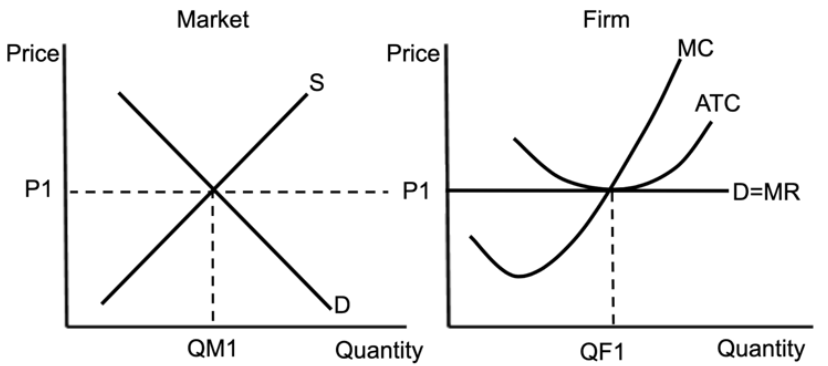
perfect competition (long run)
P1: the price is set by the market (price takers) → horizontal demand = marginal revenue curve
add in MC and ATC from short-run per unit cost curves
shows perfectly competitive firm in long-run equilibrium
you always produce where MR = MC → represents the profit maximising quantity
producing where price = marginal cost → producing amount society wants
producing at the lowest possible cost → producing productively efficient quantity
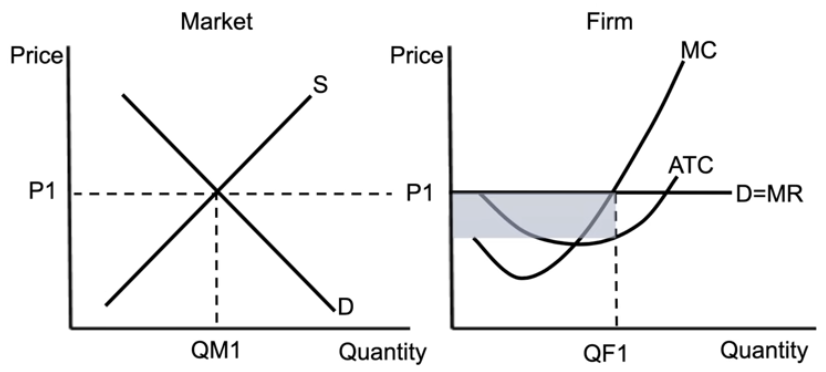
perfect competition short-run profit
the blue part
perfect competition short-run loss
the yellow part
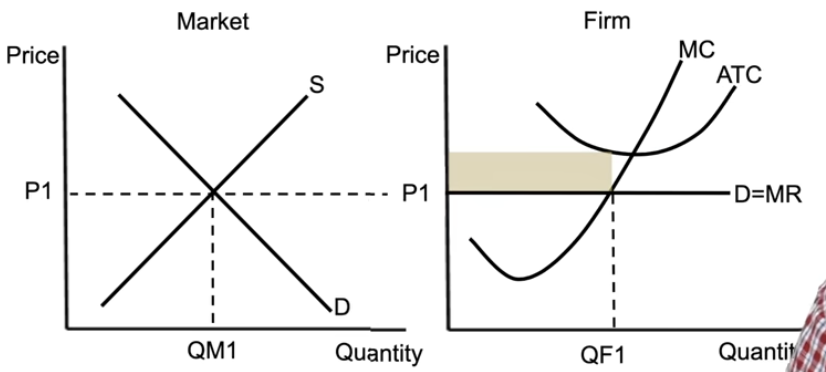
perfect competition from long run to short run back to long run
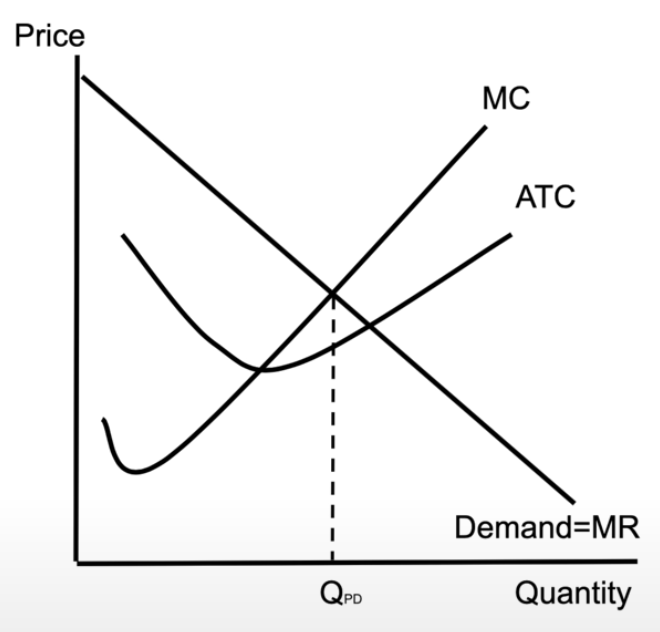
non-price discriminating monopoly
downward sloping demand curve
