INTERGUMENTARY SYSTEM
1/57
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
58 Terms
fascia
below the three layers of skin is a sheet of connective tissues that ties the skin to the underlying muscles
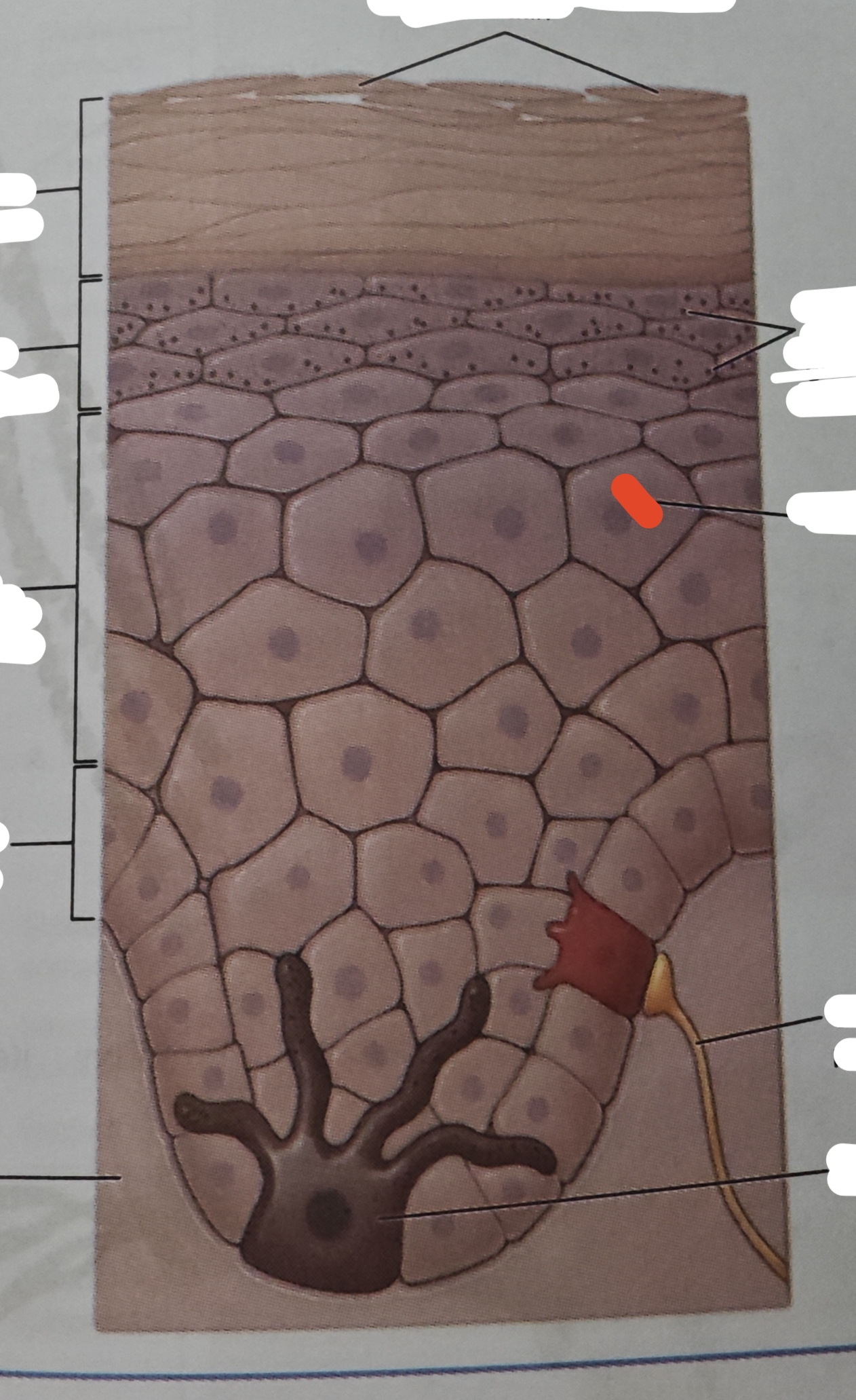
epidermis
composed of stratified squamous epithelium
epidermis
Layer of the skin that is a dry organ , keratinized, avascular and also known as keratinized stratified squamous
keratinocytes
cells in all epidermal layers except stratum basale
keratinocytes
a cell that manufactures and stores protein keratin
keratin
an intracellular fibrous protein that gives hair, nails, skin the hardness and water-resistant properties
stratum lucidum
the skin of the palms of the hand andd soles of the feet has a fifth layer called
stratum lucidum
