ANS 221- Practical 1 Material
1/156
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
157 Terms
Medulla, Cortex, Hilus
What are the three portions of the ovary?
Cortex
What is the outer portion of the ovary called (not in horses)?
Medulla
Inner portion of the ovary (not in horses)?
Hilus
The portion of the broad ligament that supports the ovary?
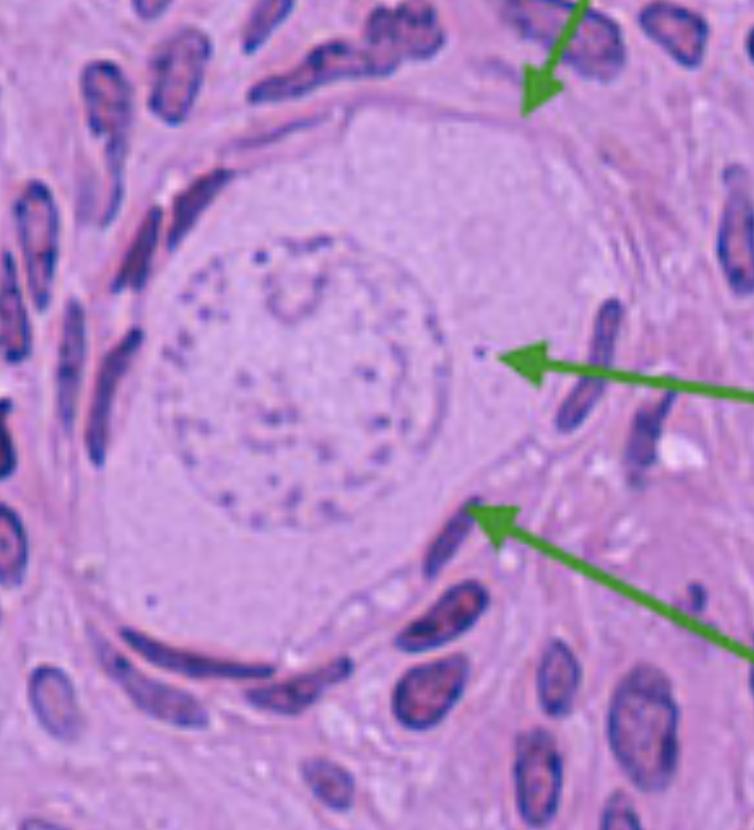
Primordial Follicle
Which follicular stage describes a dormant follicle that is present at birth, makes up the majority of follicles found on the ovary, and is surrounded by a thin layer of flattened/squamous granulosa cells?
Primary Follicle
What follicular stage describes the follicle that develops after puberty, is larger than primordial and mitotic, is surrounded by cuboidal granulosa cells, and develops from the primordial follicle?
Secondary Follicle
Which follicle can be described as having no antrum, surrounded by several layers of follicular cells and is the formation of both thecal and granulosa cells?
Developing Antral Follicle “Tertiary Follicle”
Which follicular stage is described as being surrounded by several layers of follicular cells which are differentiated by the inner granulosa cells and the surrounding thecal cells?
Developing Antral Follicle or Tertiary Follicle
In which follicular stage does the antrum form?
Graafian or Preovulatory Follicle
Which follicular stage is considered the dominant follicle and contains a secondary Oocyte? Here the follicular antrum takes up most of the follicle!
Ovulating Follicle
Which follicle is released during ovulation, involves the Cumulus Oocyte comoex, and is surrounded by granulosa cells now called cumulus cells?
ensure that the oocyte remains healthy
What do cumulus cells do?
Progesterone (P4)
What does the corpus luteum produce?
Corpus Luteum
What is essential for establishing and maintaining pregnancy? What has to be present if an animal was able to get pregnant/has a baby?
the endocrine remains of the follicle
What is the corpus luteum made up of?
Corpus Luteum
Yellow Body on Ovary
Corpus Albicans
Scar-like, White body on ovary
fibrous tissue
Corpus albicans is filled with what type of tissue?
