Traumatic Brain Injury
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
35 Terms
what is the most common cause of death and disability among young people?
TBI
who are more likely to sustain a TBI?
males
acquired brain injury
includes all brain injuries required AFTER birth; can be internal or external factors
traumatic brain injury examples
concussion, skull fx, fall, MVA, bullet
nontraumatic brain injury examples
stroke, tumor, disease, lack of oxygen
what are the leading causes of TBI?
MVA, violent acts, falls
other common causes include sporting injuries or military blasts
traumatic brain injury
alteration in brain function caused by an external force
closed TBI
caused by an external force that produces movement of brain within the skull, but is nonpenetrating
open TBI
foreign object entered the skull to cause damage; penetrating injury
how long is the recovery process for an acquired brain injury?
lifelong
a patient lost consciousness for 15 minutes and had posttraumatic amnesia for less than 6 hours. what classification of TBI did they sustain?
mild
a patient with a mild TBI would have a Glasgow scale of what?
13-15
a patient sustained a blow to the head and was unconscious for 5 hours. they woke up showing signs of posttraumatic amnesia and disorientation. what would their Glasgow scale be?
9-12
a severe TBI is characterized by what?
loss of consciousness for over 24 hours, posttraumatic amnesia for more than 7 days, disorientation and confusion
what classification of TBI is a Glasgow scale of 3-8?
severe TBI
what are the three categories of the Glasgow coma scale?
eye opening, motor response, verbal response
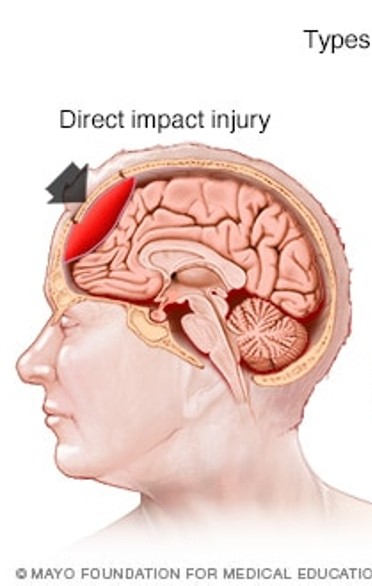
focal brain injury
direct blow to the head after contact with an external object or fall, penetration injury from weapon, collision of brain with inner parts of the skull
diffuse brain injury
happens when brain rapidly shifts inside the skull— injury occurs during acceleration/deceleration
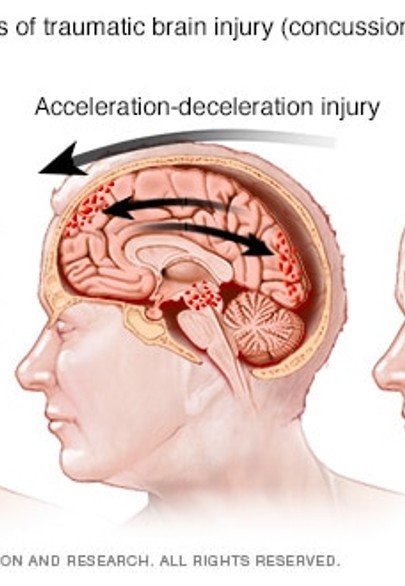
diffuse axonal injury
injury where brain accelerates, decelerates, and rotates inside the skull, causing cerebrum to rotate around the brain during impact. typically causes injury to many parts of the brain
a patient presents with ataxia, diplopia, and dysarthria. what type of brain injury did they sustain?
diffuse
diffuse injuries often damage what part of the brain?
brainstem and cerebellar pathways
primary phase of TBI
results in damage to axons and blood vessels
secondary phase of TBI
axonal swelling, loss of axonal transport, altered neurotransmission, loss of neuronal function, apoptosis, necrosis and neuronal demyelination
concussions
often referred to as mild TBI, but can be moderate-severe; characterized by immediate and transient alteration in brain function including mental status and level of consciousness
timmy roo was playing playing rugby and bashed his head with another players. timmy roo did not lose consciousness and does not have any external signs of head trauma. he couldn’t remember what happened immediately before the blow and was confused upon sitting up on the field. since then, he has had trouble concentrating and has had changes in balance and coordination. what would be timmy roo’s predicted diagnosis?
concussion
a patient is in the acute phase of TBI survivorship. what is the goal of this phase?
minimize brain swelling
in what phase of TBI survivorship does the patient receive education?
intensive phase
survival phase
recovery phase
recovery phase
coma
inability to open eyes in response to any stimuli and the absence of the sleep-wake cycle on an EEG reading
which patient would likely leave the individual in a coma?
diffuse brain injury
diffuse axonal injury
concussion
blast brain injury
diffuse axonal injury
vegetative state
complete loss of ability to interact with the environment. eyes may be open but there is no evidence of consciousness
minimally responsive
inconsistent abilities to purposely interact with their environment depending on stimuli presented
a patient recovering from a coma who can’t create new memories is in what phase of coma recovery?
phase 1
what is phase 2 of coma recovery characterized by?
cognitive impairment becomes more evident, but confusion clears
a coma emerging patient is uncharacteristically aggressive and agitated. what is the role of the care team during this phase?
provide patient education
create a safe environment
prepare patient for discharge
create safe environment
what is often used in conjunction with the Glasgow coma scale?
Ranchos los Amigos scale