Philippine Accessibility Law: IRR and Building Standards for Persons with Disabilities
1/177
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
178 Terms
What is the main purpose of Batas Pambansa 344?
To enhance the mobility of disabled persons by requiring certain buildings and public utilities to install accessibility features.
What types of buildings does Batas Pambansa 344 apply to?
Public and private buildings and related structures for public use.
What must be provided before a permit for construction or renovation is granted under Batas Pambansa 344?
Barrier-free facilities and accessibility features must be included in the plans submitted for approval.
What percentage of government-owned living accommodations must be accessible to persons with disabilities?
Ten percent (10%) of the total number of units.
What is required for ingress/egress from the street to buildings?
It must be accessible.
What types of public transport vehicles are included under Batas Pambansa 344?
Passenger buses, jeepneys, passenger trains, domestic vessels, and domestic aircraft.
What is the minimum door opening width for elevators to be accessible?
900 mm.
What is the minimum clearance for knee and leg space under tables for wheelchair users?
0.70 m.
What is the minimum clear space required to accommodate one wheelchair and one occupant?
900 mm in width.
What is the maximum forward reach for wheelchair users at eye level?
1.10 m to 1.30 m.
What is the maximum side reach across an obstruction for wheelchair users?
1200 mm.
What are the basic physical planning requirements outlined in Batas Pambansa 344?
Accessibility, reachability, usability, orientation, safety, workability, and efficiency.
What must be considered when assessing space for wheelchair users?
The specific dimensions of the wheelchair and the occupant's ability to navigate it.
What is the purpose of the accessibility features mandated by Batas Pambansa 344?
To ensure that no group of people is deprived of full participation and enjoyment of the environment due to disability.
What is the guideline for wheelchair turning spaces?
A circle of 1.80 m in diameter is suitable for planning.
What is the maximum height for obstructions that wheelchair users may encounter?
900 mm.
What must be done if the repair or renovation work diminishes the primary function space by more than 10%?
Barrier-free facilities and accessibility features may not be feasible.
What is the reach range for wheelchair users for vertical forward reach?
0.7 m to 1.20 m above the finished floor.
What is the maximum horizontal forward reach for wheelchair users?
0.90 m to 1.10 m at shoulder level.
What is the significance of the criteria for accessibility in Batas Pambansa 344?
It ensures that buildings and public spaces are usable by all individuals, including those with disabilities.
What are the implications of not providing accessibility features in new constructions?
No permit for construction, repair, or renovation will be granted.
What is the role of the United Nations in relation to accessibility?
To promote full participation and enjoyment of the environment for all people, regardless of disability.
What is the classification for Category I buildings?
Residential - comprises Group A and partly Group B Buildings.
What types of buildings fall under Category II?
Commercial and Industrial - comprises partly Groups B, C, E, F, G, H, and I Buildings.
Which buildings are classified as Category III?
Educational and Industrial - comprises partly Group C, D, E, and H Buildings.
What does Category IV encompass?
Agricultural - comprises partly Group J Buildings.
What is included in Category V?
Ancillary - comprises partly Group J Buildings.
What is the standard for accessibility in auditoriums?
Seating for persons with disabilities must be accessible from the main lobby to primary entrances and related toilet facilities.
What is required for seating capacity exceeding 500 in assembly places?
An additional wheelchair seating space must be provided for each total seating capacity increase of 100 seats.
What must all buildings ensure for persons with disabilities?
Accessible routes that are unobstructed and connect to all accessible areas and features.
What is the maximum distance for establishing accessible routes?
Within a 500-meter radius of the facility.
What should be prioritized in the design of accessible routes?
Fully-compliant, accessible street-level sidewalks.
What environmental factors must be considered along accessible routes?
Thermal comfort, including temperature, humidity, air movement, and radiant heat.
What type of signage is required in accessible facilities?
High visibility visual signage along with alternative signage for varying abilities.
What should finishes in accessible buildings enhance?
Legibility, clarity, and visibility of the built environment.
What is required for walkways and corridors in accessible buildings?
Adequate passageways that are unobstructed and navigable.
What should be ensured for doors and entrances in accessible buildings?
Accessibility from floor to floor or any point of destination.
What must accessible toilet facilities provide?
Conveniently located spaces that allow comfortable maneuvering and transfers.
What is required for parking areas in accessible buildings?
Sufficient space for persons with disabilities to allow easy transfer from the carpark.
What must handrails and grab bars provide?
Secure support for users on stairs, ramps, or elevated surfaces.
What should be ensured for flooring along wheelchair routes?
Slip-resistant surfaces during both wet and dry conditions.
What is required for drinking water facilities in accessible buildings?
