unit 2: parasitism
1/76
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
77 Terms
the negative relationship between 2 different species: the host and the parasite
"heterotypic, negative, temporal or permanent, external or internal association, among a species, the parasite (usually smaller and with a lower zoological level) and the host (bigger and higher level)"
define parasitism
parasite
which is smaller, the host or the parasite?
parasite
which is less evolved/developed, the host or the parasite?
host
which suffers, the host or the parasite?
1. definitive host (DH)/ final host (FH)
2. intermediate host (IH)
what are the 2 types of hosts regarding the stage of the parasite that it harbors?
the host that harbors the adult stage of the parasite, with sexual production
what is the definitive/final host?
definitive/final host
what is the name for the host that harbors the adult, sexual stage of the parasite?
the host that harbors the immature stages of the parasite with asexual reproduction
what is an intermediate host?
intermediate host
which type of host harbors the immature/asexual parasite?
the host where the parasite species was described for the first time
what is the "type" host?
the main, most specific host for the parasites that affect a broad host range
what is the "principal" host?
a very specific species that is essential for the parasite's life cycle
what is the "obligatory" host?
not the usual host, although it is sometimes parasitized
what is the "accidental" host?
accidental host
if a human eats a parasitized fish, what type of host is it?
a host that is not necessary for the parasite's life cycle, but eases parasite transmission
what is a "paratenic" host?
a host that is infected only in artificial/laboratory conditions
what is an artificial host?
paratenic host
although fish are not necessary for the life cycle of an anisaki (parasite), they help to spread the parasite when eaten by a cetacean. what type of host is the fish?
obligatory host
to develop throughout their life cycle, Fasciola (parasite) need to infect aquatic snails and develop inside of them. what type of host is the aquatic snail?
an invertebrate that carries a parasite to the definitive host
what is a vector?
a vector that only transports the parasite, the parasite does not develop inside of the vector
what is a mechanic vector?
a vector that carries the parasite but also harbors its development
what is a biological vector?
1. multiplicative- parasitic multiplication occurs inside of the vector
2. cyclovolutive- the parasite evolves inside of the vector
3. cyclomultiplicative- the parasite both multiplies and evolves inside of the vector
what are the 3 types of biological vectors?
mechanical vector
what is the type of vector called that only transports the parasite- the parasite does not develop inside of it?
biological vector
what type of vector both transports and harbors the parasite's development?
multiplicative vector
what type of biological vector harbors multiplication of the parasite?
cyclovolutive vector
what type of biological vector harbors evolution of the parasite (throughout its life cycle)?
cyclomultiplicative vector
what type of biological vector harbors both multiplication and evolution of the parasite?
an animal that harbors a parasite but does not suffer, only contributes to its spreading
what is a reservoir?
a host acting as a connecting to different biological cycles of the parasite
what is a bridge?
a bridge
rats connect trichinella to its domestic cycle in pigs and its sylvatic cycle in wild boars. because it connects these 2 different biological cycles, what is the rat called?
a parasite that infects plants
what is a fitoparasite?
zooparasites
what is the name of parasites that infect animals?
1. protozoa
2. helminths (plathelminthes, nemathelminthes, acanthocephalams, annelids)
3. arthopoda (arachnids, insects)
what are the 3 classes of zooparasites?
flat
plathelminthes are _____ worms
cestodes (segmented)
trematodes (unsegmented)
what are the 2 types of plathelminthes?
nematodes
what type of nemathelminthes do we study?
round
nemathelminthes are _____ worms
insecta, arachnida
what are the 2 types of arthropoda?
ectoparasites
what type of parasites live outside of the host?
arthopods, monogenea
what are the 2 classes that are ectoparasites?
parasites that live outside of the host
what are ectoparasites?
parasites that live inside of the host
what are endoparasites?
coelozoics- live in coeloma
histozoics- live in tissues
citozoics- live in cells
plasmazoics- live in cytoplasm
what are the 4 classes of endoparasites?
one that is living outside of its usual place
what is an erratic parasite?
a parasite that needs the host to complete the lifecycle
ex: hypodermal parasites need to lay their eggs under the host's skin so they can hatch
what is an obligated parasite?
a parasite that does not rely on the host for most of its life cycle
what is a facultative parasite?
a parasite that prefers not to be a parasite
ex: musca prefers to live in trash or on feces, but can live off an animal
what is an accidental parasite?
the parasite can affect a wide range of hosts
what does eurixenic mean?
one that cannot affect many hosts
what is a stenoxenic parasite?
oligoxenic
what is a parasite that can affect only a few hosts called?
monoxenic
what is a parasite that can only affect one host species called?
monoxenic
if a parasite only affects one host in their life (the DH), what is it called?
a parasite that requires one DH and one IH to complete its life cycle
what is a heteroxenic parasite?