downward sloping marginal revenue curve
MC and ATC stay the same shape
still produce where MR = MC
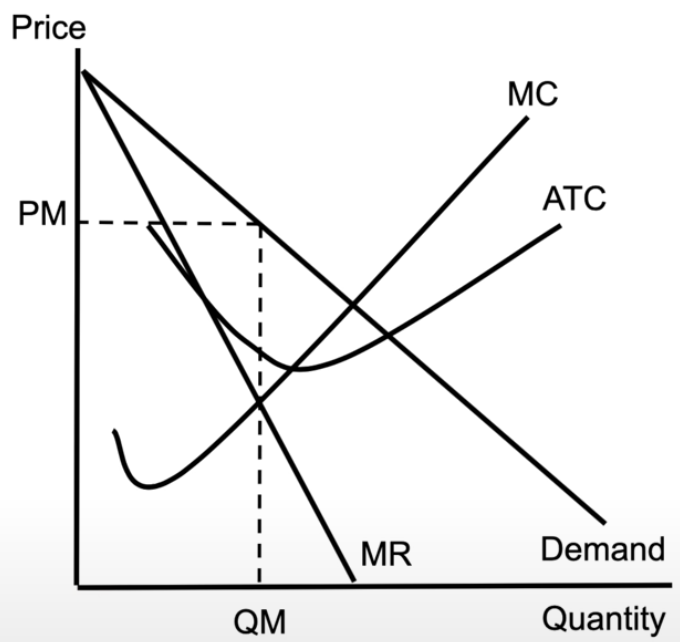
monopoly making profit
a monopoly is not allocatively efficient
not producing what society wants
it holds back production to maximise profits
monopoly making loss

monopolistic competition in the long run
ATC is tangent to the demand curve, showing no economic profit in the long run

natural monopoly
where the MC hits the demand curve (= the socially optimal quantity), the ATC is still falling
this means that the firm can produce the product at the lowest possible cost
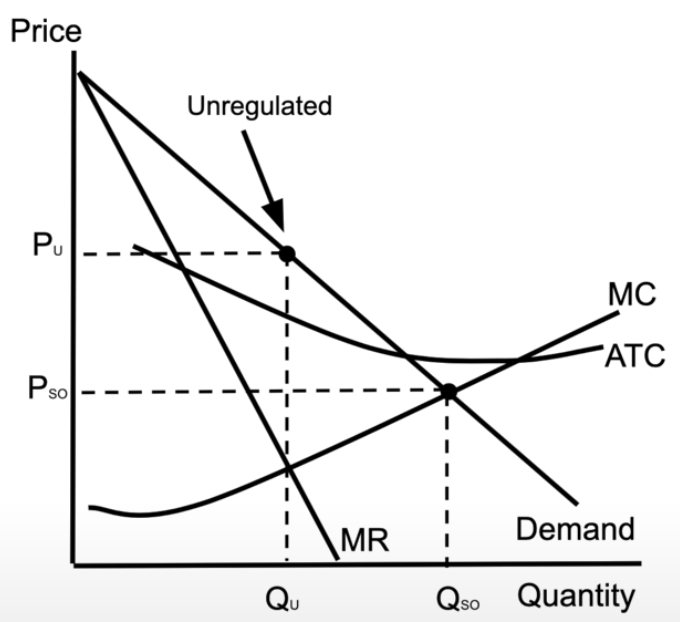
price discriminating monopoly
the monopoly is charging each consumer exactly how much they are willing to pay
demand curve = marginal revenue curve, and there is no consumer surplus → all of it becomes profit