Access for both wheelchair users and standing people, with dual access provided.
What should be indicated at escalator entrances?
A sign clearly indicating an alternative accessible pedestrian pathway.
What principles should customer service areas adopt?
Universal design principles to promote inclusivity.
What type of illumination is required along accessible routes?
Appropriate quantity and quality to ensure clear visibility.
What should be provided along accessible routes for persons with disabilities?
Appropriate resting equipment to accommodate extensive travel distances.
What is the requirement for ramps in buildings?
Changes in level shall require a ramp unless served by a dropped sidewalk, curb ramp, or elevator.
What is the minimum clear width for accessible ramps?
1200 mm
What is the maximum gradient allowed for accessible ramps?
1:20
What is required for accessible ramps longer than 10.50 m?
Intermediate landings with a minimum length of 1800 mm
What is the minimum level area required at the upper and lower ends of any ramp?
1800 mm
At what heights should handrails be installed on ramps?
700 mm and 900 mm from the finished floor
What is the required horizontal extension of handrails at ramp ends?
300 mm
What is the minimum height for raised edges on both sides of the ramp?
100 mm
Where should tactile warning strips be installed on ramps?
At the head, foot, and landings
What is the maximum rise for ramps that require handrails?
170 mm
What is the minimum width for accessible parking slots?
4000 mm
What is the minimum length for accessible parking slots?
5000 mm
What should be provided between parked cars in accessible parking areas?
A walkway with a minimum clear width of 1200 mm
What should be the luminance contrast of floor surfaces compared to adjacent walls?
30%
What is the maximum size of holes in channel covers?
13 mm
What is required for gratings in accessible areas?
They must be slip-resistant and level with the surrounding floor
What is the required diameter for handrails that require full grip?
Between 30 mm and 40 mm
What is the minimum clear distance for handrails attached to walls?
50 mm
What should be done with exposed edges of carpets?
They must be fastened to floor surfaces and have edge trims
What should be done with objects placed on top of handrails?
It is prohibited to place any objects that are not essential or do not serve a safety purpose
What is the requirement for handrails around landings less than 2100 mm?
They must be continuous throughout the entire length
What must be marked on upper handrail extensions?
The destination in Braille accompanied by written characters
What is the minimum height for railings protecting stairs, ramps, or balconies above 750 mm?
1100 mm
What should be done with wiring and outlets in accessible pathways?
They should not create tripping hazards and must be positioned away from accessible pathways
What is the minimum luminance contrast required for gratings?
30% to distinguish them from the surrounding floor
What is the requirement for the surface of accessible parking slots?
They must have a firm, level surface without aeration slabs
What should be done with channel covers to minimize tripping hazards?