a parasite whose host can act as both the IH and DH
what is an autoheteroxenic parasite?
a parasite that can make disease
what is a pathogenic parasite?
no, very few are pathogenic
because they do not want to kill the host, as they support their life
are many parasites pathogenic?
parasites that only promote disease in some situations
what is a facultatively pathogenic parasite?
yes, most are
are many parasites facultatively pathogenic?
a parasite that cannot make disease in the host
what is a non pathogenic parasite?
no, very few are
are many parasites non pathogenic?
temporary or permanent
regarding the length of the stay of the parasite in the host, it can be what 2 options?
constant
if the parasite stays in the host during its entire life, it is called....
periodical
if the parasite stays in a host during only part of its life, it is called....
one that is parasitic only during its adult stages
what is an imaginal parasite?
one that is parasitic only during its larval stages
what is a protelic parasite?
imaginal
if a parasite only infects hosts during its adult life, it is called...
protelic
if a parasite only infects hosts during its larval life, it is called...
the parasite only requires one type of host in their life cycle
what is a direct life cycle?
monoxenic parasites
what type of parasites have a direct life cycle?
DH only
in a direct life cycle, does the host infect IH or DH?
the parasite requires more than one host in their life cycle
what is an indirect life cycle?
indirect
what type of life cycle involves a IH- direct or indirect?
heteroxenic parasites
what type of parasites have an indirect life cycle?
diheteroxenic
what type of heteroxenic parasite has 1 DH and 1 IH?
1 DH
2 or more IH
a poliheteroxenic parasite has ___ DH and ____ IH
diheteroxenic- it only has 1 IH and 1 DH
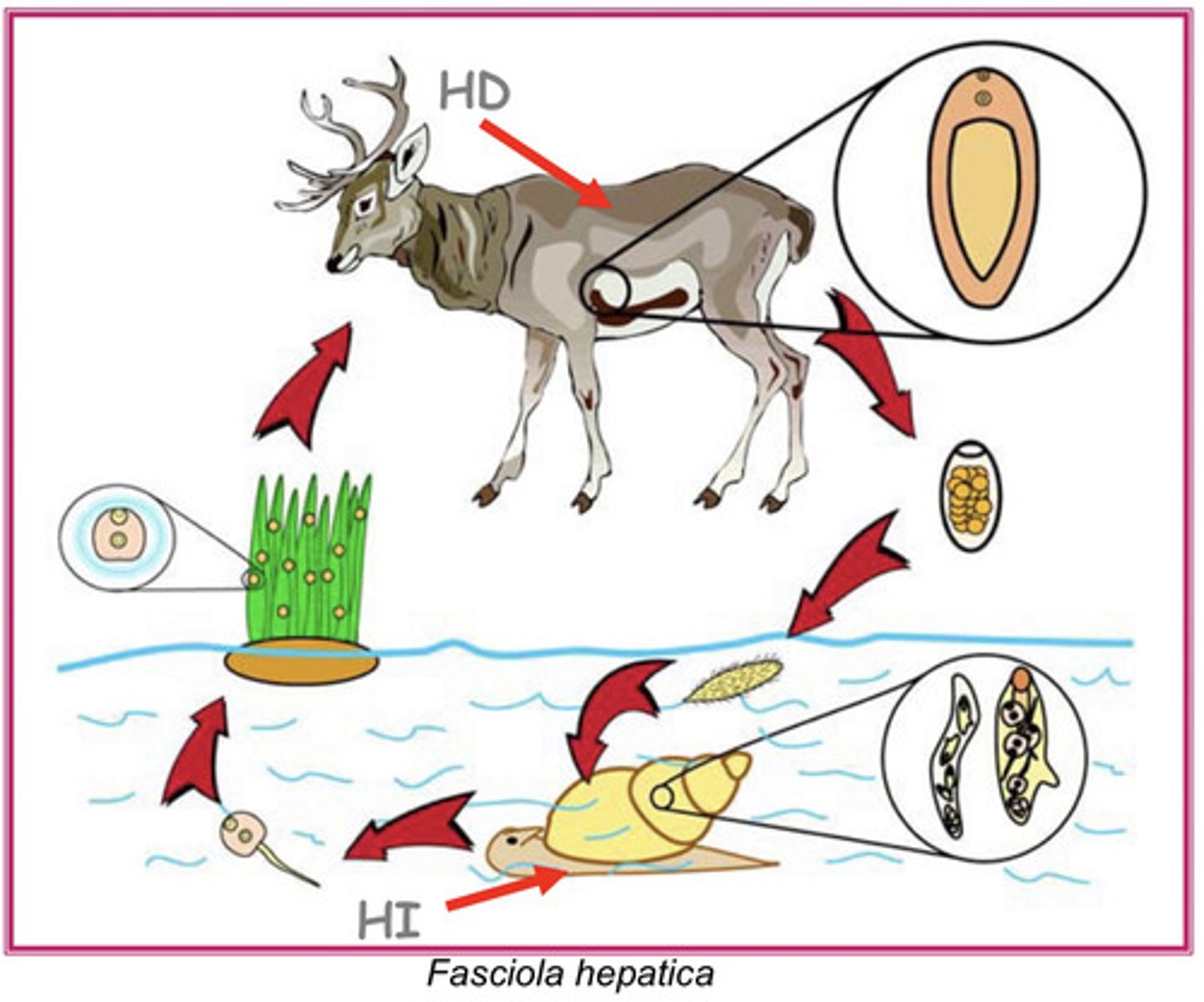
is this parasite, Faciola hepatica, diheteroxenic or poliheteroxenic?
