R305 Exam #2
5.0(2)
Card Sorting
1/80
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 4:29 AM on 3/8/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
81 Terms
1
New cards
What are setbacks?
The amount of land between the property and the street before you can begin building
2
New cards
What is the authority for regulating real estate use?
The authority to regulate land use is a result of the “police power” afforded governments at both the local and state level
3
New cards
What are the primary rationales for government interference in real estate markets?
1. Markets are imperfect and market participants may be ignorant of facts that significantly affect their welfare
2. Every land use has the potential to generate externalities that may positively or negatively influence adjacent property values
3. Real Estate values may be enhanced with good land use planning
4
New cards
What is zoning?
Zoning is the regulation of permitted land uses, as well as minimum or maximum structures, upon geographically defined contiguous districts
5
New cards
What is the purpose of zoning?
Zoning limits potential land uses and often use a cumulative type hierarchy system
6
New cards
What happens within a cumulative zoning system?
Less offensive uses are permitted even in more restrictively zoned areas, but not the reverse; highest order classifications: single family homes
7
New cards
What was the original purpose of zoning? How has this changed?
The original economic purpose of zoning was to help minimize negative externalities by grouping similar uses of land together. Today, zoning has largely become a political process as opposed to an economic process
8
New cards
What is NIMBY?
“Not in my Back Yard” - can exert a large influence over zoning decisions at the local level
9
New cards
What should we expect from zoning in the future?
* More cities are realizing the importance and benefits of mixed use developments
* We should expect to see more flexible zoning in the future
* We should expect to see more flexible zoning in the future
10
New cards
What happens by grouping similar land uses together through zoning codes?
There is less negative impair on other types of land uses that may be less noxious
11
New cards
What are building codes?
A series of standards and specifications designed to establish minimum safeguards in the erection and construction and construction of buildings, and to protect those who live and work in them
12
New cards
What are included in building codes?
Building codes describe in great detail the materials, methods, and techniques to be used in the construction of buildings
13
New cards
What have been the criticisms of building codes in recent years?
They have been criticized on the grounds that they go beyond protecting the ignorant participants in the market to inhibiting the market and constraining innovation
14
New cards
Why did tax credits become available?
In 1987, tax credits became available to encourage rehabilitation and preservation of historic real estate structures
15
New cards
What is the value of a tax credit?
A tax credit is more valuable than a deduction from income for the calculation of taxable income since tax credits are dollar for dollar tax savings
16
New cards
What is the two tiered system for tax credits?
A two tiered system is still in place today where property candidates for tax credits must either have:
* Been placed in service prior to 1936
* Be certified as “historic” through a registration/approval process administered by the Federal government via the Secretary of the Interior
* Been placed in service prior to 1936
* Be certified as “historic” through a registration/approval process administered by the Federal government via the Secretary of the Interior
17
New cards
What are the major building codes for design review and aesthetic controls?
* “Highway Beautification Act” under President Johnson
* Other design guidelines to limit the colors or control the use of lighting or signage or materials to enhance the uniformity of image
* Consistent environmental quality - EQD
* ADA requires that facilities that are generally open to the public be accessible to all members of society
* Other design guidelines to limit the colors or control the use of lighting or signage or materials to enhance the uniformity of image
* Consistent environmental quality - EQD
* ADA requires that facilities that are generally open to the public be accessible to all members of society
18
New cards
What does ADA require of real estate properties?
ADA requires that facilities that are generally open to the public be accessible to all member of society
19
New cards
How do property taxes impact a property’s value?
They exert negative influence on property values because they increase the cost of ownership
20
New cards
How do public expenditures impact a property’s value?
They exert a positive influence on property values
21
New cards
How do property taxes and public expenditures influence property value in an ideal world?
The negative influence of property taxes on property values would be more than offset by the positive value effect of good schools, nice parks, or good fire protection
22
New cards
What is fiscal redistribution?
The mismatch of service receipt and cost support - city vs. suburbs; transfer of income from higher to lower income households via tax and transfer schemes
23
New cards
Property Tax Assessment and Calculation
The appraised market value of a house
Times: The assessment ratio for personal residences
= Assessed value
The sum of the millage rate of the city, county and schools then made into a percentage of the appraised market value
Times: The assessment ratio for personal residences
= Assessed value
The sum of the millage rate of the city, county and schools then made into a percentage of the appraised market value
24
New cards
How do you calculate the effective property tax rate?
(Property taxes due each year/Appraised market value)\*100
25
New cards
How can local/state governments encourage or directly support private development?