located between the stratum corneum and stratum granulosum
stratum basale
the deepest epidermal layer and attaches the epidermis to its basement membrane, which ties the epiermis to the dermis below
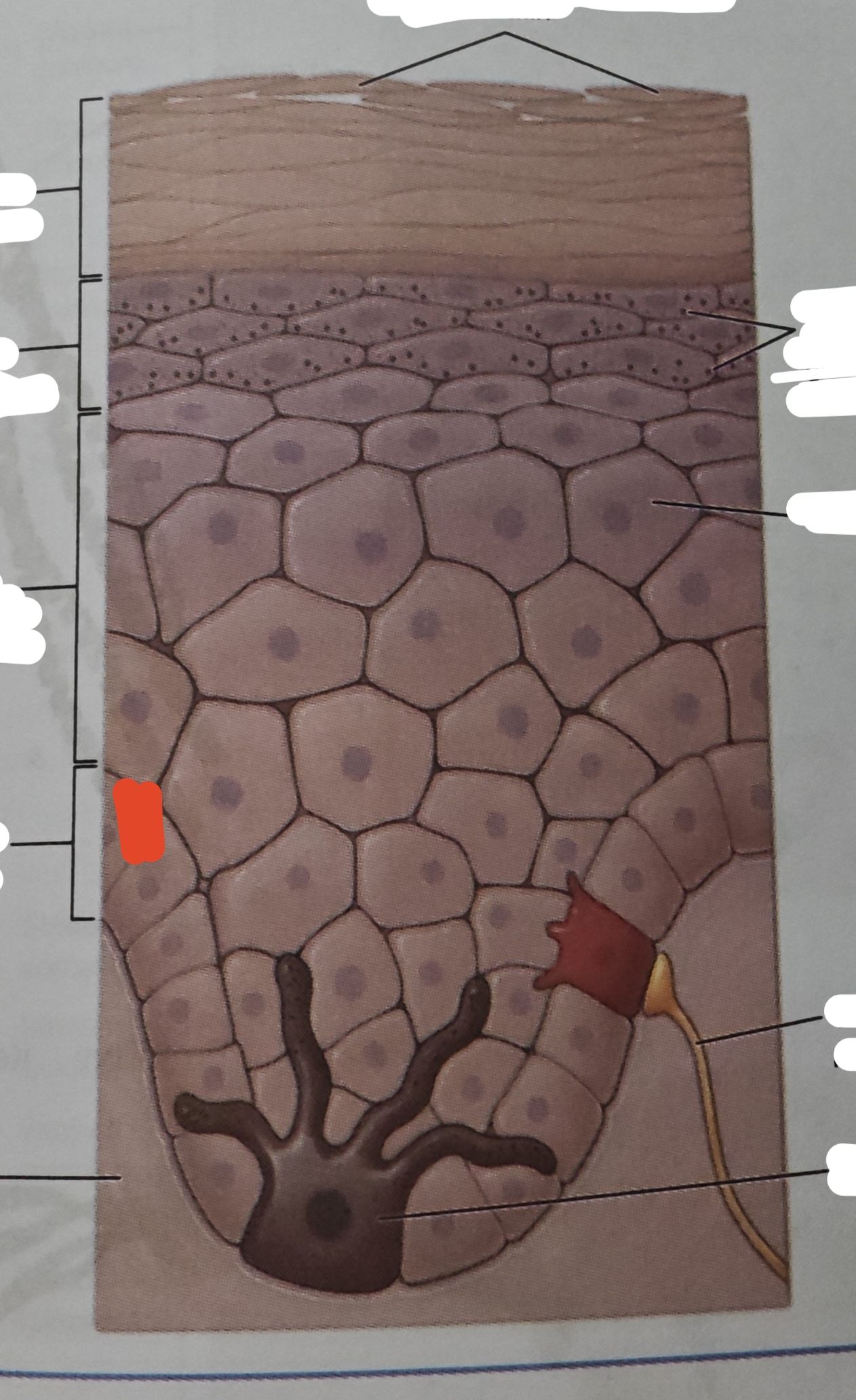
merkel cell
function as a sensory receptor and is connected to sensory nerves that sends signal about touch to the brain— these cells are abundant on the surface of the hand and feet
melanocyte
a cell that produces the pigment melanin
merkel cell, melanocyte
two other cell types found dispersed among the stem cells in the stratum basale
Melanin
a protein that can be made in two forms—fuctions to protect cells from ultraviolet (UV) radiation damage
eumelanin
black and brown melanin is called
pheomelanin
reddish hue melanin is called
folic acid
melanin prevents the break down of?