Primordial Follicle
Identify Follicular Stage
Primary Follicle
Identify Follicular Stage
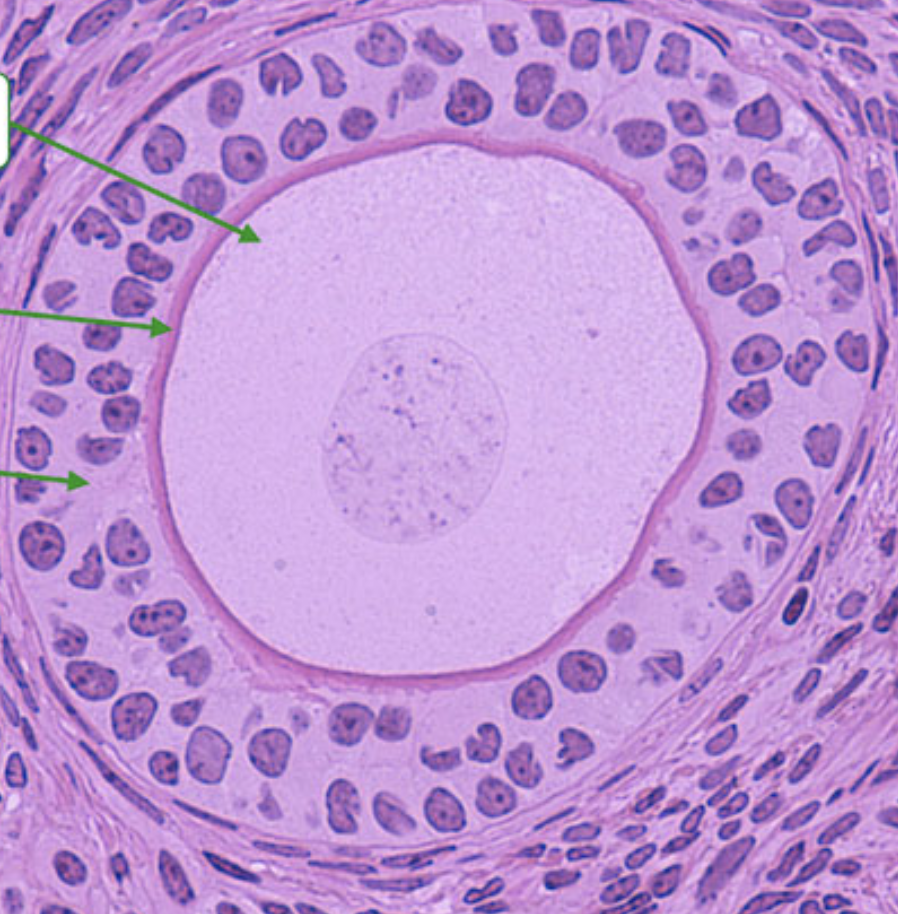
Secondary Follicle
Identify Follicular Stage
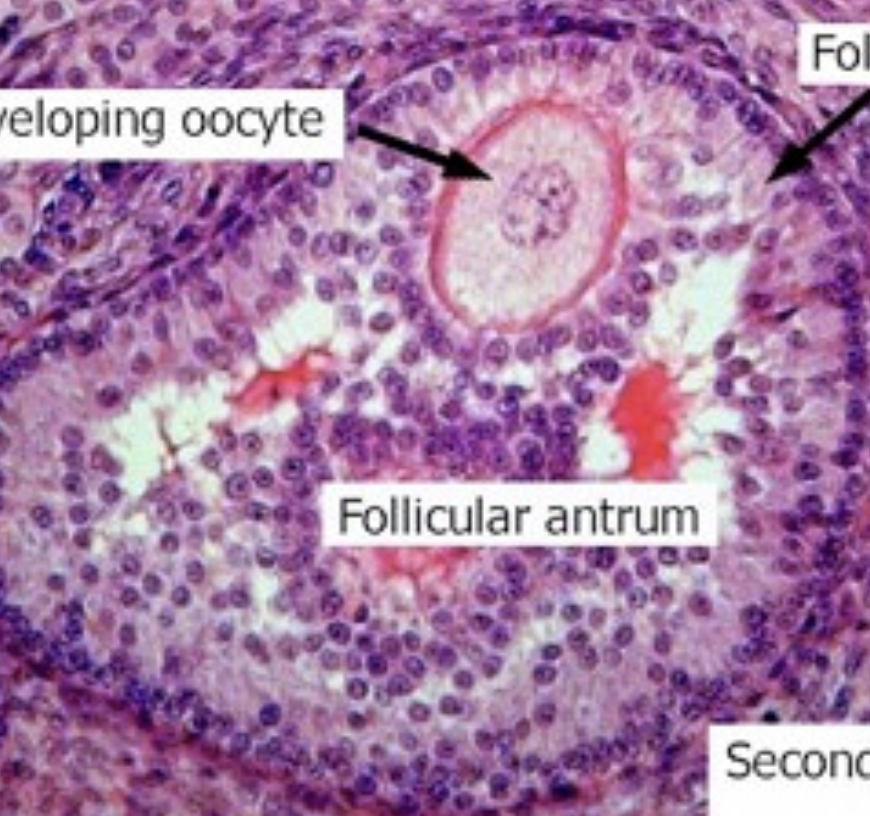
Tertiary/Developing Antral Follicle
Identify Follicular Stage
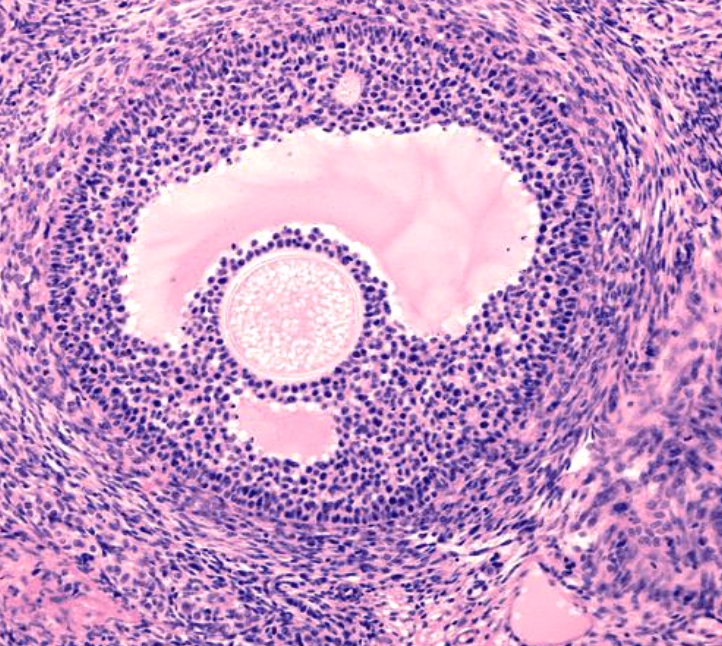
