Unit 3: AOS 1 error log
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
39 Terms
Endonucleases are _ _?
restriction enzymes
What do word do you use call smaller and bigger fragments of DNA?
shorter and longer
What could you mention when analysing a gel electrophoresis?
mention fragment length,
What effects the rate of DNA fragment movement through agarose gel?
concentration/viscosity of agarose gel, size/length of DNA fragments, voltage/power used
What safety precautions should be followed when using gel electrophoresis?
ensure the gel electrophoresis is turned off to prevent electrocution, wear safety glasses to protect the eye, dispose of materials correctly, wear gloves to prevent contamination by DNA or the chemicals being used
What are some examples of disorders or diseases that can be detected by genetic screening?
down syndrome, sickle cell anaemia, albinism, PKU, cystic fibrosis
What enzyme synthesises new DNA strands in PCR?
Taq polymerase because it can withstand the temps
How should you write an ethical implication in a question?
ask it in question form as it is clearer
How to think of a social implication in question?
check whether your answer relates to society and impacts more than one or two individuals
What is a recombinant plasmid?
a plasmid with foreign DNA
Advantages for an organism to be able to turn genes on or off?
control biochemical pathways within the cell, only produce products when required by the cell, different cells require different proteins (e.g. eye cell does not require hormones), conserve ATP for other cellular processes
Do both attenuation and repression occur when trp levels are low?
repression doesn’t happen when trp are low, so they have in common that they happen when they are high. so in a question where it says to compare, only mention the high parts
What enzyme inserts genes in a plasmid?
DNA ligase
How can you determine if two individuals could be the parents of a child using STR data?
Each person inherits one STR allele from each parent at every STR marker.
For each STR:
The child’s two numbers (alleles) must match one number from each parent.
Repeat this check for all STRs provided.
If every STR in the child can be explained by combining one allele from each parent, they could be the biological parents.
Why would concentrations of different types of proteins change?
Enzyme: If there is a change in substrate concentration, then more or less enzyme may be produced to conserve ATP
OR
Structural protein: repair or synthesis of organelles if organelles are damaged due to increased or decreased temperature
OR
Regulatory/repressor protein: more or less repressor protein is required to inhibit or promote a reaction when there is a change in substrate availability
OR
Transcription factors: more or less is required for transcription if environmental conditions result in increased or decreased need for protein synthesis.
What does a justify question require you to say?
say why my answer is correct AND incorrect
potential benefits of using the CRISPR technique to edit
genes in the future

improve IVF pregnancy rates
eliminate deadly genetic diseases before people are born
can help treat genetic diseases by fixing mutated genes
Potential concerns of using CRISPR technique to edit genes in the future
making changes to human DNA could create an error to the human gene pool that introduces disease that could be passed on to future generations
making incorrect DNA edits
creating genetically modified babies for desired traits
using viable embryos for research which are then destroyed
Explain the role played by primers and why you need two
primers will bind to a complementary DNA sequence on the target gene
it allows taq polymerase to bind to the target gene and amplify the target DNA
as one strand runs 3’ to 5’ and the other runs 5’ to 3’, you need two primers to amplify both DNA strands as the DNA sequences will be different at each end.
Describe how restriction enzymes such as BamHI are used to help insert a gene coding for a human protein into this plasmid.
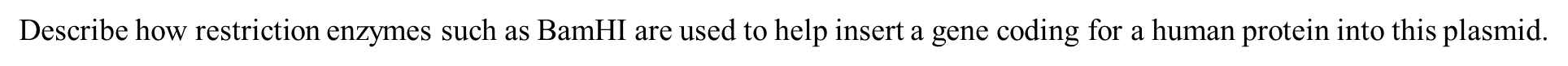
the same restriction enzyme (BAM H1 in this case) cuts the gene of intereest and plasmid at a specific sequence of base pairs. this creates sticky ends, allowing the gene to be inserted to the plasmid according to complementary base pairing rules
Explain how scientists use antibiotics to identify which of the bacterial cells have been successfully transformed with plasmids carrying the human gene
grow the bacteria on agar containing ampicillin
bacteria that grow on agar containing ampicillin have taken up the plasmid with the human gene Amp^r
bacteria that have not taken up the plasmid are killed by ampicillin
What does "gene structure" refer to in the context of comparing genes like RbcL and RbcS?
the features of a gene at the DNA level, including the presence of:
promoter (slight different in bp length) regions so RNA polymerase can bind
operator regions(where repressor protein binds)
introns and exons (in eukaryotic genes)(difference between nucelotide sequence size andd mRNA sequence size, that means introns are cut out)
terminator sequences (difference between nucleotide sequence and mRNA sequence)
It describes how a gene is organised, rather than the amino acid sequence or protein size it codes for. Slight difference in nucleotide sequence and mRNA sequence
What does DNA ligase do?
it joins phophodiester bonds between the sugar and phosphate of nucleotides/between the gene of interest and the original gene
what makes an organism genetically modified?
the DNA has bee altered using gene technology
different ways you can improve crops
improve the yield to produce more
additional nutritional value
herbicide/pesticide resistance
drought tolerance
disease resistance
Using a consequence based approach, discuss whether the use of genetically modified or transgenic plants would be considered as bioethical.
The action that leads to the best overall outcome to the most people (minimising negative effects) regardless of whether the act is right or wrong
If GM technology is used it is possible to create crops that could help populations that are vitamin deficient/produce high yields/grow better in their environment
if GM technology is not used then farmers will have to use selective breeding which could take a long amount of time to see the same phenotype
Therefore using gene technology is ethical
what does restriction enzyme do
cuts gene of interest and plasmid at specific restriction site
reminder: be specific for the question
ok
what is beneficience?
Aiming to improve others lives through charity, generosity and kindness (any two of these).
what is non-maleficence?
avoiding actions that cause harm
what is a transgenic organism?
GM organism that has received DNA from another species
how to answer explain question?
blablabla SO blabla
referencing molecular level of the GM crop
new gene and therefore new DNA
gene is transcribed and translated
therefore a new protein is expressed
how to answer question referring to consequence based approach
outcomes of option A and option B are compared to determine which will have the best overall benefits regardless of what the action is
if they do option A these postive benefits will happen
if they do option B farmers will have to rely on what is normal so these bad things may occur/not occur
the most ethical approach would be the one that provides the most benefits (say how)
Describe the possible changes the scientists can make to a gene, when using CRISPR-Cas9 technology.
insert a nucleotide
delete a gene
insert stop codon to create a shortened protein
Discuss possible known consequences of editing a genome
· Could cause a mutation in the gene and result in an altered/non functional protein
· Off target mutations (causing a mutation somewhere else in the genome)
· insertional oncogenesis to viral vector
· Immunological reaction to vector delivering Cas9
· Apoptosis of target cell occurs
what does PCR stand for?
polymerase chain reaction
why does denaturation need to be 95 degrees?
so that the hydrogen bonds between nucleotides can break, allowing the DNA strand to separate
What is the difference between a gene of interest and a target gene?
gene of interest: selected for study, isolation, or modification, used in genetic engineering or transformation.
target gene: the specific gene sequence that a technique like PCR or CRISPR is designed to act on.