stratum spinosum
the young keratinocytes have an American-football shaped apperance—meaning they are widest in the center and tapered in the end
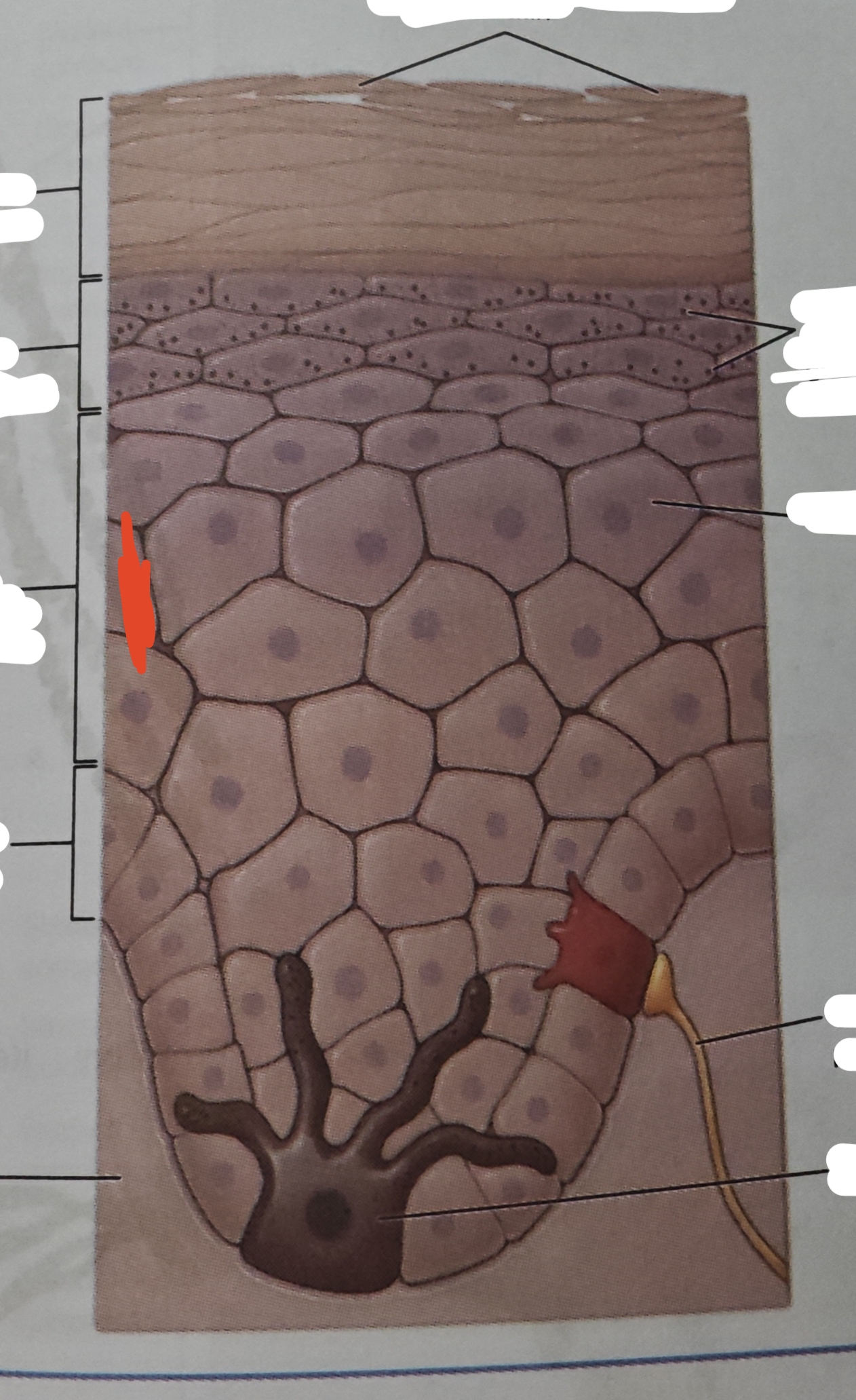
desmosomes
joined the cells—interlock the cells with each other for the skin to undergo an amount of pulling, twisting and friction and the keratinocytes will remained joined
langerhans cell
type of dendritic cell—functions similarly to macrophanges, engulfing bacteria, foreign particles and damaged cells that occur in this layer
stratum granulosum
named for its granular appearance
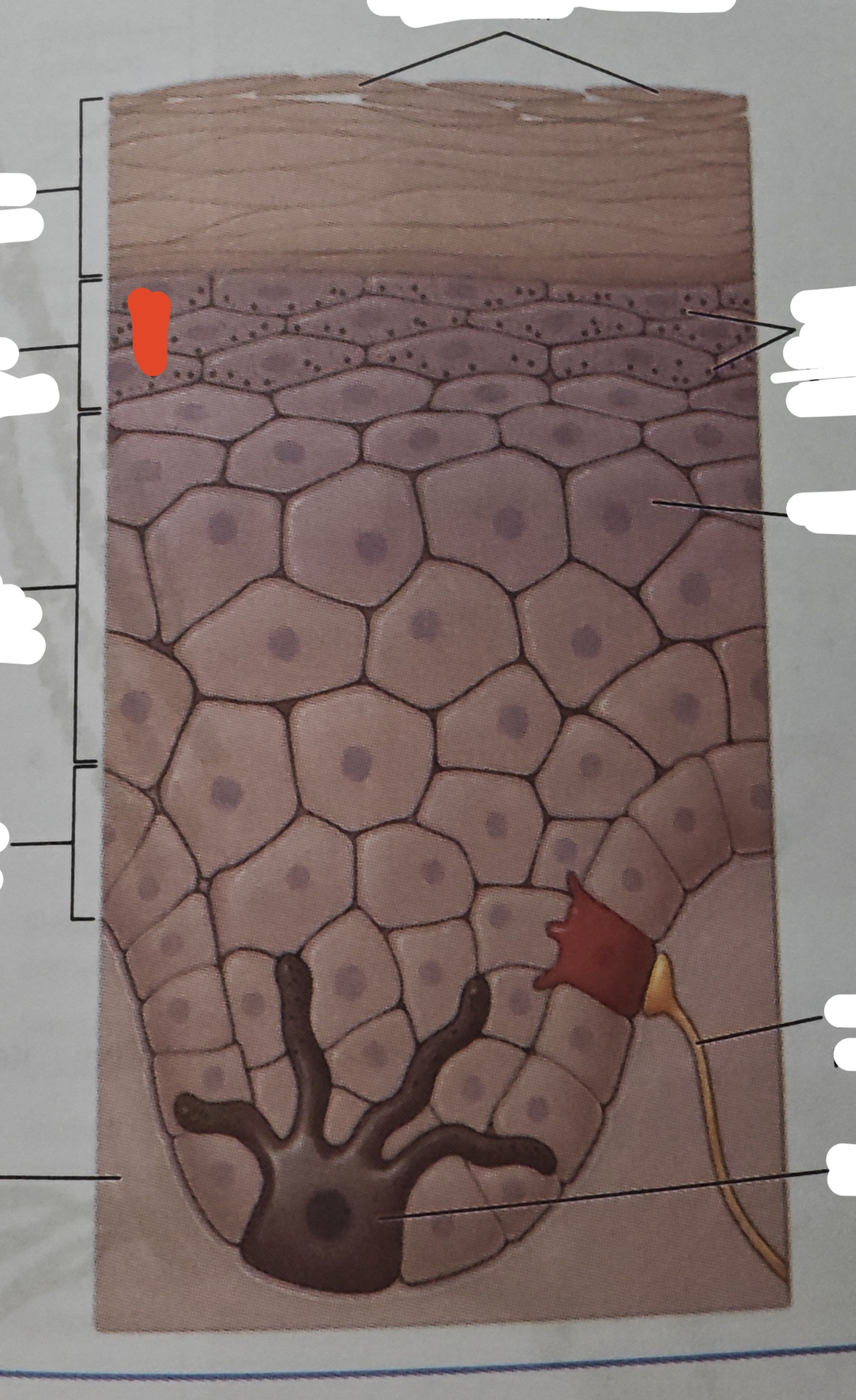
stratum lucidum
is a smooth seemingly translucent layer vof the epidermis located just superficial to the stratum granulosum and deep to the stratum corneum
eleidin
a clear protein derived from keratohyalin,which gives these cells their transparent appearance
stratum corneum
layer of the skin that is exposed to the external environment—most superficial of every epidermis
