Inorganic Chemistry - P2 [Periodic Properties]
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
Periodic table
____ - is an organized classification of element
Horizontal Rows: Periods
Vertical Rows: Group
Periodic Table is divided into [2]
►same energy level
►same valence electron (outermost energy level)
Elements on the same period = same ____ ?
Elements on same group = same ____ ?
Alkali metal
[PERIODIC TABLE OF ELEMENTS] Group 1 = ____
Alkali earth metal
[PERIODIC TABLE OF ELEMENTS] Group 2 =___
Transition metal
Example :
Lanthanide
Actinide
[PERIODIC TABLE OF ELEMENTS] Group 3 to 12 = ___
Main group elements
[PERIODIC TABLE OF ELEMENTS] ____ also called as representative elements
Boron Group
[PERIODIC TABLE OF ELEMENTS] Group 13 ___
Carbon Group
[PERIODIC TABLE OF ELEMENTS] Group 14 = _____
Pinictogen
[PERIODIC TABLE OF ELEMENTS] Group 15 = ____
Chalcogens
[PERIODIC TABLE OF ELEMENTS] Group 16 = ___
Halogen
[PERIODIC TABLE OF ELEMENTS] Group 17 = ___
Noble gases
[PERIODIC TABLE OF ELEMENTS] Group 18 = ____
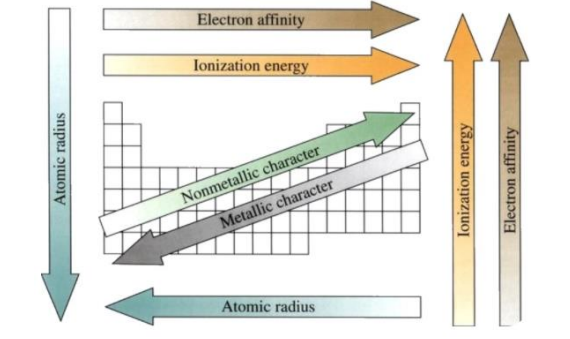
Periodic Table Trends
____are properties that can determine the composition of elements in the periodic table
Electron affinity
_____
is the energy released when electron is absorbed by a particular element
high energy = high affinity to that atom
Ionization energy
____ - is the energy needed for an atom to release / disperse electron
Ionization Energy
______ - is the energy needed to remove an electron from a gaseous atom in the ground state
Electron Affinity
____- is the energy change when an electron is added to a gaseous atom in the ground state
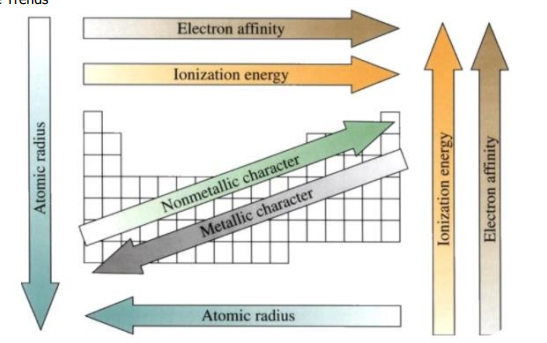
• Atomic Size:within a period, decreases from left to right; within a group, increases from top to bottom
• Size of Cation: within a period, decreases from left to right; within a group, increases from top to bottom
• Size of Anion: within a period, decreases from left to right; within a group, increases from top to bottom
• Ionization Energy (energy needed to remove an electron from a gaseous atom in the ground state):within a period, increases from left to right; within a group, decreases from top to bottom.
• Electron Affinity (energy change when an electron is added to a gaseous atom in the ground state): within a period, increases negative value from left to right; within a group, no clear trend
• Basicity of Metal Oxides: within a period, decreases from left to right; within a group, increases from top to bottom
• Acidity of Non-metal Oxides: within a period, increases from left to right; within a group, decreases from top to bottom
• Metallic Property (reducing property): within a period, decreases from left to right; within a group, increases from top to bottom
• Non-metallic Property (oxidizing property): within a period, increases from left to right; within a group, decreases from top to bottom
• Electronegativity (measure of the ability of an atom in a molecule to draw bonding electrons to itself): within a period, increases from left to right; within a group, decreases from top to bottom
Periodic Trends
Metallic Property
[Metallic / Non-metallic Property] ____ -is a reducing property
Non-metallic Property
[Metallic / Non-metallic Property] ____ -is a oxidizing g property
Electronegativity
_____ - measure of the ability of an atom in a molecule to draw bonding electrons to itself
b. smaller, and the nuclear charge is greater
1. As the atoms of the elements from atomic no. 3 to atomic no. 9 is considered in sequence from left to right across the periodic table, the atomic radius of each successive atom is:
a. smaller, and the nuclear charge is less
b. smaller, and the nuclear charge is greater
c. larger, and the nuclear charge is less
d. larger, and the nuclear charge is greater
b. IIA or 2
2. In which group do the elements usually form chloride that have the general formula MCl2?
a. IA or 1
b. IIA or 2
c. VIIA or 17
d. VIIIA or 18
d. lose electrons and form positive ions
3. Atoms of metallic elements tend to
a. gain electrons and form negative ions
b. gain electrons and form positive ions
c. lose electrons and form negative ions
d. lose electrons and form positive ion
b. F and Fr
NOTE: Electron affinity and ionization energy increases as one go from left to right and from top to bottom
4. Which pair of elements below has the highest and lowest electron affinities, respectively?
a. He and Rn
b. F and Fr
c. Ac and F
d. Li and Nb

c. Ge, As, Te
NOTE:
B, O, F, and Ne are obvious non-metals.
Ne, Ar, and Kr are noble gases.
Sc, Lr, Zn, and Uub are transition metals.
Metalloids: B, Si, Ge, As, Sb, Te, Po, At
Tip: check the B ladder.
5. Which of the following are all metalloids?
a. Sc, Lr, Zn, Uub
b. B, O, F, Ne
c. Ge, As, Te
d. Ne, Ar, Kr

Metalloids
Example: B, Si, Ge, As, Sb, Te, Po, At
Mnemonic: "Big Snakes Give Ants Some Terrible Problems, Ahhh
____aks semi -metal