spine cervical spine exam
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
what are the classifications of neck pain?
- neck pain with mobility deficits
- neck pain with movement coordination impairments
- neck pain with headaches
- neck pain with radiating pain
neck pain with mobility deficits - sxs/causes
- localized neck pain
- muscle strain, facet dysfunction, ligament strain, or disc-related issues
neck pain with movement coordination impairments - sxs/causes
- includes whiplash-associated disorder (WAD)
- sxs: neck and head pain, dizziness, tinnitus, headache
- may stem from articular, ligamentous, neurological, or vascular sources
neck pain with headaches
cervicogenic headaches
neck pain with radiating pain
- radicular sxs in neck and upper extremities
- caused by nerve root irritation from compression or tension
Neck Disability Index scoring
higher score = higher disability
pain characteristics of a visceral system
- non-mechanical pain pattern
- dull, boring, ache
- DEEP
- intermittent
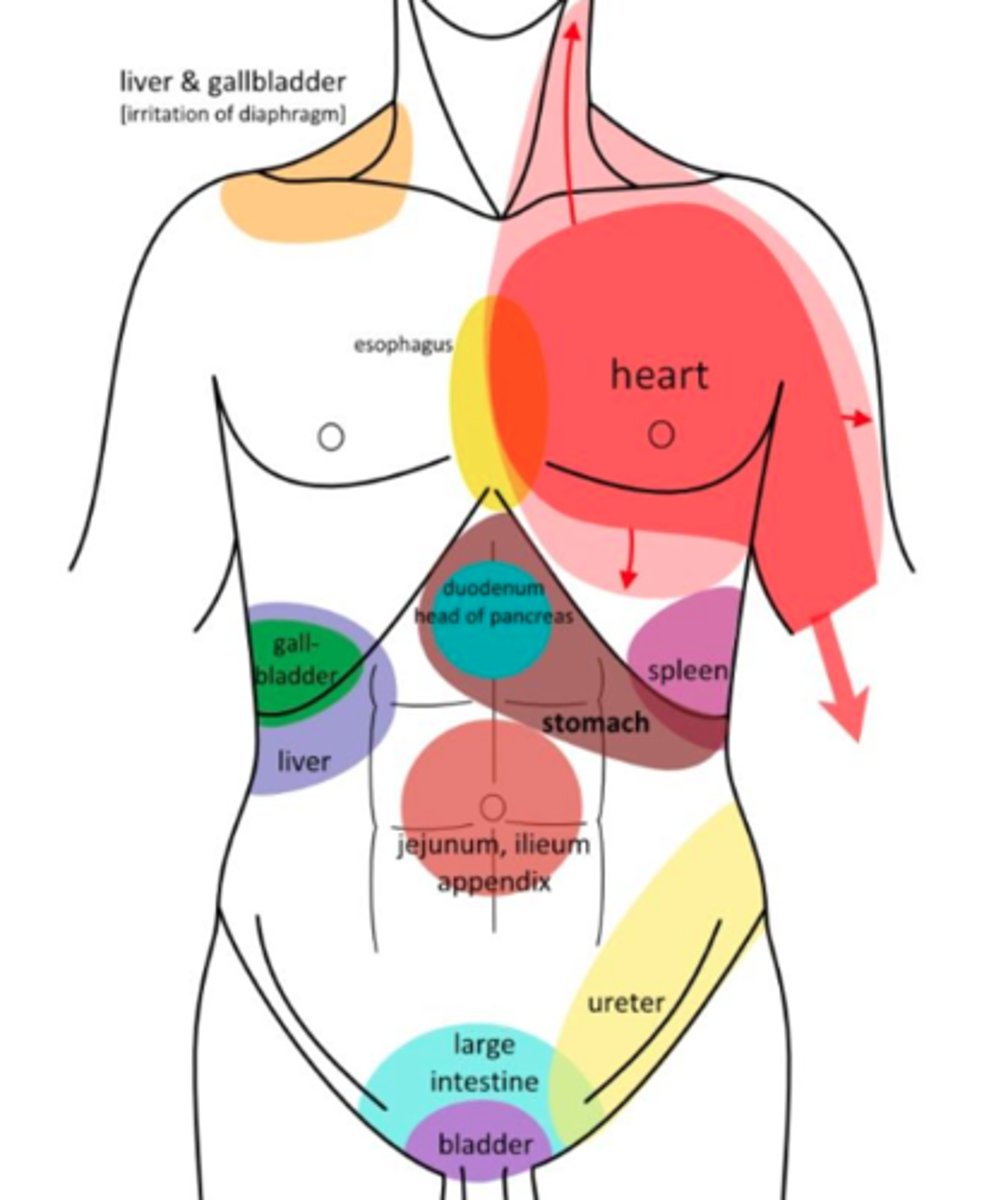
possible serious pathologies for c-spine
- central neurologic deficits (myelopathy)
- neurovascular compromise (VBI)
- fractures
- craniovertebral ligamentous instability
- malignancy
- systemic disease
Canadian C-Spine Rules High Risk Factors
1) age 65 or older
2) dangerous MOI
- fall from elevation >3 ft or 5 stairs
- axial load to the head
- high speed MVA 60-65mph
- motorized vehicle accident
- bike collision
3) paresthesia in extremities
*If yes to any of these they need an x-ray
Canadian C-spine Rules Low-Risk Factors
- Simple rear-ended MVA
- Sitting in ED
- Ambulatory at any time
- Delayed onset of neck pain
- Absence of midline tenderness
IF YES, & CAN ACTIVELY ROTATE NECK 45 deg LEFT & RIGHT - NO RADIOGRAPHY
key sxs/red flags of neurlogical compromise
- lower limb sxs triggered by neck movements
- ataxic gait (difficulty walking or poor balance)
- bowel or bladder dysfunction
- sympathetic sxs (blurred vision, sweating, tinnitus)
Signs of cervical myelopathy
- multi-segmental parathesia
- UMN signs
*spasticity
*hyperreflexia
*visual disturbances
*balance issues
*ataxia
*sudden changes in bowel/bladder function
signs to do a CN exam
- head, neck, facial pain (esp hx or trauma)
- altered movement patterns
- changes in muscle tone
- balance/coordination deficits
- muscle wasting
- speech abnormalities
- difficulty swallowing
- changes in senses
- cognitive/behavioral changes
Wallenberg Syndrome
*infarct PICA
- vertigo
- nausea
- dysphasia
- crossed sensory deficits
- includes Horner's syndrome
Horner Syndrome
- sympathetic nerve pathway brainstem --> eye
- small pupils, ptosis, anhidrosis
signs and sxs of VBI
(5 D's And 3 N's)
- dizziness
- drop attacks (fall w/o loss of consciousness)
- diplopia (double vision)
- dysarthria (hard time getting words out)
- dysphagia (swallowing problems)
- ataxic gait (clumsy when walking)
- nausea
- numbness (bilateral, quadrilateral, facial, peri oral)
- nystagumus (room is spinning)
most common nonpenetrating MOI for vertebral artery
hyperextension of the neck, with or without rotation, or cervical side flexion
in older adults what position should you avoid to not cut blood flow to VA?