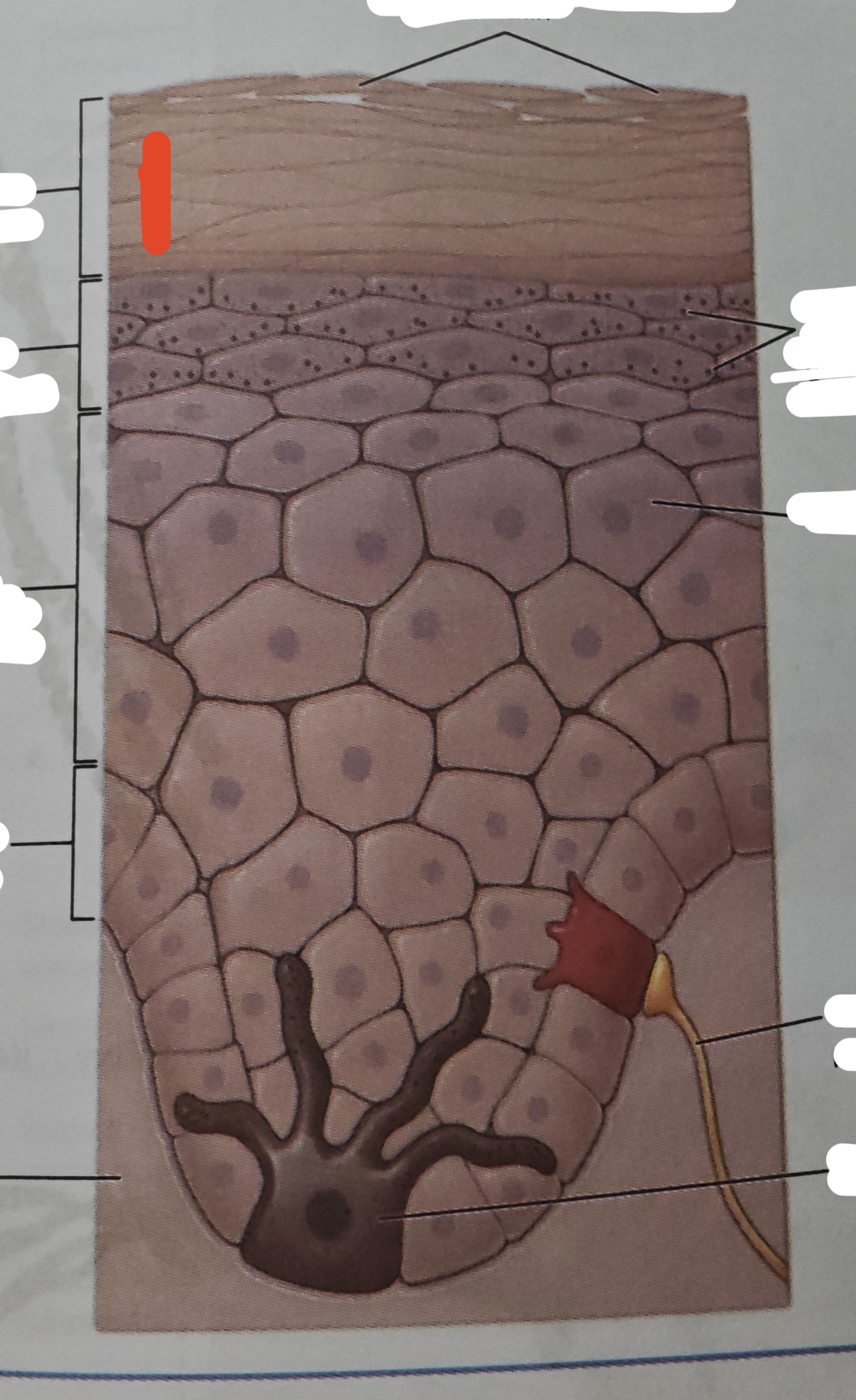
15, 30
consist of __ to__ layers of dead skin cells
dermal papillae
structural adaption to better endure friction is the?
dermis
contains blood and lymph vessels, nerves and other structures, such as the deeper portion of hair follicles and sweat glands.
papillary layer
is made with loose areolar connective tissue
tactile corpuscles
papillary layer contains nerve fibers and touch receptors called
reticular layer
composed of dense irregular connective tissue
hypodermis
consist of well-vascularized, loosed areolar connective tissue and adipose tissue and its functions includes fat storage, insulation and cushioning
hair shaft
The externally visible portion, a long filament of keratin is called
hair follicle
this shaft of hair is grown within an epidermal structure called
hair bulb
deepest portion of the hair follicle is called?
hair matrix
epethilial cells within the hair bulb form the
hair root
