Next Generation Sequencing and Sequence Analysis
1/20
Earn XP
Description and Tags
L15
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
What is particular about next generation sequencing?
they do PCR in solid support to obtain lots of copies if the same molecule in a very small space
these DNA clusters are then used for sequencing
allows us to obtain many more seqs in comparison to Sanger Sequencing
what is an example of a next gen sequencing dvlped 20yrs ago in response to the need for a higher throughput sequencing technique
Illumina sequencing
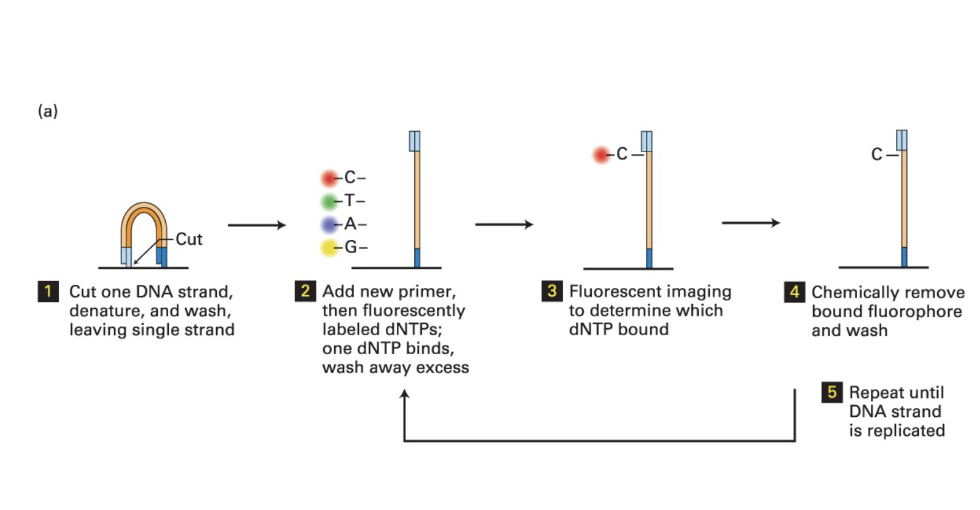
Mechanism of next gen sequencing
(1)
Double-stranded DNA is cut
Strand is denatured and washed
Leaving only one strand to be sequenced
(2)
Add new primer
then fluorescently labelled dNTPs
one dNTP binds
then wash away excess
(3)
Use fluorescent imaging to see which dNTP is bound
easier to see fluorescence when there is a lot of DNA (that’s why we do this amplificaiton)
(4)
chemically remove fluophore and wash
(5)
repeat until the DNA strand is replicated
Reversible terminators
what we call the nucleotides wiht fluophores conected to them
How many samples are there per experiment in next gen sequencing?
lots!
how did Dr. Pääblo’s grouop exploit Next Gen Sequencing (NGS) ?
sequenced the whole genome of Neanderthals
NGS provided them
high sensitivity
requiring small amts of sample
huge number of reads per experiment
What 4 things does sequence analysis provide us info about considering the basis that DNA and proteins are common to all organisms
common ancestry of gene and organisms
shared function or structure of proteins (assign to unknown)
timing events in evolution (aka when smthg occured)
identify mutations linked to disease (useful in clinic)
what are two basic concepts of seq analysis
sequence similarity
homologous sequences
very often the purpose of analysis is to test for homology between two seqs
Sequence similarity
degree of match between two sequences.
This is generally measured as a %
homologous sequences
two or more seqs derived from a common ancestral seq
generally have high similarity
two seqs can either be homologous or not
how do we search for max similarity between sequences?
we look at the options for alligning sequences that have the most matches
what increases the difficulty of finding similarity between sequences?
length
difficulty increases as seq is longer
and when sequences aren’t the same length it’s hard to compare them
often have lost or gained some nucleotides
how can we maximize match when looking at seq similarity
introduce gaps
Dot plot what is it and what is its use
a type of visualization that represents the allignment of two sequences
can be helpful to visualize changes in seqs that have occured over evolution
inversions
duplications
example of a program for seq analysis to search sequence database and its two variants
BLAST
basic
local
allignment
search
tool
—> BLASTN: nucleotide seq similarity
—> BLASTP: protein seq similarity
How does BLAST work? example with BLASTN (3 steps)
query sequences: look for exact match by “BLASTed”ing it in the database of DNA seqs (look for HIT)
Extend the match locally
Allow for short gaps in alignment
What are two newer approaches to sequencing that use single molecule sequencing and what is particular about them?
Pacific Biosciences
Oxford Nanopore Technologies
they skip” the PCR step
Nanopore Sequencing
membrane w pore
electrical current through pore that can be measured
each base has difft voltage: when molecules go through pore there is chaneg in electric potential of current
can pass DNA molecule through pore
helicase separates it but strands are linked as the end —> reads both strands like in a line
we can read the sequences w/ changes in the electrical curent
no need for PCR amplificaiton before sequencing
not based on DNA replication
no use of DNA polymerase, dNTPs, or primers
what are the advantages of nanopore sequencing?
sequencing single molecules opens possibility to study new bio Qs
very long reads minimize need for genome assembly and allows mapping of repetitive sequences
detects modifications like methylation in DNA
you can train programs to detect changes in the DNA
portable
you can take it wherever you can take a laptop
sequencing is j a small casette
What is the advantage of having a long read for sequencing
Previous sequencing techniques result in short sequences at every read
from tons of bp to abt 1kpb
when broken apart hard to tell where in genome seq belongs
significantly longer seqs done by Nanopore (tens of kbp) allow the sequencing of repeated seqs along w/ flanking seqs
making it easier to map them in the genome
e.g. now we can sequence telomeres
Studying DNA methylation with Nanopore
Methylation patterns on DNA are associated to the generation and progression of cancer (and other diseases linked to aging)
Use of DNA sequencing techniques, like Nanopore, is now being used to help make decisions at the clinic