rotation and extension (20 deg each)
intial movement testing for VBI
seated neck torsion/stool test
(more subtle) exam findings/sxs of VBI
- significant delay in verbal responses to orientation questions with some inconsistency/delay of answers
- changes in pupil size
- nystagmus
Hautant's Test
- pt sitting with shoulders flexed to 90 and forearm supinated
- pt extends and rotates head/neck and closes eyes 10-30 seconds
- (+) = loss of UE position, onset of sxs (5DA3N)
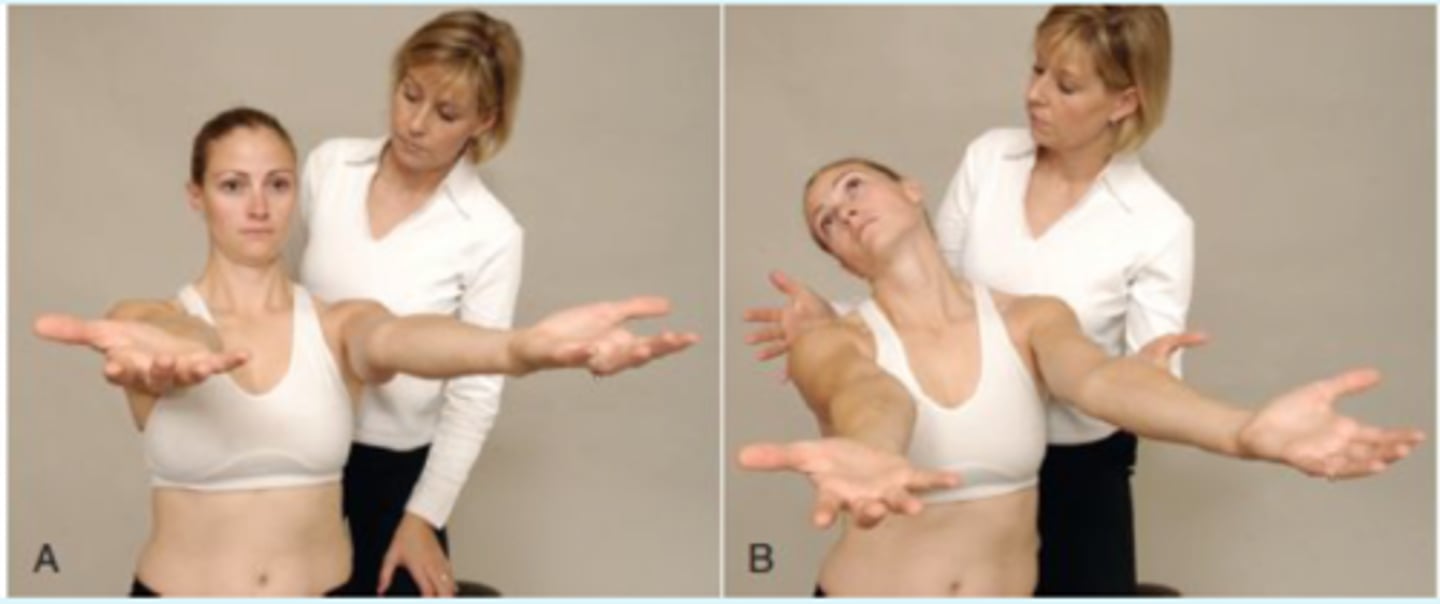
Neck Torsion/Stool Test
(VA vs Vertigo) *done only if active rotation reproduces sxs
- pt sitting on stool
- PT has hands on either side of pts head