the portion of the follicle between bulb andd the surface of the skin
medulla
central core of the hair—a fragile inner core made up of some living cells and the spaces between them
cortex
medulla is surrounded by the?—a layer of compressed keratinized cells
cuticle
an outer layer of very hard keratinized cells known as
sebaceous gland
hair follicle is associated with oil gland known as
nail bed
living component of nails
nail body
hard, bladelike structure you might paint—function to protect the tip of our fingers and toes
nail root
nail body forms at the?
pheromones
a type of chemical signal that organisms can use to communicate with each other
eccrine sweat glands
a type of sweat glands found all over the body, they produce sweat for thermoregulation
dermcidin
an antimicrobial chemical
apocrine sweat glands
associated with hair follicles and found in dense hairy areas such as armpits,genital region—
apocrine sweat glands
are larger than eccrine sweat glands and lie deeper in the dermis sometimes even reaching the hyprodermis.
sebaceous gland
type of oil gland that is found all over the body and hgelps to lubricate and waterproof the skin and hair
sebum
oily mixture—a mixture of lipids that lubricates the hair and the dry stratum corneum
tactile corpuscles
sensitive to touch—responds to light touch
lamellate corpuscles
responds to pressure and vibration
nociceptors
nerve fibers specific to communicating pain to the brain and spinal cord
thermoreceptors
sensory nerves detecting changes in temperature
symphatetic nervous system
body temperature is specifically regulated by gthe division of the nervous system called
frostbite
too much drop in the temperature can freeze the skin—a condition called
rickets
a pain disorder in children where the bone becomes misshapen due to the lack of calcium
osteomalacia
individuals who suffer from vitamin D deficiency can develop a condition called___a softening of the bones
granulation tissue
quickly made collagen bridge