Shifts analysis and output gaps
1/7
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
8 Terms
Draw AD increasing on a Keynesian
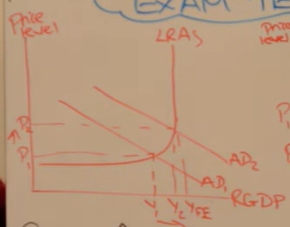
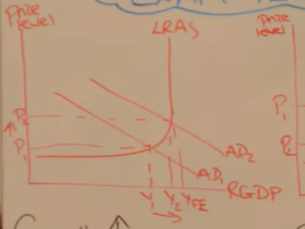
Analyse the outcomes of the diagram
Economics growth increases as firms have an incentive to meet demand with a higher quantity produced
Unemployment decreases - as labour is a derived demand so when more goods and services are demanded they need more workers to create the goods
Inflation increases - demand pull inflation due to more pressure on existing factors of production increasing the prices of these factors
Trade position worsens as demand for imports increases as well and our exports become less price competitive / imports more price competitive
Draw LRAS increasing on a keynesian
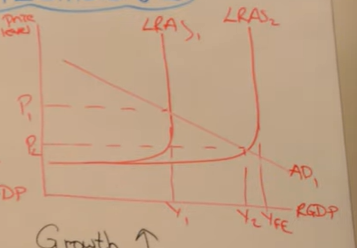
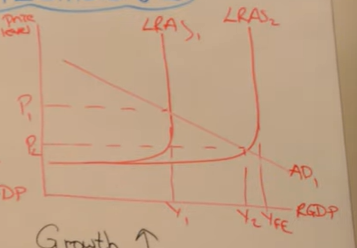
Analyse the outcomes of this diagram
Economic growth due to firms increasing output as there is more demand
Unemployment decreases due to derived demand (More goods being produced)
Inflation falls as there is reduced competition for goods and services
Trade position improves as exports become more price competitive
What is the biggest depends on point for keynesian
AD eval
Initial level of economic activity - if recession there will not be any inflation however if it is a boom there will be high levels of inflation
Size of multiplier
Extent of the change in AD
What is a negative output gap
Where firms produce output below full capacity / potential output
What is a positive output gap
Where the actual level of output is above full capacity/ potential output
Inflationary
How can output gaps be used for evaluation
AD increases traditionally will say price increases but according to Keynesian economic theory if there is spare capacity inflation will not rise
On the other hand if there is no spare capacity inflation will rise economic growth will not change
If LRAS grow unaccompanied by AD with a pre-existing negative output gap then the economy may just not change