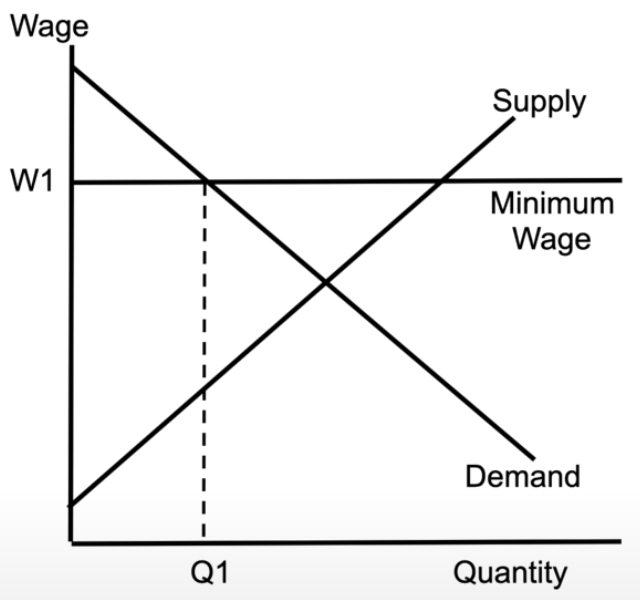
labour market (minimum wage)
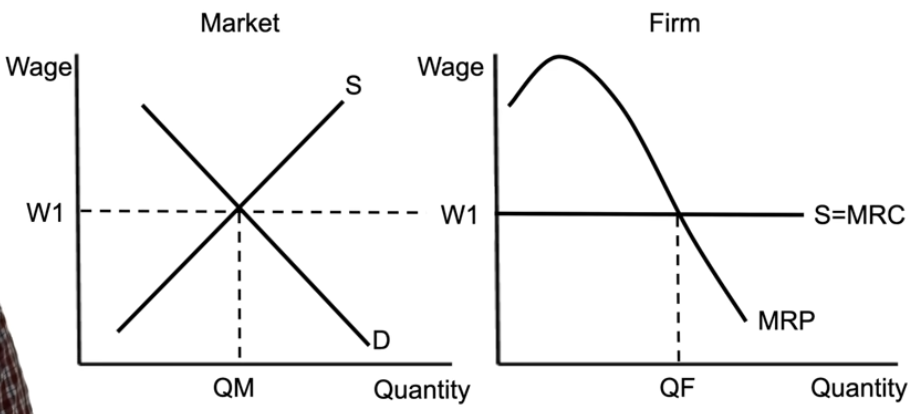
perfectly competitive resource market and firm
perfectly competitive firm in the resource market = a firm hiring workers
the wage for the firm is set by the market, gives you a horizontal supply curve, which = marginal resource cost
marginal revenue product = how much each worker generates → downward sloping, tells you exactly how many workers to hire (where MRP = MRC)
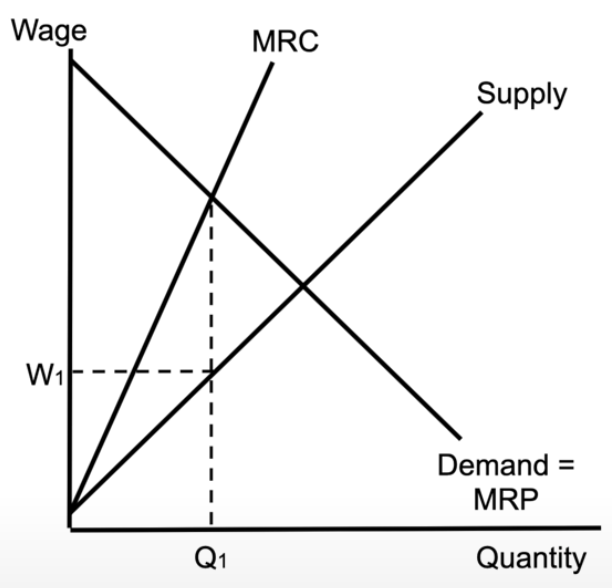
monopsony
there is only 1 firm hiring, so the supply of labour is upward sloping
there is an upward sloping marginal resource cost
you hire where MRC = MRP
the wage is below the equilibrium wage that would exist at perfect competition
firms that hire workers at a lower wage, because they are the only firm hiring
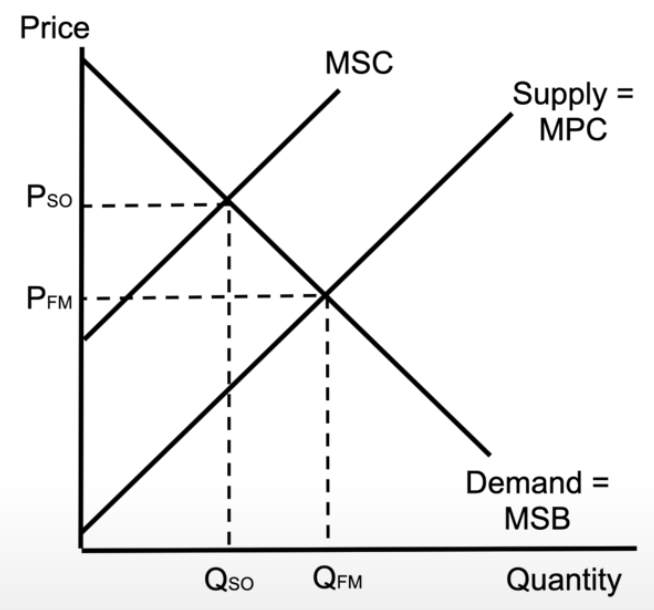