Graafian (Preovulatory) Follicle
Identify Follicular Stage
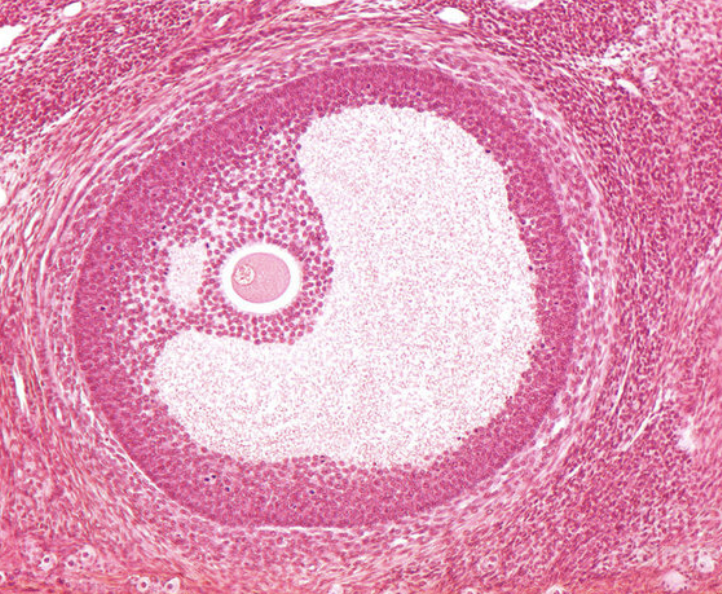
In cow cortex is on outside and in mare cortex in on inside. Mare must ovulate through the ovulation fossa whereas cows can ovulate over the whole surface of the ovary.
What is the main structural difference observed in cow and mare ovaries?