- head is held stable while pt rotates his or her body to the L and R in sitting
- (+) = signs of VA compromise with both cervical rotation and body rotation
causes of upper cervical instability
- trauma (especially hyperflexion)
- inflammatory conditions (RA, psoriatic arthritis, ankylosing spondylitis)
- corticosteroid use (weaknes dens and transverse lig)
- pediatric conditions (recurrent upper respiratory infections, Grisel syndrome)
- congenital conditions (down syndrome)
- osteoporsis
signs/sxs of cervical instability
- lump in the throat
- bilateral/quadrilateral extremity sxs
- lip parathesia
- nausea or vomiting
- severe headache and muscle spasm
- dizziness
upper cervical stability tests
(SCAAT)
- sharp-purser test
- cranial atlas test
- alar ligament
- atlas axis shear
- tectorial membrane
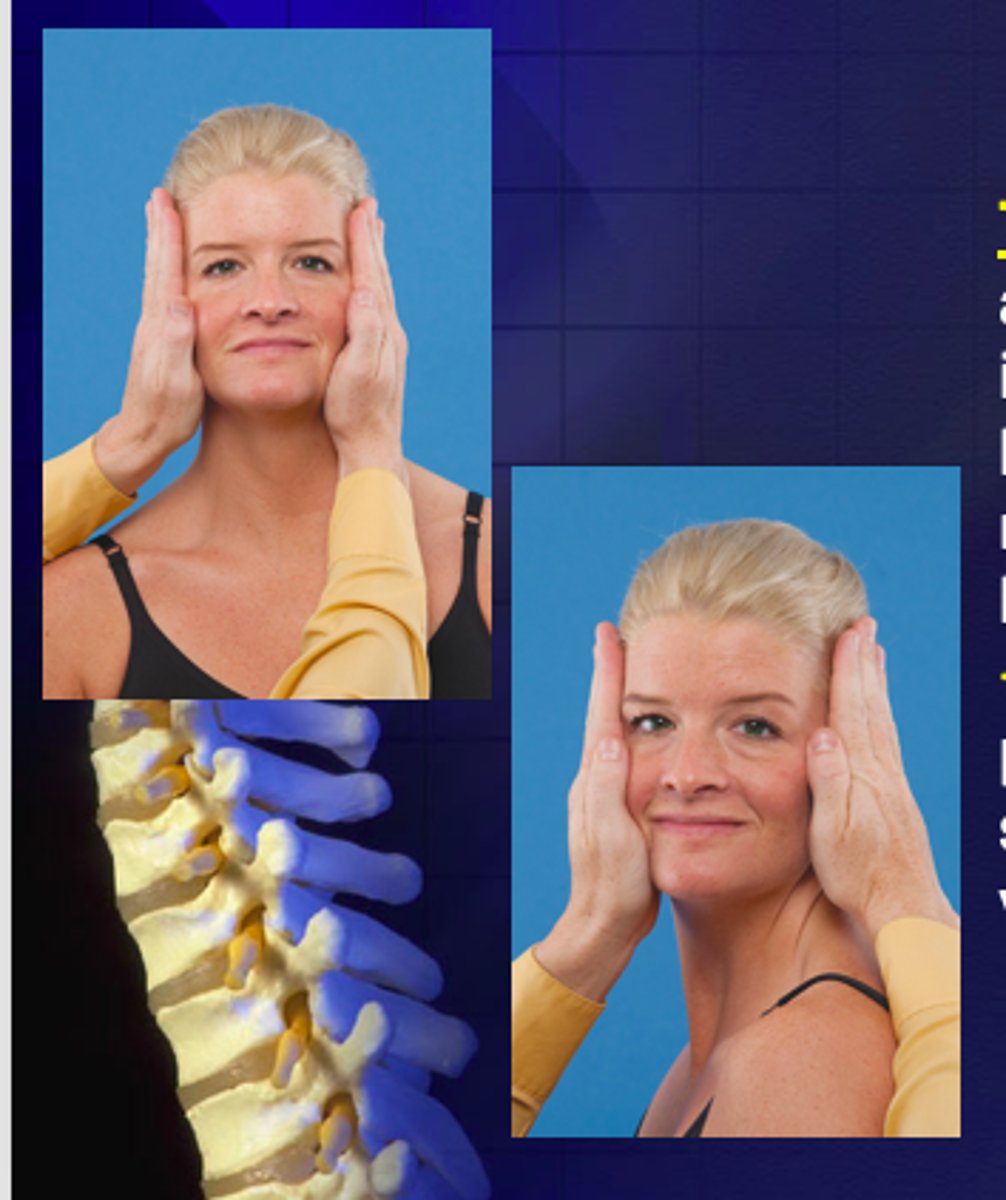
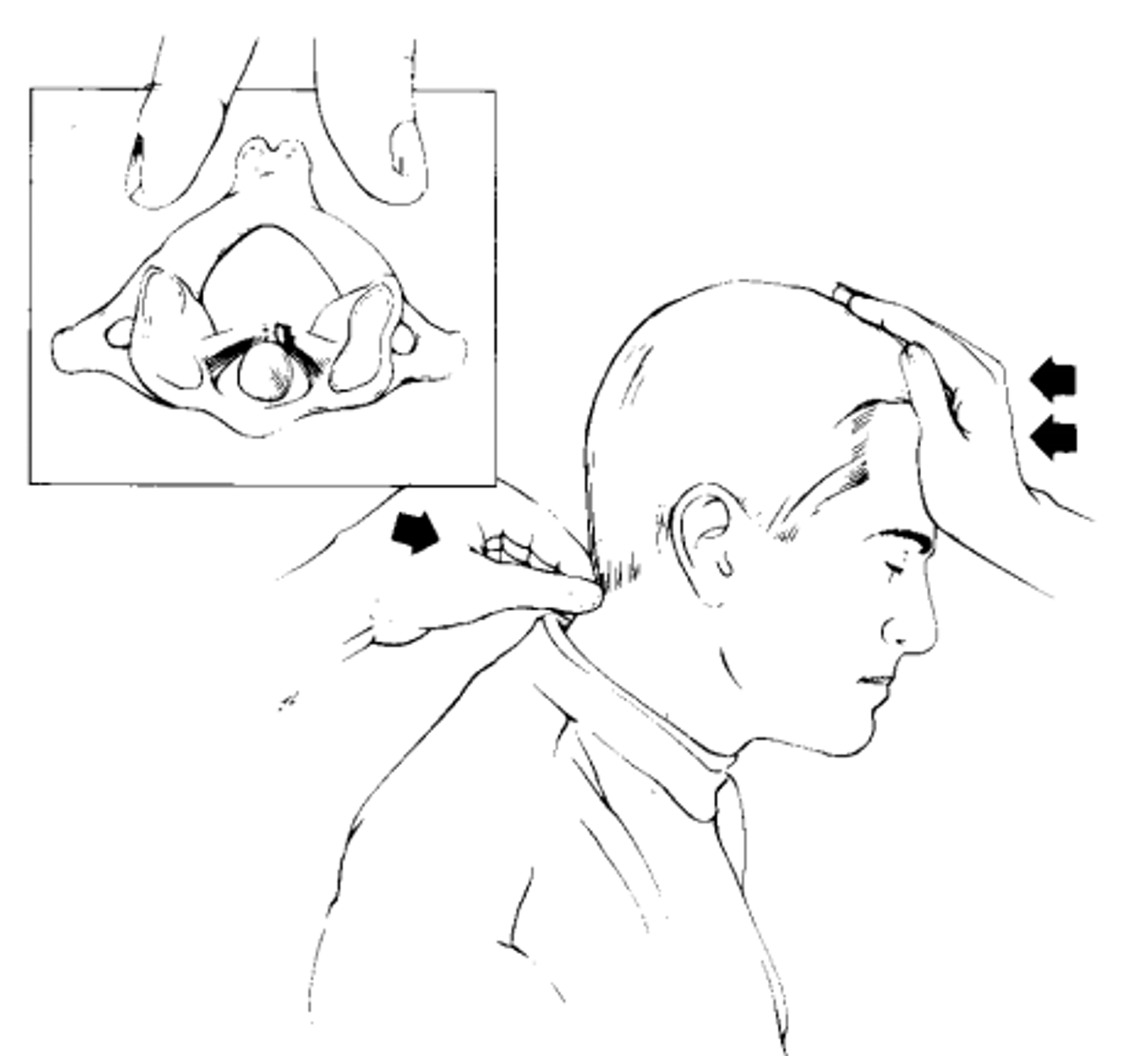
Sharp-purser test
*sagittal stability of AA
- pt seated, short neck flexion
- pt reports any sxs or clunking sensation
- if symptomatic, clinician stabilizes C2 posteriorly and applies posterior force to forehead
- (+) = reduction or resoution of sxs with posterior force
what does a positive sharp-purser test suggest
- excessive atlas translation
- terminate exam immediately
