Unit 4: Genetics and Inheritance
1/11
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
12 Terms
mitosis- interphase
G1 phase is cell growth
S phase is DNA synthesis
G2 phase is further cell growth
interrupted by mitosis and cytokinesis
cells that do not reproduce remain in G0
these phases are controlled by cyclins
mitosis- prophase
chromosomes visible, unordered
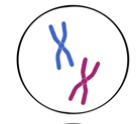
mitosis- metaphase
chromosomes separating
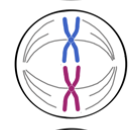
mitosis- anaphase
chromosomes line up and are drawn to poles by spindle fibres
mitosis- telophase
chromosomes grouped in two at poles of cell
mitosis- cytokinesis
cell splits in two by closing off membrane down cleavage, chromosomes less distinct as they uncoil, returns to interphae
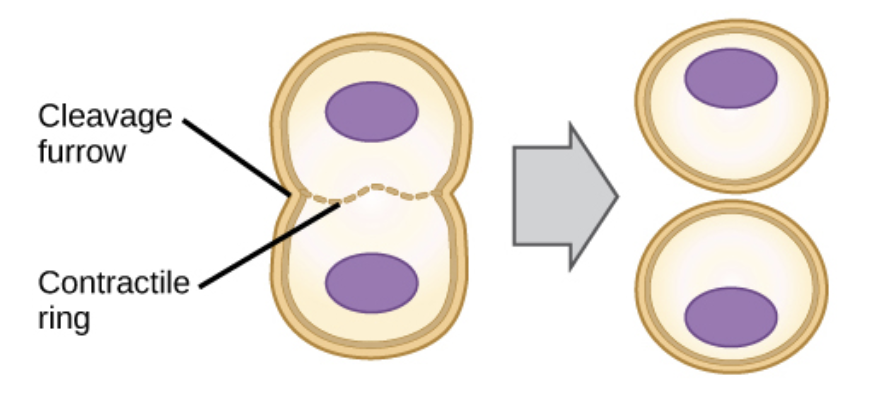
cytokinesis in animal cell
ends not touching
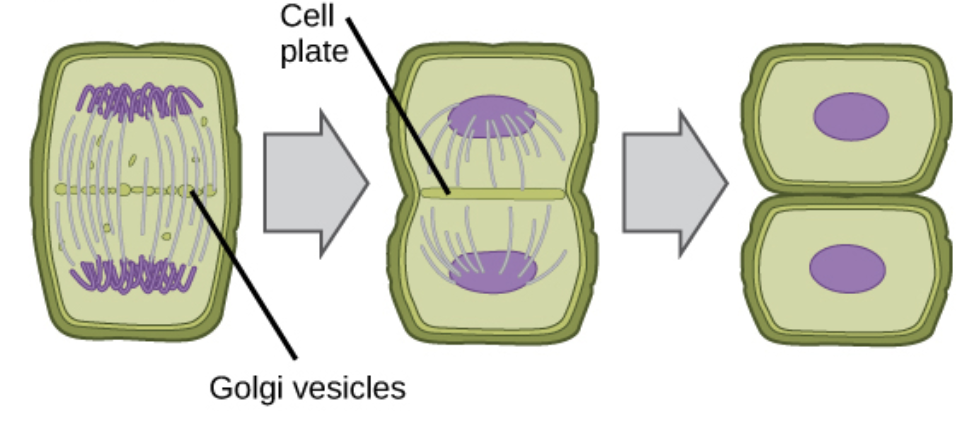
cytokinesis in plant cell
ends touching
cyclins
proteins that contribute to the regulation of the cell cycle. They reach a threshold concentration and prevent reproduction of cell until needed.
C gradually increases and decreases across the cell cycle
E triggers G1 → S
A triggers S → G2
B triggers G2 → mitosis
Cyclin Dependent Kinases (CDKs)
phosphorylate other proteins, activating them to carry out specific tasks
Apoptosis- if a cell fails a checkpoint during Interphase or Mitosis, it self destructs
substrate — (kinases) → substrate P
phosphofructokinase (enzyme)
histone proteins
basic proteins: their positive charges allow them to associate with DNA, which is negatively charged. Some function as spools for the thread-like DNA to wrap around.
tumours