Primary Follicle
Secondary Follicle
Tertiary or Developing Antral Follicle
Medulla
Cortex
Preovulatory or Graafian Follicle
Ovulating Follicle/ Cumulus-Oocyte Complex
Corpus Luteum
Corpus Albicans
Hilus/Mesovarium
primordial Follicle
Identify Parts
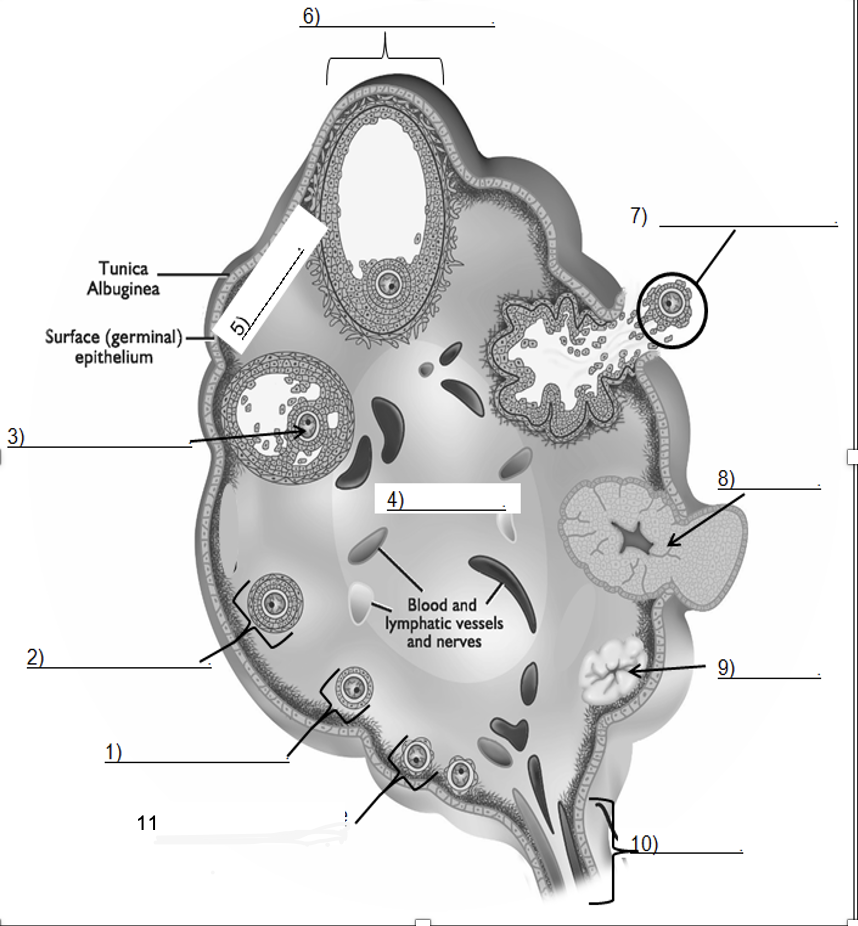
Cow
Swine
Cervix
Vagina
Ovary
Infundibulum
Broad Ligament
Uterine Horn
Oviduct
Identify parts (1 and 2 are the animals which the system belongs to)
before they hit puberty
When are pigs housed in groups?
aggression
Why would it be good to separate boars/house boars individually?
collection cup
vinyl gloves
gauze
List the equipment needs for a boar collection
it reduces the chances of killing sperm, as latex and other materials are spermicidal
what is the importance of using vinyl gloves when collecting a sperm sample?
it catches the gel fraction, which is important for keeping the ejaculate viable
What is the purpose of the gauze placed over the collection cup during boar collection?
5 months of age
At what age do boars reach puberty?
around 6 months of age, after hitting puberty
When do they start training boars for collection?
when he is around 8 months of age
When will a farm begin using a boar’s semen?
no!
can you use an artificial vagina when collecting from a boar?
Boars require pressure, as well as temperature, to ejaculate, and the necessary pressure cannot be achieved via AV.
Why can you not use an artificial vagina for boar collection?
gloved hand method
what is the method we use for boar collection?