negative externality
supply and demand show you the quantity produced in the free market → the free market quantity is wrong
if this product creates a negative externality and there is additional costs on society, we end up with a marginal social cost (MSC)
MSC hits marginal social benefit, which shows the socially optimal quantity, which is less than the free market is making
result: dead weight loss (overproducing, because we didn’t take into account the additional costs on society)
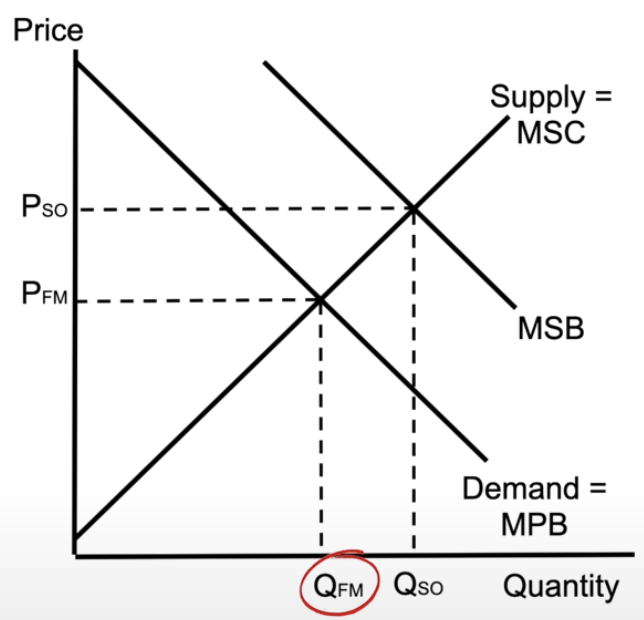
positive externality
quantity of the free market is less than the socially optimal quantity
not factoring in all the additional benefits that society gets from the product
dead weight loss → the free market is underproducing something that society wants more of
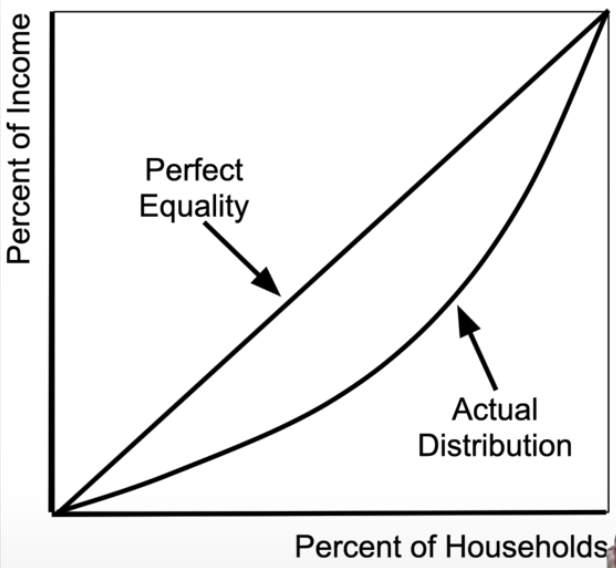
lorenz curve