- issue cervical collar
- refer to physician immediately
Cranial Atlas Lift
- pt supine with head and neck in neutral
- PT has both hands supporting occiput with the fingers over the atlas
- occiput and atlas are translated anteriorly without flexion or extension and held for 15 seconds
- (+) = end feel is soft or in presence of spasm, nausea, vertigo, paresthesia, nystagmus, or esophageal pressure
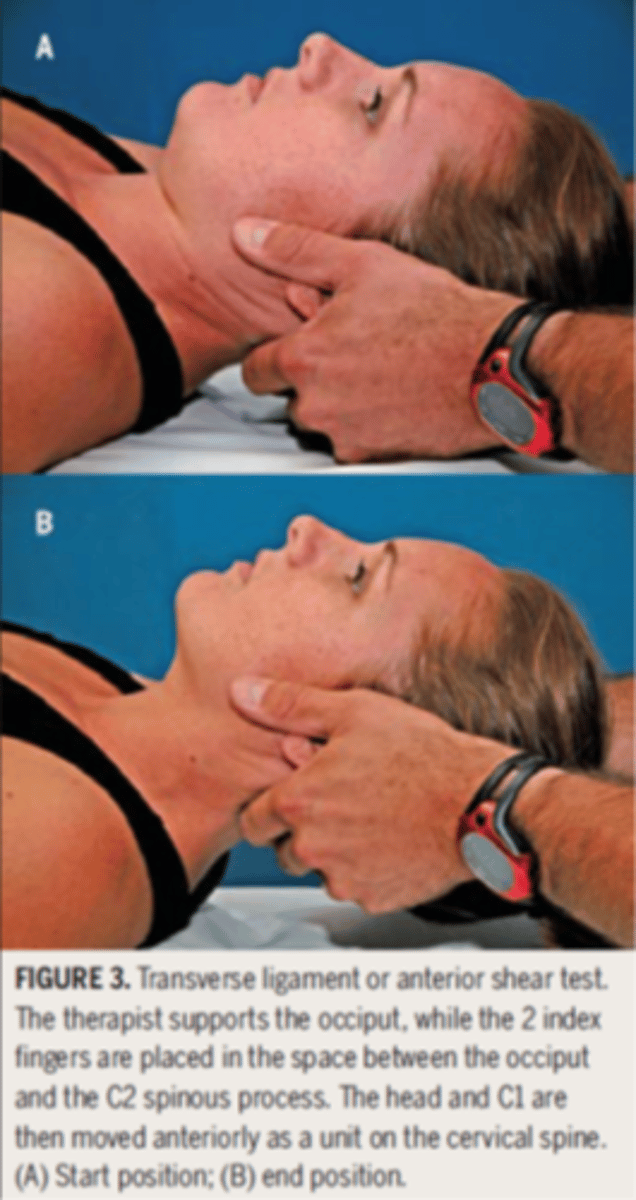
Alar ligament test
- pt supine, neutral neck
- PT supports the occiput with both hands while the index fingers palpate the SP of the axis
- occiput is side bent slightly to each side