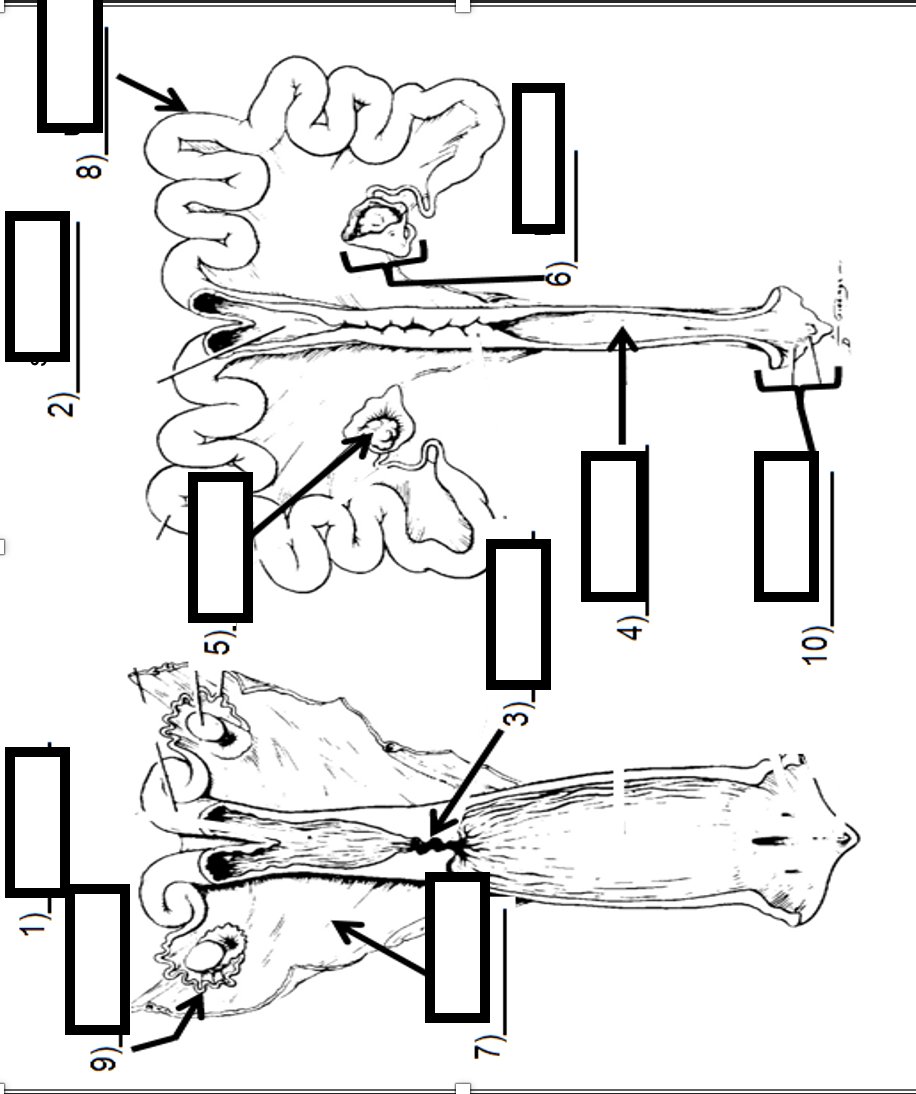
Sigmoid Flexure
Testes/Testicle
Scrotum
Epididymis
Retractor Penis Muscle
Seminal Vesicle
Ureter
Urinary Bladder
Pelvic Bone
Rectum
Cowper’s Gland/Bulbourethral Gland
Prostate Gland
Ischio Cavernous Muscle
Vas Deferens
Penis
Identify
domestic animals do not produce the hormone hCG or human chorionic gonadotropin, which the tests detect
Why can’t we use a human pregnancy test on domestic animals?
ELISA
What do we use to test pregnancy in domestic animals?
Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay
What does ELISA stand for?
Progesterone
What does teh Target Vet Bovine Kit we used in class detect?
Saliva, Feces, CSF, Urine, Blood, Milk
What can be used to test for pregnancy/progesterone in animals?
there is a cup with hormone antibodies on it, which will idn to progesterone if it is present in the milk, creating a Hormone-Hormone Antibody complex. If it truns blue, there is no progesterone or very little progesterone. If it is white the cow does have progesterone present in her milk.
How do Assays work?
true
True or False: if the milk was high in progesterone not much of the "enzyme antibody linked progesterone" bound... only the "enzyme antibody linked progesterone" will bind to the enzyme and cause the color change.
the colors are subjective
What is a con of using the Target Progesterone Assay?