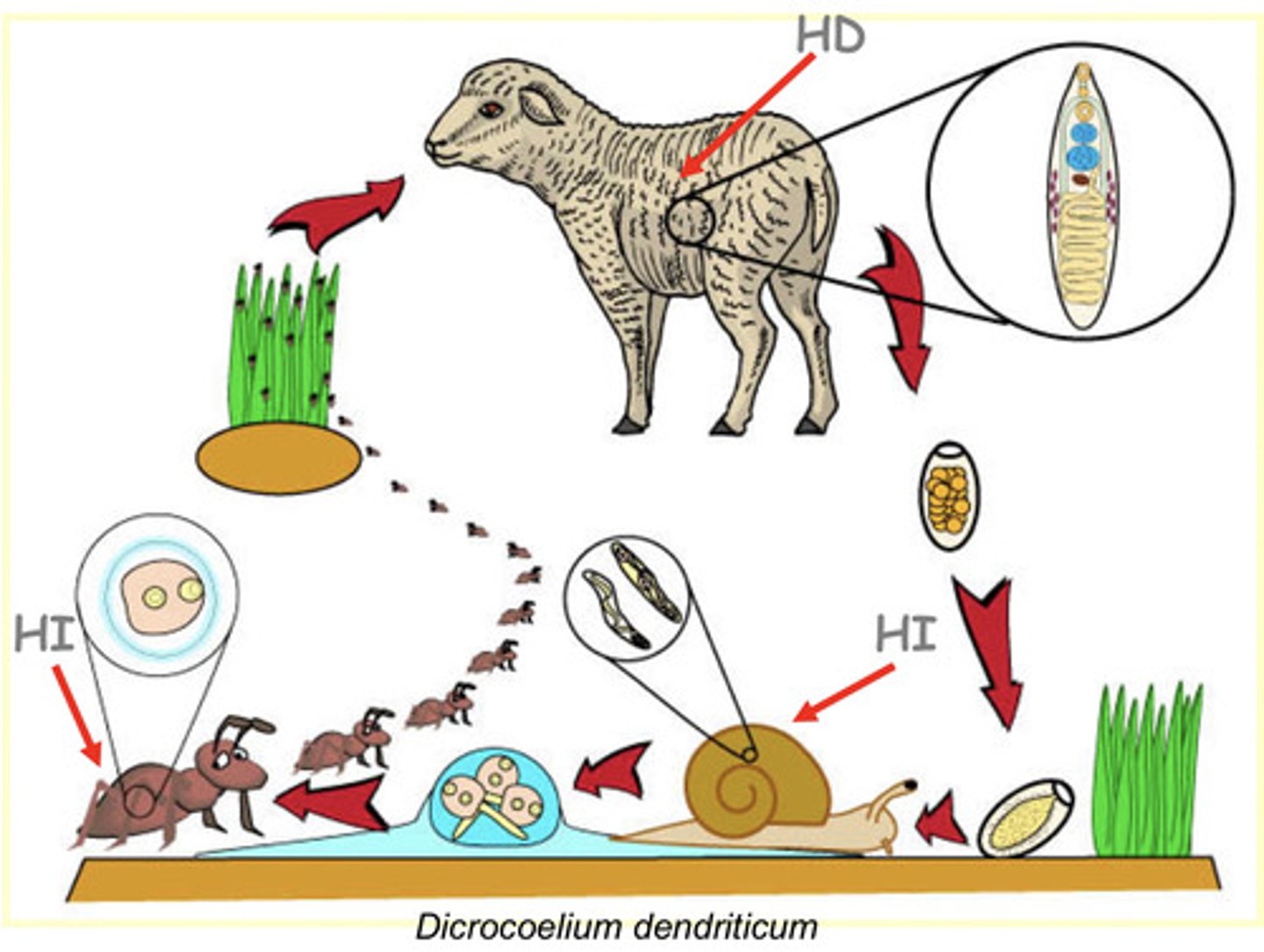
poliheteroxenic- it has 2 IH and 1 DH
is this parasite, Dicrocoelium dendriticum, diheteroxenic or poliheteroxenic?