- (+) = delay in movement of SP of the axis, which rotates ipsilateral to the direction of side bending
(if positive perform in flexion and extension)
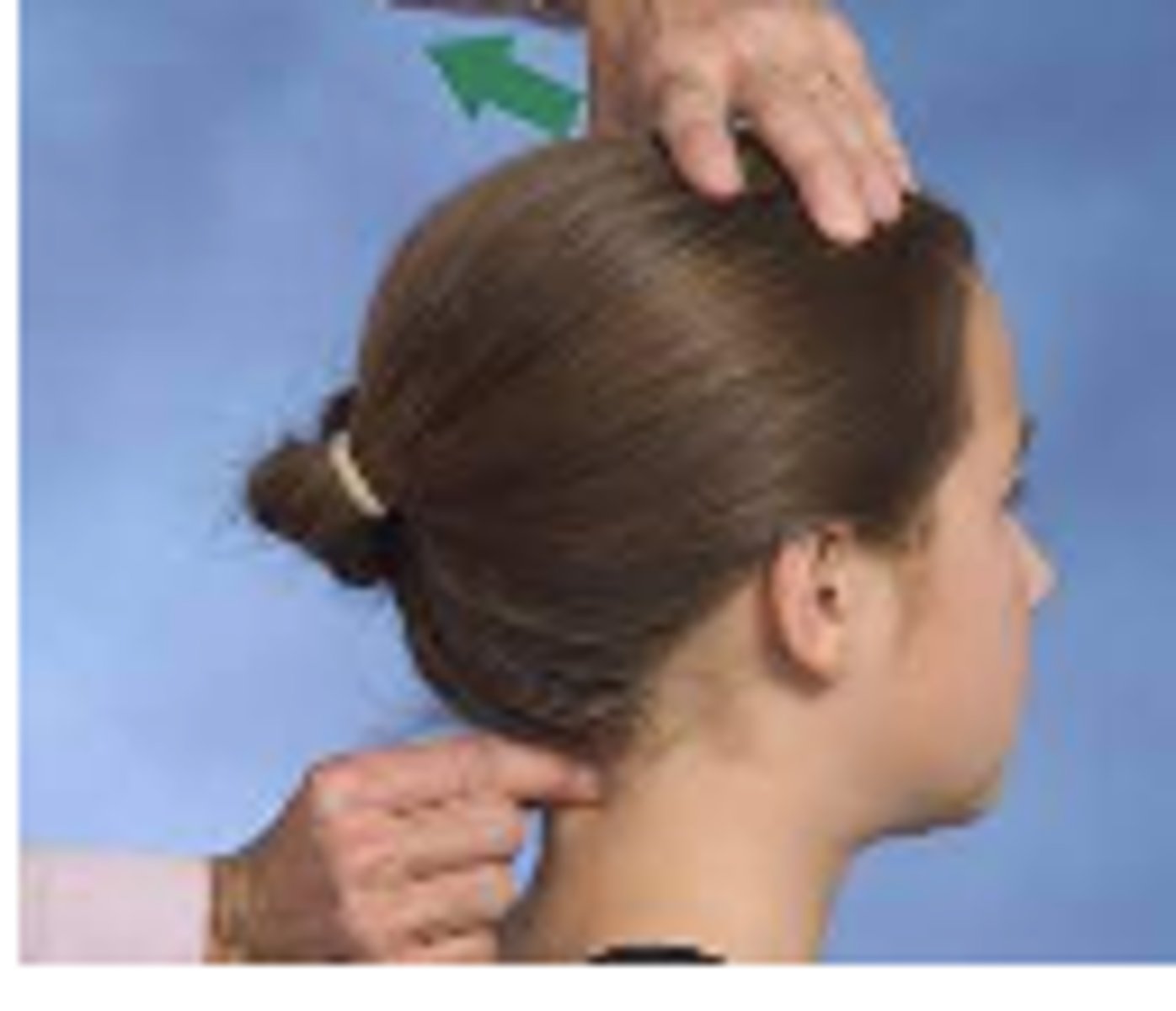

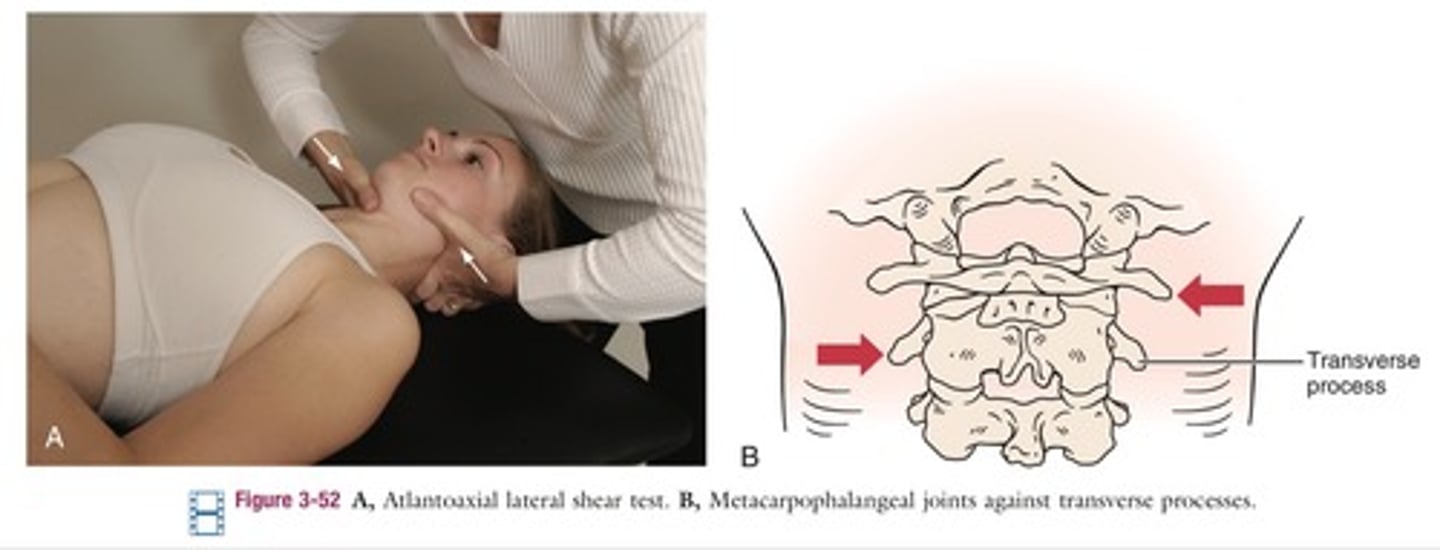
Atlas Axis Shear
*assess transverse stability between C1&C2
- pt supine
- PT places the soft aspect of each second metacarpal head on the opposite TP and laminae of C1&C2
- palms face each other
- stabilize C1 & attempt to translate C2 transversely
- change palpating/stabilizing hand and repeat
- expected result = no movement should be felt in a stable joint
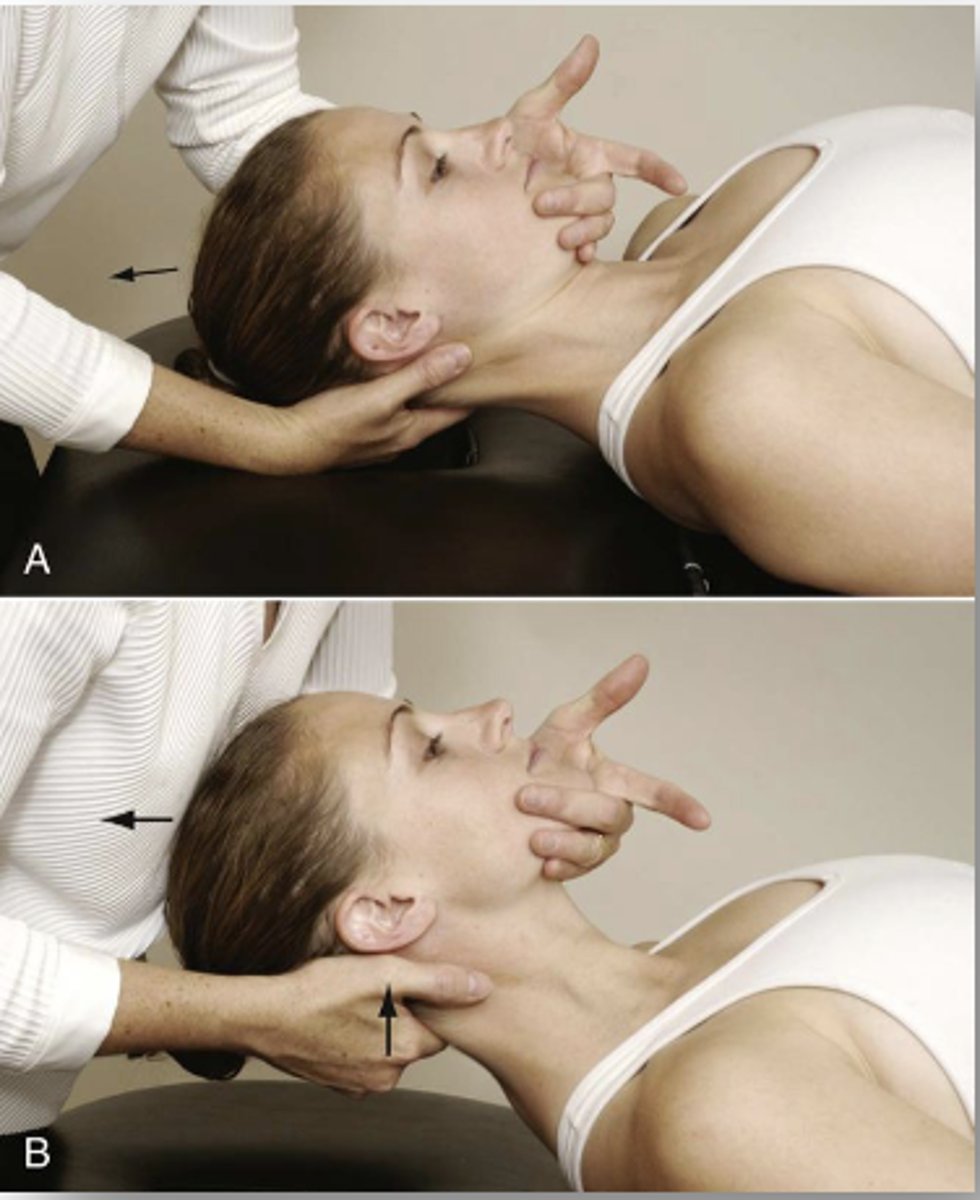
Tectorial Membrane Test