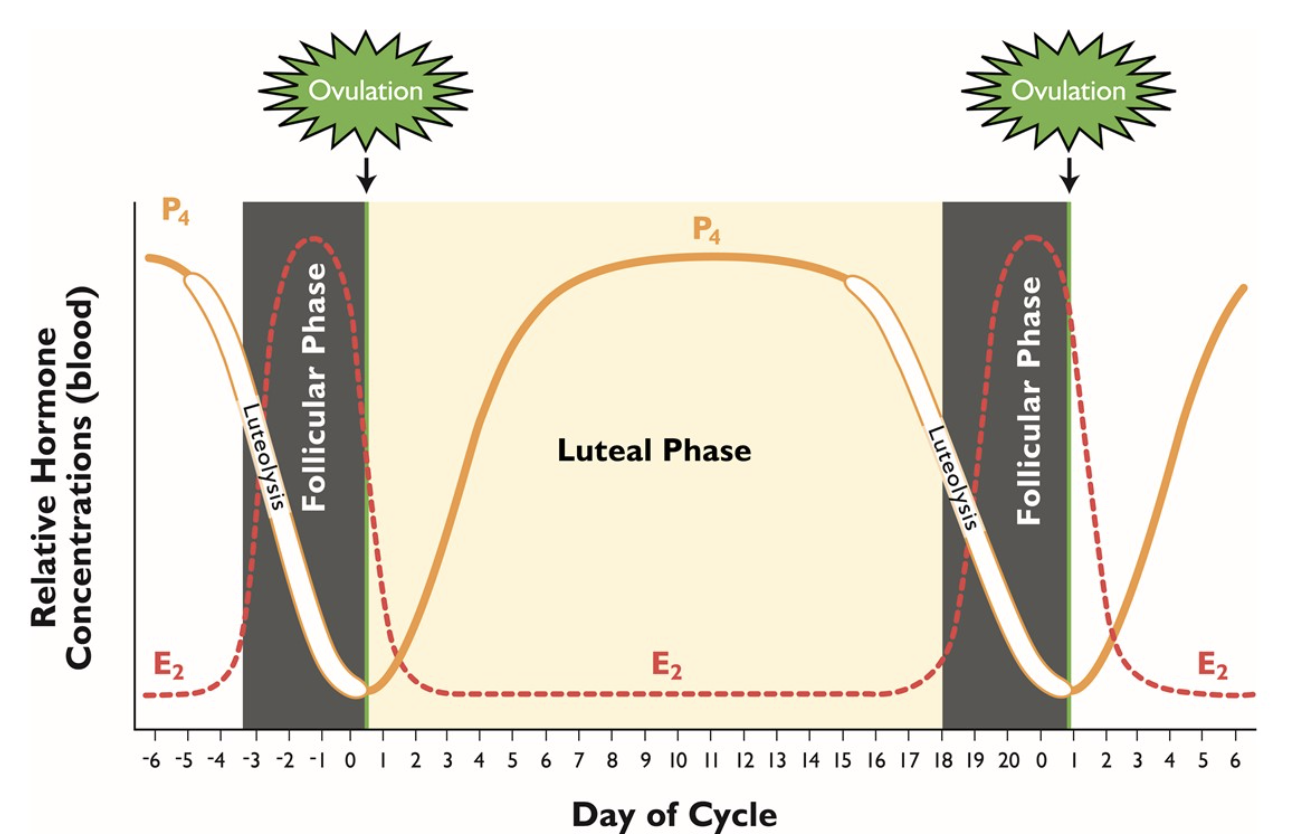
Drawing Challenge: Draw the estrous cycle chart and be sure to label when ovulation occurs, when follicular phases are luteolysis, and the luteal phase, as well as the respective estrogen and progesterone levels.
7 days apart for 21 days, 3 samples total
How far apart should each sample of milk be taken for a target progesterone assay?
Pregnant!
What does it mean if the Assay results are High-High-High?
Anestrous
What does it mean if the Assay results are Low-Low-Low?
Ovulated about 14 days ago
What does it mean if the Assay results are Low-Low-High?
sub-functional CL, cow ovulated but CL regressed early
What does it mean if Assay results are Low-Medium-High?
Gonadotropin Releasing Hormone, this is released by the Hypothalamus. GnRH induces ovulation and causes the release of the gonadotropins - LH and FSH
What is GnRH, its function, and where it is released?
Luteinizing Hormone and Follicle-Stimulating Hormone, released from the pituitary in response to GnRH.
What are LH and FSH? Where are they released and when?
causes ovulation and helps maintain the CL
What is the role of Luteinizing Hormone (LH)?
stimulates follicular growth
What is the role of Follicle Stimulating Hormone?
Estradiol, released by the ovaries (from the follicles specifically); causes standing estrus, also triggers the release of GnRH when there is a lack of progesterone
What is E2 and its function? Where is it released and when?
Progesterone, maintains pregnancy and inhibits ovulation, released by CL
What is P4, what is its purpose and where is it released?
