9.4 Translocation
1/9
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
10 Terms
Translocation
Energy-Requiring (active) process transporting assimilates, particularly sucrose between the sources (e.g. leaves) and sinks (e.g. roots, meristem)
Sources
Green leaves and stems
Storage organs (tubers, tap roots)
Unload their stores at beginning of growth period
Food stores in seeds when they germinate
Sinks
Roots that are growing and/or actively absorbing mineral ions
Meristems that are actively dividing
Any parts of the plan that are laying down food stores e.g. developing seeds, fruits, or storage organs
Why is sucrose the main carb transported rather than glucose?
Not used in metabolism as readily as glucose so is therefore less likely to be metabolized during transport process
Is also more soluble
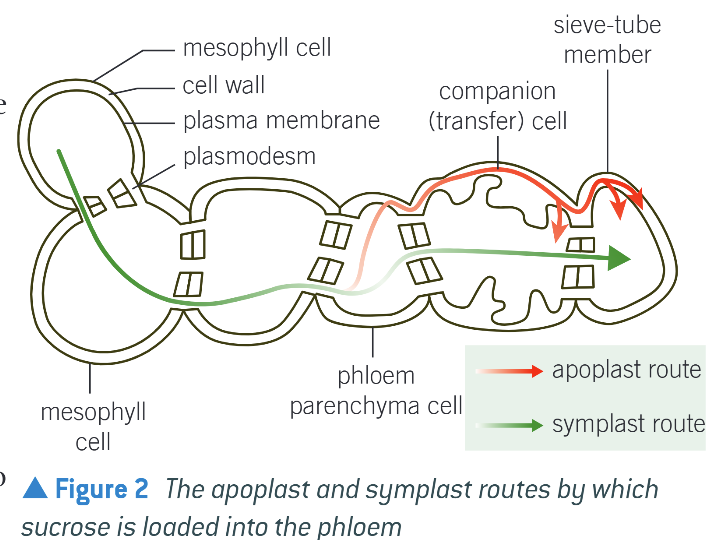
Phloem loading - Symplast route (conc. of sucrose low)
Passive route (uses diffusion)
Sucrose moves thru plasmodesmata down conc. g.
Sucrose ends up in sieve elements & water follows by osmosis
Creates a pressure of water that moves sucrose thru phloem by mass flow
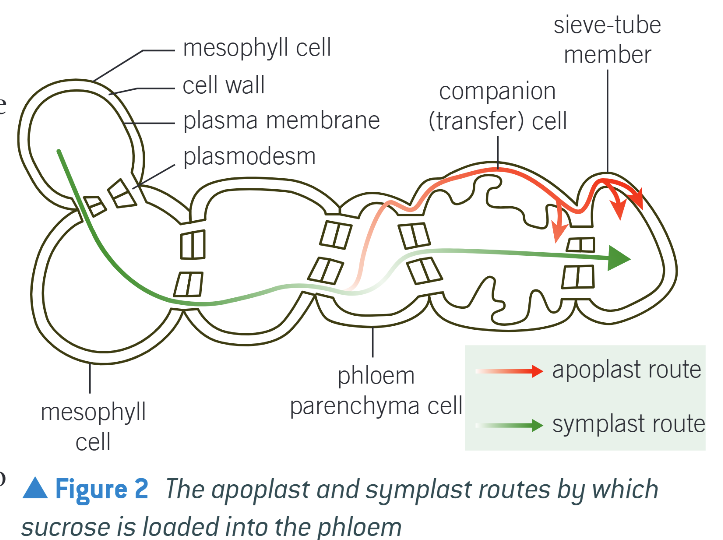
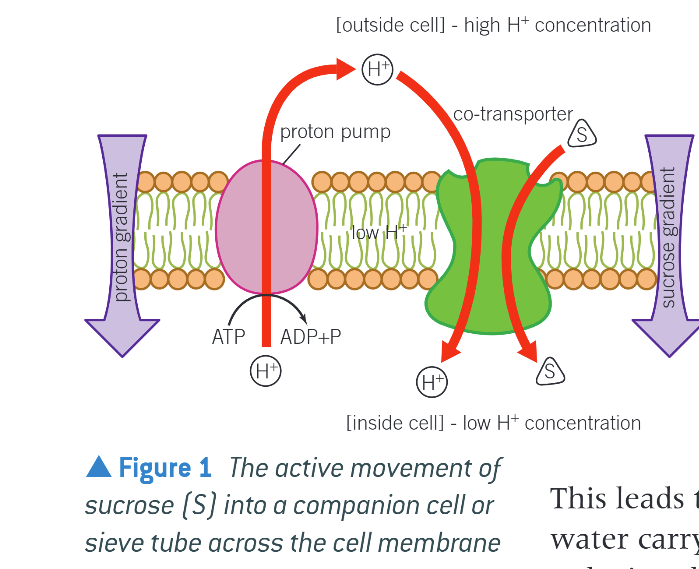
Phloem loading - Apoplast Route
In companion cells, sucrose moved into cytoplasm across CSM in an active process
Proton Pump actively pumps H+ out of companion cell into surrounding tissue using ATP
H+ move down conc. gradient & return to companion cell w. sucrose via a co-transporter protein
Sucrose diffuses into sieve tube elements
Adaptations of companion cells
Many infoldings in cell membranes, gives increased SA for active transport of sucrose into cell cytoplasm
Many mitochondria, supplies ATP needed for transport pumps
What happens as a result of built up sucrose in companion cell & sieve tube element?
Water moves in by osmosis
Build up of turgor pressure
Water carrying assimilates moves into tubes of sieve elements
Reduces pressure in companion cells
Water moves up or down plant by mass flow to areas of lower pressure (sinks)