- step 1: apply general traction to the entire cervical region
- step 2: if negative, apply traction with CV flexion
- step 3: if negative, stabilize C2 with CV flexion, apply traction
- (+) = soft end feel, reproduction of sxs, apprehension
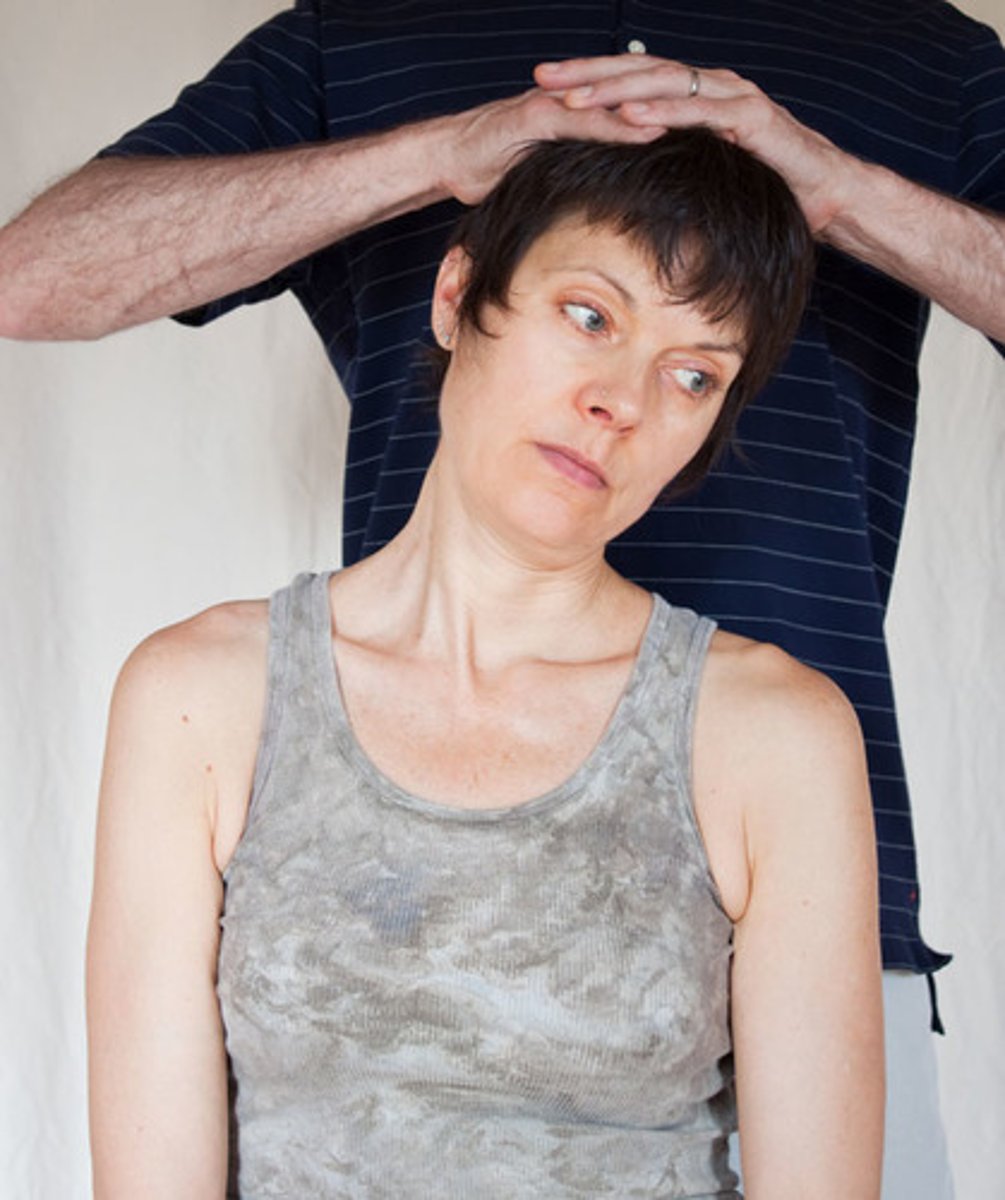
quadrant testing - spurling A and B
*test for cervical radiculopathy
- pt sitting
- passively position neck into ipsilateral side bending & apply gentle compression
- passively position neck into extension, ispi SB, and ipsi rotation & apply gentle compression
- (+) = reproduction of sxs

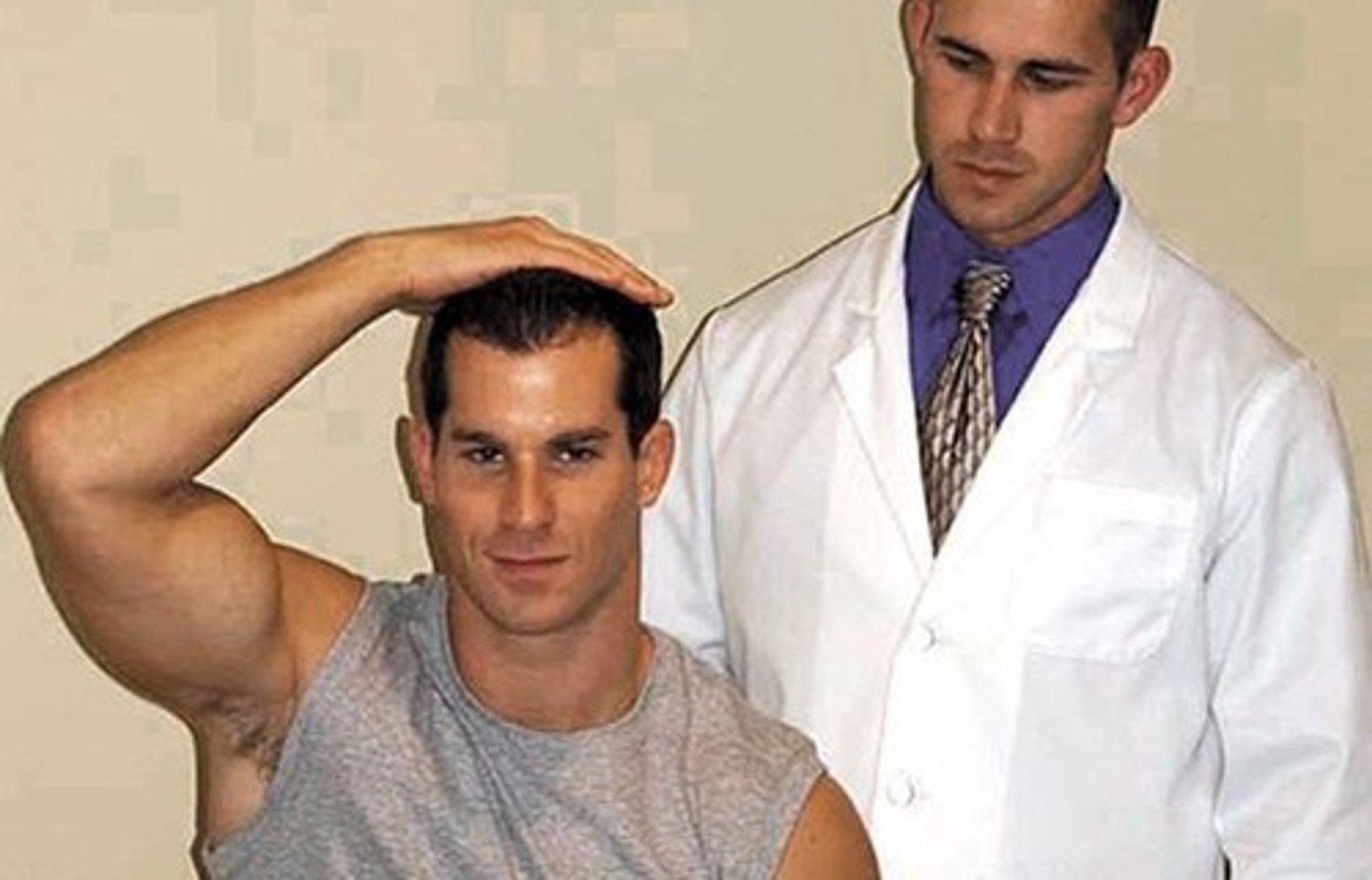
shoulder abduction test - bakody sign