Prostaglandin F2 Alpha is released by the uterus and regresses the CL
What is PGF2alpha? What is its function and where is it released from?
anytime progesterone is high, estrogen is low; anytime estrogen is high, progesterone is low. This inverse relationship is very important!
what is true about progesterone and estrogen’s relationship?
Cholesterol
What is the base of any steroid?
Progesterone, Estrogen, Testosterone
What are the three steroidal hormones?
Peptides like GnRH and Oxytocin
What kinds are hormones are produced by the hypothalamus: Peptides or Steroids?
They go to the pituitary which releases the proteins LH, FSH, hCG, PMSG, bST (all gonadotropins)
Where do peptides travel to once they leave the hypothalamus? what does this structure release?
GnRH or Gonadotropins such as Cystorelin, pLH, Pregnyl
What would we give if we want our animal to ovulate?
Prostaglandin F2α, such as Lutalyse
What would we give if we want to regress (or lyse) the CL?
In order to block ovulation, we would want to give progesterone such as Matrix, a CIDR, Regumate - Regumate is commonly used in performance horses to stop mares from cycling as this can hamper their performance
What would we use if we don't want our animal to cycle at all?
estrogen
what is never given to any US food animal?
can identify short cycles, and promotes better management of animals estrous cycles
what are some advantages of using the testing kit assay we used in class?
PG-600 (Matrix)
induces puberty in prepubertal gilts
FSH-P, Super OV, FollitropinV, Gestyl
allows for super-ovulating embryo transfer donors in cattle
Regumate
Controls out of season or early season breeding in mares
Lutalyse, Prostamate
induces luteolysis regression in cattle
oxytocin, Pinocin
increases intensity of uterine contractions during labor
Cystorelin, Fertagyl, Facteral, Follutein, Pregnyl
treats ovarian cystic follicles in cattle
CIDR, MGA, Progesterone
Blocks ovarian function
Posilac
increases milk yield
when you want to regress the CL for timed AI, in pigs it will cause parturition
when would you use PGF2alpha?
21 days
how long is the general estrus cycle for cattle?
Progesterone
During the Luteal phase, what hormone is higher in concentration?
at the end of follicular phase
During what phase of estrus is estrogen in higher concentrations?
low
does estrogen remain low or high during ovulation?
Prostaglandin F2 Alpha
If the animal is not pregnant, what will be released into the body, causing ing the CL to regress, and progesterone levels to decrease?
Parlodel
What is the Brand Name for the prolactin inhibitor used to induce abortion in dogs ?
Dr.Charlotte Farin
Who designed the NC Synch Protocol?
it is used to plan insemination when we know the animal is going to ovulate
What is the purpose of NC Synch
give PGF2 alpha (Lutalyse)
What do you do on day 1 of the NC Synch protocol?
give GnRH (Factrel or Cystorelin)
What do you do on day 8 of the NC Synch protocol?
give another injection of PGF2 alpha
What do you do on day 15 of the NC Synch protocol?
give GnRH again and Artificially inseminate!
What do you do on day 18 of the NC Synch protocol?
it can be expensive purchasing all of these drugs
What are the disadvantages of the NC Synch protocol?
CIDR
What is typically used if the NC Synch protocol is not?
releases progesterone, which causes a lowering in estrogen production and prevents ovulation until the removal of the CIDR
How does a CIDR work?
PGF2 alpha or PG 600
What is recommended to give after removing a CIDR?
ideal for third-world countries since it only requires 1 shot each time, wasting fewer materials and causing less progesterone contamination in our streams and landfills.
What are the advantages of the NC Synch protocol?
interest in a buck - place a buck in a pen, does the doe run up to it? Or place a doe in a pen and see if the buck goes up to it.
Vocalizations
Red/swollen vulva
Raised tail
Sometimes mucus from the vagina is also present
What are signs of estrus in doe or ewes?
in the uterine body. It is important to deposit the semen in the uterine body, and not a uterine horn, as we do not know which horn may have ovulated.
Where is semen deposited during AI? Why?
Place doe in a stanchion and raise the hindquarters
Clean the vulva
Apply lube to the speculum
Enter the vulva with the duckbill speculum
Grab the wall of the cervical os with the forceps at around the 1:00 position
Rotate the forceps 90 degrees clockwise - this opens the cervical passage
Place a catheter through the rings of the cervix
Deposit semen in the uterine body
What are the steps of artificial insemination in does/ewes?
150 days
How long is a doe/ewes gestation length?