* Property tax abatement for many years
* Land buy downs
* Industrial revenue financing
* Tax increment financing (TIF)
* Infrastructure improvements
* Land buy downs
* Industrial revenue financing
* Tax increment financing (TIF)
* Infrastructure improvements
26
New cards
What is the most common form of public assistance today?
Tax increment financing (TIF)
27
New cards
What do part of property taxes paid go to?
Part of the property taxes normally paid, e.g. 75% are diverted and used to support local government bonds that are issued at the time of development. These bonds may be used for a variety of subsidy approaches
28
New cards
State/Local Level Subsidies
* Use of abating local and state income taxes on the earnings of a new local employer in order to encourage a location move to an area in a given statement and/or county or city
* Competition for large employers has been so strong in some urban areas, especially in areas that border two states, that governments end up in a bidding war of economic incentive packages
* At the local level, the investment required to lure a key employer into an area might well be worth the cost
* However, at the national level, it is a zero sum game
* Competition for large employers has been so strong in some urban areas, especially in areas that border two states, that governments end up in a bidding war of economic incentive packages
* At the local level, the investment required to lure a key employer into an area might well be worth the cost
* However, at the national level, it is a zero sum game
29
New cards
What is the focus of environmental regulation?
Most environmental regulation, like early building codes, is focused on protecting the health, safety and welfare of our citizens
30
New cards
What is environmental activism?
Environmental activism officially began at the Federal level in 1969 with the passage of the National Environmental Policy Act
31
New cards
What is the environmental impact statement?
The first assessment of the impact of any proposed development
32
New cards
What is CERCLA?
Comprehensive Environmental Response, Compensation, and Liability Act of 1980
The primary federal statute that may result in personal liability from the acquisition, ownership or operation of real property
The primary federal statute that may result in personal liability from the acquisition, ownership or operation of real property
33
New cards
What is the purpose of CERCLA?
This is also referred to as the “Superfund”, it sets forth a complex regulatory scheme to identify, investigate, analyze, and remediate property contaminated with hazardous waste
34
New cards
Who is liable in CERCLA?
Current/past owners, generators/possessors and transporters of hazardous substances
35
New cards
CERCLA liability is ___________
strictly retroactive
36
New cards
What is the result of CERLA?
There are three defined stages of mandates reports and actions to try and avoid liability for clean up costs of a contaminated site, or investigate the extent/cost of actual clean up
37
New cards
What are the phases of CERCLA?
Phase 1: To determine whether there is evidence of past or current environmental problems on the subject site
Phase 2: To test and verify the extent of the actual contamination
Phase 3: Actual action plan that usually includes remedial cleanup efforts
Phase 2: To test and verify the extent of the actual contamination
Phase 3: Actual action plan that usually includes remedial cleanup efforts
38
New cards
How did wetlands used to be perceived? How are they viewed now?
For many years, wetlands were thought to be useless mosquito infested swamps. Today we are learning that they are wondrous sources of life and diversity, with species that are crucial for a healthy environment. Wetlands help control floods, which are important ecological processes
39
New cards
What is green design?
Green design involves a more environmentally oriented approach to building design, construction and maintenance
40
New cards
What is sustainable development?
Sustainable development plans include a more holistic approach to the environmental impact of the entire development
41
New cards
What characterizes a developer?
Developers must have vision and see the opportunities, requires strong analytical and people skills
* New concept
* Follow the path tested by others
* New concept
* Follow the path tested by others
42
New cards
What is the highest risk sector in the industry?
Real Estate Development
43
New cards
Why is real estate development most risky?
* Most opportunity for value and most opportunity for challenges/mistakes
* Usually a high use of leverage
* Usually a high use of leverage
44
New cards
Who are the players in real estate development?
* Developers
* Designers and physical planners
* Environmental consultants
* Regulators
* Neighbors
* Competitors
* Tenants or buyers
* Leasing or sales agents
* Property managers or facilities managers
* Lenders
* Owners/investors
* Designers and physical planners
* Environmental consultants
* Regulators
* Neighbors
* Competitors
* Tenants or buyers
* Leasing or sales agents
* Property managers or facilities managers
* Lenders
* Owners/investors
45
New cards
What is the chronology of development?
* Conceptual stage
* Resource assembly and planning
* Implementation and contractual period
* Absorption and operational period
* Harvesting and disposal
* Resource assembly and planning
* Implementation and contractual period
* Absorption and operational period
* Harvesting and disposal
46
New cards
Who is the father of feasibility analysis?