*test for cervical radicular sxs
- pt elevates the arm through abduction, placing hand or forearm on top of the head
- sxs relief: herniated disc/nerve root compression
- sxs worsen: increased pressure in the interscalene triangle (possible TOS)

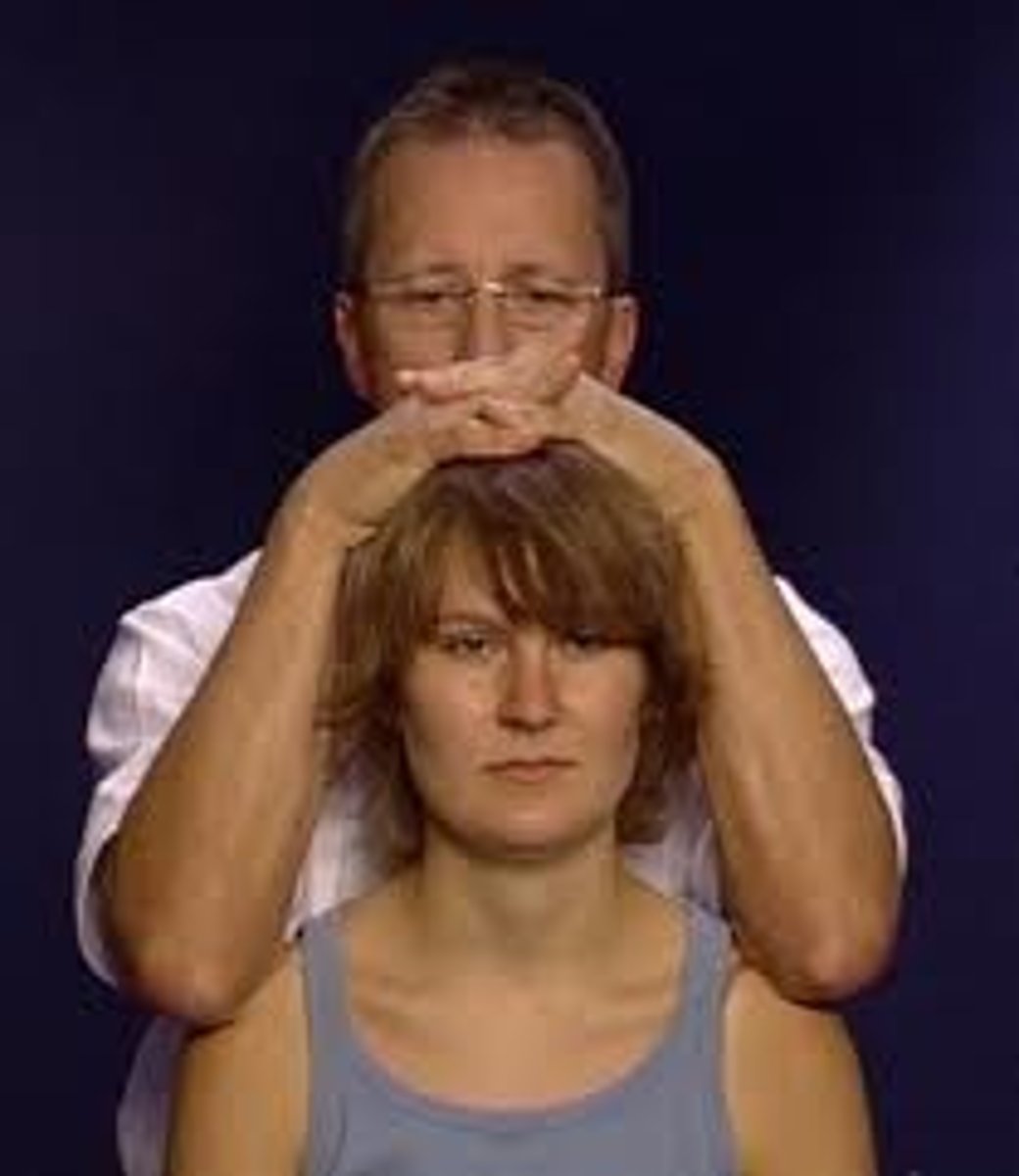
cervical distraction and compress
ion test
- pt seated or supine
- sxs relief with traction: nerve root compression or facet joint unloading
- sxs reproduction with compression: disc, facet joint irritation, foraminal narrowing, fracture

median nerve ULTT
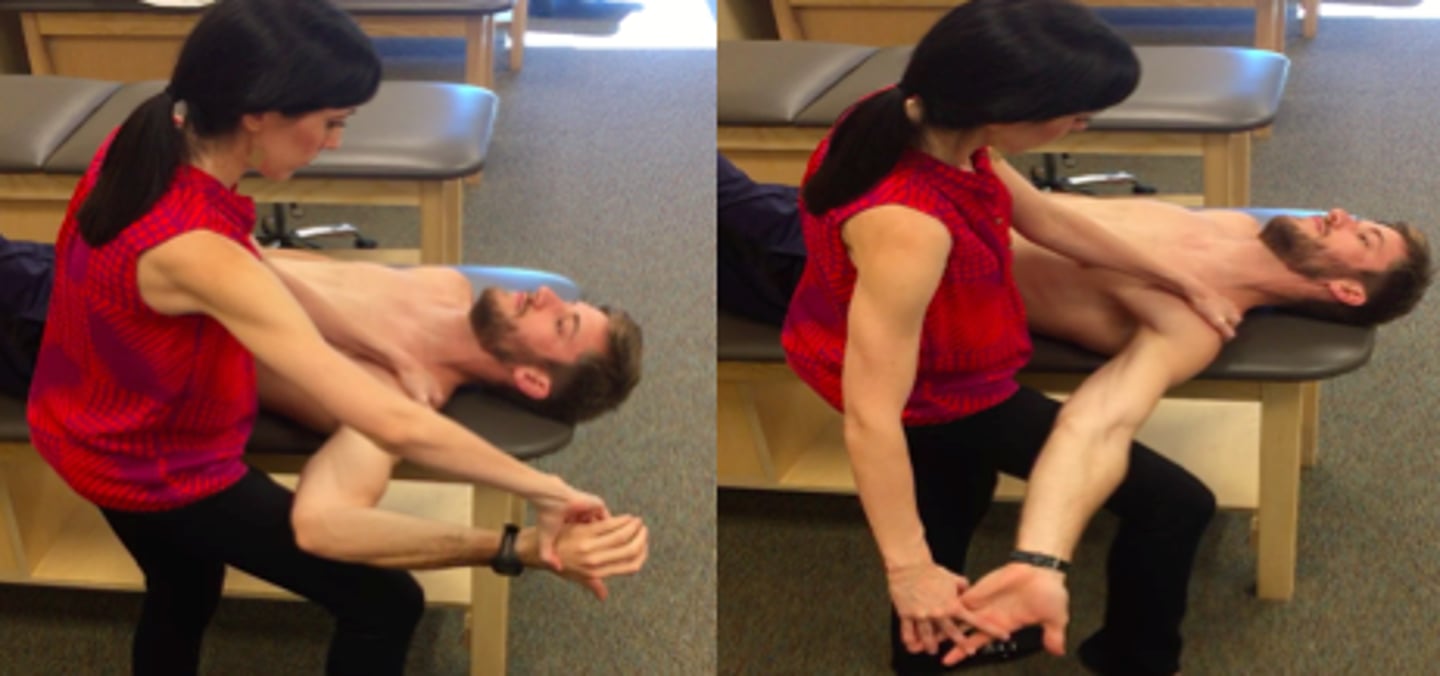
ulnar nerve ULTT
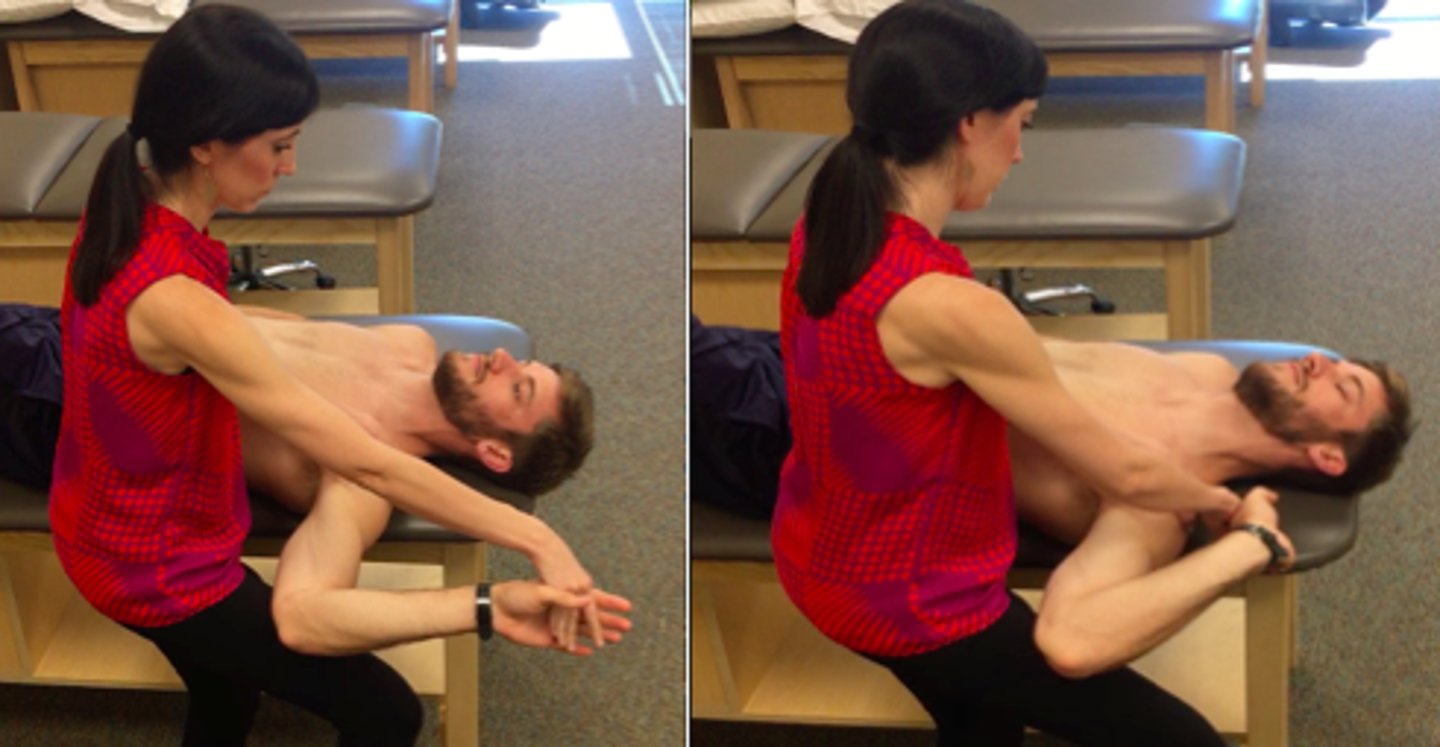
radial nerve ULTT