They should be flushed with the surface of the floor
What is the requirement for tactile warning blocks at ramps?
They must have a depth of 600 mm and be installed 300 mm from the head and foot of the ramp
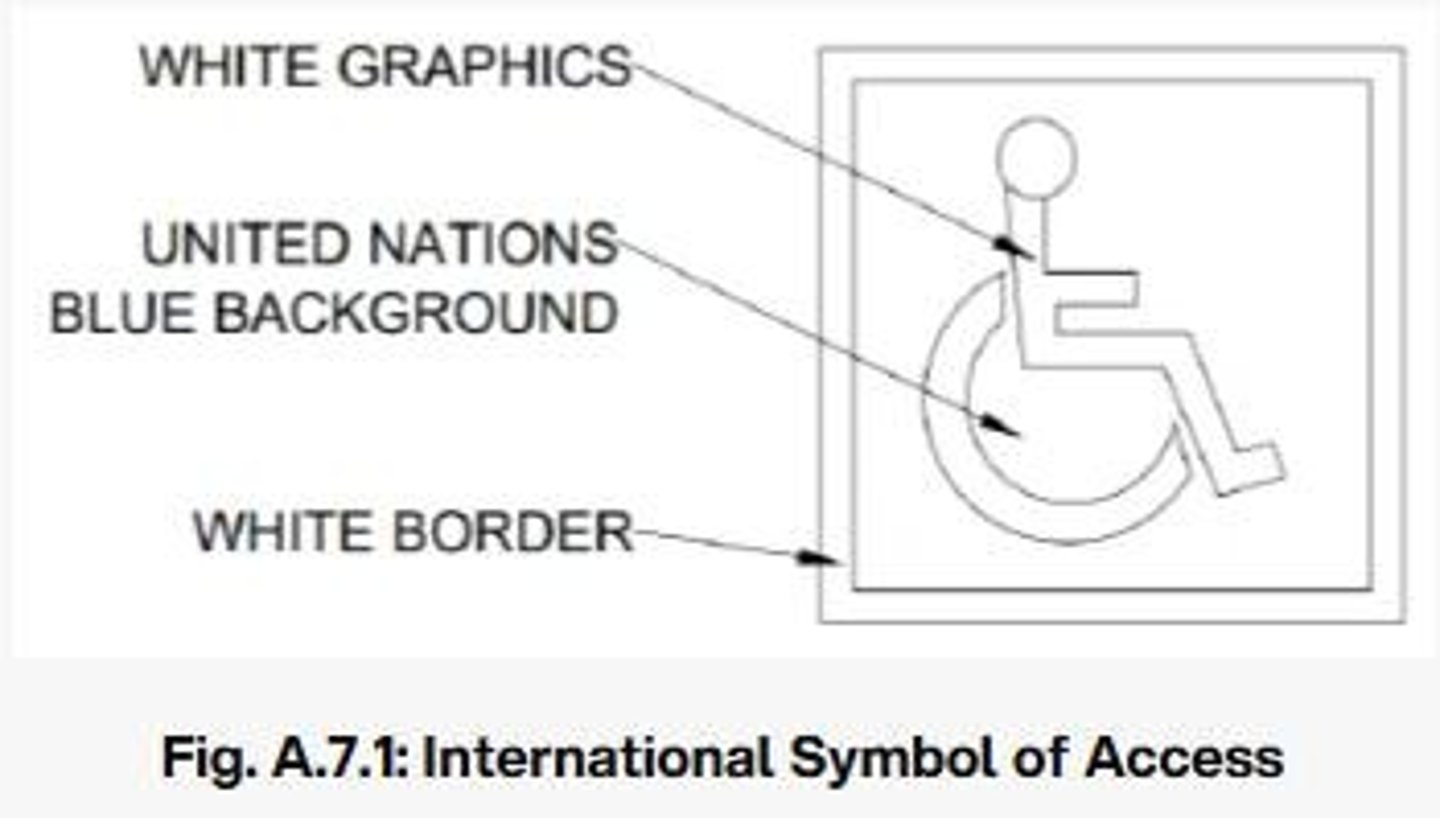
What does the International Symbol of Access (ISA) represent?
A white symbolized figure of a person in a wheelchair on a square background with United Nations Blue color.
What is the minimum clear width for tactile floor surfaces?
600 mm away from tripping hazards, walls, columns, and other elements.
What are tactile floor surfaces designed to assist?
People with visual disabilities.
Where should tactile floor surfaces be provided?
In stairways, escalators, elevators, ramps, and areas where pedestrian and vehicular traffic intersect.
What is the minimum luminance contrast required for tactile floor surfaces?
50% from adjacent floor finishes.
What is the recommended maximum riser height for stairs?
150 mm.
What is the minimum tread depth for stairs?
300 mm.
What should be installed at the top, bottom, and intermediate landings of stairs?
A tactile strip (warning tactile blocks) with a depth of 600 mm.
What is the minimum width for accessible staircases?
1.50 m to allow for two-way traffic.
What type of staircases are not allowed according to the accessibility guidelines?
Winding and spiral staircases.
What should be the minimum illumination level in corridors or on stairways?
100 lux.
What is the purpose of reflective finishes along accessible routes?
To assist individuals with hearing disabilities in perceiving their surroundings.
What is the minimum luminance contrast required for surfaces or features?
30% to aid individuals with visual disabilities.
What should be the finish of characters and backgrounds on signage?
Eggshell, matt, or other non-glare finishes with light characters on a dark background.
What is the width to height ratio for tactile letters and numbers on signages?
Between 3:5 and 1:1.
What is the stroke width to height ratio for tactile letters and numbers?
Between 1:5 and 1:10.
What should be the height of raised characters on signage?
At least 16 mm high, but no higher than 50 mm.
What is the minimum height for a raised edge on both sides of a staircase?
100 mm, except when a wall is in place.
What is the minimum landing depth for stairs?
Not less than 1500 mm and equivalent to the clear width of the stairs.
What should be provided at intervals of 3 meters or less on staircases?
Landings for rest.
What type of surfaces should be used to reduce visual distractions for individuals with cognitive disabilities?
Muted surfaces.
What is the recommended minimum illumination level for accessible routes?
100 lux.
What is the requirement for handrails on staircases?
They must extend horizontally at least 300 mm beyond the first and last step.
What is the minimum clear space required before and after a staircase?
At least 1.20 m in depth.
What should tactile maps include?
Raised and Braille characters, pictorial symbols, and verbal descriptions.
What should be the characteristics of surfaces along accessible routes?
They should be smooth or have trailing bars or handrails for individuals with visual disabilities.