Dr. James Graaskamp (Univ. of Wisconsin)
47
New cards
What are the two primary situations for feasibility analysis?
* Site looking for a use
* Use looking for a site
* Use looking for a site
48
New cards
What are the five major components of feasibility analysis?
* Strategic analysis
* Market and competitive analysis
* Political and legal analysis
* Physical and design analysis
* Financial analysis
* Market and competitive analysis
* Political and legal analysis
* Physical and design analysis
* Financial analysis
49
New cards
What are the components of financial analysis?
* Project costs
* Front door/back door techniques to determine feasibility
* Front door/back door techniques to determine feasibility
50
New cards
What are the types of project costs?
* Hard costs and soft costs
* Absorption costs
* Absorption costs
51
New cards
What are the front door/back door techniques to determine feasibility?
* Front door = costs to rent
* Back door = rent to costs
* Back door = rent to costs
52
New cards
Graaskamp’s Approach to Feasibility Analysis
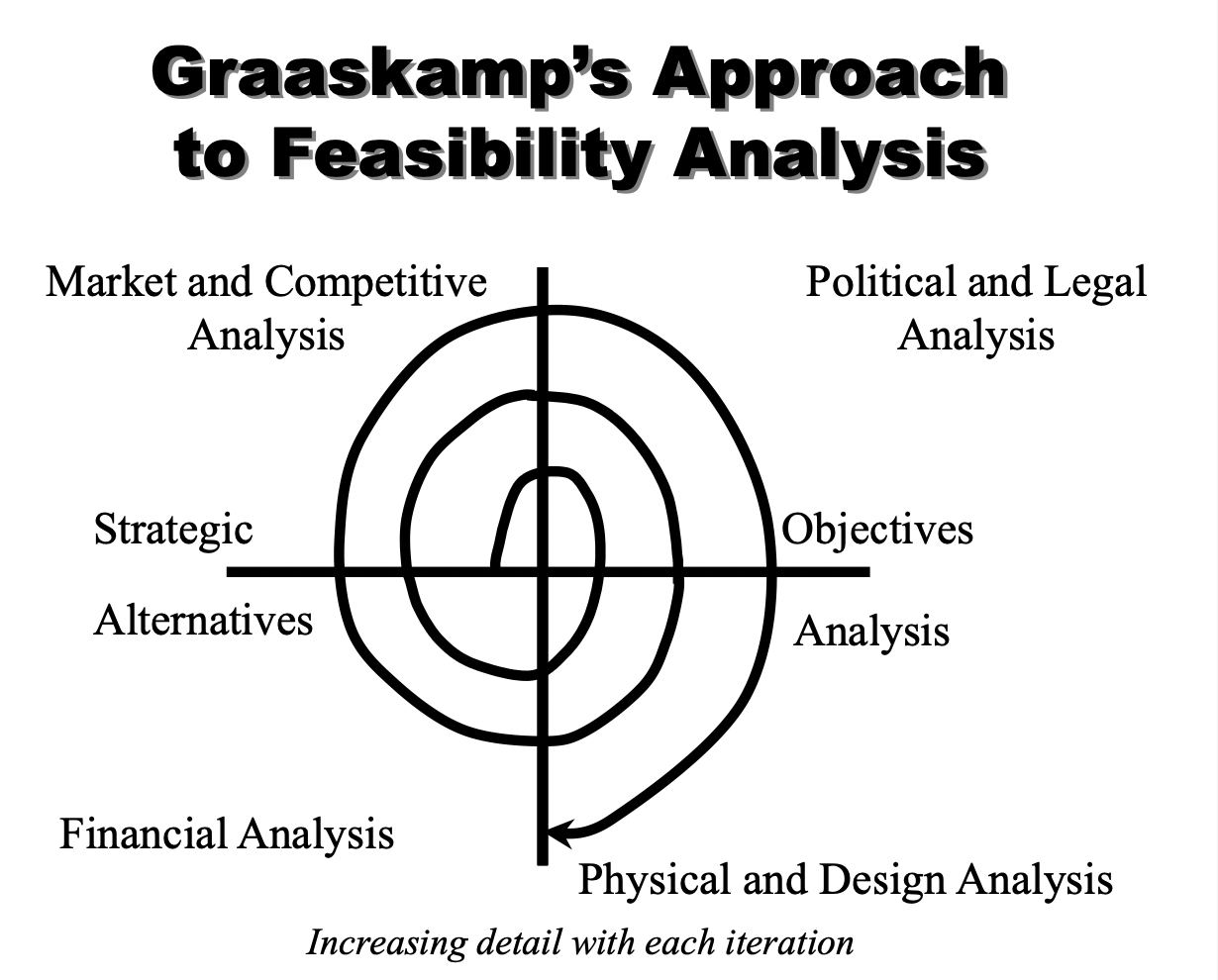
53
New cards
What are office market trends?
* Parking
* Energy supply
* Wired or wireless
* Energy supply
* Wired or wireless
54
New cards
Warehouse Trends
55
New cards
Retail Property Types and Trends
56
New cards
Single Family Housing
57
New cards
Multifamily Housing
58
New cards
What does a developer do?
Creates value
59
New cards
What are the four major risks that a developer faces?
Entitlement risk, financing risk, construction risk, and absorption risk
60
New cards
What is the value created by developers?
Difference between total project costs & stabilized value
61
New cards
What is stabilized value?
Property value realized at stabilized rents and stabilized occupancy
62
New cards
What is included in total project costs?
Includes land costs, hard costs, soft costs, and absorption costs (Note: Some developers may include a portion of developer profit in total project costs)
63
New cards
Describe absorption costs
Monthly operating expenses + monthly leasing/marketing fees + monthly construction loan interest carry in excess of monthly EGI
64
New cards
Describe breakeven cash flow
Monthly EGI = monthly operating expense + monthly leasing/marketing fees + monthly construction interest due (“interest carry”); i.e. no more accumulation of project costs
65
New cards
Why is breakeven critical?
Because if costs continue to accumulate past their budgeted amounts it decreases the value created, i.e. starts defeating the developer’s purpose and very likely may be reduced at a rapid rate to zero or worse after years of work and risks. On the other hand breaking even earlier than projected provides the opportunity to create more value than projected, i.e. a higher margin
66
New cards
How much value should a developer create?
Enough to compensate him or her for the risks taken
67
New cards
How do we estimate sufficient value creation?
* Percentage mark up over total project costs, i.e. more risk more markup
* Return on Costs v. Cap Rate of Return on Value
* Return on Costs v. Cap Rate of Return on Value
68
New cards
What is the rule of thumb?
It assumes total costs do not include developer profit
* 20% low risk (Build to suit or similar)
* 35 to 50% higher risk (speculative)
* 20% low risk (Build to suit or similar)
* 35 to 50% higher risk (speculative)
69
New cards
Return on Costs v. Cap Rate or Return on Value
Ex. NOI = 100,000, Total Costs = 1,000,000, Market Cap Rate = 8%
Ex. NOI = 100,000, Total Costs = 1,000,000, Market Cap Rate = 8%
ROC = 100,000/1,000,000 = 10% > 8% cap rate by 2% or 200 basis points; value creation equals the difference between value and total costs, i.e. value is NOI/cap rate or 100,000/.08 = 1,250,000 less total costs of 1,000,000 or $250,000
70
New cards
What financial analyses’ do we relate to our mark up percentage?
Construction Cost Analysis for total project costs, and GRM, Traditional income approach or discounted cash flow approaches for value
71
New cards
How do we decide the specifics of a potential development plan?
Feasibility analysis
72
New cards
What four areas are considered in executing the project’s strategy and goals?
* Market
* Political
* Physical
* Financial
* Political
* Physical
* Financial
73
New cards
What does an “iterative” process mean?
Run scenario after scenario through the areas of the feasibility analysis, one impacting the other, until a recommended development plan consistent with the decided strategy and goals is achieved
74
New cards
Hard costs
Amounts of capital committed in development projects to materials, labor, and other tangible or nonservice inputs
75
New cards
Soft costs
A component of construction cost including the cost of permits, legal fees, financing and insurance fees, architectural and design costs, other professional fees, and the cost of marketing
76
New cards
Stabilized value
The value of a property after it reaches projected occupancy rate and operating expenses
77
New cards
Tax rate
(The budgeted expenditures - the income from sources other than property tax)/(The total assessed value of all properties - the value of property exemptions)
78
New cards
Taxable value
Assessed value - Exemptions
79
New cards
Millage Rate
the tax rate converted into mills (dollars per $1000 of value
Millage Rate x Taxable Value = Taxes Levied
Millage Rate x Taxable Value = Taxes Levied
80
New cards
Return on Costs
NOI/Total Cost
81
New cards
Return on Value
(NOI/Cap Rate) - Total Costs